Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.2.2.2.3 Registration with AMF re-allocation p. 55
When an AMF receives a Registration request, the AMF may need to reroute the Registration request to another AMF, e.g. when the initial AMF is not the appropriate AMF to serve the UE. The Registration with AMF re-allocation procedure, described in Figure 4.2.2.2.3-1, is used to reroute the NAS message of the UE to the target AMF during a Registration procedure.
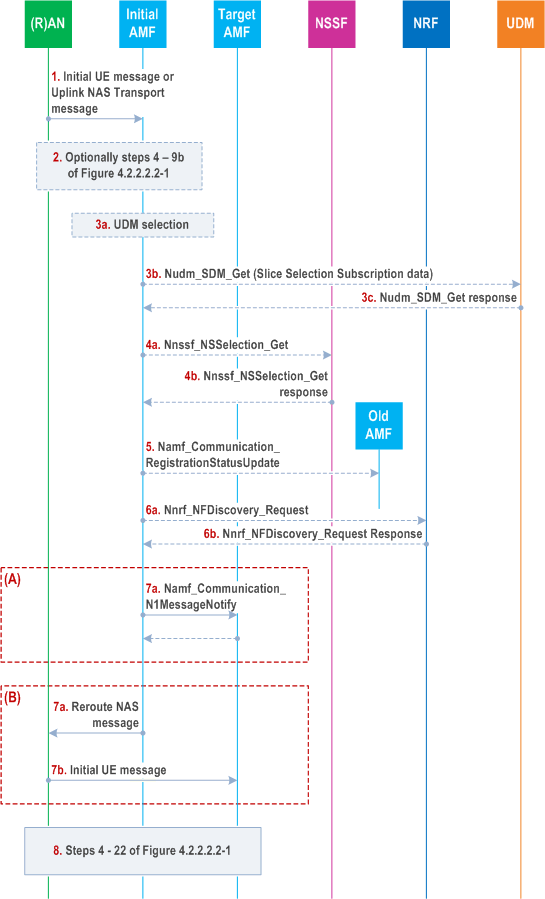
The initial AMF and the target AMF register their capability at the NRF.
Step 1.
If the UE is in CM-IDLE State, steps 1 and 2 of Figure 4.2.2.2.2-1 have occurred and the (R)AN sends the Registration request message within an Initial UE message to the initial AMF. If the UE is in CM-CONNECTED state and triggers registration procedure, the NG-RAN sends Registration request message in the Uplink NAS Transport message to the serving AMF which is initial AMF. The AMF may skip step 2-3.
Step 2.
If the AMF needs the SUPI and/or UE's subscription information to decide whether to reroute the Registration Request or if the Registration Request was not sent integrity protected or integrity protection is indicated as failed, then AMF performs steps 4 to 9a or to 9b of Figure 4.2.2.2.2-1.
Step 3a.
[Conditional] If the initial AMF needs UE's subscription information to decide whether to reroute the Registration Request and UE's slice selection subscription information was not provided by old AMF, the AMF selects a UDM as described in clause 6.3.8 of TS 23.501.
Step 3b.
Initial AMF to UDM: Nudm_SDM_Get (SUPI, Slice Selection Subscription data).
The initial AMF request UE's Slice Selection Subscription data from UDM by invoking the Nudm_SDM_Get (see clause 5.2.3.3.1) service operation. UDM may get this information from UDR by Nudr_DM_Query (SUPI, Slice Selection Subscription data).
For a Disaster Roaming Registration, the AMF may provide the indication of Disaster Roaming service to the UDM.
Step 3c.
UDM to initial AMF: Response to Nudm_SDM_Get . The AMF gets the Slice Selection Subscription data including Subscribed S-NSSAIs.
UDM responds with slice selection subscription data to initial AMF.
For a Disaster Roaming Registration, the UDM responds with the slice selection subscription data for a Disaster Roaming service to initial AMF based on the local policy and/or the local configuration as specified in clause 5.40.4 of TS 23.501.
Step 4a.
[Conditional] Initial AMF to NSSF:
NSSelection_Get service operation from the NSSF by including Requested NSSAI, optionally Mapping Of Requested NSSAI, Subscribed S-NSSAIs with the default S-NSSAI indication, [NSSRG Information], Allowed NSSAI for the other access type (if any), Mapping of Allowed NSSAI, PLMN ID of the SUPI and the TAI of the UE. If the AMF needs to indicate the NSSF to return the Configured NSSAI to obtain network slice configuration when it receives from the UDM an indication that subscription has changed for the UE (see step 14b of clause 4.2.2.2.2) to ensure that the information returned by the NSSF includes the new Configured NSSAI for the UE which can be used to update UE network slicing configuration (see step 21 of clause 4.2.2.2.2), the AMF indicates to the NSSF that the AMF needs a Configured NSSAI by providing the Default Configured NSSAI Indication as described in clause 5.15.5.2.1 of TS 23.501.
The AMF includes, if available, the NSSRG Information for the S-NSSAIs of the HPLMN, defined in clause 5.15.12 of TS 23.501, including information whether the UE has indicated support of the subscription-based restrictions to simultaneous registration of network slices and whether the UDM has indicated to provide all subscribed S-NSSAIs for non-supporting UEs.
If the UE context includes Partially Allowed NSSAI, then the AMF includes the S-NSSAIs of the Partially Allowed NSSAI in the Allowed NSSAI and includes the corresponding HPLMN S-NSSAI in the Mapping Of Allowed NSSAI.
Step 4b.
Nnssf_NSSelection_Get (
If there is a need for slice selection, (see clause 5.15.5.2.1 of TS 23.501), e.g. the initial AMF cannot serve all the S-NSSAI(s) from the Requested NSSAI permitted by the subscription information, the initial AMF invokes the Nnssf_
Requested NSSAI,
[Mapping Of Requested NSSAI],
Subscribed S-NSSAI(s) with the default S-NSSAI indication,
[NSSRG Information],
TAI,
Allowed NSSAI for the other access type (if any),
[Mapping of Allowed NSSAI],
PLMN ID of the SUPI
).
[Mapping Of Requested NSSAI],
Subscribed S-NSSAI(s) with the default S-NSSAI indication,
[NSSRG Information],
TAI,
Allowed NSSAI for the other access type (if any),
[Mapping of Allowed NSSAI],
PLMN ID of the SUPI
[Conditional] NSSF to Initial AMF:
Step 5.
Response to Nnssf_NSSelection_Get (
The NSSF performs the steps specified in point (B) in clause 5.15.5.2.1 of TS 23.501. The NSSF returns to initial AMF the Allowed NSSAI for the first access type, optionally the Mapping Of Allowed NSSAI, the Allowed NSSAI for the second access type (if any), optionally the Mapping of Allowed NSSAI and the target AMF Set or, based on configuration, the list of candidate AMF(s). The NSSF may return NSI ID(s) associated to the Network Slice instance(s) corresponding to certain S-NSSAI(s). The NSSF may return the NRF(s) to be used to select NFs/services within the selected Network Slice instance(s). It may return also information regarding rejection causes for S-NSSAI(s) not included in the Allowed NSSAI. The NSSF may return Configured NSSAI for the Serving PLMN and possibly the associated mapping of the Configured NSSAI. If the NSSRG information was included in the request, the NSSF provides the Configured NSSAI as described in clause 5.15.12 of TS 23.501.
AMF Set or list of AMF addresses,
Allowed NSSAI for the first access type,
[Mapping Of Allowed NSSAI],
[Allowed NSSAI for the second access type],
[Mapping of Allowed NSSAI],
[NSI ID(s)],
[NRF(s)],
[List of rejected (S-NSSAI(s), cause value(s))],
[Configured NSSAI for the Serving PLMN],
[Mapping Of Configured NSSAI]
).
Allowed NSSAI for the first access type,
[Mapping Of Allowed NSSAI],
[Allowed NSSAI for the second access type],
[Mapping of Allowed NSSAI],
[NSI ID(s)],
[NRF(s)],
[List of rejected (S-NSSAI(s), cause value(s))],
[Configured NSSAI for the Serving PLMN],
[Mapping Of Configured NSSAI]
[Conditional] Initial AMF to old AMF: Namf_Communication_RegistrationStatusUpdate (failure cause).
If the UE was in CM-IDLE and another AMF is selected, the initial AMF sends a reject indication to the old AMF telling that the UE Registration procedure did not fully complete at the initial AMF. The old AMF continues as if the Namf_Communication_UEContextTransfer had never been received.
Step 6a.
[Conditional] Initial AMF to NRF: Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request (NF type, AMF Set).
If the initial AMF does not locally store the target AMF address and if the initial AMF intends to use direct reroute to target AMF or the reroute via (NG-R)AN message needs to include AMF address, then the initial AMF invokes the Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request service operation from the NRF to find a proper target AMF which has required NF capabilities to serve the UE. The NF type is set to AMF. The AMF Set is included in the Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request .
Step 6b.
[Conditional] NRF to AMF: Response to Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request (list of (AMF pointer, AMF address, plus additional selection rules and NF capabilities)).
The NRF replies with the list of potential target AMF(s). The NRF may also provide the details of the services offered by the candidate AMF(s) along with the notification end-point for each type of notification service that the selected AMF had registered with the NRF, if available. As an alternative, it provides a list of potential target AMFs and their capabilities and optionally, additional selection rules. Based on the information about registered NFs and required capabilities, a target AMF is selected by the initial AMF.
If the security association has been established between the UE and initial AMF, to avoid a registration failure, the initial AMF shall forward the NAS message to the target AMF by executing step 7(A).
If the initial AMF is not part of the target AMF Set and is not able to get a list of candidate AMF(s) by querying the NRF with the target AMF Set (e.g. the NRF locally pre-configured on AMF does not provide the requested information, the query to the appropriate NRF provided by the NSSF is not successful, or the initial AMF has knowledge that the initial AMF is not authorized as serving AMF etc.) then the initial AMF shall forward the NAS message to the target AMF via (R)AN executing step 7(B) unless the security association has been established between the UE and initial AMF; the Allowed NSSAI, optionally the Partially Allowed NSSAI and the AMF Set are included to enable the (R)AN to select the target AMF as described in clause 6.3.5 of TS 23.501.
Step 7(A).
If the initial AMF, based on local policy and subscription information, decides to forward the NAS message to the target AMF directly, the initial AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify to the target AMF, carrying the rerouted NAS message. The Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation includes AN access information (e.g. the information enabling (R)AN to identify the N2 terminating point, CAG Identifier(s) of the CAG cell) and the complete Registration Request message in clear text as specified in TS 33.501 and the UE's SUPI and MM Context if available. If the initial AMF has obtained the information from the NSSF as described at step 4b, that information except the AMF Set or list of AMF addresses is included. The target AMF then updates the (R)AN with a new updated N2 termination point for the UE in the first message from target AMF to RAN in step 8.
Step 7(B).
[Conditional] if the UE was in CM-IDLE, if the initial AMF, based on local policy and subscription information, decides to forward the NAS message to the target AMF via (R)AN unless the target AMF(s) are returned from the NSSF and identified by a list of candidate AMF(s), the initial AMF sends a NGAP Reroute NAS Request message to the (R)AN (step 7a). The NGAP Reroute Request NAS message includes the information about the target AMF and the complete Registration Request message. If the initial AMF has obtained the information as described at step 4b, that information is included. The (R)AN sends the Initial UE message to the target AMF (step 7b) indicating reroute due to slicing including the information from step 4b that the NSSF provided.
Step 8.
After receiving the Registration Request message transmitted at step 7(A)a or step 7(B)b, the target AMF continues with the Registration procedure from step 4 until 22 of Figure 4.2.2.2.2-1 (with the target AMF corresponding to the new AMF), which includes the UE context retrieved from old AMF. If the 5G security context is received from the initial AMF, the target AMF continue using that one instead of the 5G security context the target AMF may have retrieved from the old AMF. If the initial AMF decides to forward the NAS message to the target AMF (step 7(A), the first message from the target AMF to (R)AN (either Initial Context Setup Request, or Downlink NAS Transport) contain the AMF name of the initial AMF and target AMF UE NGAP ID.
4.2.2.2.4 Registration with Onboarding SNPN |R17| p. 59
This clause specifies how a UE can register to an ON-SNPN for provisioning the UE with SO-SNPN credentials and other information to enable SNPN access as defined in clause 5.30.2.10 of TS 23.501.
The Registration procedure for Onboarding SNPN over 3GPP access shall be supported as specified in clause 4.2.2.2.2 with the following changes compared to the steps in the call flow represented in Figure 4.2.2.2.2-1, covering three cases, i.e. when DCS is hosting AAA Server and when DCS is hosting AUSF/UDM and when DCS is not involved, as shown in Figure 4.2.2.2.4-1.
The Registration procedure for Onboarding SNPN over untrusted non-3GPP access shall be supported as specified in clause 4.12.2.2. The Registration procedure for Onboarding SNPN over trusted non-3GPP access shall be supported as specified in clause 4.12a.2.2.
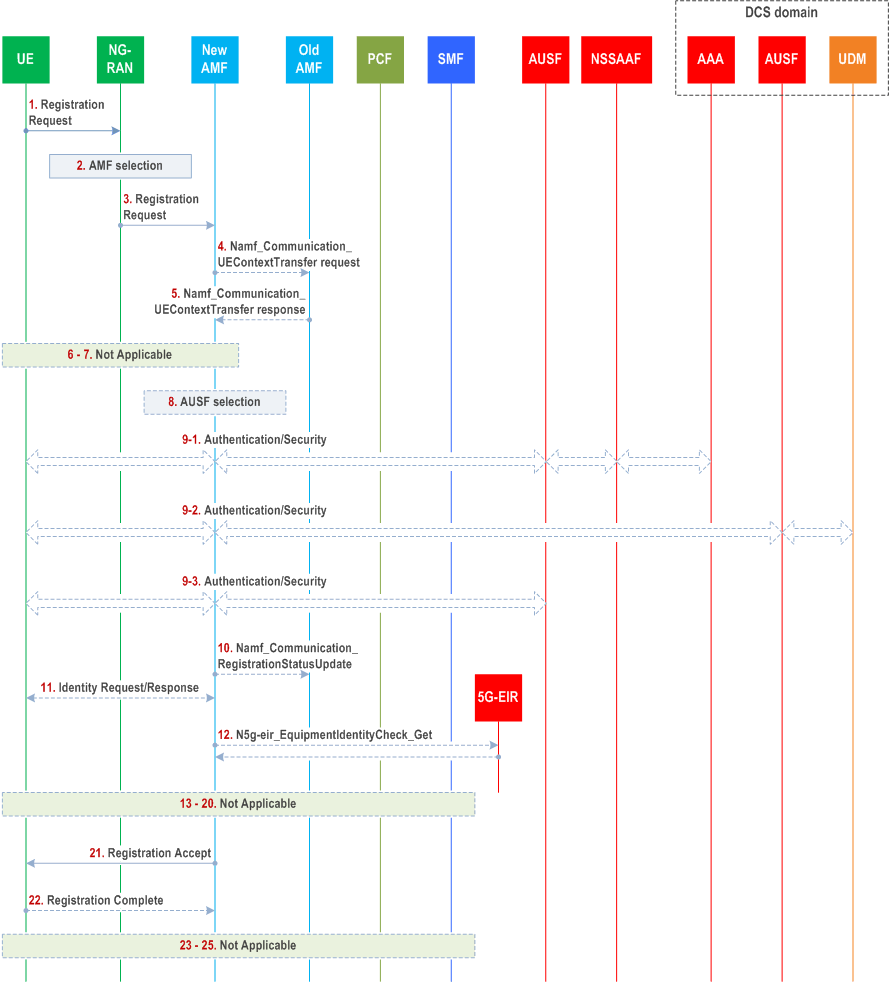
Step 1.
UE to NG-RAN: AN parameters shall include Onboarding indication if the UE is accessing 5GS for Onboarding. The Registration Type "SNPN Onboarding" indicates that the UE wants to perform SNPN Onboarding Registration (i.e. allows the UE to access an ON-SNPN for the purpose of provisioning the UE with SO-SNPN credentials). For SNPN Onboarding Registration, a SUCI generated from a SUPI derived from Default UE Credentials shall be included as described in clause 5.30.2.10.2.6 of TS 23.501.
If the UE has registered in the ON-SNPN for onboarding, the UE can perform a Mobility Registration Update, or a Periodic Registration Update as specified in clause 4.2.2.2.2. If the onboarding registered UE wants to perform a Mobility Registration Update the AN parameters shall also include an Onboarding indication that the UE is registered for onboarding.
Step 2.
Based on the Onboarding indication in step 1, the NG-RAN selects an AMF as described in clause 6.3.5 of TS 23.501.
Step 3.
NG-RAN to AMF: The N2 message contains the Registration Request as described in step 1.
Step 4.
[Conditional] new AMF to old AMF: Namf_Communication_UEContextTransfer (complete Registration Request).
Step 5.
[Conditional] old AMF to new AMF: Response to Namf_Communication_UEContextTransfer (SUPI, UE Context in AMF (as per Table 5.2.2.2.2-1)). Once the registration is completed successfully, the new AMF may start an implementation specific deregistration timer for when to deregister the onboarding registered UE if the UE context contains the indication that the UE is registered for onboarding.
Step 6-7.
Skipped.
Step 8.
When the AMF receives a NAS Registration Request with the 5GS Registration Type set to "SNPN Onboarding", the AMF applies locally configured AMF Configuration Data for Onboarding in order to restrict UE network usage to only onboarding and stores in the UE Context in AMF an indication that the UE is registered for onboarding. The AMF selects an AUSF as described in clause 5.30.2.10.2.6 of TS 23.501. Based on ON-SNPN policies, the AMF may start an implementation specific deregistration timer configured for UE Onboarding as described in TS 23.501.
Step 9.
The authentication is performed as described in TS 33.501.
For DCS hosting AAA Server as shown in step 9-1, based on local configuration (e.g. using the realm part of the SUCI), the AUSF sends the SUPI towards the AAA Server in the DCS domain via the NSSAAF, then the AAA Server in the DCS domain authenticates the UE based on received data from AUSF. During authentication procedure the AAA Server in the DCS domain may provide PVS FQDN(s) and/or PVS IP address(es) for the UE to the AUSF via the NSSAAF, the AUSF then provides PVS FQDN(s) and/or PVS IP address(es) to the AMF.
For DCS hosting AUSF/UDM as shown in step 9-2, the AUSF in DCS domain performs UDM selection. The AMF sends the SUCI and Default UE credentials received from the UE towards the AUSF in DCS domain, which authenticates the UE based on received data from AMF and subscription data from the UDM in DCS domain. During authentication procedure, the AUSF in the DCS domain provides PVS FQDN(s) and/or PVS IP address(es) to the AMF.
When DCS is not involved during primary authentication as shown in step 9-3, the AMF selects a local AUSF as defined in clause 6.3.4 of TS 23.501 and performs primary authentication towards the local AUSF using Default UE credentials as described in TS 33.501.
Step 10.
[Conditional] new AMF to old AMF: Namf_Communication_RegistrationStatusUpdate .
Step 11.
[Conditional] AMF to UE: Identity Request/Response (PEI).
If the PEI was not provided by the UE, the Identity Request procedure is initiated by AMF sending an Identity Request message to the UE to retrieve the PEI.
Step 12.
Optionally the new AMF initiates ME identity check by invoking the N5g-eir_EquipmentIdentityCheck_Get service operation (see clause 5.2.4.2.2).
The PEI check is performed as described in clause 4.7.
Step 13-20.
Skipped.
Step 21.
AMF to UE: The AMF sends a Registration Accept message to the UE indicating that the Registration Request for Onboarding SNPN has been accepted. The Allowed NSSAI containing the S-NSSAI from the AMF Onboarding Configuration Data is included in the N2 message to NG-RAN.
Step 21b.
Skipped.
Step 22.
UE to AMF: The UE sends a Registration Complete message to the AMF.
Step 23-25.
Skipped.