Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.25 Procedures for NEF based Non-IP Data Delivery
4.25.1 General
4.25.2 SMF-NEF Connection Establishment
4.25.3 NIDD Configuration
4.25.4 NEF Anchored Mobile Originated Data Transport
4.25.5 NEF Anchored Mobile Terminated Data Transport
...
...
4.25 Procedures for NEF based Non-IP Data Delivery |R16| p. 672
4.25.1 General p. 672
Non-IP Data Delivery (NIDD) it is a means for delivering data via a PDU Sessions of type "Unstructured". The subsequent clauses describe the procedures necessary to support NEF based NIDD.
4.25.2 SMF-NEF Connection Establishment p. 672
When the UE performs the PDU Session establishment with PDU Session type of "Unstructured" and the subscription information corresponding to the UE requested DNN includes the "NEF Identity for NIDD" (NEF ID), then the SMF initiates a SMF-NEF Connection establishment procedure towards the NEF corresponding to the "NEF ID" for that DNN / S-NSSAI Combination.
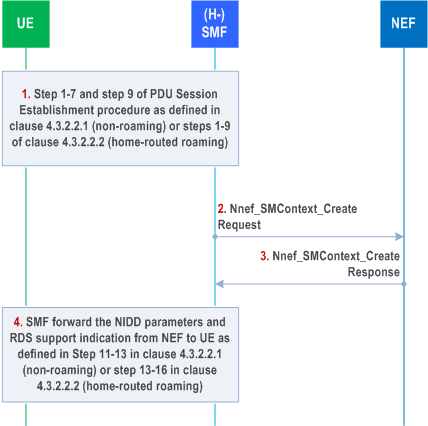
Step 1.
Steps 1-7 and step 9 of clause 4.3.2.2.1 for UE-requested PDU Session Establishment Procedure for non-roaming scenarios or steps 1-9 of clause 4.3.2.2.2 for UE-requested PDU Session Establishment Procedure for home-routed roaming scenarios. The (H-)SMF receives the Session Management Subscription data for the corresponding SUPI, DNN and S-NSSAI that is associated with NEF Identity for NIDD and NIDD information such GPSI and AF Identifier.
Step 2.
If the subscription information corresponding to DNN and S-NSSAI includes the "NEF Identity for NIDD" (NEF ID), the SMF shall create a PDU session towards the NEF. The SMF invokes Nnef_SMContext_Create Request (User Identity, PDU Session ID, SMF ID, NIDD information, S-NSSAI, DNN, [RDS support indication], [Small Data Rate Control parameters], [Small Data Rate Control Status], [Serving PLMN Rate Control parameters]) message towards the NEF. The RDS support indication is included if the UE capability to support Reliable Data Service (RDS) is included in the PCO in the PDU Session Establishment Request message. The SMF provides Small Data Rate Control parameters to the NEF for PDU Session, if required. The SMF provides the Small Data Rate Control Status to the NEF, if received from the AMF. If the Serving PLMN intends to enforce Serving PLMN Rate Control (see clause 5.31.14.2 of TS 23.501) for this PDU session then the SMF shall provide Serving PLMN Rate Control parameters to NEF for limiting the rate of downlink control plane data packets.
If no AF has previously performed the NIDD Configuration procedure with the NEF for the User Identity received in step 2, then the NEF initiates the NIDD Configuration procedure (see clause 4.25.3) before step 3.
Step 3.
The NEF creates an NEF PDU session Context and associates it with User Identity and PDU session ID. The NEF invokes Nnef_SMContext_Create Response (Cause, [RDS support indication], [Extended Buffering Support indication], [NIDD parameters]) towards the SMF confirming establishment of the PDU session to the NEF for the UE. If NEF supports and allows use of RDS, it includes the RDS support indication to SMF and the SMF includes it in the PCO. If NEF supports Extended Buffering, NEF includes Extended Buffering Support indication in the response and subscribes for mobility-related events with the AMF to receive an indication when the UE becomes reachable. The NIDD parameters (e.g. maximum packet size) are sent to the SMF, if available.
Step 4.
Steps 11-13 of clause 4.3.2.2.1 for UE-requested PDU Session Establishment Procedure for non-roaming scenarios or steps 13-16 of clause 4.3.2.2.2 for UE requested PDU Session Establishment Procedure for home-routed roaming scenarios.
4.25.3 NIDD Configuration p. 673
Figure 4.25.3-1 illustrates the procedure for configuring necessary information for data delivery via the NIDD API.
The NIDD Configuration procedure can be NEF initiated or AF triggered: in the former case the procedure starts at step 1, in the latter case it starts at step 2.
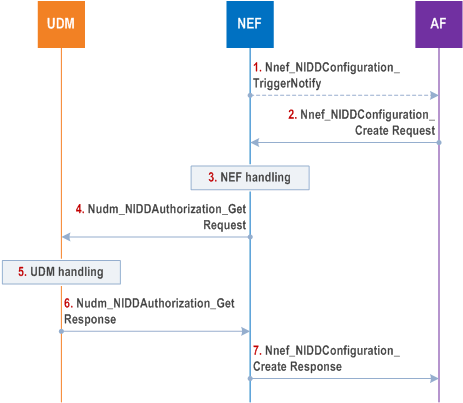
Step 1.
[Optional] If the NEF requires a NIDD configuration with a given AF, then the NEF sends a Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_TriggerNotify (GPSI, AF Identifier, NEF ID) message to the AF for asking the Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Request for the UE identified by the GPSI.
Step 2.
The AF sends a Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Request message (GPSI or External Group Identifier, AF Identifier, NIDD Duration, T8 Destination Address, Requested Action, TLTRI, Reliable Data Service Configuration, MTC Provider Information) to the NEF.
Reliable Data Service Configuration is an optional parameter that is used to configure the Reliable Data Service (as defined in clause 5.31.6 of TS 23.501) including port numbers for originator application(s) and receiver application(s). TLTRI is included in the request if the Requested Action is set to "Update" or "Cancel", otherwise TLTRI is not included in the request and the NEF assigns a TLTRI to the NIDD Configuration. If Reliable Data Service Configuration is present, the Reliable Data Service Configuration may include the mobile terminated and mobile originated serialization format(s) that are supported by the AF for each port number.
Step 3.
If the Requested Action is set to "Cancel" it indicates that the purpose of the request is to cancel the transaction identified by TLTRI and the flow proceeds to step 7. If the Requested Action is set to "Update", the purpose of the transaction is to update the parameters associated with the configuration (i.e. Reliable Data Service). Otherwise, the request is for a new NIDD configuration and the NEF stores the received GPSI or External Group Identifier, AF Identifier, T8 Destination Address and NIDD Duration. If either the AF is not authorised to perform this request (e.g. based on policies, if the SLA does not allow for it) or the Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Request is malformed, the NEF performs step 7 and provides a Cause value appropriately indicating the error. Depending on the configuration, the NEF may change the NIDD Duration.
Step 4.
The NEF sends an Nudm_NIDDAuthorisation_Get Request (GPSI or External Group Identifier, S-NSSAI, DNN, AF Identifier, MTC Provider Information, NIDD Duration, Update Notification Address) message to the UDM to authorise the NIDD configuration request for the received External Group Identifier or GPSI.
Step 5.
The UDM examines the Nudm_NIDDAuthorisation_Get Request message.
If the authorisation is successful and if an External Group Identifier was included in step 4, the UDM maps the External Group Identifier to an Internal-Group Identifier and a list of GPSIs and maps GPSIs to SUPIs.
Step 6.
The UDM sends an Nudm_NIDDAuthorisation_Get Response (single value or list of (SUPI and GPSI), Result) message to the NEF to acknowledge acceptance of the Nudm_NIDDAuthorisation_Get Request. If the UDM determines that the list size exceeds the message capacity, the UDM shall segment the list and send it in multiple messages (for details on segmentation, see TS 29.503). The SUPI(s) and if available, the GPSI(s) (when Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Request contains an GPSI) are returned by the UDM in this response. This allows the NEF to correlate the AF request received in step 2 of this procedure with the SMF-NEF Connection to be established for each UE or each group member UE. Depending on the configuration (e.g. based on DNN), the UDM may change the NIDD Duration and include the updated value of the NIDD Duration in the response to the NEF.
Step 7.
The NEF sends a Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Response (TLTRI, Maximum Packet Size, Reliable Data Service Indication and Cause) message to the AF to acknowledge acceptance of the Nnef_NIDDConfiguration_Create Request. If the NIDD Configuration was accepted, the NEF assigns a TLTRI to the NIDD Configuration and sends it to the AF. The NEF creates an association between the TLTRI, GPSI or External Group Identifier, SUPI and PDU session ID which is received from the SMF in step 2 of the SMF-NEF Connection procedure in clause 4.25.1. In the MT NIDD procedure, the NEF will use TLTRI and either GPSI or External Group Identifier to determine the SUPI(s) and PDU session ID(s) of PDU Session(s) for delivering unstructured data. In the MO NIDD procedure, the NEF will use the SUPI(s) and PDU session ID(s) to obtain the TLTRI, GPSI. The Reliable Data Service Indication indicates if the Reliable Data Service is enabled in the NIDD configuration. The Maximum Packet Size is the maximum NIDD packet size. The response may include an updated value of the NIDD Duration.
4.25.4 NEF Anchored Mobile Originated Data Transport p. 675
Figure 4.25.4-1 illustrates the NEF Anchored Mobile Originated Data Transport procedure.
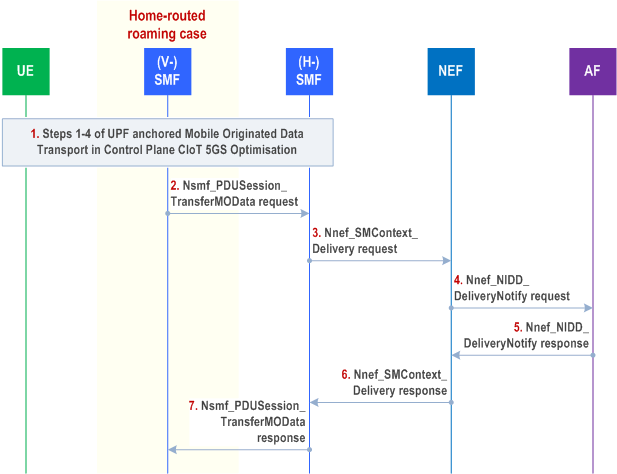
Step 1.
The UE sends a NAS message with unstructured data according to steps 1-4 of the procedure for UPF anchored Mobile Originated Data Transport in Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation (see clause 4.24.1). The Reliable Data Service header is included if the Reliable Data Service is enabled.
Step 2.
[Conditional] In the case of home-routed roaming the V-SMF sends the Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMOData request to the H-SMF including MO small data.
Step 3.
The (H-)SMF sends the Nnef_SMContext_Delivery Request (User Identity, PDU session ID, unstructured data) message to the NEF.
Step 4.
When the NEF receives the unstructured data and finds an NEF PDU Session context and the related T8 Destination Address, then it sends the unstructured data to the AF that is identified by the T8 Destination address in a Nnef_NIDD_DeliveryNotify Request (GPSI, unstructured data, Reliable Data Service Configuration). If no T8 Destination address is associated with the UE's PDN connection, the data is discarded, the Nnef_NIDD_DeliveryNotify Request is not sent and the flow continues at step 6. The Reliable Data Service Configuration is used to provide the AF with additional information such as indicate if an acknowledgement was requested and port numbers for originator application and receiver application, when the Reliable Data Service is enabled.
Step 5.
The AF responds to the NEF with a Nnef_NIDD_DeliveryNotify Response (Cause).
Step 6.
The NEF sends Nnef_SMContext_Delivery Response to the SMF. If the NEF cannot deliver the data, e.g. due to missing AF configuration, the NEF sends an appropriate error code to the SMF.
Step 7.
[Conditional] In the case of home-routed roaming, the H-SMF responds to the V-SMF with a Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMOData (Result Indication) Response.
4.25.5 NEF Anchored Mobile Terminated Data Transport p. 676
Figure 4.25.5-1 illustrates the procedure using which the AF sends unstructured data to a given user as identified via External Identifier or MSISDN.
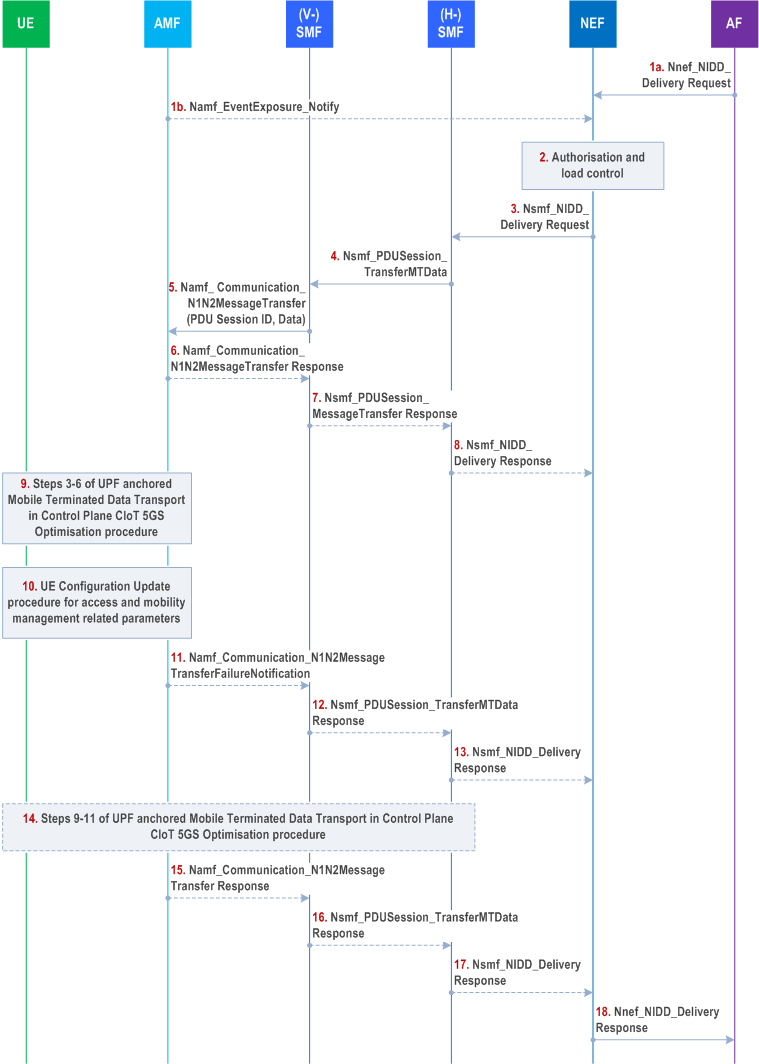
Step 1a.
If AF has already activated the NIDD service for a given UE and has downlink unstructured data to send to the UE, the AF sends a Nnef_NIDD_Delivery Request (GPSI, TLTRI, unstructured data, Reliable Data Service Configuration) message to the NEF. Reliable Data Service Configuration is an optional parameter that is used to configure the Reliable Data Service, it may be used to indicate if a Reliable Data Service acknowledgement is requested and port numbers for originator application and receiver application.
Step 1b.
AMF indicates to NEF that the UE has become reachable. Based on this the NEF re-starts delivering buffered unstructured data to the UE.
Step 2.
The NEF determines the 5GS QoS Flow Context based on the DNN associated with the NIDD configuration and the User Identity. If an NEF 5GS QoS Flow Context corresponding to the GPSI included in step 1 is found, then the NEF checks if the AF is authorised to send data and if it does not exceed its quota or rate. If these checks fail, then steps 3-15 are skipped and an appropriate error code is returned in step 17.
Step 3.
The NEF forwards the unstructured data to the (H-)SMF using Nsmf_NIDD_Delivery Request. If NEF has indicated support of Extended Buffering in Nnef_SMContext_Create Response during SMF-NEF connection establishment, then NEF keeps a copy of the data.
Step 4.
In the roaming case, the H-SMF sends the Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMTData to the V-SMF including MT small data.
Step 5.
The (V-)SMF determines whether Extended Buffering applies based on local policy and based on whether NEF has indicated support of Extended Buffering in Nnef_SMContext_Create Response during SMF-NEF connection establishment. (V-)SMF compresses the header if header compression applies and forwards the data and the PDU session ID to the AMF using the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation. If Extended Buffering applies, then (V-SMF) includes "Extended Buffering support" indication in Namf_Communication_N1N2Message Transfer.
Step 6.
If AMF determines the UE is unreachable for the SMF (e.g. if the UE is in MICO mode or the UE is configured for extended idle mode DRX), then the AMF rejects the request from the SMF. The AMF may include in the reject message an indication that the SMF need not trigger the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer Request to the AMF, if the SMF has not subscribed to the event of UE reachability.
If the SMF included Extended Buffering support indication, the AMF indicates the Estimated Maximum Wait time, in the reject message, for the SMF to determine the Extended Buffering time. If the UE is in MICO mode, the AMF determines the Estimated Maximum Wait time based on the next expected periodic registration timer update expiration or by implementation. If the UE is configured for extended idle mode DRX, the AMF determines the Estimated Maximum Wait time based on the start of next PagingTime Window. The AMF stores an indication that the SMF has been informed that the UE is unreachable.
Step 7.
In the roaming case V-SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMTData (Result Indication) response to H-SMF. If the V-SMF receives an "Estimated Maximum Wait time" from the AMF and Extended Buffering applies, the V-SMF also passes the "Estimated Maximum Wait time" to the H-SMF.
Step 8.
If the (H-)SMF receives a failure indication, (H-)SMF also sends a failure indication to NEF. If (H-)SMF has received the "Estimated Maximum Wait time" and Extended Buffering applies, the (H-)SMF includes Extended Buffering time in the failure indication. The Extended Buffering time is determined by the (H-)SMF and should be larger or equal to the Estimated Maximum Wait time. The NEF stores the DL data for the Extended Buffering time. The NEF does not send any additional Nsmf_NIDD_Delivery Request message if subsequent downlink data packets are received. The procedures stop at this step.
Step 9.
If the AMF determines the UE to be reachable in Step 5, then Steps 3 to 6 of the UPF anchored Mobile Terminated Data Transport in Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation procedure (clause 4.24.2) apply.
If the Reliable Data Service header indicates that the acknowledgement is requested, then the UE shall respond with an acknowledgement to the DL data that was received.
Step 10.
If the AMF has paged the UE to trigger the NAS procedure in step 9, the AMF shall initiate the UE configuration update procedure as defined in clause 4.2.4.2 to assign a new 5G-GUTI.
Step 11.
If the UE has not responded to paging, the AMF sends a failure notification to the (V-)SMF. Otherwise the procedure continues at step 13.
Step 12.
In the roaming case, if V-SMF has received a failure notification from AMF, then V-SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMTData (Result Indication) response to H-SMF.
Step 13.
If (H-)SMF receives a failure notification, then SMF indicates to the NEF that the requested Nsmf_NIDD_Delivery has failed. If Extended Buffering applies, then NEF purges the copy of the data. The procedure continues at step 17.
Step 14.
Steps 9 to 11 of the UPF anchored Mobile Terminated Data Transport in Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation procedure (clause 4.24.2) apply.
Step 15.
AMF informs (V-)SMF that data has been forwarded.
Step 16.
In the roaming case, V-SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_TransferMTData (Result Indication) response to H-SMF that the data has been forwarded.
Step 17.
(H-)SMF indicates to NEF that the data has been forwarded. If Extended Buffering applies then NEF purges the copy of the data.
Step 18.
The NEF sends a Nnef_NIDD_Delivery Response (cause) to the AF.
The Reliable Data Service Acknowledgement Indication is used to indicate if an acknowledgement was received from the UE for the MT NIDD. If the Reliable Data Service was requested in step 1, then the Nnef_NIDD_Delivery Response is sent to the AF after the acknowledgement is received from the UE or, if no acknowledgment is received, then the Nnef_NIDD_Delivery Response is sent to the AF with a cause value indicating that no acknowledgement was received.