Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.15.3.2.5 Information flow for downlink data delivery status with SMF buffering
4.15.3.2.6 GMLC service operations information flow
4.15.3.2.7 Information flow for Availability after DDN Failure with SMF buffering
4.15.3.2.8 Information flow for downlink data delivery status with UPF buffering
4.15.3.2.9 Information flow for Availability after DDN Failure with UPF buffering
4.15.3.2.10 Number of UEs and PDU Sessions per network slice notification procedure
4.15.3.2.11 Network-initiated explicit event notification subscription cancel procedure
4.15.3.2.13 Handling AF requests when the UE is identified via UE addressing information
...
...
4.15.3.2.5 Information flow for downlink data delivery status with SMF buffering |R16| p. 413
The procedure is used if the SMF requests the UPF to forward downlink data packets that are subject of extended buffering in the SMF. The procedure describes a mechanism for the Application Function to subscribe downlink data delivery status notifications. The downlink data delivery status notifications relates to high latency communication, see also clauses 4.24.2 and 4.2.3.3.
Cancelling the subscription is done by sending Nnef_EventExposure_Unsubscribe request identifying the subscription to cancel with Subscription Correlation ID in the same order as indicated in Figure 4.15.3.2.5-1 for the corresponding subscribe requests. Step 0 and the notification steps 7 to 9 are not applicable in cancellation case.
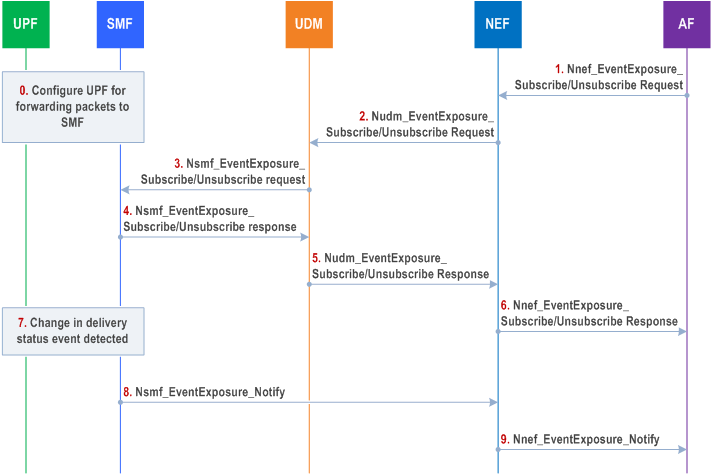
Step 0.
The SMF (in the non-roaming case the SMF, in the roaming case the V-SMF, in the case of PDU session with I-SMF the I-SMF) configures the relevant UPF to forward downlink data packets towards the SMF as described in clause 5.8.3 in TS 23.501. The SMF decides to apply this behaviour based on the "expected UE behaviour". Alternatively, step 0 is triggered by step 3,
Step 1.
The AF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe Request to NEF requesting notification for event "Downlink data delivery status" with traffic descriptor (e.g. the source of the downlink IP or Ethernet traffic) for a UE or group of UEs. If the reporting event subscription is authorized by the NEF, the NEF records the association of the event trigger and the requester identity. The Downlink data delivery status events include:
Step 2.
-
First downlink Packet in extended buffering event:
- This event is triggered when the first new downlink data packet is buffered with extended buffering matching the traffic descriptor.
- in notifications about this Downlink data delivery status, the SMF provides the Extended Buffering time as determined in clause 4.2.3.3.
-
First downlink Packet discarded:
- This event occurs when the first packet matching the traffic descriptor is discarded because the Extended Buffering time, as determined by the SMF, expires or the amount of downlink data to be buffered is exceeded.
-
First Downlink Packet transmitted:
- This event occurs when the first packet matching the traffic descriptor is transmitted after previous buffering or discarding of corresponding packet(s) because the UE of the PDU Session becomes ACTIVE and buffered data can be delivered to UE according to clause 4.2.3.3.
The NEF sends the Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe Request to UDM. Identifier of the UE or group of UEs, the traffic descriptor, monitoring event received from AF in step 1 and notification endpoint of the NEF are included in the message. If the reporting event subscription is authorized by the UDM, the UDM records the association of the event trigger and the requester identity. Otherwise, the UDM continues in step 5 indicating failure.
Step 3.
The UDM sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe Request message to each SMF where at least one UE identified in step 2 has a PDU session established. If the UDM is able to derive the applicable DNN and S-NSSAI from the traffic descriptor via configured information, the UDM may send Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe Request messages only to SMFs with PDU sessions with that DNN and S-NSSAI for such UEs and includes the Identifier of the UE or Internal-Group-Id, traffic descriptor, monitoring event and the notification endpoint of NEF received in step 2 are included in the message. If the UDM becomes aware that such a UE has a PDU session established with the DNN and S-NSSAI corresponding to the traffic descriptor at a later time than when receiving step 2, the UDM then executes step 3.
In the case of home-routed PDU session or PDU session with I-SMF, the UDM sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe Request message to each H-SMF or SMF and the H-SMF or SMF further sends Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe Request message to each related V-SMF or I-SMF. Steps 7-8 are performed by V-SMF or I-SMF.
Step 4.
The SMF sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe Response message to the UDM.
Step 5.
The UDM send sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe response message to the NEF.
Step 6.
The NEF sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe response to the AF.
Step 7.
The SMF detects a change in Downlink Data Delivery Status event as described in clause 4.2.3. The SMF becomes aware that Downlink Packet(s) require extended buffering via a Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation with the AMF. If the SMF decides to discard packets, the "Downlink Packet(s) discarded event" is detected. The SMF detects that previously buffered packets can be transmitted by the fact that the related PDU session becomes ACTIVE.
Step 8.
The SMF sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Notify with Downlink Delivery Status event message to NEF.
Step 9.
The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify with Downlink Delivery Status event message to AF.
4.15.3.2.6 GMLC service operations information flow |R16| p. 414
The procedure is used by the NF to subscribe to notifications and to explicitly cancel a previous subscription. The GMLC service operations information flow is defined in clause 6.1.2 and clause 6.3 of TS 23.273.
4.15.3.2.7 Information flow for Availability after DDN Failure with SMF buffering |R16| p. 414
The procedure is used if the SMF requests the UPF to forward packets that are subject of buffering in the SMF. The procedure describes a mechanism for the Application Function to subscribe to notifications about availability after downlink data notification failure. The Availability after Downlink Data Notification failure event is related to high latency communication, see also clauses 4.24.2 and 4.2.3.3.
Cancelling the subscription is done by sending EventExposure_Unsubscribe requests identifying the subscription to cancel with the Subscription Correlation ID in the same order as indicated in Figure 4.15.3.2.7-1 for the corresponding subscribe requests (the AMF unsubscribes the DDN Failure status notification by sending the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request message to each SMF in step 5). Step 0 and the notification steps 9 to 13 are not applicable in the cancellation case.
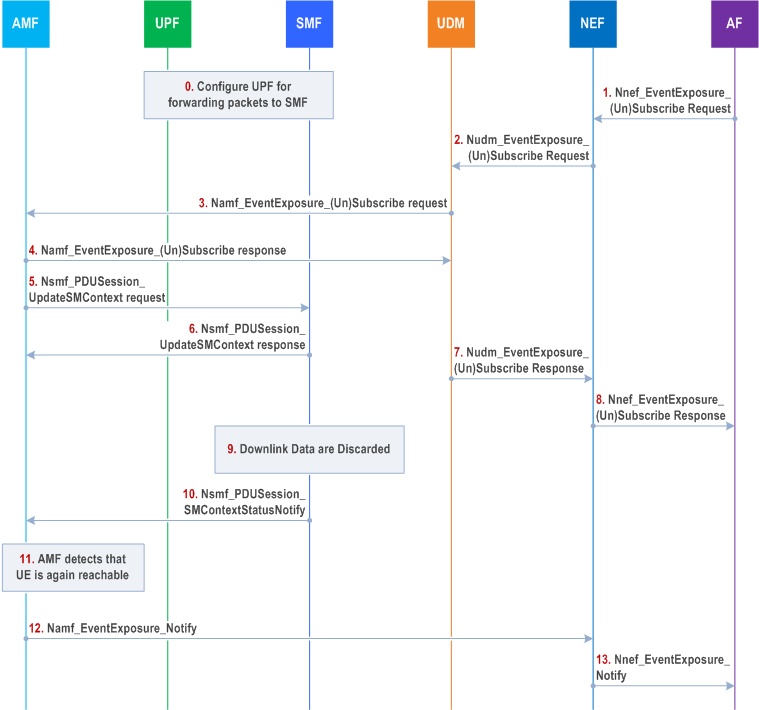
Step 0.
The SMF (in the no-roaming case the H-SMF. in the roaming case the V-SMF, in the case of PDU session with I-SMF the I-SMF) configures the relevant UPF to forward packets to the SMF as described in clause 5.8.3 in TS 23.501. The SMF decides to apply this behaviour based on the "expected UE behaviour". Alternatively, step 0 is triggered by step 5.
Step 1.
The AF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe Request to the NEF requesting notifications for "Availability after DDN Failure" for a UE or group of UEs and providing a traffic descriptor identifying the source of the downlink IP or Ethernet traffic. If the reporting event subscription is authorized by the NEF, the NEF records the association of the event trigger and the requester identity.
The AF may include Idle Status Indication request in the Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe Request. If Idle Status Indication request is included, the NEF includes it in Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe message. If the NEF does not support the requested Idle Status Indication, then depending on operator policies, the NEF rejects the request.
Step 2.
The NEF sends the Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe Request to UDM. Identifier of the UE or group of UEs, the traffic descriptor, monitoring event received from AF at step 1 and notification endpoint of the NEF are included in the message. If the reporting event subscription is authorized by the UDM, the UDM records the association of the event trigger and the requester identity. Otherwise, the UDM continues in step 7 indicating failure.
If the UDM receives Idle Status Indication request, it includes it in Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe message.
Step 3.
The UDM sends Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe messages to the AMF(s) which serve the UE(s) identified in step2 to subscribe to "Availability after DDN Failure". The UDM includes the DNN and S-NSSAI as well as the Traffic Descriptor if available A separate subscription is used for each UE. The NEF notification endpoint received in step 2 is included in the message. If the UDM becomes aware that such a UE is registered at a later time than when receiving step 2, the UDM then executes step 3.
Step 4.
The AMF acknowledges the execution of Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe .
Step 5.
If PDU Session exists for the DNN and S-NSSAI, the AMF subscribes to DDN Failure status notification by sending the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request message to each SMF, requesting the SMF to notify DDN Failure. The AMF also includes in Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext the Traffic Descriptor and NEF correlation ID if received from the UDM. For new PDU Session establishment towards a DNN and S-NSSAI, the AMF subscribes to DDN Failure status notification in Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request message if the UDM has subscribed to Availability after DDN Failure event.
In the case of home-routed PDU session or PDU session with I-SMF, the AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request message(s) to the related V-SMF(s) or I SMF(s). Steps 9-10 are performed by those V-SMF(s) or I-SMF(s).
Step 6.
The (I/V-)SMF sends the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response message to the AMF.
Step 7.
The UDM sends the Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe response to the NEF.
Step 8.
The NEF sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe response to the AF.
Step 9-10.
The SMF is informed that the UE is unreachable via a Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation. The SMF then decides to discard downlink packets received from the UPF. By comparing those discarded downlink packets received from the UPF with the Traffic Descriptor(s) received in the event subscription(s), the SMF determines whether DDN Failure due to any traffic from an AF is to be notified to the AMF and if so, the SMF sends the DDN Failure status, by means of Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify message including NEF Correlation ID, to the AMF. If the UE is not reachable after the AMF received the DDN Failure notification from the SMF, the AMF shall set a Notify-on-available-after-DDN-failure flag corresponding to the NEF Correlation ID.
Step 11-12.
[Conditional] The AMF detects the UE is reachable and sends the event report(s) based on the Notify-on-available-after-DDN-failure flag, by means of Namf_EventExposure_Notify message(s), only to the NEF(s) indicated as notification endpoint(s) identified via the corresponding subscription in step 3. In this way, only the AF(s) for which DL traffic transmission failed are notified.
If the AMF received Idle Status Indication request in step 3 and the AMF supports Idle Status Indication, the AMF includes also the Idle Status Indication.
Step 13.
The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify message with the "Availability after DDN Failure" event to AF.
4.15.3.2.8 Information flow for downlink data delivery status with UPF buffering |R16| p. 416
The procedure is used if the SMF requests the UPF to buffer packets. The procedure describes a mechanism for the Application Function to subscribe to notifications about downlink data delivery status. The downlink data delivery status notifications relates to high latency communication, see also clauses 4.24.2 and 4.2.3.3.
Cancelling is done by sending Nnef_EventExposure_Unsubscribe request identifying the subscription to cancel with Subscription Correlation ID. Steps 2 to 5 are not applicable in the cancellation case.
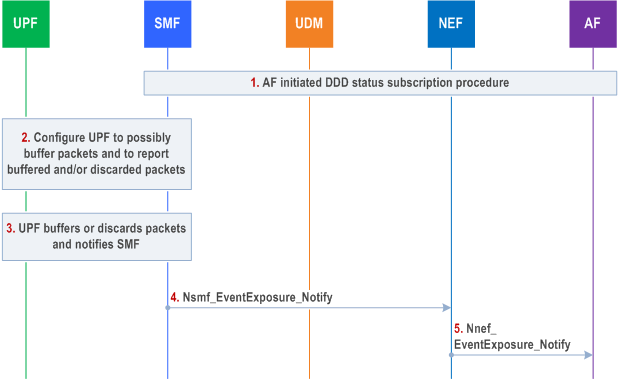
Step 1.
AF interacts with NEF to subscribe DDD status event in SMF as described in steps 0-6 of clause 4.15.3.2.5.
In the case of subscription cancelling and SMF having interacted with the PCF during event subscription, the SMF reports to the PCF the unsubscribe of the DDD status event. The PCF updates or removes the PCC rule and this triggers the SMF to update or remove the corresponding PDR in the UPF. In case of home-routed PDU Session, the SMF unsubscribes the DDD status event from the V-SMF which in turn updates the N4 information (deactivating the notifications) in the V-UPF. In case of PDU Session with I-SMF, the SMF provides updated N4 information (deactivating the notifications) to the I-SMF which in turn updates the I-UPF.
Step 2.
If the UPF is configured to apply extended buffering, step 2 is executed immediately after step 1. Otherwise, step 2 is executed when the SMF is informed that the UE is unreachable via a Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation as described in clause 4.2.3 and the SMF then also updates the PDR(s) for flows requiring extended buffering to requests the UPF to buffer downlink packets. If the DDD status event with traffic descriptor has been received in the SMF in step 1, if extended DL Data buffering in the UPF applies, the SMF checks whether an installed PDR for the Traffic Descriptor exists and if so, requests the UPF to provide the requested type(s) of notifications. If PCC is not used and there is no installed PDR with the exact same traffic descriptor, the SMF copies the installed PDR that would have previously matched the incoming traffic described by the traffic descriptor, but provides that traffic descriptor, a higher priority and the requested type(s) of notifications. If PCC is used and if the "DDD Status event subscription with Traffic Descriptor" PCRT is set as defined in clause 6.1.3.5 of TS 23.503, the SMF interacts with the PCF and forwards the traffic descriptor before contacting the UPF; the PCF then updates an existing PCC rule or provides a new PCC rule taking into consideration the traffic descriptor for the subscribed DDD status event.
In the case of home-routed PDU Session, the V-SMF generates the N4 information (activating the notifications) for the V-UPF based on local configuration.
In the case of PDU Session with I-SMF, the SMF provides N4 information (activating the notifications) to the I-SMF based on local policy or the "DDD Status event subscription with Traffic Descriptor" PCRT from PCF. The I-SMF updates the I-UPF with this N4 information.
For home-routed PDU Session or PDU Session with I-SMF, steps 3-4 below are performed by V-SMF/V-UPF or I-SMF/I-UPF.
Step 3.
The UPF reports when there is buffered or discarded traffic matching the received PDR to the SMF. The SMF detects that previously buffered packets can be transmitted by the fact that the related PDU session becomes ACTIVE.
Step 4.
The SMF sends the Nsmf_EventExposure_Notify with Downlink Delivery Status event message to NEF.
Step 5.
The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify with Downlink Delivery Status event message to AF.
4.15.3.2.9 Information flow for Availability after DDN Failure with UPF buffering |R16| p. 417
The procedure is used if the SMF requests the UPF to buffer packets. The procedure describes a mechanism for the Application Function to subscribe to notifications about availability after DDN failure.
Cancelling is done by sending Nnef_EventExposure_Unsubscribe request identifying the subscription to cancel with Subscription Correlation ID. Steps 2 to 7 are not applicable in the cancellation case.
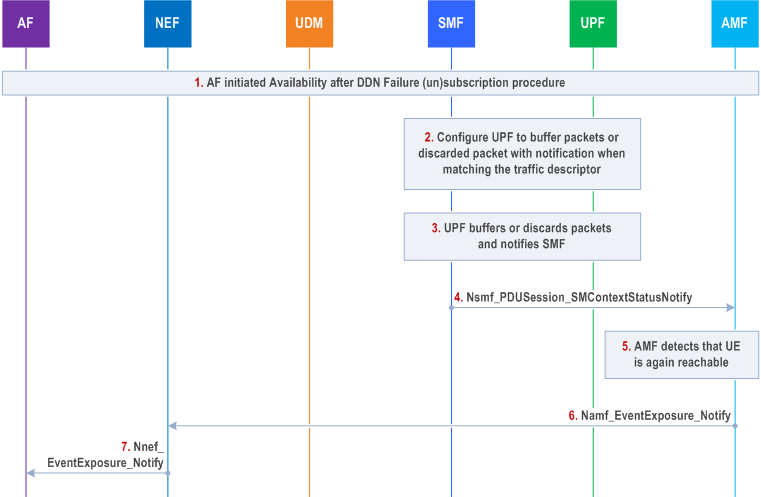
Step 1.
AF interacts with NEF to subscribe availability after DDN failure event in AMF/SMF as described in steps 0-8 of clause 4.15.3.2.7.
In case of subscription cancelling from AMF and SMF having interacted with the PCF during event subscription, the SMF reports to the PCF for the unsubscribe of DDN failure event. The PCF updates or removes the PCC rule and this triggers the SMF to update or remove the corresponding PDR and FAR in the UPF.
In the case of PDU Session with I-SMF or home-routed PDU Session, the AMF unsubscribes the DDN failure event towards I/V-SMF. In case of home-routed PDU Session, the V-SMF updates the N4 information (deactivating the notifications) in the V-UPF. In case of PDU Session with I-SMF, the I-SMF may request N4 information (deactivating the notifications) from the SMF and provides the Traffic Descriptor to the SMF. The SMF provides updated N4 information (deactivating the notifications) to the I-SMF which in turn updates the I-UPF.
Step 2.
The SMF checks whether an installed PDR for the Traffic Descriptor exists and if so, requests the UPF to report when the first downlink packet is received and when it is discarded in the UPF. If PCC is not used and there is no installed PDR with the exact same traffic descriptor, the SMF copies the installed PDR that would have previously matched the incoming traffic described by the traffic descriptor, but provides that traffic descriptor, a higher priority, and requests the UPF to report when the first downlink packet is received and when it is discarded in the UPF.
If PCC is used and if the "DDN Failure event subscription with Traffic Descriptor" PCRT is set as defined in clause 6.1.3.5 of TS 23.503, the SMF interacts with the PCF and forwards the traffic descriptor before contacting the UPF; the PCF then updates an existing PCC rule or provides a new PCC rule taking into consideration the traffic descriptor for the subscribed DDN failure event.
In the case of PDU Session with I-SMF or home-routed PDU Session, the AMF subscribes the DDN failure event towards the I/V-SMF. In the case of home-routed PDU Session, the V-SMF generates the N4 information (activating the notifications) for the V-UPF based on local configuration.
In the case of PDU Session with I-SMF, the I-SMF may request N4 information (activating the notifications) from the SMF based on local configuration and provides the Traffic Descriptor to the SMF. The SMF provides updated N4 information (activating the notifications) to the I-SMF which in turn updates the I-UPF.
For home-routed PDU Session or PDU Session with I-SMF, steps 3-4 below are performed by V-SMF/V-UPF or I-SMF/I-UPF.
Step 3-4.
When the first downlink packet matching the traffic descriptor is received in the UPF, if in step 2 the SMF indicated drop notification to the UPF, the UPF notifies the SMF and the SMF reports the DDN Failure status with NEF Correlation ID, by means of Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify message, to the AMF indicated as notification endpoint.
When the first downlink packet matching the traffic descriptor is received in the UPF, if in step 2 the SMF indicated buffer notification to the UPF, the UPF notifies the SMF and the SMF may initiate Network Triggered Service Request as specified in clause 4.2.3.3. If the AMF responds Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer response with failure (e.g. due to UE not reachable, or paging no response), in addition to what is specified in clause 4.2.3.3, the SMF reports DDN Failure status with NEF Correlation ID, by means of Nsmf_PDUSession_SMContextStatusNotify message, to the AMF indicated as notification endpoint.
When the AMF receives DDN Failure status from the SMF, the AMF shall set a Notify-on-available-after-DDN-failure flag corresponding to the Notification Correlation Id and the identifier of the UE if available.
Step 5-6.
[Conditional] The AMF detects the UE is reachable and sends the event report(s) based on the Notify-on-available-after-DDN-failure flag, by means of Namf_EventExposure_Notify message(s), only to the NEF(s) indicated as notification endpoint(s) identified via the corresponding subscription in step 1. In this way, only the AF(s) for which DL traffic transmission failed are notified.
If the AMF received Idle Status Indication request in step 1 and the AMF supports Idle Status Indication, the AMF includes also the Idle Status Indication in Namf_EventExposure_Notify message.
Step 7.
The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify message with the "Availability after DDN Failure" event to AF.
4.15.3.2.10 Number of UEs and PDU Sessions per network slice notification procedure |R17| p. 419
4.15.3.2.10.1 Reported value(s) aggregated at NEF p. 419
This procedure depicts the case of an AF subscribing to receive the registered number of UEs, or the number of PDU sessions in a specific S-NSSAI. The procedure handles the case when there is a single NSACF in the PLMN responsible for the S-NSSAI (single Service Area) or when there are multiple NSACFs responsible for the S-NSSAI in the PLMN (multiple Service Areas).
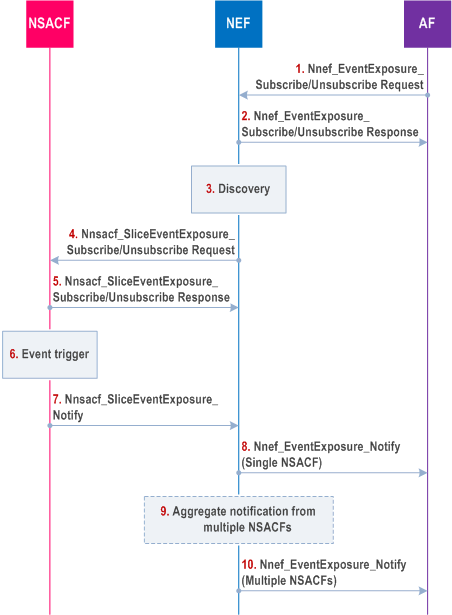
Figure 4.15.3.2.10.1-1: Reported value(s) aggregated at NEF per network slice notification procedure
Step 1.
If the hierarchical NSAC architecture is deployed in the PLMN for the NSAC of an S-NSSAI and the number of UEs, number of UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection, or number of PDU Sessions are aggregated at NEF, the same procedure as above can be reused. In this case Primary NSACF behaves as a normal NSACF.
To subscribe or unsubscribe for the number of UEs or the number of PDU Sessions per network slice notification with the NEF, the AF sends Nnef_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe Request (Event ID, Event Filter, Event Reporting information, S-NSSAI) message to the NEF. The Event ID parameter defines the subscribed event ID, i.e. Number of Registered UEs or Number of Established PDU Sessions. The Event Filter parameter defines the S-NSSAI, in case of a trusted AF or AF-Service-Identifier as defined in TS 29.522 for an untrusted AF, for which reporting is required. The Event Reporting information parameter defines the mode of reporting, which includes threshold reporting with a threshold value or periodic reporting with included periodicity time interval. The S-NSSAI is the slice for which the subscription is requested
The AF may request one-time reporting or immediate reporting.
Notifications related to the threshold based subscriptions behave as follows:
Step 2.
- A single notification is sent only when the number of registered UEs or the number of established PDU Sessions reaches the threshold. A single notification is sent every time there is a change from being below the threshold to reach the threshold.
- A single notification is sent only once when the number of registered UEs or the number of established PDU Sessions go below the threshold after reaching it. A single notification is sent every time there is a change from reaching the threshold to coming down below the threshold.
The NEF confirms with Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe /Unsubscribe Response message to the AF. This message may include the event reporting, if available in the NEF and immediate reporting or one-time reporting was requested by the AF. In the case of Untrusted AF, the NEF includes the AF-Service-Identifier corresponding to the S-NSSAI in the returned notification.
If immediate reporting or one-time reporting is requested, step 2 occurs after step 5 and the subscription response contains the immediate or one-time report. For the case of one-time reporting, no subscription is created at the NEF/NSACF.
Step 3.
The NEF may query the NRF to find the NSACF(s) responsible for the requested S-NSSAI. If needed, the NEF translates the AF-Service-Identifier to the corresponding S-NSSAI prior to performing the query.
Step 4.
If the NEF has not already subscribed to the event from the NSACF for the requested S-NSSAI, the NEF initiates the request Nnsacf_SliceEventExposure_Subscribe /Unsubscribe Request (Event ID, Event Filter, Event Reporting information, immediate reporting, S-NSSAI) to all the NSACFs supporting the requested S-NSSAI. The NEF stores the AF requested Event Reporting Information. If multiple NSACFs are selected for the requested S-NSSAI, the NEF may set the Event Reporting Information to periodic in its request to the NSACFs. If single NSACF is selected, the NEF sets the Event Reporting Information identical to the received request from the AF. The NEF also sets the Event ID and Event Filter identical to the received request from the AF
Step 5.
The NSACF(s) confirms with Nnsacf_SliceEventExposure_Subscribe /Unsubscribe Response message to the NEF. This message may include the event reporting if available at NSACF and immediate reporting or one-time reporting was requested by the NEF.
Step 6.
When the reporting condition for a subscribed event is fulfilled, the NSACF triggers a notification towards the NEF.
Step 7.
The NSACF sends the Nnsacf_SliceEventExposure_Notify (Event ID, Event Reporting information) message to the NEF. If the subscription is for event based notification (e.g. based on the monitored event reaching a threshold value), the Event Reporting information parameter contains confirmation for the event fulfilment. If the subscription is for periodic notification or for immediate reporting, the Event Reporting information parameter provides information for the current number of UEs registered with a network slice (e.g. represented in percentage of the maximum number of the UEs registered with the network slice) or information for the current number of PDU Sessions on a network slice (e.g. represented in percentage of the maximum number of the UEs established on the network slice).
Step 8.
When a single NSACF is returned from the discovery procedure, the NEF sends the Nnef_EventExposure_Notify (Event ID, Event Reporting information) message since the reporting condition is fulfilled. In the case of Untrusted AF, the NEF includes the AF-Service-Identifier corresponding to the S-NSSAI in the returned notification.
Step 9.
When multiple NSACFs are selected for the requested NSSAI the NEF performs the aggregation from reporting NSACF(s) and maintain the overall usage of the S-NSSAI for the selected NSACFs as long as the subscription is active.
Step 10.
When multiple NSACFs are selected for the requested S-NSSAI and when the reporting condition for a subscribed event by the AF is fulfilled, the NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify (Event ID, Event Reporting information) message towards the AF. In case of untrusted AF; the NEF includes the AF-Service-Identifier corresponding to the S-NSSAI in the returned notification.
4.15.3.2.10.2 Reported value(s) aggregated at Primary NSACF p. 421
If the hierarchical NSAC architecture is deployed in the PLMN for the NSAC of an S-NSSAI, the Primary NSACF needs to be aware of the current status of registered UEs, UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection, or established PDU sessions at all NSACFs with whom it is interacting, so it can dynamically adapt and adjust the local Maximum number of UEs, local Maximum number of UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection, or PDU sessions configured at the NSACFs. In this case, it is possible to leverage this capability and provide subscribing AFs to receive the registered number of UEs, number of UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection, or the number of PDU sessions for the requested S-NSSAI without NEF aggregation. Such a procedure is depicted below.
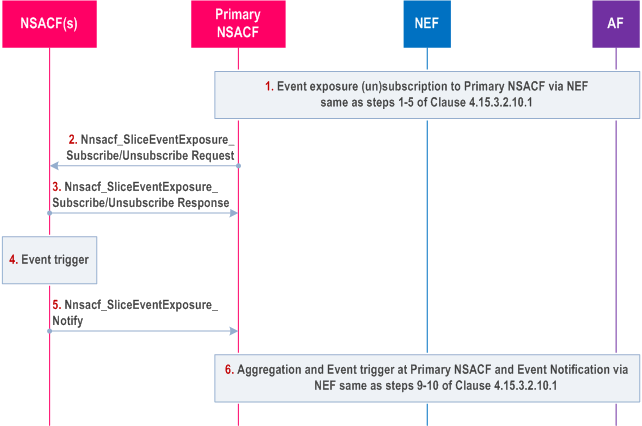
Step 1.
The AF subscribes (or unsubscribe) to the number of UEs, or the number of PDU Sessions per network slice notification to the NEF. The NEF finds the primary NSACF responsible for the requested S-NSSAI. Based on the network configuration, the NEF does not to do the aggregation. The procedure is same as steps 1-5 of clause 4.15.3.2.10.1 with the following differences:
Step 2-6.
- Based on the network configuration the NEF is aware that one NSACF can serve entire PLMN for the requested S-NSSAI, i.e. existence of the Primary NSACF. The NEF queries the NRF to find the corresponding primary NSACF responsible for the requested S-NSSAI. Besides the requested S-NSSAI, the Serving Area information of "Entire PLMN" is included as querying parameter. In the case of Trusted AF, the AF can discover and subscribe (or unsubscribe) directly with the Primary NSACF.
- The NEF sets the Event Reporting Information identical to the received request from the AF. The NEF also sets the Event ID and Event Filter identical to the received request from the AF. The Primary NSACF responsible for the requested S-NSSAI performs the aggregation per network configuration.
The Primary NSACF subscribes (or unsubscribes) to the number of UEs, or the number of PDU Sessions per network slice notification to all the NSACFs supporting the requested S-NSSAI(s). The procedure is same as steps 4-7 of clause 4.15.3.2.10.1 for multiple NSACFs case with the Primary NSACF replacing the NEF and the following differences:
- Step 2, based on the received event subscription from NEF, the Primary NSACF triggers the slice event subscription to NSACF(s) if it does not exist before.
- Step 6, the Primary NSACF performs the aggregated values from reporting NSACF(s) including itself (if available) and maintain the overall usage of the S-NSSAI(s) for the indicated Event ID parameter, i.e. the number of UEs registered with a network slice, number of UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection, or the number of PDU Sessions established on a network slice, from the selected NSACFs as long as the subscription is active. When the reporting condition for a subscribed event is fulfilled, the Primary NSACF triggers a notification for the event towards the NEF. As values from the NSACF(s) has been aggregated at the Primary NSACF, there is no aggregation to be performed further at the NEF. NEF forwards the received values to AF.
4.15.3.2.11 Network-initiated explicit event notification subscription cancel procedure |R17| p. 423
The procedure is used by the UDM to delete an event notification subscription (see clause 4.15.1).
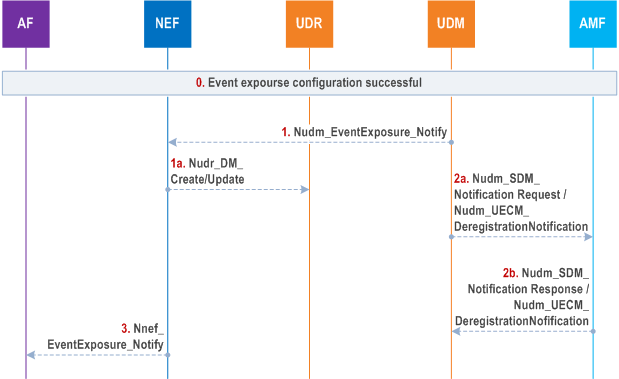
Step 0.
An event notification subscription procedure according to clause 4.15.3.2.2 or clause 4.15.3.2.2 has already executed successfully.
Step 1-1a.
If UE subscription is withdrawn in UDM, UE authorisation to the subscribed monitoring event or UE is removed from the subscribed target group, the UDM triggers Nudm_EventExposure_Notify towards the associated notification endpoint indicating the removal of the event notification along with the time stamp. The NEF may store the information in the UDR along with the time stamp using either Nudr_DM_Create or Nudr_DM_Update service operation as appropriate.
In order to remove certain UEs in a group of UEs for which there is an event notification subscription, the UDM provides impacted UE information (e.g. SUPI, MSISDN or External Identity) to the NEF and indicates the removal of the event notification subscription for these UE(s).
Step 2a-2b.
If UE subscription information changes (e.g. UE group information changes), the UDM sends Nudm_SDM_Notification request to related serving AMF(s) to update event notification subscription information. If the UE was a group member of a previous accepted group-based event notification subscription, the AMF shall stop the event notifications for the impacted UEs. If Maximum number of Reports is applied, the AMF shall set the number of reports of the indicated UE(s) to Maximum Number of Reports.
If UE subscription data is withdrawn, the UDM sends Nudm_UECM_DeregistrationNotification request to related serving AMF(s) to remove UE subscription information. If the UE was a group member of a previous accepted group-based event notification subscription, the AMF shall keep the accepted group-based event notification subscription unless all UEs subscriptions in the group are withdrawn.
Step 3.
The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify to the AF reporting event received by Nudm_EventExposure_Notify .
If the NEF receives UE Identifier(s) in step 1 for a group-based event notification subscription and the Maximum Number of Reports applies to the group-based event notification subscription, the NEF sets the number of reports of the indicated UE(s) to Maximum Number of Reports. The NEF sends Nnef_EventExposure_Notify to the AF and includes MSISDN(s) or External Identifier(s). If NEF determines that the reporting for the group is complete based on the update above, the NEF deletes the associated event notification subscription and requests that the UDM deletes the related event notification subscription for the group.
4.15.3.2.12 Void
4.15.3.2.13 Handling AF requests when the UE is identified via UE addressing information |R17| p. 424
An AF may request, via the NEF, the Event Exposure (as defined in clause 4.15.3) or the parameter provisioning (as defined in clause 4.15.6) targeting an individual UE, identifying the target UE by providing UE addressing information.
In this case the 5GC first needs to retrieve a UE Identifier based on:
- the UE addressing information as provided by the AF: this may correspond to an UE IP address as allocated by 5GC or to a MAC address of the UE (when Ethernet PDU Sessions are targeted),
- the corresponding DNN and/or S-NSSAI: this may have been provided by the AF or, alternatively, determined by the NEF using the identity of the AF.