Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.15.9.4 Procedures for management of 5G access stratum time distribution
4.15.9.5 Procedures for subscription and management of network timing synchronization status monitoring
4.15.9.5.1 Network timing synchronization status
4.15.9.5.2 5G access stratum time distribution status reporting to the UE
4.15.10 AF specific UE ID retrieval
4.15.10A MSISDN retrieval
4.15.10B MSISDN verification
4.15.12 UPF Event Exposure Direct Reporting
4.15.12.1 General
4.15.12.2 QoS monitoring exposure
4.15.12.3 Notification of Handling of Payload Header Events
...
...
4.15.9.4 Procedures for management of 5G access stratum time distribution p. 491
The AF can use the procedure to activate, update or delete the 5G access stratum time distribution for one UE or a group of UEs.
The AF may query the status of the 5G access stratum time distribution using Nnef_ASTI_Get service operation. The Nnef_ASTI_Create and Nnef_ASTI_Update request may contain the parameters as described in Table 4.15.9.4-1. The AF may subscribe to 5G access stratum time synchronization status simultaneously while creating or updating the ASTI service. The AF may receive 5G access stratum time distribution status updates via Nnef_ASTI_UpdateNotify service operation.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 5G access stratum time distribution indication (enable, disable) | Indicates that the access stratum time distribution via Uu reference point should be activated or deactivated for the associated UE identities. |
| Time synchronization error budget | Indicates the time synchronization error budget for the time synchronization service (as described in clause 5.27.1.9 of TS 23.501). [optional] |
| Temporal Validity Condition | Indicates start-time and stop-time attributes that describe the time period when the time synchronization service is active. [optional] |
| Spatial Validity Condition | Indicates a geographical area (e.g. a civic address or shapes) or a TA list in which time synchronization service is enabled (NOTE 1). [optional] |
| Clock quality detail level | It indicates whether and which clock quality information to provide to the UE and can take one of the following values "clock quality metrics" or "acceptable/not acceptable indication". [optional] |
| Clock quality acceptance criteria | It indicates acceptance criteria for the UE. It is defined based on the attributes specified in Table 5.27.1.12-1 of TS 23.501. The parameter shall be included if the "clock quality detail level" = "acceptable/not acceptable". [conditional] |
|
NOTE 1:
A geographical area requested by an AF includes at least one tracking area (TA), i.e. the granularity is restricted to a TA level in this release of the specifications.
|
|
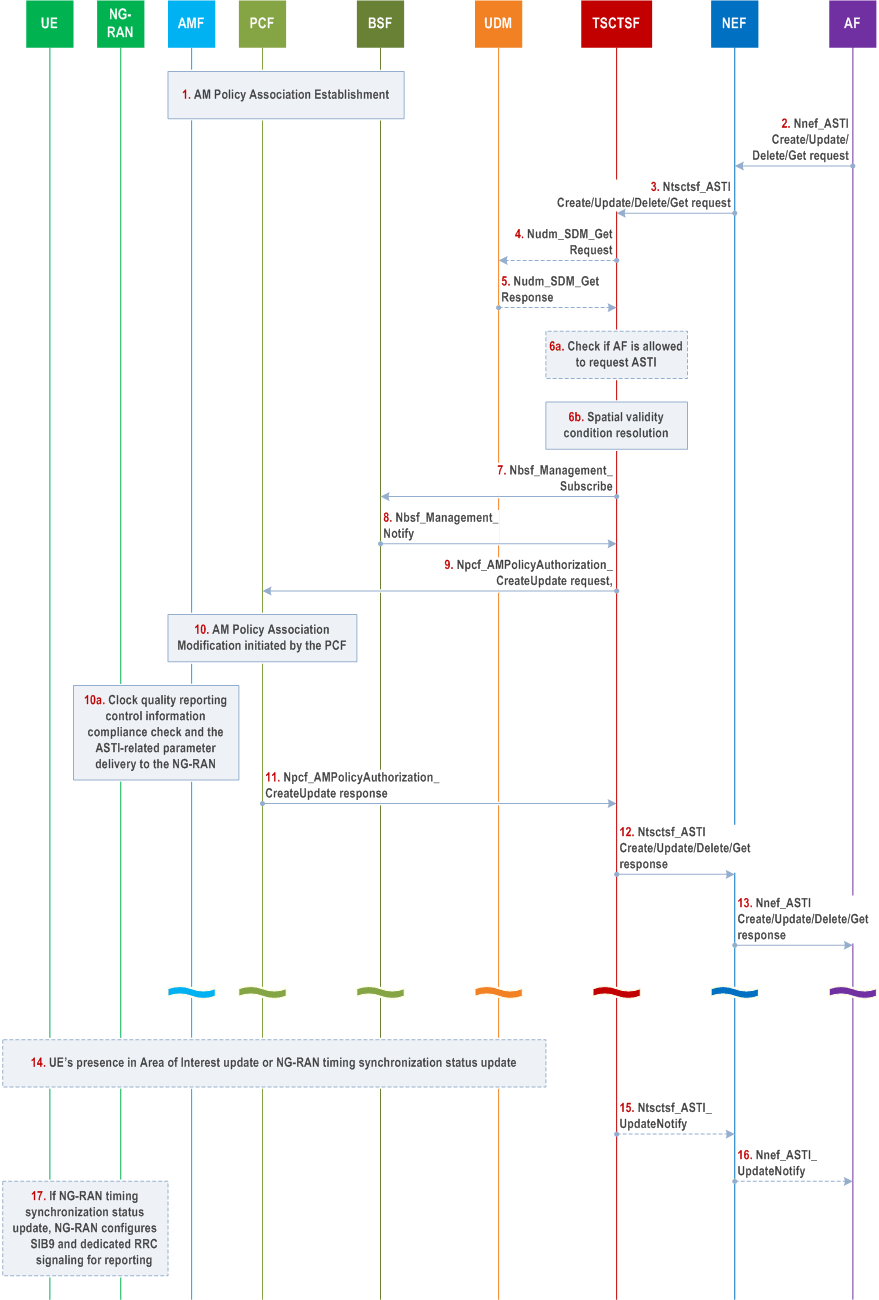
Step 1.
AM Policy Association establishment as described in clause 4.16.1.
Step 2.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
Step 3.
-
To create a new request, the AF provides access stratum time distribution parameters to the NEF using the Nnef_
ASTI_ service operation (together with the AF identifier and potentially further inputs as specified in Table 4.15.9.4-1), including a target (one UE identified by SUPI or GPSI, a group of UEs identified by an External Group Identifier. The NEF forwards the GPSI or the External Group Identifier to the TSCTSF by including it inside the Ntsctsf_Create ASTI_ request.Create -
To update or remove an existing request, the AF invokes an Nnef_
ASTI_ or Nnef_Update ASTI_ service operation providing the corresponding time synchronization configuration id.Delete -
To query the status of the access stratum time distribution, the AF invokes Nnef_
ASTI_ service operation providing the target (a list of UE identities (SUPI or GPSIs) or an External Group Identifier).Get - If the AF includes clock quality detail level, the request creates a subscription at the NEF (for untrusted AF) or TSCTSF (for trusted AF) for notifications for the changes in 5G access stratum time distribution status.
- The create request creates also a subscription for the changes in 5G access stratum time distribution status. To subscribe to NG-RAN timing synchronization status updates, the AF can subscribe to notifications as described in clause 4.15.9.5.1.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
Step 4.
-
The NEF authorizes the request. After successful authorization, the NEF invokes the Ntsctsf_
ASTI_ /Update/Delete/Get service operation with the TSCTSF discovered and selected as described in clause 6.3.24 of TS 23.501.Create - The TSCTSF determines whether the targeted UE is part of a PTP instance in 5GS, if so the TSCTSF rejects the request (steps 4-11 are skipped).
- The TSCTSF checks whether the AF requested parameters for the targeted UE comply with the stored Time Synchronization Subscription Data as defined in clause 5.27.1.11 of TS 23.501. If the AF request targets a group of UEs, steps 4-5 mapping an External/Internal Group Identifier to SUPI(s) are executed before the compliance check in step 6a between UE's subscription and the AF requested parameters.
-
The TSCTSF calculates the Uu time synchronization error budget as described in clause 5.27.1.9 of TS 23.501. This does not apply in case of Ntsctsf_
ASTI_ service operation.Delete - If the AF/NEF includes clock quality detail level, the request creates a subscription at the TSCTSF for notifications for the changes in 5G access stratum time distribution status.
- The TSCTSF calculates the Uu time synchronization error budget as described in clause 5.27.1.9 of TS 23.501 for corresponding SUPIs that are part of the PTP instance.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
If the AF targeted UE(s) are identified by GPSI(s) or an External/Internal Group Identifier, the TSCTSF uses the Nudm_SDM_Get request to retrieve the subscription information (SUPI(s)) from the UDM using each GPSI or the External Group Identifier as received from the NEF, or an Internal Group Identifier as provided by the AF directly.
Step 5.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
The UDM provides the Nudm_SDM_Get response containing SUPI(s) that are mapped from each received GPSI or the External/Internal Group Identifier and identify the targeted UEs.
Step 6a.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
The TSCTSF checks the AF request with the stored Time Synchronization Subscription data as described in clause 5.27.1.11 of TS 23.501 for any targeted UE. If the AF is not authorized, steps 7-11 are skipped.
Step 6b.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
If the Ntsctsf_ASTI_Create request in step 2 contains a spatial validity condition, then the TSCTSF performs the following operations:
Step 7.
-
For each target UE, TSCTSF checks with the stored Time Synchronization Subscription data if the spatial validity condition is allowed. The TSCTSF determines whether the TSCTSF has subscribed for the UE presence in Area of Interest composed by the TAs list in the spatial validity condition. If not, the TSCTSF may either discover the AMF(s) serving in the TAs comprising the spatial validity condition or discovers the serving AMF(s) for each UE identified by a GPSI/SUPI as described in clause 5.27.1.10 of TS 23.501.
Then the TSCTSF subscribes to the AMF(s) to receive notifications about the UE presence in Area of Interest using Namf_
EventExposure operation with the corresponding event filters as described in clause 5.2.2.3 and in clause 5.3.4.4 of TS 23.501. The subscribed area of interest may be the same as the spatial validity condition or may be a subset of the spatial validity condition (e.g. a list of TAs) based on the latest known UE location. -
In order to ensure that a TAI list specifying the AoI for the AMF is aligned with UE's Registration Area (RA), the following steps shall be performed:
- When invoking the subscription with the AMF(s), the TSCTSF may provide an indication, a new Parameter Type = "Adjust AoI based on RA", that the AMF may adjust the received AoI depending on UE's RA.
-
After receiving the Namf_
EventExposure_ request from the TSCTSF with the Parameter Type = "Adjust AoI based on RA" and specified AoI, the AMF compares TAs from the AoI with the UE's Registration Area (RA). If the AoI includes one or more TA(s) that are part of UE's current RA, the AMF reports the UE is inside the Area Of Interest, otherwise the AMF reports the UE is outside the Area Of Interest, as described in Annex D.Subscribe -
The AMF notifies the TSCTSF about the UE's presence in the AoI using the Namf_
EventExposure_ service operation.Notify -
Based on the notification from the AMF and spatial validity condition received in step 1, the TSCTSF determines whether to activate time synchronization service for this UE:
- If the UE location is within the spatial validity condition, the TSCTSF determines to enable access stratum time distribution for the UE.
- If the UE location is outside the spatial validity condition, the TSCTSF determines to disable access stratum time distribution for the UE.
ASTI_ request in step 2 contains a temporal validity condition with a start-time and/or the stop-time that is in the future, the TSCTSF maintains the start-time and stop-time for the time synchronization service for the corresponding time synchronization configuration. If the start-time is in the past, the TSCTSF treats the request as if the time synchronization service was activated immediately. When the start-time is reached, the TSCTSF proceeds with the subsequent steps. When the stop-time is reached for active time synchronization service configuration, the TSCTSF proceeds as if Nnef_Create ASTI_ was received.Delete
The TSCTSF searches the PCF for the UE using Nbsf_Management_Subscribe with a SUPI as an input parameter, indicating that it is searching for the PCF that handles the AM Policy Association of the UE.
Step 8.
The BSF provides to the TSCTSF the identity of the PCF for the UE for the requested SUPI via an Nbsf_Management_Notify operation. If matching entries already existed in the BSF when step 7 is performed, this shall be immediately reported to the TSCTSF.
Step 9.
The TSCTSF sends to the PCF for the UE its request for the AM policy of the UE (identified by SUPI) using Npcf_AMPolicyAuthorization request, containing the 5G access stratum time distribution indication (enable, disable), optionally the calculated Uu time synchronization error budget, optionally the clock quality detail level and clock quality acceptance criteria.
(When the procedure is triggered by PTP instance activation, modification, or deactivation in the TSCTSF):
The TSCTSF ensures the 5G access stratum time distribution for the UE is enabled if at least one of the PTP instances the UE is part of is active.
Step 10.
If the PCF receives multiple time synchronization error budgets for a given UE, then the PCF picks the most stringent budget. The PCF takes a policy decision and then the PCF may initiate an AM Policy Association Modification procedure for the UE as described in clause 4.16.2.2 to provide AMF the 5G access stratum time distribution parameters. As part of this:
Step 10a.
- The AMF shall, if supported, store the 5G access stratum time distribution indication (enable, disable), the Uu time synchronization error budget, clock quality detail level and clock quality acceptance criteria, and the UE reconnection indication in the UE context in AMF; If the AMF receives Uu time synchronization error budget in the Access Stratum Time Synchronization Service Authorization as part of the Access and Mobility Subscription data during registration procedure (see clause 4.28.2.1) and in the AM Policy, the AMF should use the value received from the AM policy.
The AMF shall send the 5G access stratum time distribution indication (enable, disable), the Uu time synchronization error budget, clock quality detail level and clock quality acceptance criteria when they are available, to NG-RAN during mobility registration, AM policy modification, Service Request, N2 Handover and Xn handover as specified in TS 38.413. The NG-RAN node shall, if supported, store the information in the UE Context. Based on this information, the NG-RAN node provides the 5GS access stratum time to the UE according to the Uu time synchronization error budget as provided by the TSCTSF (if supported by UE and NG-RAN) and NG-RAN provides timing synchronization status reports to the UE (as described in clause 4.15.9.5.2).
Step 11.
The PCF of the UE replies to the TSCTSF with the result of Npcf_AMPolicyAuthorization operation.
Step 12.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
The TSCTSF responds the AF with the Ntsctsf_ASTI_Create /Update/Delete/Get service operation response.
Step 13.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
The NEF informs the AF about the result of the Nnef_ASTI_Create /Update/Delete/Get service operation performed in step 2.
Step 14.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
If TSCTSF received spatial validity condition as part of the Ntsctsf_ASTI_Create request in step 2, upon the reception of a change in the UE presence in Area of Interest notification, the TSCTSF determines if the spatial validity condition shall trigger an activation or deactivation of the access stratum time distribution:
ASTI_Create request in step 2, upon a reception of a UE presence in Area of Interest notification, the TSCTSF determines if the UE is impacted correlating UE presence in Area of Interest notifications provided by the serving AMF and the timing synchronization status received (e.g. degradation, failure, recovery) as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501.
Step 15-16.
- If the UE has moved inside the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, then the TSCTSF determines to enable access stratum time distribution for the UE.
- If the UE has moved outside the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, then the TSCTSF determines to disable access stratum time distribution for the UE.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution):
If TSCTSF determines to modify access stratum time distribution for the UE in step 14 for which the AF requested access stratum time distribution, the TSCTSF notifies the service status to AF.
If the TSCTSF determines a change in the support of the clock quality acceptance criteria for the UE in step 14 for which the AF requested access stratum time distribution, the TSCTSF includes the clock quality acceptance criteria result to the notification to the AF. Based on this notification, the AF decides whether to modify the ASTI service configured for the UE using Ntsctsf_ASTI_Update service.
Step 17.
If there was a failure/degradation/improvement event in step 14, the NG-RAN provides timing synchronization status reports to the UE (as described in clause 4.15.9.5.2).
4.15.9.5 Procedures for subscription and management of network timing synchronization status monitoring |R18| p. 498
4.15.9.5.1 Network timing synchronization status p. 498
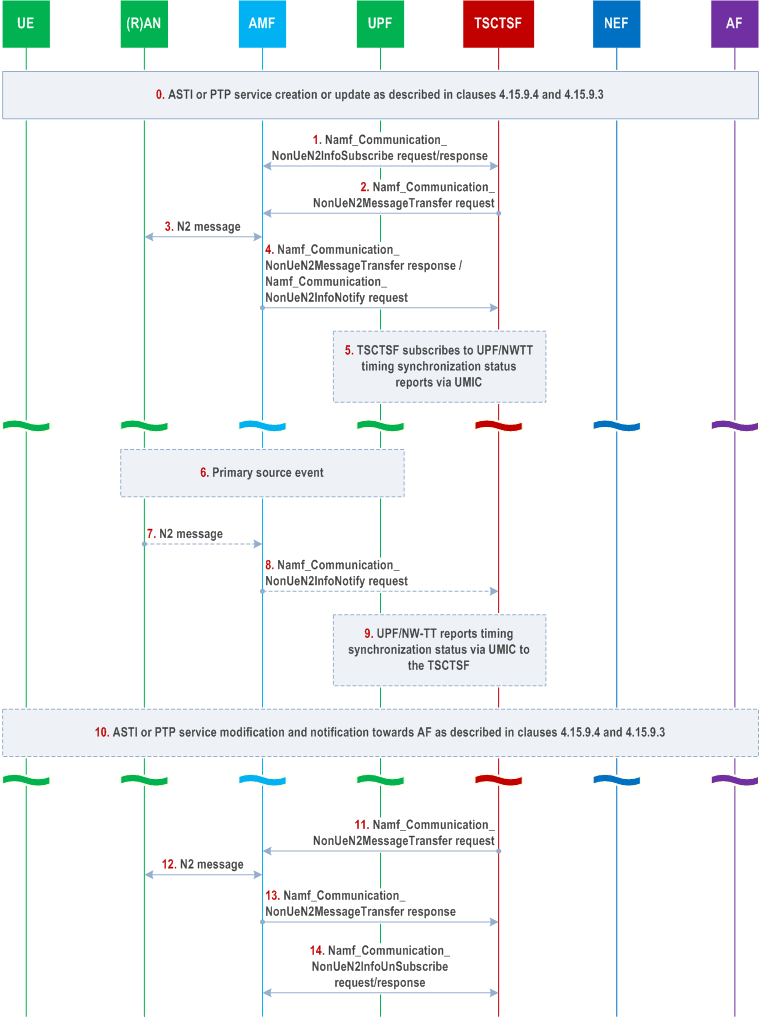
Step 0.
The AF requests creation or modification of ASTI or PTP based time synchronization service as described in clauses 4.15.9.4 and 4.15.9.3 including clock quality detail level and clock quality acceptance criteria (if applicable) in the request.
If the request is received at the NEF, it checks whether the AF is authorized to send the request and forwards the request to the TSCTSF.
If network timing synchronization status reports are provisioned using node-level signalling via control plane, the TSCTSF determines the serving AMF(s) and the UPF/NW-TT nodes (if applicable) for the UE(s) that needs to initiate network timing synchronization status monitoring.
Otherwise, if network timing synchronizations status reports are provisioned via OAM, steps 1-4 and 7-9 are skipped.
Step 1.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request to influence the 5G access stratum time distribution or by PTP instance activation, modification):
Upon the reception of the clock quality detail level and clock quality acceptance criteria (if applicable) in the AF request in step 0, the TSCTSF needs to be subscribed to NG-RAN timing synchronization status updates at the NG-RAN nodes that may provision access stratum time distribution information to the target UE. NG-RAN timing synchronization status updates provisioning may be configured via AMF (with node level signalling as illustrated in steps 1-4).
Step 2.
The TSCTSF invokes an Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer request to the AMF. Inside this request, the TSCTSF includes an N2 Container indicating to the NG-RAN to start reporting TSS attributes and containing the TSCTSF Instance ID. Additionally, in this request the TSCTSF may specify TA(s) and/or NG-RAN node(s). Based on local configuration and/or TA or NG-RAN node information as received from the TSCTSF, the AMF may request some or all NG-RAN nodes in the TA(s) to perform the timing synchronizations status reporting.
Step 3-4.
The AMF sends the corresponding N2 messages to all applicable NG-RAN nodes. Upon receiving a response(s) from the NG-RAN node(s), the AMF includes in the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer response or Namf_Communication_N2InfoNotify request to the TSCTSF a list of N2 Containers containing response messages from the NG-RAN nodes and the corresponding NG-RAN node identifier(s). The AMF may aggregate the response messages it receives from the NG-RAN nodes.
Step 5.
(When the procedure is triggered by the AF request for PTP instance activation, modification and if the UPF/NW-TT is involved in providing time information to DS-TT):
Upon the reception of the clock quality acceptance criteria in the AF request in step 0, the TSCTSF needs to be subscribed to UPF/NW-TT timing synchronization status updates at the UPF/NW-TT that may provision time information via PTP to the target UE. UPF/NW-TT timing synchronization status updates provisioning may be configured via OAM or via UMIC.
Step 6.
The RAN node and TSCTSF are pre-configured for the thresholds for each timing synchronization status attribute as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501.
Step 7-8.
If the NG-RAN node detects a change on its timing synchronization status as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501 and the timing synchronization status reporting is configured via the AMF in steps 1-3, the NG-RAN node notifies the AMF providing a NG-RAN timing synchronization status update. The update can contain the information elements listed in Table 5.27.1.12-1 of TS 23.501, TSCTSF Instance ID and the scope of the timing synchronization status (as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501). The AMF forwards the latest received NG-RAN timing synchronization status update in the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoNotify to the specific TSCTSF instance identified by the TSCTSF Instance ID as specified in step 2.
Step 9.
If the UPF/NW-TT detects a change on its timing synchronization status and timing synchronization status reporting is configured via UMIC in step 3, the UPF/NW-TT notifies the TSCTSF providing a UPF/NW-TT timing synchronization status update via UMIC. The update can contain the information elements listed in Table K.1-2 of TS 23.501.
Step 10.
Upon the reception of a change in the NG-RAN and/or NW-TT timing synchronization status update, the TSCTSF shall determine if the UE is impacted and whether the clock quality acceptance criteria can still be met. For each scope of the timing synchronization status received from the RAN in step 6, if the status indicates degradation, TSCTSF may set the Area of Interest to gNB node ID(s) or Cell IDs in the scope of the timing synchronization status. The TSCTSF uses the resulted Area of Interest to subscribe for the UE presence in Area of Interest from the AMF that is serving the gNB node ID as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501. If the status indicates improvement, the TSCTSF may remove the corresponding scope from the subscription.
Upon reception of notification for the UE presence in the Area of Interest, if the TSCTSF determines that the UE is impacted for ASTI service, the TSCTSF performs steps 15-16 in clause 4.15.9.4 to notify the AF the acceptance criteria result.
Upon reception of notification for the UE presence in the Area of Interest, if the TSCTSF determines that the UE is impacted for PTP service, the TSCTSF performs steps 9-11 in clause 4.15.9.3.2 to notify the AF the acceptance criteria result.
Step 11-14.
If the TSCTSF determines to unsubscribe from the NG-RAN timing synchronization status updates, the following steps need to be taken:
Step 11.
The TSCTSF instance invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer request that includes its TSCTSF Instance ID and an N2 Container indicating to the NG-RAN(s) to stop reporting the TSS attributes.
Step 12.
The AMF sends the corresponding N2 message to the applicable NG-RAN nodes.
Step 13.
NG-RAN responds to the AMF, and the AMF provides a response to the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer request from the TSCTSF instance.
NG-RAN stops reporting the TSS attributes to the AMF for the TSCTSF instance has sent the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer with an N2 Container indicating to stop reporting NG-RAN timing synchronization status.
NG-RAN stops reporting the TSS attributes to the AMF once all the TSCTSF have requested to stop reporting.
Step 14.
After receiving an Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer response or Namf_Communication_N2InfoNotify request, the TSCTSF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoUnSubscribe service operation to the AMF to unsubscribe from the NG-RAN timing synchronization status updates.
4.15.9.5.2 5G access stratum time distribution status reporting to the UE p. 500
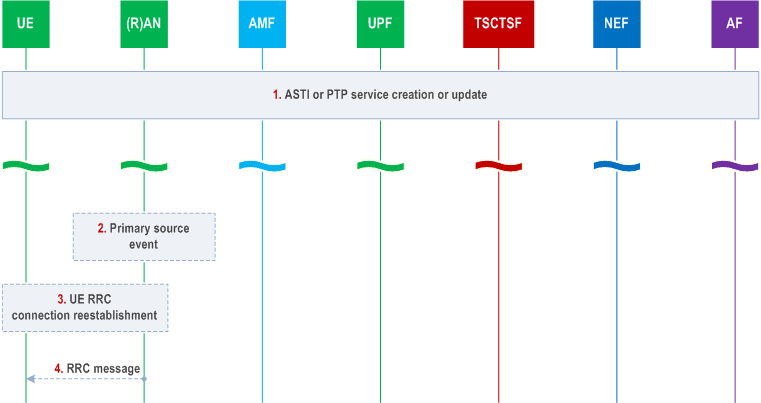
Step 1.
Creation or update of ASTI or PTP based time synchronization service (AF requested ASTI or PTP based time synchronization service is described in clauses 4.15.9.4 and 4.15.9.3; subscription based ASTI is described in clause 4.28.2.1) including in the request clock quality detail level indication and optionally the clock quality acceptance criteria. The clock quality level indication and optionally the clock quality acceptance criteria are sent to the NG-RAN and the UE reconnect indication is sent to the UE as described in clause 4.15.9.4.
Step 2.
The RAN node is pre-configured for the thresholds for each timing synchronization status attribute as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501. If there is a change on its primary source so that the thresholds are exceeded or met again, the NG-RAN node indicates the status via SIB information as described in clause 5.27.1.12 in TS 23.501.
Step 3.
(When the UE is in RRC_INACTIVE or RRC_IDLE state):
If supported by the UE and If the UE determines, based on the reading of SIB9 information as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501, a clock quality information update is available, and the AMF has provided the UE reconnection indication in step 10 of clause 4.15.9.4, the UE reconnects to the network as described in TS 24.501.
Step 4.
(When the UE is in RRC_CONNECTED state):
The NG-RAN node notifies the UE providing clock quality information as configured in step 0 (i.e. sending clock quality metrics or acceptable/not acceptable indication) using unicast RRC signalling whenever the UE enters RRC_CONNECTED state and while the UE remains in RRC_CONNECTED, when any of the clock quality metrics or the acceptable/not acceptable indication for the UE changes.
4.15.10 AF specific UE ID retrieval |R17| p. 501
This clause contains the detailed description and the procedures for the AF specific UE ID retrieval. The AF specific UE Identifier is represented by the External Identifier as defined in TS 23.003.
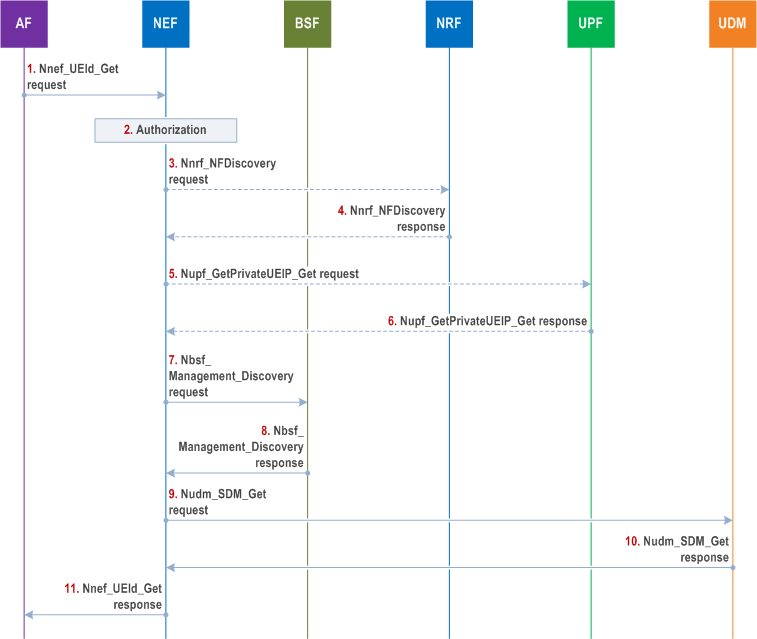
Step 1.
If the NEF has received a Port Number in step 1, based on configuration, the NEF may recognize the address received is an IP address which is different from the actual private UE IP address assigned by 5GC, i.e. the UE is behind a NAT in UPF. If so, the NEF performs steps 3 to 6. Otherwise, steps 3 to 6 are skipped.
AF requests to retrieve UE ID via the Nnef_UEId_Get service operation. The request message shall include UE address (IP address or MAC address) and AF Identifier, it may include, MTC Provider Information, Application Port ID, IP domain. The MTC Provider Information identifies the MTC Service Provider and/or MTC Application. If available the AF may also provide the corresponding DNN and/or S-NSSAI.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the AF request. If the authorisation is not granted, the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating authorisation failure; otherwise the NEF proceeds with the following steps. The NEF determines corresponding DNN and/or S-NSSAI information: this may have been provided by the AF or is determined by the NEF based on the requesting AF Identifier, MTC Provider Information.
Step 3.
The NEF uses the Nnrf_NFDiscovery service operation to obtain the address of the UPF implementing NAT functionality for the UE (public) IP address. The request includes the UE (public) IP address. The NEF may also include the DNN and S-NSSAI associated with the AF ID, as well as the IP domain.
Step 4.
The NRF responds with a Nnrf_NFDiscovery response message including the UPF address of the UPF implementing NAT functionality for the UE (public) IP address.
Step 5.
The NEF uses the Nupf_GetUEPrivateIPaddrAndIdentifiers_Get service operation to request UE's (private) IP address from the UPF. The request includes the UE (public) IP address and Port Number and optionally IP domain, DNN and S-NSSAI associated with the AF ID.
Step 6.
The UPF responds with the Nupf_GetUEPrivateIPaddrAndIdentifiers_Get response message including UE's IP address and optionally, the IP domain. If the UPF has applied a NAT functionality, the UE's IP address returned by the UPF is the private UE IP address. If IP domain of UE private IP address is returned from UPF, it always takes precedence regardless of whether the IP domain information also provided by AF when it invokes Nnef_UEId_Get service operation. If UPF has the SUPI or GPSI of the UE, the UPF may return SUPI or GPSI and in this case steps 7-8 are skipped.
For HR-SBO case as described in clause 4.3.6.1 and in TS 23.548, an indication that the UE PDU session is working in HR-SBO mode, SUPI and HPLMN DNN and S-NSSAI of the PDU session are also provided by UPF.
Step 7-8.
The NEF uses the Nbsf_Management_Discovery service operation with UE address and IP domain and /or DNN and/or S-NSSAI to retrieve the session binding information of the UE. If no SUPI is received in the session binding information from the BSF, the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating that the UE ID is not available.
Step 9.
The NEF interacts with UDM to retrieve the AF specific UE Identifier via the Nudm_SDM_Get service operation. The request message includes SUPI or GPSI and at least one of Application Port ID, MTC Provider Information or AF Identifier.
Step 10.
The UDM responds to the NEF with an AF specific UE Identifier represented as an External Identifier for the UE which is uniquely associated with the Application Port ID, MTC provider Information and/or AF Identifier.
Step 11.
The NEF further responds to the AF with the information (including the AF specific UE Identifier represented as an External Identifier) received from the UDM.
4.15.10A MSISDN retrieval |R18| p. 502
This clause contains the detailed description and procedures for UE ID retrieval in the GPSI format of MSISDN as defined in TS 23.003 by AFs. Depending on operator policy and local regulation, GPSI in MSISDN format may be exposed through the NEF to an authenticated and authorized AF. Depending on operator policy and local regulation, user consent may be required when exposing MSISDN. For the corresponding user consent check, one of the followings is used:
- if CAPIF, defined in TS 23.222, is deployed and RNAA feature is supported, then RNAA, defined in clause 6.5.3 of TS 33.122, is used; or
- the UDM is used to check user consent for MSISDN exposure.
- description of the AF specific UE ID retrieval is replaced as the MSISDN retrieval;
- description of the AF specific UE Identifier represented as an External Identifier is replaced as the UE Identifier in the GPSI form of MSISDN; and
- in step 10, the UDM checks the user consent for MSISDN exposure based on the operator policy.
4.15.10B MSISDN verification |R19| p. 503
This clause contains the detailed description and procedures for the NEF verification (matching) of a retrieved MSISDN from the UDM against an AF-provided MSISDN. Depending on the operator policy and local regulation, the NEF verification result of the MSISDN may also be exposed to an authenticated and authorized AF. Depending on operator policy and local regulation, user consent may be required for MSISDN verification as described in clause 4.15.10A.
The Figure and procedures of clause 4.15.10 shall be applicable for MSISDN verification exposure with the following differences:
- description of the AF specific UE ID retrieval is replaced as the MSISDN verification exposure;
- description of the AF specific UE Identifier represented as an External Identifier is replaced as the UE Identifier in the form of MSISDN; and
-
in step 1, the AF request message is replaced by Nnef_
UEId_ service operation and it shall also include GPSI in the form of MSISDN; andVerificationGet -
in step 11, the NEF responds with Nnef_
UEId_ response indicating "true" or "false" depending on whether the retrieved MSISDN from the UDM and the AF-provided MSISDN match or not (for additional information see clause 5.2.6.27.7).VerificationGet
4.15.11 Void
4.15.12 UPF Event Exposure Direct Reporting |R18| p. 503
4.15.12.1 General |R19| p. 503
UPF may expose information directly via a service based interface by means of the UPF Event Exposure service described in clause 5.2.26.2 and as described in clause 5.6.17 of TS 23.501.
Exposure of QoS Monitoring via direct interaction between UPF and Local NEF/AF is described in clause 4.15.12.1 and Notification of Handling of Payload Headers events in clause 4.15.12.2.
UPF event exposure direct reporting as part of UPF data collection procedures is described in clause 4.15.4.5.
4.15.12.2 QoS monitoring exposure |R19| p. 503
This clause contains the description and the procedure for the exposure of QoS monitoring information via direct interaction between UPF (L-PSA UPF) and Local NEF/AF.
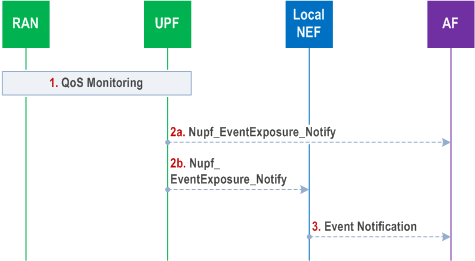
Step 1.
Step 2.
The UPF sends the notification related with QoS monitoring information over Nupf_EventExposure_Notify service operation according to the configuration from SMF as defined in clause 5.8.2.18 of TS 23.501. The notification is sent to the Notification Target Address that may correspond (4a) to the AF or (4b) to the Local NEF.
Step 3.
If the Local NEF is used, it reports the QoS monitoring information to the AF by invoking Nnef_EventExposure_Notify service operation.
4.15.12.3 Notification of Handling of Payload Header Events |R19| p. 504
When AF subscribes to UPF event for Handling of Payload Headers, it provides reporting control information (i.e. Header Handling Reporting Endpoints, etc) as described in clause 5.6.17 of TS 23.501 and PCF includes it in the PCC Rule.
When SMF receives a PCC Rule with Header Handling Control information, if it is including reporting control information for Handling of Payload Header Events, SMF includes it in the instructions to UPF as described in clause 5.8.5.6 of TS 23.501. The SMF may also decide based on local configuration to subscribe itself to notifications of Handling of Payload Header event as described in clause 5.6.17 of TS 23.501.
When a notification reporting trigger is met, UPF notifies the notification endpoint(s) (i.e. AF/NEF and/or SMF) using Nupf_EventExposure_Notify service operation according to the instructions received from SMF. Figure 4.15.12.3-1 shows the notification procedure.
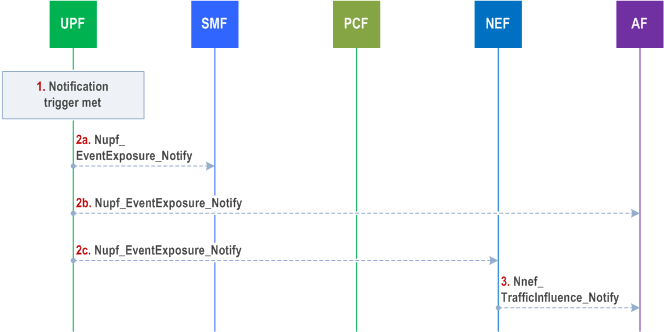
In this procedure, UPF has received instructions for Handling of Payload Headers including reporting control information as described in clause 5.8.5.6 of TS 23.501. At some moment in time:
Step 1.
The conditions for notification of Handling of Payload Headers event is met.
Step 2.
UPF sends notification(s) to the notification endpoint(s) received in the instructions from SMF by means of Nupf_EventExposure_Notify :
Step 2a.
Step 3.
to SMF, if SMF has subscribed to Handling of Payload Headers and it has included its own Notification Target address;
Step 2b.
to AF, if AF has subscribed to Handling of Payload Headers event and the Notification Target address that UPF receives is the AF;
Step 2c.
to NEF, if AF has subscribed to Handling of Payload Headers event and the Notification Target address that UPF receives is the NEF.
If NEF receives a Nupf_EventExposure_Notify from UPF (step 2c), it notifies to AF by means of Nnef_TrafficInfluence_Notify .