Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.9 Handover procedures
4.9.1 Handover procedures in 3GPP access
4.9.1.1 General
4.9.1.2 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover
4.9.1.2.1 General
4.9.1.2.2 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover without User Plane function re-allocation
4.9.1.2.3 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover with insertion of intermediate UPF
4.9.1.2.4 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover with re-allocation of intermediate UPF
...
...
4.9 Handover procedures p. 238
4.9.1 Handover procedures in 3GPP access p. 238
4.9.1.1 General p. 238
These procedures are used to hand over a UE from a source NG-RAN node to a target NG-RAN node using the Xn or N2 reference points. This can be triggered, for example, due to new radio conditions, load balancing or due to specific service e.g. in the presence of QoS Flow for voice, the source NG-RAN node being NR may trigger handover to E-UTRA connected to 5GC.
As defined in TS 38.413 a generic mechanism exists for the source NG-RAN node to retrieve information on the level of support for a certain feature at the target NG-RAN side associated with an NGAP IE. The mechanism makes use of the Source to Target and Target to Source transparent containers.
The Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover procedure specified in clause 4.9.1.3 may also be used for intra-NG-RAN node handover.
The RRC Inactive Assistance Information is included in N2 Path Switch Request Ack message for Xn based handover or Handover Request message for N2 based handover (see clause 5.3.3.2.5 of TS 23.501).
4.9.1.2 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover p. 238
4.9.1.2.1 General p. 238
Clause 4.9.1.2 includes details regarding the Xn based inter NG-RAN handover with and without UPF re-allocation.
Xn handovers are only supported for intra-AMF mobility. New AMF can be selected by the target NG-RAN node as specified in clause 5.21.2 of TS 23.501.
The handover preparation and execution phases are performed as specified in TS 38.300, in the case of handover to a shared network, source NG-RAN determines a PLMN or an SNPN to be used in the target network as specified by TS 23.501. If the serving PLMN or SNPN changes during Xn-based handover, the source NG-RAN node shall indicate to the target NG-RAN node (in the Mobility Restriction List) the selected PLMN ID or SNPN ID to be used in the target network. During Xn based handover into a shared NG-RAN node the source NG RAN node shall include the serving NID (if available) in the Mobility Restriction List to be used by the target NG-RAN node.
If the AMF generates the N2 downlink signalling during the ongoing handover and receives a rejection to a N2 interface procedure (e.g. Location Reporting Control; DL NAS message transfer; etc.) from the NG-RAN with an indication that a Xn based handover procedure is in progress, the AMF may reattempt the same N2 interface procedure either when the handover is complete or the handover is deemed to have failed, when possible. The failure is known by expiry of the timer guarding the N2 interface procedure.
Upon reception for an SMF initiated N1 and/or N2 request(s) with an indication that the request has been temporarily rejected due to handover procedure in progress, the SMF starts a locally configured guard timer. Any NF (e.g. the SMF) should hold any signalling messages targeted towards AMF for a given UE during the handover preparation phase unless it detects that the handover execution is completed or handover has failed/cancelled. The NF (e.g. the SMF) may re-attempt, up to a pre-configured number of times, when either it detects that the handover is completed or has failed using message reception or at expiry of the guard timer.
For the MBSR mobility as specified in clause 5.35A.3 of TS 23.501, the MBSR-UE may operate without any PDU session. In that case, the NG-RAN and the AMF behave as specified in clause 5.35A.3.4 of TS 23.501.
4.9.1.2.2 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover without User Plane function re-allocation p. 239
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a source NG-RAN to Target NG-RAN using Xn when the AMF is unchanged and the SMF decides to keep the existing UPF. The UPF referred in this clause 4.9.1.2.2 is the UPF which terminates N3 interface in the 5GC for non-roaming or local breakout roaming scenario, V-UPF which terminates N3 interface in 5GC for home routed roaming scenario. The SMF referred in this clause 4.9.1.2.2 is the V-SMF for home routed roaming scenario. The presence of IP connectivity between the Source UPF and Target NG-RAN is assumed.
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.9.1.2.2-1.
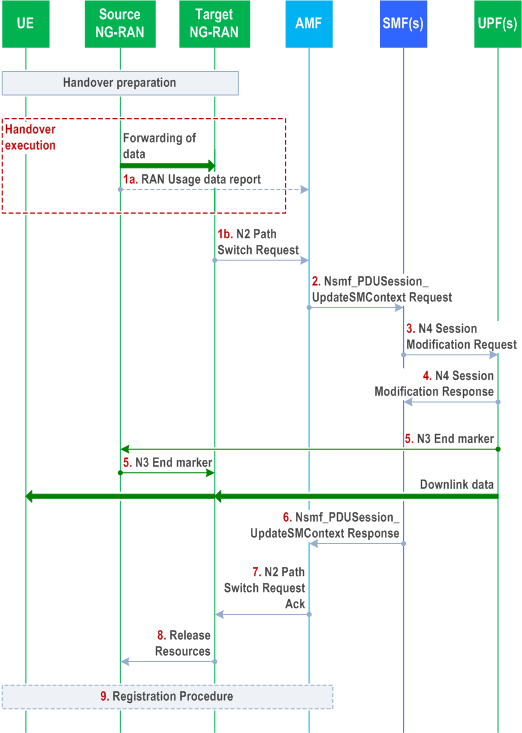
Step 1a.
Step 1b.
Step 2.
Step 3.
Step 4.
Step 5.
Step 6.
Step 7.
Step 8.
Step 9.
For the mobility related events as described in clause 4.15.4, the AMF invokes the Namf_
If the PLMN has configured secondary RAT usage reporting, the source NG-RAN node during the handover execution phase may provide RAN usage data Report (N2 SM Information (Secondary RAT usage data), Handover Flag, Source to Target transparent container) to the AMF. The source NG-RAN node shall provide this only when the Target NG-RAN has confirmed handover over Xn interface. The Handover Flag indicates to the AMF that it should buffer the N2 SM Information containing the usage data report before forwarding it.
If the source NG RAN and Target NG RAN support RACS as defined in TS 23.501, the source NG-RAN provides the UE's UE Radio Capability ID to the Target NG-RAN. If the source NG-RAN has knowledge that the Target NG-RAN might not have a local copy of the Radio Capability corresponding to the UE Radio Capability ID (i.e. because the source NG-RAN had itself to retrieve the UE's Radio Capability from the AMF) then the source NG-RAN may also send some or all of the UE's Radio Capability to the Target NG-RAN (the size limit based on local configuration) in Xn signalling as defined in TS 38.423 . In the case of inter-PLMN handover, when the source and Target NG-RAN support RACS as defined in TS 23.501 and the source NG-RAN determines based on local configuration that the Target PLMN does not support the UE Radio Capability ID assigned by the source PLMN, then the source NG-RAN shall provide the UE radio access capabilities to the Target NG-RAN and shall not send the UE Radio Capability ID. If, as permitted in TS 38.423, the Target NG-RAN during the handover preparation received the UE radio access capabilities but did not receive the UE Radio Capability ID, NG-RAN shall proceed with handover using the received UE radio access capabilities. If the Target NG-RAN received both the UE radio access capabilities and the UE Radio Capability ID, then the Target NG-RAN shall use any locally stored UE radio access capability information corresponding to the UE Radio Capability ID. If none are stored locally, the Target NG-RAN may request the full UE radio access capability information from the core network. If the full UE radio access capability information is not promptly received from the core network, or the Target NG-RAN chooses not to request them, then the Target NG-RAN shall proceed with the UE radio access capabilities sent by the source NG-RAN. The Target NG-RAN shall not use the UE radio access capability information received from the source NG-RAN for any other UE with the same the UE Radio Capability ID.
Step 1b.
Target NG-RAN to AMF: N2 Path Switch Request (List of PDU Sessions To Be Switched with N2 SM Information, List of PDU Sessions that failed to be established with the failure cause given in the N2 SM information element, UE Location Information, established QoS Flows status (active/not active) (for one of the following: congestion information monitoring, ECN marking for L4S at PSA UPF ECN marking for L4S at NG-RAN), PDU Set Based Handling Support Indication included in the N2 SM information).
The Target NG-RAN sends an N2 Path Switch Request message to an AMF to inform that the UE has moved to a new Target cell and provides a List Of PDU Sessions To Be Switched. AN Tunnel Info for each PDU Session to be switched is included in the N2 SM Information.
If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows in the PDU Session, two AN Tunnel Info are provided by the Target NG-RAN and the Target NG-RAN indicates to the SMF one of the AN Tunnel Info is used as the redundancy tunnel of the PDU Session as described in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501. If only one AN Tunnel Info is provided by the Target NG-RAN for the PDU session, the SMF may release these QoS Flows by triggering PDU Session Modification procedure as specified in clause 4.3.3 after the handover procedure.
The serving PLMN ID is included in the message. The Target NG-RAN shall include the PDU Session in the PDU Sessions Rejected list:
- If none of the QoS Flows of a PDU Session are accepted by the Target NG-RAN; or
- If the corresponding network slice is not supported in the Target NG-RAN; or
- When the NG-RAN cannot set up user plane resources fulfilling the User Plane Security Enforcement with a value Required, the NG-RAN rejects the establishment of user plane resources for the PDU Session.
Step 2.
AMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (N2 SM information received from T-RAN in step 1b and N2 SM Information from source NG-RAN (Secondary RAT usage data), UE Location Information, UE presence in LADN service area). The N2 SM Information here from source NG-RAN is the one buffered at step 1a when applicable.
The AMF sends N2 SM information by invoking the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext request service operation for each PDU Session in the lists of PDU Sessions received in the N2 Path Switch Request.
The Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request contains either an indication that the PDU Session Is To Be Switched (together with information on the N3 addressing to use and on the transferred QoS flows) or an indication that the PDU Session is to be Rejected (together with a rejection cause).
If the AMF, based on configuration, as described in clause 5.43.4 of TS 23.501, is aware that satellite backhaul category has changed due to the handover and needs to be updated to the SMF, the AMF includes the new Satellite backhaul category as described in clause 5.43.4 of TS 23.501.
If the AMF, based on configuration, as described in clause 5.43.2 of TS 23.501, is aware that the UE is accessing over a gNB using GEO satellite backhaul and GEO Satellite ID needs to be updated to the SMF, the AMF may include the latest GEO Satellite ID as described in clause 5.43.2 of TS 23.501.
For a PDU Sessions to be switched to the Target NG-RAN, upon receipt of the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext request, the SMF determines whether the existing UPF can continue to serve the UE. If the existing UPF cannot continue to serve the UE, steps 3-11 of clause 4.9.1.2.3 or 4.9.1.2.4 are performed depending on whether the existing UPF is a PDU Session Anchor. Otherwise, the following steps 3 to 6 are performed if the existing UPFs can continue to serve the PDU Session.
In the case that the AMF determines that the PDU Session is related to a LADN, then the AMF provides the "UE presence in LADN service area" to the SMF. If the AMF does not provide the "UE presence in LADN service area" indication and the SMF determines that the DNN corresponds to a LADN, then the SMF considers that the UE is OUT of the LADN service area. The SMF takes actions for the LADN PDU Session as defined in clause 5.6.5 of TS 23.501 based on the "UE presence in LADN service area" indication.
If a PDU Session is rejected by the Target NG-RAN with an indication that the PDU session was rejected because User Plane Security Enforcement is not supported in the Target NG-RAN and the User Plane Enforcement Policy indicates "Required" as described in clause 5.10.3 of TS 23.501, the SMF triggers the release of this PDU Session. In all other cases of PDU Session rejection, the SMF can decide whether to release the PDU Session or to deactivate the UP connection of this PDU Session.
If some of the QoS Flows of a PDU Session are not accepted by the Target NG-RAN, the SMF shall initiate the PDU Session Modification procedure to remove the non-accepted QoS Flows from the PDU Session(s) after the handover procedure is completed.
For the PDU Session(s) that do not have active N3 UP connections before handover procedure, the SMF(s) keep the inactive status after handover procedure.
If the UE moves into a non-Allowed Area, the AMF also notifies via Namf_EventExposure_Notify to each NF Consumer (e.g. SMFs of the established PDU Sessions) which has subscribed for UE reachability event, that the UE is only reachable for regulatory prioritized services. The SMF then deactivates the PDU session if this PDU Session is not for emergency service.
Step 3.
SMF to UPF: N4 Session Modification Request (AN Tunnel Info)
For PDU Sessions that are modified by the Target NG-RAN, the SMF sends an N4 Session Modification Request message to the UPF. The SMF may notify the UPF that originated the Data Notification to discard downlink data for the PDU Sessions and/or to not provide further Data Notification messages.
Depending on the network deployment, the CN Tunnel Info of UPF used for connection to Target NG-RAN and connection to Source NG-RAN may be different, e.g. due to Source and Target NG-RAN are in different IP domains. In this case the SMF may ask the UPF to allocate new CN Tunnel Info, providing the target Network Instance.
Step 4.
UPF to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (CN Tunnel Info)
For the PDU Sessions that are switched, the UPF returns an N4 Session Modification Response message to the SMF after requested PDU Sessions are switched. Tunnel identifiers for UL traffic are included only for PDU Sessions whose user plane resources are not being released and was requested by the SMF. If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of a PDU Session and different CN Tunnel Info were requested by the SMF, the UPF allocates two different CN Tunnel Info and indicates the SMF that one CN Tunnel Info is used as the redundancy tunnel of the PDU session as described in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501. For the PDU Sessions that are deactivated, the UPF returns an N4 Session Modification Response message to the SMF after the N3 (R)AN tunnel information is released.
Step 5.
In order to assist the reordering function in the Target NG-RAN, the UPF (as specified in clause 5.8.2.9 of TS 23.501) sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path. The UPF starts sending downlink packets to the Target NG-RAN.
Step 6.
SMF to AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (N2 SM information)
The SMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (N2 SM Information (CN Tunnel Info, updated CN PDB for the accepted QoS Flows, Updated TSCAIs for the accepted QoS Flows)) to the AMF for PDU Sessions which have been switched successfully. The CN Tunnel Info of UPF send to AMF is used to setup N3 tunnel. If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of a PDU Session, two CN Tunnel Info are sent and the SMF indicates to the Target NG-RAN one of the CN Tunnel Info is used as the redundancy tunnel of the PDU Session as described in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501. The SMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response without including the CN Tunnel Info to the AMF for the PDU Sessions for which user plane resources are deactivated or released and then the SMF releases the PDU Session(s) which is to be released using a separate procedure as defined in clause 4.3.4. For each accepted GBR QoS Flow of Delay-critical resource type, the dynamic CN PDB and TSCAI may be updated and sent to the Target NG-RAN by the SMF. The SMF may update the CN PDB and TSCAI in the response or using a separate PDU Session Modification procedure, based on local configuration.
If the Source NG-RAN does not support Alternative QoS Profiles (see TS 23.501) and the Target NG-RAN supports them, the SMF sends the Alternative QoS Profiles (see TS 23.501) to the Target NG-RAN on a per QoS Flow basis, if available.
Step 7.
AMF to NG-RAN: N2 Path Switch Request Ack (N2 SM Information, Failed PDU Sessions, UE Radio Capability ID).
Once the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response is received from all the SMFs, the AMF aggregates received CN Tunnel Info and sends this aggregated information as a part of N2 SM Information along with the Failed PDU Sessions in N2 Path Switch Request Ack to the Target NG-RAN. If none of the requested PDU Sessions have been switched successfully, the AMF shall send an N2 Path Switch Request Failure message to the Target NG-RAN.
If the UE Radio Capability ID is included in the N2 Path Switch Request Ack message, when there is no corresponding UE radio capabilities set for UE Radio Capability ID at the Target NR-RAN, the Target NG-RAN shall request the AMF to provide the UE radio capabilities set corresponding to UE Radio Capability ID to the Target NG-RAN.
Step 8.
By sending a Release Resources message to the Source NG-RAN, the Target NG-RAN confirms success of the handover. It then triggers the release of resources with the Source NG-RAN.
Step 9.
[Conditional] The UE may initiate Mobility Registration Update procedure if one of the triggers of registration procedure applies as described in clause 4.2.2.2.2. In this case, only steps 1, 2, 3, 17 and 21 in clause 4.2.2.2.2 are performed.
4.9.1.2.3 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover with insertion of intermediate UPF p. 243
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a Source NG-RAN to a Target NG-RAN using Xn when the AMF is unchanged and the SMF decides that insertion of a new additional intermediate UPF is needed. If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of a PDU Session to be switched to the Target NG-RAN, the SMF may select two Intermediate UPFs (I-UPFs) and set up two N3 and N9 tunnels between the Target NG-RAN and the UPF (PSA) via the two I-UPFs as described in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501.
In the case of using UL CL, the I-UPF can be regarded as UL CL and additional PSA providing local access to a DN. In the case of using Branching Point, the I-UPF can be regarded as BP.
It is assumed that the PDU Session for the UE comprises of only one UPF that acts as a PDU Session Anchor at the time of this Handover procedure for non-roaming and local breakout roaming scenario. In the case of home routed roaming scenario, the PDU Session of the UE comprises of at least one UPF in the VPLMN and one UPF in the HPLMN at the time of this handover procedure. In this case, additional insertion of an N3 terminating intermediate UPF will not have impact on the connectivity between the UPF in VPLMN and UPF in HPLMN. The presence of IP connectivity between the UPF (PDU Session Anchor) and Source NG-RAN, between the UPF (PDU Session Anchor) and Target NG-RAN and between the intermediate UPF (I-UPF) and Target NG-RAN, is assumed. (If there is no IP connectivity between UPF (PDU Session Anchor) and Target NG-RAN, it is assumed that the N2-based handover procedure in clause 4.9.1.3 shall be used instead).
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.9.1.2.3-1.
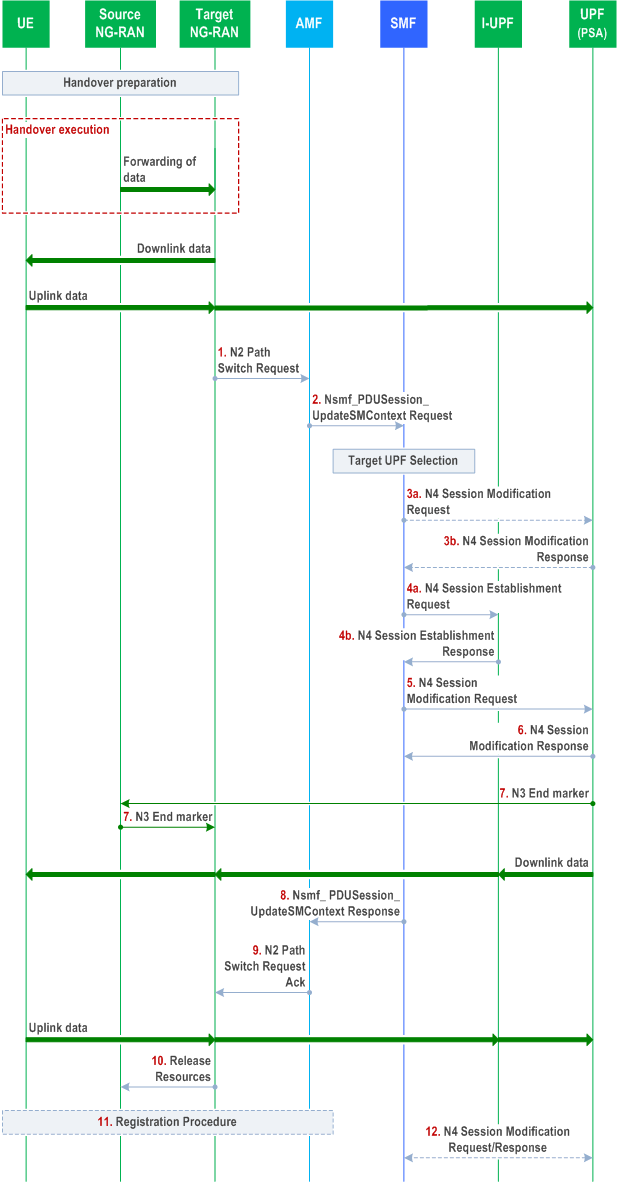
Steps 1-2 are the same as described in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 3a.
[Conditional] SMF to UPF (PSA): N4 Session Modification Request.
If the SMF selects a new UPF to act as intermediate UPF for the PDU Session and the different CN Tunnel Info need be used, the SMF sends N4 Session Modification Request message to UPF (PSA).
Step 3b.
[Conditional] UPF (PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
The UPF (PSA) sends an N4 Session Modification Response message to the SMF. The UPF provides CN Tunnel Info (on N9) to the SMF. If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of the PDU Session, the UPF (PSA) provides two CN Tunnel Info (on N9) to the SMF and indicates the SMF that one CN Tunnel Info is used as redundancy tunnel of the PDU Session as described in in clause 5.33.2.2 of TS 23.501. The UPF (PSA) associate the CN Tunnel Info (on N9) with UL Packet detection rules provided by the SMF.
Step 4a.
SMF to I-UPF: N4 Session Establishment Request (Target NG-RAN Tunnel Info, CN Tunnel Info of the PDU Session Anchor)
For PDU Sessions to be updated, if the UE has moved out of the service area of UPF connecting to the serving NG-RAN node, the SMF then selects an I-UPF based on UPF Selection Criteria according to clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501. An N4 Session Establishment Request message is sent to the I-UPF. The CN Tunnel Info of the PDU Session Anchor, which is used to setup N9 tunnel, is included in the N4 Session Establishment Request message.
Step 4b.
I-UPF to SMF: N4 Session Establishment Response.
The I-UPF sends an N4 Session Establishment Response message to the SMF. The UL and DL CN Tunnel Info of I-UPF is sent to the SMF.
If SMF select two Intermediate UPFs (I-UPFs) to perform redundant transmission for a PDU session, step 4a and 4b are performed between the SMF and each I-UPF.
Step 5.
SMF to PDU Session Anchor: N4 Session Modification Request (DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF).
The SMF sends N4 Session Modification Request message to the PDU Session Anchor.
If a different CN Tunnel Info is used on N9 in UPF (PSA), the SMF starts a timer to release the CN Tunnel for N3. Otherwise the SMF does not need to start a timer to release the CN Tunnel Info used on N3 in UPF(PSA) (i.e. CN Tunnel Info is common for both N3 and N9).
If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of the PDU Session, the SMF provides two DL CN Tunnel Info (for N9) to the UPF (PSA) and indicates to the UPF (PSA) one of the DL CN Tunnel Info is used as redundancy tunnel of the PDU Session.
Step 6.
PDU Session Anchor to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
The PDU Session Anchor responds with the N4 Session Modification Response message after requested PDU Sessions are switched. At this point, PDU Session Anchor starts sending downlink packets to the Target NG-RAN via I-UPF.
Step 7.
In order to assist the reordering function in the Target NG-RAN, the PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the Target NG-RAN.
Step 8.
SMF to AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (N2 SM Information (UL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF, updated QoS parameters for accepted QoS Flows)).
The SMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response to the AMF.
Step 8-11.
Steps 8-11 are same as steps 6-9 defined in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 12.
After the timer set in step 5 expires, the SMF informs the PDU Session Anchor to remove the CN Tunnel for N3 via N4 Session Modification procedure.
4.9.1.2.4 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover with re-allocation of intermediate UPF p. 244
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a Source NG-RAN to a Target NG-RAN using Xn when the AMF is unchanged and the SMF decides that the intermediate UPF (I-UPF) is to be changed. In the case of using UL CL, the I-UPF can be regarded as UL CL and additional PSA provides local access to a DN, the simultaneous change of UL-CL and the additional PSA is described in clause 4.3.5.7. In the case of using Branching Point, the I-UPF can be regarded as BP.
It is assumed that the PDU Session for the UE comprises of a UPF that acts as a PDU Session Anchor and an intermediate UPF at the time of this Handover procedure for non-roaming and local breakout roaming scenario. In the case of home routed roaming scenario, the PDU Session of the UE comprises of at least one UPF in the VPLMN and UPF in the HPLMN which acts as a PDU Session Anchor at the time of this handover procedure. The Source UPF referred in this clause 4.9.1.2.4 is the UPF which terminates N3 interface in the 5GC. The presence of IP connectivity between the Source UPF and Source NG-RAN, between the source UPF and Target NG-RAN and between the Target UPF and Target NG-RAN, is assumed. (If there is no IP connectivity between source UPF and Target NG-RAN, it is assumed that the N2-based handover procedure in clause 4.9.1.3 shall be used instead).
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.9.1.2.4-1.
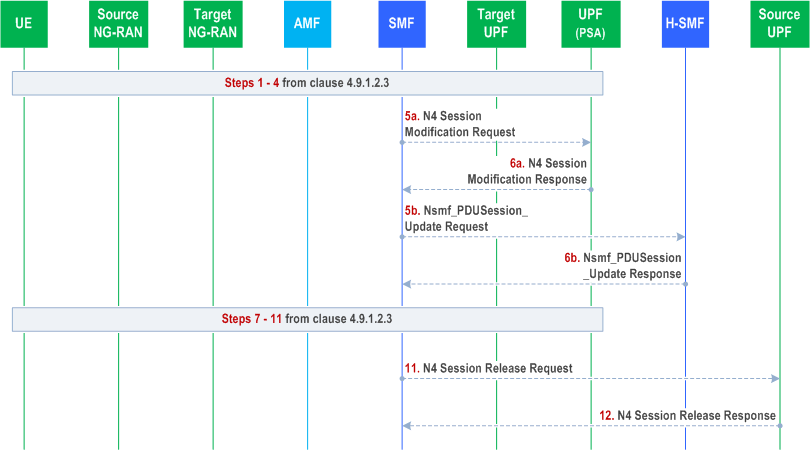
Steps 1-4 are same as steps 1-4 described in clause 4.9.1.2.3 except that the I-UPF in clause 4.9.1.2.3 is replaced by Target UPF.
Step 5.
[Conditional] The SMF sends N4 Session Modification Request message to the PDU Session Anchor. The DL CN Tunnel Info of the Target UPF is included in this message. If redundant transmission is performed for one or more QoS Flows of the PDU Session, the SMF provides two DL CN Tunnel Info (for N9) to the UPF (PSA) and indicates to the UPF (PSA) one of the DL CN Tunnel Info is used as redundancy tunnel of the PDU Session.
In the case of home routed roaming, if the N9 terminating V-UPF, which is connected to with home UPF, is changed, the V-SMF invokes an Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request (DL CN Tunnel Info) service operation toward the H-SMF.
Step 6.
[Conditional] The SMF associated with the PDU Session Anchor responds with the N4 Session Modification Response message. In the case of home routed roaming, the H-SMF responds with the Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Response service operation toward the V-SMF once H-UPF is updated with the DL Tunnel Info of the T-UPF. At this point, PDU Session Anchor starts sending downlink packets to the Target NG-RAN via Target UPF.
Step 7-11.
Steps 7-11 are same as steps 7-11 described in clause 4.9.1.2.3 except that the I-UPF in clause 4.9.1.2.3 is replaced by Target UPF.
If the Source UPF acts as a UL CL or BP, the SMF indicates to only one of the PDU Session Anchors to send the "end marker" packets. To ensure the "end marker" is the last user plane packet on the old path, the SMF should modify the path on other PDU Session Anchors before it indicates the PDU Session Anchor to send the "end marker" packets.
Step 11.
The timer is started in step 4 if the source UPF is not the PSA UPF. When this timer is expired, the SMF initiates Source UPF(s) Release procedure by sending an N4 Session Release Request (Release Cause).
Step 12.
The Source UPF(s) acknowledges with an N4 Session Release Response message to confirm the release of resources.