Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.23 Support of deployments topologies with specific SMF Service Areas
4.23.1 General
4.23.2 I-SMF selection
4.23.3 Registration procedure
4.23.3a Deregistration procedure
4.23.4 Service Request procedures
4.23.5 PDU Session Management procedure
4.23.6 I-SMF Related Procedures with PCF
...
...
4.23 Support of deployments topologies with specific SMF Service Areas |R16| p. 611
4.23.1 General p. 611
This clause captures changes to 5GC procedures in other clauses of this specification and new procedures to support deployments topologies with specific SMF Service Areas that are defined in clause 5.34 of TS 23.501.
In the case of roaming for a Home Routed PDU Session the following cases may occur:
- A UE moves out of V-SMF serving area in the serving PLMN;
- A UE moves to another (serving) VPLMN;
- A UE moves between HPLMN and a VPLMN.
- Registration as defined in clause 4.23.3,
- Service Request as defined in clause 4.23.4,
- Xn Hand-over as defined in clause 4.23.11, or
- N2 Hand-Over as defined in clause 4.23.7.
4.23.2 I-SMF selection p. 612
For non-roaming or LBO roaming case, the AMF selects an SMF serving the PDU Session as described in clause 4.3.2.2.3. If the service area of the selected SMF does not control UPF that can serve the UE location, the AMF selects an I-SMF as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501. Additionally, if Local Offloading Management is allowed as per the subscription data, the AMF may select/re-select an I-SMF as described in clause 6.10 of TS 23.548.
After the PDU Session is established, if the selected SMF cannot serve the target DNAI requested by the PCC rule, the SMF issues Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify to provide the target DNAI information to the AMF. Then AMF selects an I-SMF that serves this target DNAI as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501.
For home routed roaming case, the AMF selects V-SMF as described in clause 4.3.2.2.3.2 and reselects V-SMF as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501.
When the delegated discovery is used, the SCP selects the SMF as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501 and in Annex E.
4.23.3 Registration procedure p. 612
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.2.2.2 (Registration procedure) when the UE has established PDU Session(s):
- Step 5: The UE context transferred from old AMF includes SMF information. If I-SMF is available for the PDU Session(s), the received SMF information includes I-SMF information and SMF information.
-
Step 10: The (target) AMF determines whether I-SMF insertion/change/removal is needed. If the (target) AMF does not have the service area of the SMF(s), the (target) AMF queries the NRF to get service area information of the received SMF(s). The (target) AMF determines on a per PDU Session basis whether a (new) I-SMF needs to be selected based on UE location and service area of the received SMF information. It includes the following cases:
- if the received SMF information includes only SMF information and service area of SMF includes the area where the UE camps, new I-SMF selection is not needed; or
- if the received SMF information includes both I-SMF information and SMF information and service area of I-SMF includes the area where the UE camps, the I-SMF can be reused; or
- if the received SMF information includes both I-SMF information and SMF information and the UE moves into the service area of SMF, the I-SMF removal process is triggered; or
- if the received SMF information includes only SMF information and the service area of SMF does not include the area where the UE camps, the (target) AMF selects an I-SMF. The I-SMF insertion process is triggered; or
- if the received SMF information includes both I-SMF and SMF information and the service area of SMF and I-SMF does not include the area where the UE camps, the (target) AMF selects a new I-SMF. The change of I-SMF process is triggered.
-
For each PDU Session, if the UE context retrieved from the old AMF includes an I-SMF and the (target) AMF determines the I-SMF needs to be changed or removed, the (target) AMF includes a corresponding indication in Namf_
Communication_ sent to old AMFRegistrationStatusUpdate -
Step 17: the (target) AMF contacts the SMF/I-SMF ("cases" below are same as for step 10).
For case a), no additional change to step 17 of clause 4.2.2.2.2 is needed for the update of the PDU Session.
For case b), the SMF in step 17 of clause 4.2.2.2.2 is changed to I-SMF and in addition, the reference clause 4.2.3.2 is changed to clause 4.23.4.2. If the AMF has changed, the new AMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ (SM Context ID at SMF) towards the I-SMF. For case c) i.e. for I-SMF removal, the (target) AMF invokes Nsmf_UpdateSMContext PDUSession_ (SM Context ID at SMF) towards the SMF. Steps from step 10 onwards as described in clause 4.23.4.3 are executed. For cases d) and e), i.e. for I-SMF insertion or change, the (target) AMF invokes Nsmf_CreateSMContext PDUSession_ (PDU Session ID, SM Context ID at SMF) towards the new I-SMF. Steps from step 3 onwards as described in clause 4.23.4.3 are executed with the following enhancements:.CreateSMContext - Step 9 (for cases d and e): The N2 SM information is only provided by the I-SMF to the AMF when N3 tunnel needs to be established (i.e. due to buffered DL data in old I-SMF/old-I-UPF or AMF has indicated to I-SMF to active user plane for the PDU session based on List of PDU Sessions To Be Activated received from the UE).
- Step 16 (i.e. case c): The N2 SM information is only provided by the SMF to the AMF when N3 tunnel need to be established (i.e. due to buffered DL data in old I-SMF/old-I-UPF or the AMF has indicated to the SMF to active user plane for the PDU session based on List of PDU Sessions To Be Activated received from the UE).
- Step 17 is executed when N3 tunnel needs to be established. The NAS message Service Accept is replaced with Registration Accept (i.e. step 21 in clause 4.2.2.2).
- Step 17a and 17b is triggered by old AMF towards the old I-SMF based on the I-SMF change or removal indication received from target AMF, when the timer (i.e. started in step 5 of clause 4.2.2.2) in old AMF expires.
- Steps 18 to 21 (i.e. cases d and e) and steps 22 to 25 (i.e. case c): These steps are executed if N2 SM information is provided by the I-SMF/SMF in step 9 or step 16 above.
- Step 21: This step is omitted if step 17 of clause 4.23.4.3 is executed as described above.
4.23.3a Deregistration procedure p. 614
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.2.2.3 (Deregistration procedures) when the UE has established PDU Session(s):
The V-SMF is replaced with I-SMF and the H-SMF is replaced with SMF.
In step 2, if ULCL/BP is included in the data path, the I-SMF releases the local UPF (PSA) and includes N4 information in the Nsmf_PDUSession_Release request.
4.23.4 Service Request procedures p. 614
4.23.4.1 General p. 614
The following two scenarios are considered:
- The I-SMF is available for the PDU Session and I-SMF is not changed or removed during the service request procedure. The procedure to support this scenario is described in clause 4.23.4.2.
- The I-SMF is inserted, changed or removed during service request procedure. The procedure to support this scenario is described in clause 4.23.4.3.
4.23.4.2 UE Triggered Service Request without I-SMF change/removal p. 614
When both I-SMF and SMF are available for a PDU session and no I-SMF change or removal is needed during the service request procedure, the procedure in this clause is used. Compared to the procedure in clause 4.2.3.2, the SMF is replaced with the I-SMF and the impacted intermediate UPF(s) are UPFs that are controlled by I-SMF. Difference are captured below:
- Steps 6a-6b, these steps are not needed as the CN Tunnel Info of UPF (PSA) allocated for N9 is available at the I-SMF when the I-SMF is inserted.
-
Step 7a, if a new intermediate UPF is selected, the I-SMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request (DN Tunnel Info of the new intermediate UPF. The I-SMF may also include UE location Information, Time Zone RAT type, Access Type and Operation Type set to "UP Activate", if those information is changed and need to be notified to SMF. If DL Tunnel Info of new intermediate UPF is received, the SMF provides the DL Tunnel Info of new intermediate UPF received from I-SMF to UPF(PSA).Update - Step 10, this step does not apply as in this scenario the I-UPF is always needed.
-
Step 16, If the I-SMF needs to update SMF with e.g. change of UE location information, change of Time Zone, change of RAT type and/or change of Access type, the I-SMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request to send User Location Information, Time Zone, RAT type and/or Access Type to SMF. If the I-SMF invoked Nsmf_Update PDUSession_ Request in step 7a with Operation Type "UP Activate", the I-SMF also includes an Operation Type set to "UP Activated". If dynamic PCC is deployed and if Policy Control Request Trigger condition(s) have been met (e.g. change of Access Type, change of UE location), the SMF performs SMF initiated SM Policy Modification procedure as defined in clause 4.16.5.1, and may get the updated policy.Update - Steps 18a-18b, these steps do not apply as in this scenario the I-UPF is always needed.
- Step 21a, this step does not apply as in this scenario the I-UPF is always needed.
4.23.4.3 UE Triggered Service Request with I-SMF insertion/change/removal p. 615
When, as part of a UE Triggered Service Request, I-SMF is to be inserted, changed or removed, the procedure in this clause is used. It includes the following cases:
- the UE moves from SMF service area to new I-SMF service area, a new I-SMF is inserted (i.e. I-SMF insertion); or
- the UE moves from old I-SMF service area to new I-SMF service area, the I-SMF is changed (i.e. I-SMF change); or
- the UE moves from old I-SMF service area to SMF service area, the old I-SMF is removed (i.e. I-SMF removal).
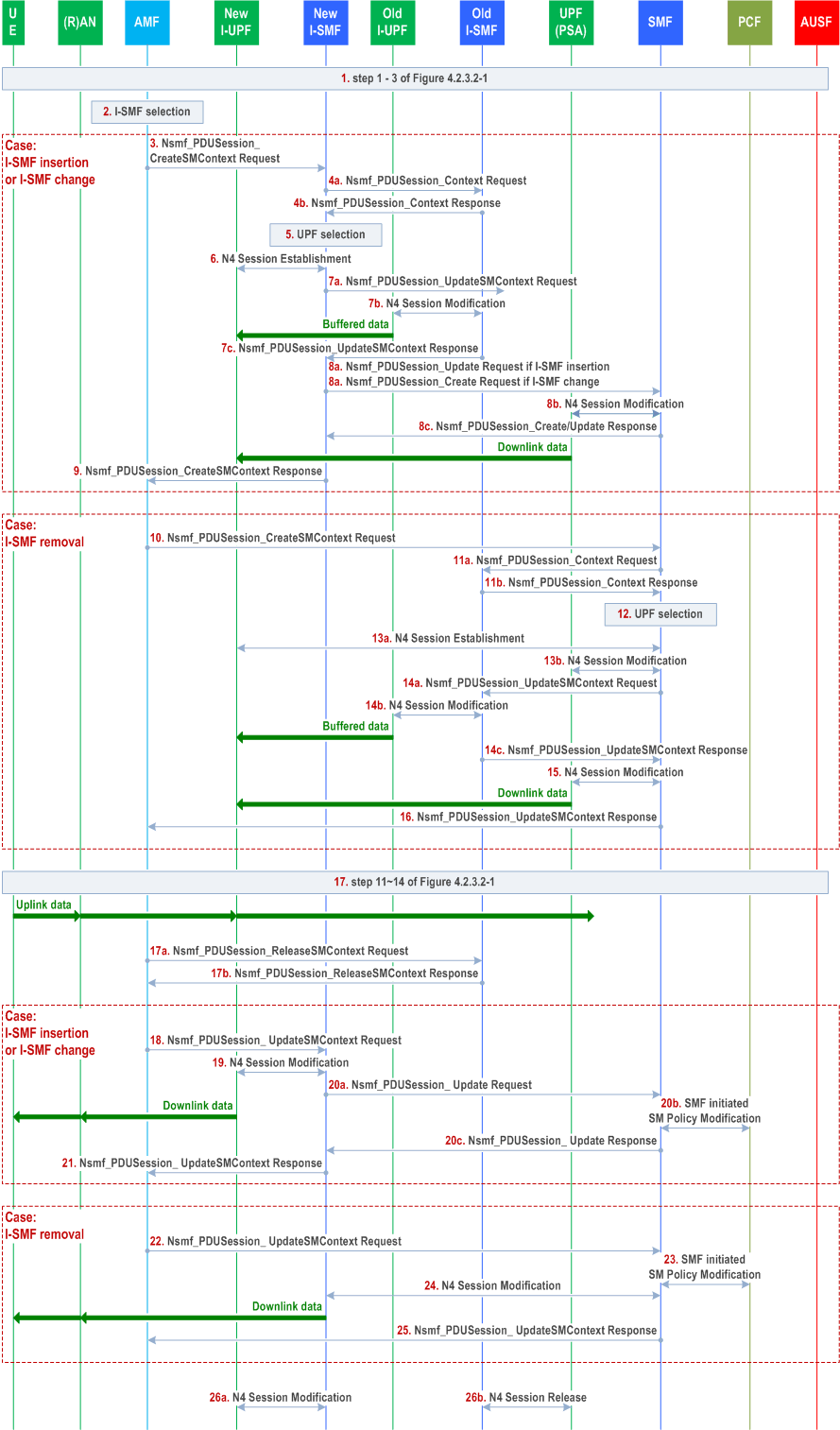
Step 1.
Step 2.
Case: I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change, steps 3-9 are skipped for I-SMF removal case.
Same as the steps 1-3 defined clause 4.2.3.2.
Step 2.
The AMF determines whether new I-SMF needs to be selected based on UE location and service area of the SMF, if new I-SMF needs to be selected, the AMF selects a new I-SMF as described in clause 4.23.2.
Step 3.
Step 4a.
Step 4b.
Step 5.
Step 6.
Step 7a.
Step 7b.
Step 7c.
Step 8a.
Step 8b.
Step 8c.
Step 9.
Case: I-SMF removal: steps 10 to 16 are skipped for I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change cases.
If the AMF has selected a new I-SMF, the AMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request (PDU Session ID, SM Context ID, UE location info, Access Type, RAT Type, Operation Type) to the new I-SMF. The SM Context ID points to the old I-SMF in the case of I-SMF change or to SMF in the case of I-SMF insertion.
The AMF Set the Operation Type to "UP activate" to indicate establishment of N3 tunnel User Plane resources for the PDU Session(s). The AMF determines Access Type and RAT Type based on the Global RAN Node ID associated with the N2 interface.
If the UE Time Zone has changed compared to the last reported UE Time Zone then the AMF shall include the UE Time Zone IE in this message.
Step 4a.
The new I-SMF retrieves SM Context from the old I-SMF (in the case of I-SMF change) or SMF (in the case of I-SMF insertion) by invoking Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request (SM context type, SM Context ID). The new I-SMF uses SM Context ID received from AMF for this service operation. SM Context ID is used by the recipient of Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request in order to determine the targeted PDU Session. SM context type indicates that the requested information is all SM context, i.e. PDN Connection Context and 5G SM context.
Step 4b.
The old I-SMF in the case of I-SMF change or SMF in the case of I-SMF insertion responds with the SM context of the indicated PDU Session.
If there is Extended Buffering is applied and the Extended Buffering timer is still running in old-SMF or old I-UPF, or the service request is triggered by downlink data, the old I-SMF or SMF includes a forwarding indication in the response to indicate that a forwarding tunnel is needed for sending buffered downlink packets. For I-SMF insertion, if I-UPF controlled by SMF was available for the PDU Session, the SMF includes a forwarding indication.
Step 5.
The new I-SMF selects a new I-UPF: Based on the received SM context, e.g. S-NSSAI and UE location information, the new I-SMF selects a new I-UPF as described in clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 6.
The new I-SMF initiates a N4 Session Establishment to the new I-UPF. The new I-UPF provide tunnel endpoints to the new I-SMF.
If forwarding indication was received, the new I-SMF also requests the new I-UPF to allocate tunnel endpoints to receive the buffered DL data from the old I-UPF and to indicate end marker reception on this tunnel via usage reporting. In this case, the new I-UPF begins to buffer the downlink packet(s) received from the UPF (PSA).
Step 7a.
If the tunnel endpoints for the buffered DL data were allocated, the new I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (tunnel endpoints for buffered DL data) to the old I-SMF in the case of I-SMF change in order to establish the forwarding tunnel. The new I-SMF uses the SM Context ID received from AMF for this service operation.
Step 7b.
The old I-SMF, in the case of I-SMF change initiates a N4 session modification to the old I-UPF to send the tunnel endpoints for buffered DL data to the old I-UPF. After this step, the old I-UPF starts to send buffered DL data to the new I-UPF.
If the old I-UPF receives end marker packets and there is no associated tunnel to forward these packets, the old I-UPF discards the received end marker packets and does not send any Data Notification to SMF.
Step 7c.
The old I-SMF, in the case of I-SMF change responds the new I-SMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response.
Step 8a.
In the case of I-SMF change, the new I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request (SM Context ID, new I-UPF DL tunnel information, SM Context ID at I-SMF, Access Type, RAT Type, DNAI list supported by the new I-SMF, Operation Type) towards the SMF. The new I-SMF uses the SM Context ID at SMF received from old I-SMF for this service operation.
In the case of I-SMF insertion, the new I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Request (new I-UPF DL tunnel information, new I-UPF tunnel endpoint for buffered DL data, SM Context ID at I-SMF, Access Type, RAT type, DNAI list supported by the new I-SMF, Operation Type) towards the SMF.
The SM Context ID at I-SMF is to be used by the SMF for further PDU Session operation, e.g. to notify the new I-SMF of PDU Session Release. If SM Context ID at the I-SMF exists (i.e. in the case of I-SMF change), the SMF shall replace the SM Context ID at I-SMF.
The new I-UPF tunnel endpoint for buffered DL data is used to establish the forwarding tunnel (from old I-UPF controlled by SMF to new I-UPF controlled by new I-SMF).
If the old I-UPF receives end marker packets and there is no associated tunnel to forward these packets, the old I-UPF discards the received end marker packets and does not send any Data Notification to SMF.
The Operation Type is set to "UP activate" to indicate that User Plane resource for the PDU Session is to be established.
Step 8b.
The SMF initiates N4 Session Modification toward the PDU Session Anchor UPF. During this step:
- The SMF provides the new I-UPF DL tunnel information.
- If different CN Tunnel Info need be used by PSA UPF, i.e. the CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N3 and N9 are different, a CN Tunnel Info for the PDU Session Anchor UPF is allocated.
- For I-SMF insertion, if a new I-UPF tunnel endpoint for buffered DL data is received, the SMF triggers the transfer of buffered DL data to the new I-UPF tunnel endpoint for buffered DL data.
Step 8c.
The SMF responds to the new I-SMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Response (the DNAI(s) of interest for this PDU Session in the case of I-SMF change) or Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Response (the DNAI(s) of interest for this PDU Session, Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA) for UL data in the case of I-SMF insertion if it is allocated in step 8b).
In the case of I-SMF insertion and the PDU session corresponds to a LADN, the SMF shall release the PDU session after the service request procedure is completed.
In the case of I-SMF insertion the SMF starts a timer to release resource, i.e. resource for the indirect data forwarding tunnel.
In the case of I-SMF insertion and the CN Tunnel Info at PSA for N9 is received in the response, I-SMF provides the CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N9 to I-UPF via N4 Session Modification Request.
Step 9.
The new I-SMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (N2 SM information (PDU Session ID, QFI(s), QoS profile(s), CN N3 Tunnel Info, S-NSSAI, User Plane Security Enforcement, UE Integrity Protection Maximum Data Rate), N1 SM Container, Cause)) to the AMF. The CN N3 Tunnel Info is the UL Tunnel Info of the new I-UPF.
If the PDU Session has been assigned any EPS bearer ID, the new I-SMF also includes the mapping between EPS bearer ID(s) and QFI(s) into the N2 SM information to be sent to the NG-RAN.
The new I-SMF starts a timer to release resource, i.e. resource for the indirect data forwarding tunnel.
Step 10.
Step 11a.
Step 11b.
Step 12.
Step 13.
Step 14a.
Step 14b.
Step 14c.
Step 15.
Step 16.
Step 17.
Step 17a.
Step 17b.
Case: I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change: steps 18 to 21 are skipped for the I-SMF removal case.
If the UE has moved from service area of old I-SMF into the service area of SMF, the AMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request (SUPI, PDU Session ID, AMF ID, SM Context ID at I-SMF, UE location info, Access Type, RAT Type) to the SMF.
If the UE Time Zone has changed compared to the last reported UE Time Zone then the AMF shall include the UE Time Zone IE in this message.
The AMF Set the Operation Type to "UP activate" to indicate establishment of User Plane resources for the PDU Session(s). The AMF determines Access Type and RAT Type based, as defined in clause 4.2.3.2.
Step 11a.
The SMF retrieves SM Context from the I-SMF by invoking Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request (SM context type). The SMF uses SM Context ID received from AMF for this service operation. SM context type indicates that the requested SM context is all, i.e. PDN Connection Context and 5G SM context.
Step 11b.
The old I-SMF responds with the SM context of the indicated PDU Session. If there is Extended Buffering is applied and the Extended Buffering timer is still running in old-SMF or old I-UPF, or the service request is triggered by downlink data (i.e. the old I-SMF received downlink data notification from old I-UPF), the old I-SMF includes a forwarding indication in the response to indicate that a forwarding tunnel is needed for sending buffered downlink packets from old I-UPF to new I-UPF or PSA (in the case that new I-UPF is not selected).
Step 12.
The SMF may select a new I-UPF: If the SMF determines that the service area of the PSA does not cover the UE location, the SMF selects a new I-UPF based on S-NSSAI and UE location information as described in clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 13.
If a new I-UPF is selected by SMF, the SMF initiates a N4 Session Establishment to the new I-UPF. The new I-UPF provides tunnel endpoints to the SMF. If forwarding indication was received, the SMF requests the new I-UPF to allocate tunnel endpoints for forwarding data and to indicate end marker reception on this tunnel. In this case, the new I-UPF begins to buffer the downlink packet(s) received from the UPF (PSA).
If the new I-UPF is not selected, i.e. the PSA can serve the UE location, the SMF may initiate N4 Session Modification to the PSA to allocate UL N3 tunnel endpoints Info of PSA. The PSA provides the UL N3 tunnel endpoints to SMF. If the forwarding indication was received, the SMF requests the PSA to allocate the tunnel endpoints for the buffered DL data from the old I-UPF and indicate the PSA via usage reporting rule to report end marker to the SMF. In this case, the UPF (PSA) begins to buffer the DL data it may receive at the same time from the N6 interface. The UPF (PSA) sends one or more "end marker" packets according to the indication from SMF for each N9 tunnel to the old I-UPF immediately after switching the path to (R)AN. If indicated by the SMF, the UPF (PSA) reports to SMF when "end marker" packet is received. Then the SMF initiates N4 Session Modification procedure to indicate the UPF (PSA) to send the DL data received from the N6 interface.
Step 14a.
If the tunnel endpoints for the buffered DL data were allocated, the SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (tunnel endpoints for buffered DL data) to the old I-SMF in order to establish the forwarding tunnel. The SMF uses the SM Context ID received from AMF for this service operation.
Step 14b.
The old I-SMF initiates a N4 session modification to the old I-UPF and sends the tunnel endpoints for buffered DL data to the old I-UPF. After this step, the old I-UPF start to send buffered DL data to the new I-UPF or PSA if new I-UPF is not selected.
If the old I-UPF receives end marker packets and there is no associated tunnel to forward these packets, the old I-UPF discards the received end marker packets and does not send any Data Notification to SMF.
Step 14c.
The old I-SMF responds the SMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response.
Step 15.
If a new I-UPF was selected by SMF, the SMF initiates N4 Session Modification toward the PDU Session Anchor UPF, providing the new I-UPF DL tunnel information. The PSA begins to send the DL data to the new I-UPF as indicated in the new I-UPF DL tunnel information. If the forwarding indication was received, the SMF indicates the PDU Session Anchor UPF to send one or more "end marker" packets. The UPF (PSA) sends one or more "end marker" packets according to the indication from SMF for each N9 tunnel to the old I-UPF immediately after switching the path to new I-UPF. If indicated by the SMF in step 13, the new I-UPF reports to SMF when "end marker" packet is received. The SMF initiates N4 Session Modification procedure to indicate the new I-UPF to send the DL packet(s) received from the UPF (PSA).
Step 16.
The SMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (N2 SM information (PDU Session ID, QFI(s), QoS profile(s), CN N3 Tunnel Info, S-NSSAI), N1 SM Container, Cause)) to the AMF. The CN N3 Tunnel Info is the UL Tunnel Info of the new I-UPF.
If the PDU Session has been assigned any EPS bearer ID, the SMF also includes the mapping between EPS bearer ID(s) and QFI(s) into the N2 SM information to be sent to the NG-RAN.
The SMF starts a timer to release the resource, i.e. resource for indirect data forwarding tunnel.
Step 17.
These steps are same as steps 12 to 14 in clause 4.2.3.2. After step 16, the Uplink data is transferred from (R)AN via new I-UPF (if exists) to PSA. If procedure in clause 4.2.3 is triggered together with this procedure, this step can be executed together with the corresponding steps in clause 4.2.3.
Step 17a.
If the step 9 or step 16 was successful response, in the case of I-SMF removal or change, the AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext Request (I-SMF only indication) to old I-SMF for the release of resources in old I-SMF. The I-SMF only indication indicates to old I-SMF not to invoke resource release in SMF.
The old I-SMF starts a timer to release resources, i.e. resource for indirect data forwarding tunnel.
Step 17b.
The old I-SMF responds to AMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext response.
Step 18.
Step 19.
Step 20a.
Step 20b.
Step 20c.
Step 21.
Case: I-SMF removal: steps 22 to 25 are skipped for the I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change cases.
The AMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (N2 SM information, RAT type, Access type) to the new I-SMF.
If the AMF received N2 SM information (one or multiple) in step 17, then the AMF shall forward the N2 SM information to the relevant new I-SMF per PDU Session ID.
Step 19.
The new I-SMF updates the new I-UPF with the AN Tunnel Info and List of accepted QFI(s). Downlink data is now forwarded from new I-UPF to UE.
Step 20a.
The new I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_Update request (RAT type, Access type, Operation Type) to SMF. The SMF updates associated access of the PDU Session.
The Operation Type is set to "UP activated" to indicate User Plane resource for the PDU Session has been established.
Step 20b.
If dynamic PCC is deployed, SMF may initiate notification about new location information to the PCF (if subscribed) by performing an SMF initiated SM Policy Modification procedure as defined in clause 4.16.5.1. The PCF may provide updated policies. If the PCC rule(s) are updated, the SMF may initiate a N4 Session Modification procedure to UPF (PSA) based on the updated PCC rule(s).
Step 20c.
The SMF responds with Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Response.
Step 21.
The new I-SMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response to AMF.
Step 22.
Step 23.
Step 24.
Step 25.
Step 26a.
Step 26b.
The AMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (N2 SM information, RAT Type, Access Type) to the SMF. The AMF determines Access Type and RAT Type based on the Global RAN Node ID associated with the N2 interface.
If the AMF received N2 SM information (one or multiple) in step 17, then the AMF shall forward the N2 SM information to the relevant new I-SMF per PDU Session ID.
Step 23.
If dynamic PCC is deployed, SMF may initiate notification about new location information to the PCF by performing an SMF initiated SM Policy Modification procedure as defined in clause 4.16.5.1. The PCF may provide updated policies.
Step 24.
If a new I-UPF was selected by the SMF, the SMF updates the new I-UPF with the AN Tunnel Info and List of accepted QFI(s), otherwise, the SMF updates the PSA with the AN Tunnel Info and List of accepted QFI(s).
Step 25.
The SMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response to AMF.
Step 26a.
In the case of I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change, upon timer set in step 9 expires and the indirect data forwarding tunnel was established before, the new I-SMF sends N4 Session Modification request to new I-UPF to release resources for the forwarding tunnel.
In the case of I-SMF removal, upon timer set in step 16 expires and the indirect data forwarding tunnel was established before, the SMF sends N4 Session Modification request to the new I-UPF or PSA to release the resource for the forwarding tunnel.
Step 26b.
In the case of I-SMF removal or change, upon timer set in step 17a expires and the indirect data forwarding tunnel was established before, the old I-SMF sends N4 Session Release request to the old I-UPF to release resources for the PDU Session. The old I-SMF releases the SM Context for the PDU Session. If the old I-UPF acts as UL CL and is not co-located with local PSA, the old I-SMF also sends N4 Session Release request to the local PSA to release resources for the PDU Session.
In the case of I-SMF insertion, upon timer set in step 8c expires and the indirect data forwarding tunnel was established before, the SMF sends N4 Session Release request to the old I-UPF to release the resource for the PDU Session.
4.23.4.4 Network Triggered Service Request p. 621
For network triggered service request procedure, if the procedure is triggered by downlink packet, the procedure in clause 4.2.3.3 are impacted as following:
- if the I-SMF is available for the PDU Session, the procedure is triggered by I-SMF. Correspondingly, the SMF in that procedure is replaced by the I-SMF.
- The referenced clause 4.4.4 for pause of charging is changed to clause 4.23.14.
-
Step 4a:
- If I-SMF is not available for the PDU Session and no I-SMF insertion is needed, no additional change is needed.
- If I-SMF is available for the PDU Session and no I-SMF change or removal is needed, steps 12 to 22 in clause 4.23.4.2 is performed where the SMF in that procedure is replaced by the I-SMF.
- If I-SMF will be inserted, changed or removed, steps 2 to 25 in clause 4.23.4.3 is performed.
-
Step 6: If the UE is in CM-IDLE state in 3GPP access, upon reception of paging request for a PDU Session associated to 3GPP access:
- If I-SMF is not available for the PDU Session and no I-SMF insertion is needed, no additional change is needed.
- If I-SMF is available for the PDU Session and no I-SMF change or removal is needed, UE Triggered Service Request procedure as defined in clause 4.23.4.2 is performed.
- If I-SMF will be inserted, changed or removed, UE Triggered Service Request procedure as defined in clause 4.23.4.3 is performed.
4.23.5 PDU Session Management procedure p. 621
4.23.5.1 PDU Session establishment procedure p. 621
For non roaming or LBO roaming, it includes the following cases:
- If the service area of the selected SMF includes the current UE location and if the Local Offloading Management specified in TS 23.548 is not applied, the UE requested PDU Session Establishment procedure is same as described in clause 4.3.2.2.1.
- If the service area of the selected SMF does not include the current UE location and the UE does not request for a MA-PDU Session, the AMF selects an I-SMF that serves the area where UE camps. The UE requested PDU Session Establishment procedure for Home-routed Roaming defined in clause 4.3.2.2.2 is used to establish the PDU Session. Compared to the procedure defined in clause 4.3.2.2.2, the V-SMF and V-UPF are replaced by I-SMF and I-UPF and H-SMF and H-UPF are replaced by SMF and UPF(PSA) respectively. Also, only the S-NSSAI with the value defined by the serving PLMN is sent to the SMF. The I-SMF provides the DNAI list it supports to SMF and the SMF provides the DNAI(s) of interest for this PDU Session to I-SMF based on the DNAI list information received from I-SMF as defined in Figure 4.23.9.1-1 step 1. This may happen e.g. at PDU Session mobility from non-3GPP access to 3GPP access as defined in clause 4.23.15.
- If the service area of the selected SMF does not include the current UE location and the UE requests a MA-PDU Session, then the AMF rejects the MA-PDU Session Establishment procedure.
- When the delegated discovery is used, the SCP selects the SMF as described in Annex E.
- If an I-SMF is selected and the PDU Session supports mechanisms for redundant transmission defined in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501, the SMF rejects the PDU Session Establishment Request.
- If an I-SMF is selected and the PDU Session supports Time Sensitive Communications (as defined in clauses 5.27 and 5.28 of TS 23.501), or if the PDU session supports redundant transmission defined in clauses 5.33.2.1 or 5.33.2.3 of TS 23.501, the SMF may, based on local policy, reject the PDU Session Establishment Request.
-
If the selected SMF cannot serve the target DNAI requested by the PCC rule, the SMF issues Nsmf_
PDUSession_ to provide the target DNAI information to the AMF. The procedure of Home-routed Roaming defined in clause 4.3.2.2.2 is used to establish the PDU Session. Compared to this procedure, the V-SMF and V-UPF are replaced by I-SMF and I-UPF respectively and H-SMF and H-UPF are replaced by SMF and UPF(PSA) respectively. The AMF selects an I-SMF that serves this target DNAI in step 2. Then AMF sends a Nsmf_SMContextStatusNotify PDUSession_ Request to the I-SMF as defined in step 3a, and the target DNAI received from SMF is included in the message.CreateSMContext - The S-NSSAI registered to UDM by SMF is always the S-NSSAI of HPLMN.
- If the service area of the selected V-SMF does not include the current UE location and the UE requests a MA-PDU Session, then the AMF rejects the MA-PDU Session Establishment procedure.
4.23.5.2 PDU Session Release procedure p. 622
For the non roaming or LBO roaming case, the procedure defined in clause 4.3.4.3 (UE or network requested PDU Session Release for Home-routed Roaming) is used to release the PDU Session, with the V-SMF and V-UPF are replaced by I-SMF and I-UPF and H-SMF and H-UPF are replaced by SMF and UPF(PSA) respectively. Also if the ULCL/BP is included in the data path, in step 1 the I-SMF releases the local UPF (PSA) and includes N4 information in the Nsmf_PDUSession_Release or Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request respectively.
For AMF triggers PDU Session Release procedure in Registration procedure (see step 17 of clause 4.2.2.2.2) and Deregistration procedure (see step 2 of clause 4.2.2.3.2), if I-SMF is used for the session, the AMF invokes PDU Session Release operation towards the I-SMF, then I-SMF releases the PDU Session towards SMF.
4.23.5.3 PDU Session modification procedure p. 622
For the non-roaming or LBO roaming case, the procedure defined in clause 4.3.3.3 (UE or network requested PDU Session Modification for Home-routed Roaming) is used to modify the PDU Session, with the V-SMF and V-UPF are replaced by I-SMF and I-UPF and H-SMF and H-UPF are replaced by SMF and UPF(PSA) respectively.
If the QoS Monitoring as defined in clause 5.33.3 of TS 23.501 is triggered, the following enhancement to clause 4.3.3.3 applies:
-
In step 3, if the SMF determines the need for QoS Monitoring for a QoS flow according to the information received from the PCF in step 1b, or based on SMF local policy, SMF includes QoS Monitoring indication and how frequently QoS Monitoring reporting to be performed, in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request message.Update -
In step 3, if, according to the information received from the PCF in step 1b, or based on SMF local policy, the SMF determines the need for GTP-U Path Monitoring as defined in clause 5.33.3.3 of TS 23.501, the SMF includes QoS monitoring policy in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request message.Update -
In step 4b, if in step 3 the I-SMF received QoS Monitoring indication and may receive how frequently QoS Monitoring reporting to be performed in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request the I-SMF includes the QoS Monitoring indication and how frequently QoS Monitoring reporting to be performed in N2 SM message sent to the 5G AN.Update -
In step 4b, if in step 3 the I-SMF received QoS monitoring policy indication and may receive how frequently QoS Monitoring reporting to be performed in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request, the I-SMF includes such QoS monitoring policy also to I-UPF for GTP-U path monitoring.Update -
In step 15, the I-SMF sends Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Response to SMF. The SMF updates N4 session of the UPF PSA as defined for the case where is no I-SMF.Update -
If later on the RAN provides over N2 the QoS Monitoring Result with UL packet delay information comprising the packet delays of RAN and N3 interface, the I-SMF forwards this information to the SMF in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request message.Update - I-SMF shall forward monitoring report (for QoS monitoring per GTP-U path) from I-UPF to SMF.
4.23.5.4 SMF triggered I-SMF selection or removal |R17| p. 623
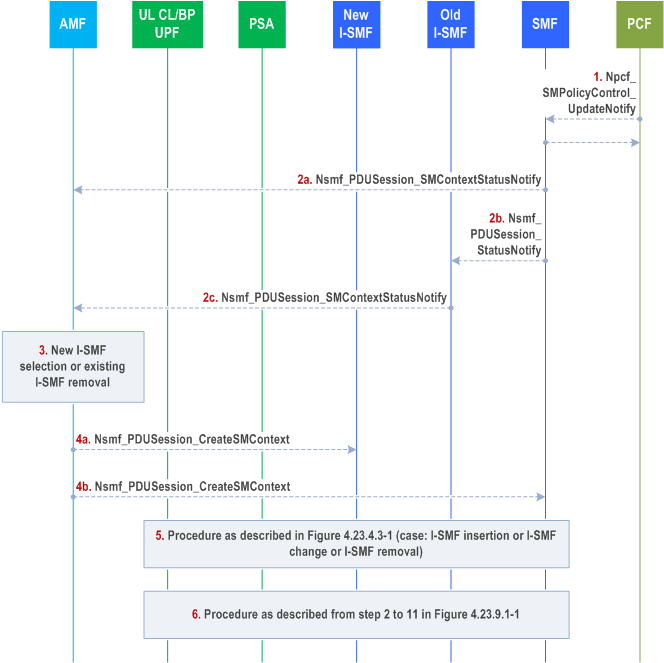
Step 1.
The PCF sends to the SMF PCC rule(s) which may include DNAI(s) for the PDU sessions by invoking Npcf_SMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify service operation.
Based on the received DNAI(s), the SMF may subscribe to UE mobility event notification from the AMF (e.g. UE moves into or out of Area of Interest corresponding to the received DNAI(s)).
The SMF may determine the target DNAI(s) which are applicable to the current UE location and which can be based on common DNAI (if applicable) as described in TS 23.548. Then the SMF may decide a target DNAI finally.
Step 2.
The SMF invokes a Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify service operation (or Nsmf_PDUSession_StatusNotify ) in the following cases:
PDUSession_StatusNotify and then the I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify message to send the target DNAI information for existing PDU session to AMF.
Step 3.
- if the SMF (or the associated old I-SMF) cannot serve the target DNAI, or
- if an I-SMF is used for the PDU Session and the SMF decides that the DNAI currently served by I-SMF is no longer be used for the PDU Session anymore hence the existing I-SMF is not needed, or
- if an I-SMF is used for the PDU Session and the SMF decides that the SMF itself can serve the target DNAI hence the existing I-SMF is not needed.
If the I-SMF selection or removal is expected, the AMF selects a new I-SMF which can serve the target DNAI or remove the existing I-SMF (if the AMF decides that the SMF can serve the Target DNAI, or if the AMF receives a target DNAI information without including target DNAI) for the existing PDU Session as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 4.
The AMF sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request to the new I-SMF as described in step 3 of clause 4.23.4.3, or to the SMF as described in step 10 of clause 4.23.4.3, with the following enhancement:
Step 5.
The AMF includes target DNAI received from SMF in the message. When the UE is in CONNECTED state the AMF also include indication of no NG-RAN change.
The procedure described in clauses 4.23.4.3 (case: I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change) starting from step 4 takes place with the following difference:
Step 6.
In step 4a, the (target)new I-SMF sends the indication of no NG-RAN change to the old I-SMF or SMF as it is received from AMF.
In step 4b, when the old I-SMF or SMF receives indication of no NG-RAN change it include the additional Downlink Tunnel Info of NG-RAN in the SM context of the PDU Session.
In step 5, the I-SMF selects the I-UPF based on target DNAI.
In step 6, the target I-SMF should reuse the downlink Tunnel Info of serving RAN node if received from old I-SMF/SMF as described in clause 4.23.4.3.
In step 9, if the new I-SMF receives the Downlink Tunnel Info of NG-RAN, the N2 SM information includes PDU Session Resource Modification message.
The procedure described in clause 4.23.4.3 (case: I-SMF removal) starting from step 11 takes place with the following difference:
In step 11a, the SMF sends an indication of no NG-RAN change to the old I-SMF as it received from AMF.
In step 11b, when the old I-SMF receives indication of no NG-RAN change it include the additional Downlink Tunnel Info of NG-RAN in the SM context of the PDU Session.
In step 12, the SMF selects a new I-UPF based on target DNAI.
In step 16, if the SMF receives the Downlink Tunnel Info of NG-RAN, the N2 SM information includes PDU Session Resource Modification message.
If the UE is in IDLE state the step 17-21 are skipped. Steps 17a and 17b are still performed to release the old I-SMF.
[Conditional] In the case that I-SMF insertion or I-SMF change is performed in step 5, the PSA and UL CL/BP controlled by I-SMF is inserted as described from steps 2 to 11 in Figure 4.23.9.1-1 with the following difference:
In step 2, the I-SMF selects a new PDU Session Anchor (PSA2) based on the target DNAI received in step 4.
For the case of I-SMF removal, the PSA and UL CL/BP controlled by SMF is inserted as described from steps 2 to 8 in Figure 4.3.5.4-1 with the following difference:
In step 2, the SMF selects a new PDU Session Anchor (PSA2) based on the target DNAI if received in step 4.
4.23.6 I-SMF Related Procedures with PCF p. 625
4.23.6.1 General p. 625
This clause provides PCC related details for scenarios including an I-SMF.
4.23.6.2 Policy Update Procedures with I-SMF p. 625
Figure 4.23.6.2-1 shows procedures related to provisioning of PCC rules containing traffic steering information related to an I-SMF.
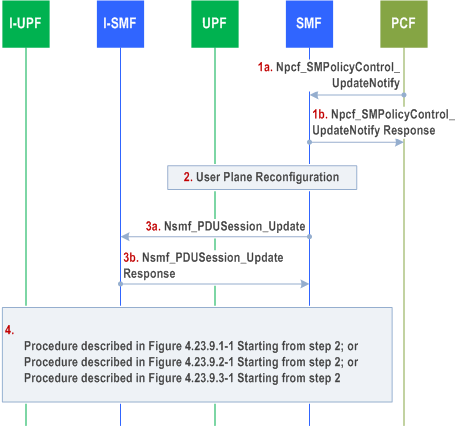
In cases where step 1a in Figure 4.23.6.2-1 is triggered in response to PCF receiving AF request, below steps 3 and 4 are applicable, in addition to those steps as explained in clause 4.3.6.1.
Step 3.
SMF provides to I-SMF with DNAI(s) of interest for this PDU Session for local traffic steering. If PCC rule changes for traffic offloaded via ULCL/BP due to the AF request, the SMF provides the updated N4 information to the I-SMF. If PCC rule changes Local Offloading Policy, SMF provides Local Offloading Policy to I-SMF.
Step 4.
4.23.6.3 Reporting UP path change to the AF p. 625
Figure 4.23.6.3-1 shows procedures related Reporting UP path change to the AF.
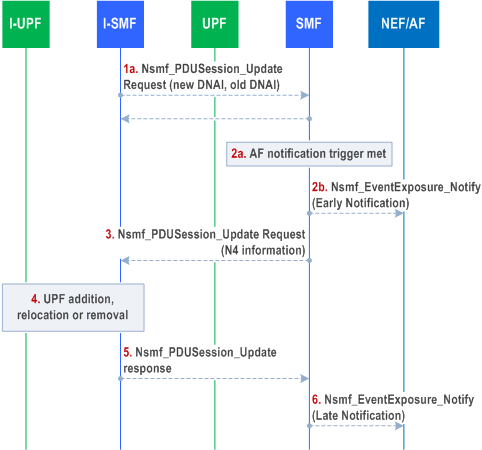
Step 1a.
I-SMF indicates that UP path change may occur for the PDU Session via Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request as described in clause 4.23.9; the SMF responds to the I-SMF.
Step 2.
If early notification has been requested by a PCC rule on behalf of AF as described in clause 4.3.6.2, then the SMF notifies the AF accordingly by invoking Nsmf_EventExposure_Notify service operation as described in clause 4.3.6.3. In this case the SMF may wait for further instructions of the AF.
Step 3.
SMF initiates Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request with N4 information to control the local PSA and ULCL/BP as described in clause 4.23.9.
Step 4.
I-SMF enforces the change of DNAI or addition, change, or removal of UPF as described in clause 4.23.9.
Step 5.
I-SMF answers back to the Nsmf_PDUSession_Update from the SMF.
Step 6.
If late notification has been requested by a PCC rule on behalf of AF as described in clause 4.3.6.2, then the SMF notifies the AF accordingly by invoking Nsmf_EventExposure_Notify service operation as described in clause 4.3.6.3.