Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.23.11 Xn based handover
4.23.12 N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF
4.23.13 Non N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF
4.23.14 Pause of charging
4.23.15 PDU Session mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP access
4.23.16 Handover of a PDU Session procedure between 3GPP and untrusted non-3GPP access
4.23.16a Handover of a PDU Session procedure between 3GPP and trusted non-3GPP access
4.23.17 Additional considerations for Home-routed roaming
...
...
4.23.11 Xn based handover p. 652
4.23.11.1 General p. 652
This clause describes the Xn based handover with the insertion, reallocation and removal of I-SMF.
To support the EAS session continuity upon UL CL relocation (allowing the UE to go on exchanging with the source EAS despite the fact that a new UL CL has been allocated to the PDU Session), the N9 forwarding tunnel between the Source UL CL and Target UL CL is established and released as described in clause 4.23.9.4 or clause 4.23.9.5.
4.23.11.2 Xn based handover with insertion of intermediate SMF p. 652
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a Source NG-RAN to a Target NG-RAN using Xn interface (in this case the AMF is unchanged) and the AMF decides that insertion of a new intermediate I-SMF is needed. This procedure is used for non-roaming or local breakout roaming scenario.
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.23.11.2-1.
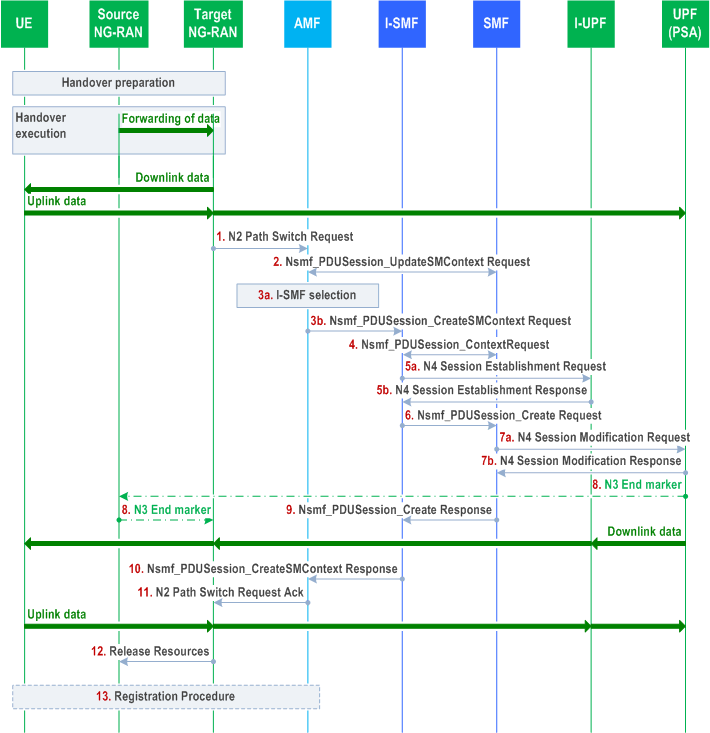
Step 1.
The rest of this procedure applies for each PDU Session To Be Switched.
Step 1 is the same as described in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 2.
For each PDU Session Rejected in the list of PDU Sessions received in the N2 Path Switch Request, the AMF perform same step as step 2 in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 3a.
The AMF checks if an I-SMF needs to be selected as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 3b.
If a new I-SMF is selected the AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request (SUPI, AMF ID, SMF ID, SM Context ID, PDU Session To Be Switched with N2 SM Information (Secondary RAT usage data), UE Location Information, UE presence in LADN service area) to the new selected I-SMF.
Step 4.
The new I-SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request (SM context type, SM Context ID) to SMF to retrieve the SM Context.
The new I-SMF uses SM Context ID received from AMF for this service operation. SM context type indicates that the requested information is all SM context, i.e. PDN Connection Context and 5G SM context. The SM Context ID is used by the recipient of Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request in order to determine the targeted PDU Session.
Step 5a.
I-SMF to I-UPF: N4 Session Establishment Request (Target NG-RAN Tunnel Info).
The I-SMF then selects a I-UPF based on UPF Selection Criteria according to clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501. An N4 Session Establishment Request message is sent to the I-UPF. The target NG-RAN Tunnel Info is included in the N4 Session Establishment Request message.
Step 5b.
I-UPF to I-SMF: N4 Session Establishment Response.
The I-UPF sends an N4 Session Establishment Response message to the I-SMF. The UL CN Tunnel Info and DL CN Tunnel Info of I-UPF are sent to the I-SMF.
Step 6.
Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Request to the SMF (SUPI, PDU Session ID, Secondary RAT usage data, UE Location Information, UE presence in LADN service area, DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF, DNAI list supported by the I-SMF).
The I-SMF provides the DNAI list it supports to the SMF as defined in Figure 4.23.9.1-1 step 1.
Secondary RAT usage data is extracted from N2 SM Information within PDU Session To Be Switched received from NG RAN.
Step 7a.
SMF to UPF (PSA): N4 Session Modification Request (DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF).
The SMF provides the DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF to the UPF(PSA).
If old I-UPF controlled by SMF does not exist and if different CN Tunnel Info need to be used by PSA UPF, i.e. the CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N3 and N9 are different, the CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N9 needs to be allocated. The CN Tunnel Info is provided from UPF to SMF in the response.
Step 7b.
UPF (PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
The PDU Session Anchor responds with the N4 Session Modification Response message after requested PDU Sessions are switched. At this point, PDU Session Anchor starts sending downlink packets to the Target NG-RAN via I-UPF.
PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3/N9 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the target NG-RAN.
Step 8.
In order to assist the reordering function in the Target NG-RAN, the PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3/N9 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the target NG-RAN.
Step 9.
SMF to I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Response(Information for local traffic steering location, CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N9, updated CN PDB in the QoS parameters for accepted QoS Flows).
The SMF may update the CN PDB in the response or using a separate PDU Session Modification procedure, based on local configuration.
Step 9a.
If the CN Tunnel Info at PSA for N9 is allocated, it is included in the response and the I-SMF provides the CN Tunnel Info at the PSA for N9 to I-UPF via N4 Session Modification Request.
In the case of I-SMF insertion and the PDU session corresponds to a LADN, the SMF shall release the PDU session after the handover procedure is completed.
Step 10.
Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (UL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF, updated CN PDB in the QoS parameters for accepted QoS Flows).
The SMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext response to the AMF.
Step 11-13.
Steps 11-13 are same as steps 7-9 defined in clause 4.9.1.2.2 with the following addition:
If a Source I-UPF controlled by SMF was serving the PDU Session, the SMF initiates Source I-UPF Release procedure by sending an N4 Session Release Request toward the Source I-UPF.
4.23.11.3 Xn based handover with re-allocation of intermediate SMF p. 654
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a Source NG-RAN to a Target NG-RAN using Xn interface (in this case the AMF is unchanged) and the AMF decides that the intermediate SMF(I-SMF) is to be changed. This procedure is used for non-roaming or local breakout roaming scenario. In the case of home routed roaming scenario, this procedure is also used except the I-SMF is replaced by V-SMF.
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.23.11.3-1.
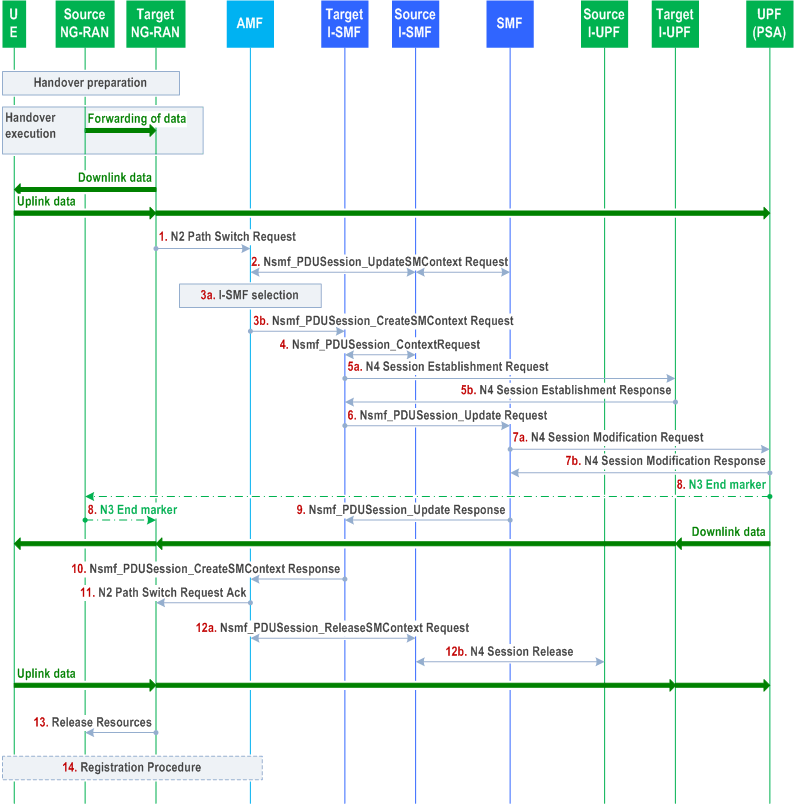
Step 1-3.
Steps 1-3 are same as steps 1-3 described in clause 4.23.11.2 except that in step 2 the AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request to source I-SMF and then the source I-SMF sends the Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request to SMF.
Step 4.
The target I-SMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request to Source I-SMF to retrieve 5G SM Context.
Step 5a-11.
Steps 5a-11 are same as steps 5a-11 described in clause 4.23.11.2 with the following difference:
In step 6, the target I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request (Secondary RAT usage data, UE Location Information, UE presence in LADN service area, DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF, DNAI list supported by target I-SMF) toward the SMF;
In step 9, the SMF respond with Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Response. The SMF may provide the DNAI(s) of interest for this PDU Session to I-SMF as described in step 1 of Figure 4.23.9.1-1. The SMF may update the CN PDB in the response or using a separate PDU Session Modification procedure, based on local configuration.
Secondary RAT usage data is extracted from PDU Session To Be Switched with N2 SM Information received from NG RAN.
Step 12a.
The AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext Request (I-SMF only indication) to source I-SMF. The source I-SMF removes the SM context of this PDU session. An indication is included in this message to avoid invoking resource release in SMF.
Step 12b.
The source I-SMF sends N4 Session Release to release the resource in source I-UPF. If the source I-UPF acts as UL CL and is not co-located with local PSA, the source I-SMF also sends N4 Session Release to the local PSA to release the resource for the PDU Session.
Step 13-14.
Steps 13-14 are same as steps 12-13 described in clause 4.23.11.2.
4.23.11.4 Xn based handover with removal of intermediate SMF p. 656
This procedure is used to hand over a UE from a Source NG-RAN to a Target NG-RAN using Xn interface(in this case the AMF is unchanged) and the AMF decides that removal of intermediate I-SMF is needed. This procedure is used for non-roaming or local breakout roaming scenario.
The call flow is shown in Figure 4.23.11.4-1.
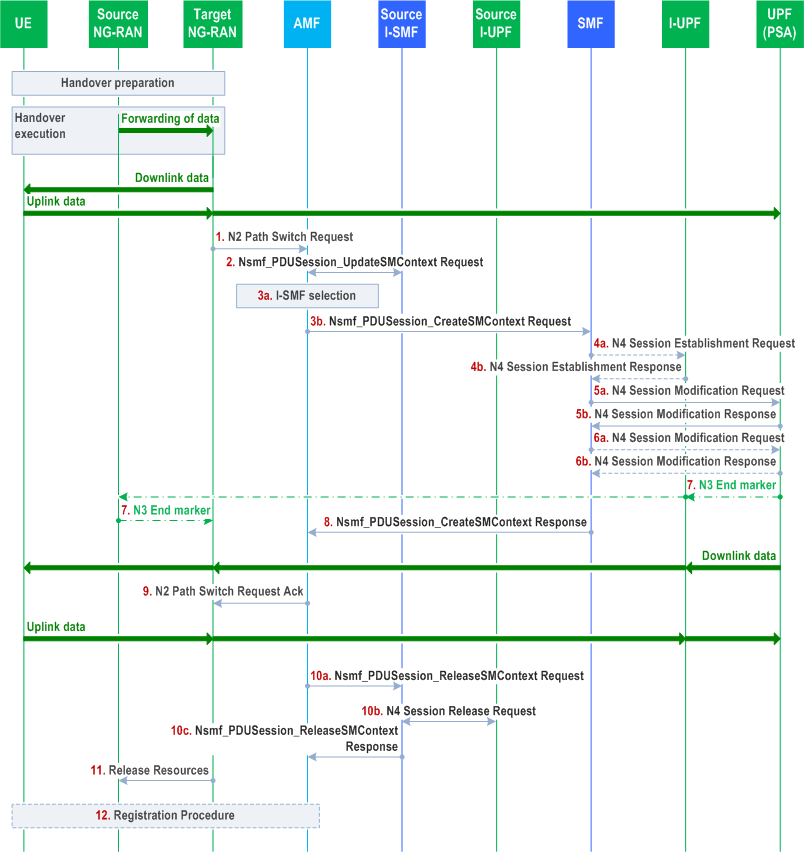
Step 1.
The rest of this procedure applies for each PDU Session To Be Switched.
Step 1 is the same as described in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 2.
For each PDU Session Rejected in the list of PDU Sessions received in the N2 Path Switch Request, the AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request to source I-SMF and then the source I-SMF sends the Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request to SMF forwarding the failure cause. The SMF decides whether to release the PDU Session.
Step 3a.
The AMF performs I-SMF selection as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501 and the AMF decides to remove I-SMF in this case.
Step 3b.
The AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Request (SUPI, PDU Session ID, AMF ID, PDU Session To Be Switched with N2 SM Information (Secondary RAT usage data), UE Location Information, UE presence in LADN service area, Target NG-RAN Tunnel Info) to the SMF.
Step 4a.
[Conditional] SMF to I-UPF: N4 Session Establishment Request (Target NG-RAN Tunnel Info, UL CN Tunnel Info of the UPF (PSA)).
The SMF may select an I-UPF based on UPF Selection Criteria according to clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501. If an I-UPF is selected, an N4 Session Establishment Request message is sent to the I-UPF. The target NG-RAN Tunnel Info is included in the N4 Session Establishment Request message.
Step 4b.
I-UPF to SMF: N4 Session Establishment Response.
The I-UPF sends an N4 Session Establishment Response message to the I-SMF. The UL and DL CN Tunnel Info of I-UPF is sent to the I-SMF.
Step 5a.
SMF to UPF (PSA): N4 Session Modification Request (DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF if I-UPF is selected, or Target NG-RAN Tunnel Info if I-UPF is not selected).
The SMF provides the DL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF to the UPF (PSA) if I-UPF is selected.
If an I-UPF is not selected, the SMF provides the target NG-RAN Tunnel Info to the UPF (PSA). If different CN Tunnel Info need to be used by PSA UPF, i.e. the CN Tunnel Info for N3 and N9 are different, the SMF retrieves the new CN Tunnel Info from UPF.
Step 5b.
UPF (PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
If different CN Tunnel Info needs to be used by PSA UPF, i.e. the CN Tunnel Info for N3 and N9 are different, the CN Tunnel Info is allocated by the UPF and provided to the SMF.
The PDU Session Anchor responds with the N4 Session Modification Response message after requested PDU Sessions are switched. PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3/N9 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the target NG-RAN. At this point, PDU Session Anchor starts sending downlink packets to the Target NG-RAN via I-UPF.
Step 6a.
[Conditional] SMF to I-UPF: N4 Session Modification Request (UL CN Tunnel Info of the UPF (PSA)).
If the UL CN Tunnel Info of the UPF (PSA) has been changed, the SMF provides the UL CN Tunnel Info of the UPF (PSA) to I-UPF.
Step 6b.
I-UPF to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
The I-UPF responds with the N4 Session Modification Response message.
Step 7.
In order to assist the reordering function in the Target NG-RAN, the PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3/N9 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the target NG-RAN.
Step 8.
SMF to AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (UL CN Tunnel Info of the I-UPF if I-UPF is selected, or CN Tunnel Info (on N3) of UPF (PSA) if I-UPF is not selected, updated CN PDB in the QoS parameters for accepted QoS Flows). The SMF may update the CN PDB in the response or using a separate PDU Session Modification procedure, based on local configuration.
The SMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext response to the AMF.
Step 9.
Step 9 is same as step 7 defined in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
Step 10a.
AMF to source I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext request (I-SMF only Indication).
The AMF sends Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext request to source I-SMF. The I-SMF only indication is included in this message to avoid invoking resource release in SMF.
Step 10b.
Source I-SMF to source I-UPF: N4 Session Release Request/Response.
The source I-SMF sends N4 Session Release Request to source I-UPF in order to release resources for the PDU Session.
Step 10c.
Source I-SMF to AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext Response.
The source I-SMF responds to AMF with Nsmf_PDUSession_ReleaseSMContext response.
Step 11-12.
Steps 11-12 are same as steps 8-9 defined in clause 4.9.1.2.2.
4.23.11.5 Xn based handover without change of intermediate SMF p. 658
When both I-SMF and SMF are available for a PDU Session and no I-SMF change or removal is needed during Xn based handover procedure, compared to the procedure defined in clause 4.9.1.2.2 and clause 4.9.1.2.4 the SMF is replaced with the I-SMF.
4.23.12 N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF p. 658
4.23.12.1 General p. 658
When UE moves from EPS to 5GS, for a each PDU Session, the AMF determines whether I-SMF needs to be inserted based on UE location and service area of the SMF+PGW-C.
This clause describes the N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF insertion when UE move from EPS to 5GS and removal when UE moves from 5GS to EPS.
4.23.12.2 5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 interface with I-SMF removal p. 658
For 5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 with I-SMF removal, the procedure "5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 interface" defined in clause 4.11.1.3.2 for the home routed-roaming case are re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF, H-SMF is replaced by SMF and V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF (PSA).
4.23.12.2A 5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 interface with Data forwarding and I-SMF removal p. 658
For 5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 with data forwarding and I-SMF removal, the procedure "5GS to EPS Idle mode mobility using N26 interface with data forwarding" defined in clause 4.11.1.3.2A for the home-routed roaming case is re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF.
- Data forwarding tunnel resource is established and the tunnel information is exchanged through N26 interface. Data buffered in I-SMF/I-UPF is forwarded to UE via Serving GW.
4.23.12.3 EPS to 5GS mobility registration procedure (Idle and Connected State) using N26 interface with I-SMF insertion p. 658
For EPS to 5GS Mobility registration procedure using N26 with I-SMF insertion, the procedure "EPS to 5GS Mobility Registration Procedure (Idle and Connected State) using N26 interface" defined in clause 4.11.1.3.3 for the home routed-roaming case are re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-SMF selection is replaced by the I-SMF selection.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA).
4.23.12.3A EPS to 5GS Idle mode mobility using N26 interface with Data forwarding and I-SMF insertion p. 659
For EPS to 5GS Mobility registration procedure using N26 with data forwarding and I-SMF insertion, the procedure "EPS to 5GS Idle Mobility using N26 interface with data forwarding" defined in clause 4.11.1.3.3A for the home routed-roaming case is re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-SMF selection is replaced by the I-SMF selection.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA).
- Data forwarding tunnel resource is established and the tunnel information is exchanged through N26 interface. Data buffered in Serving GW is forwarded to UE via I-SMF/I-UPF.
4.23.12.4 Procedures for EPS bearer ID allocation p. 659
The EPS Bearer ID allocation procedure, EPS Bearer ID transfer procedure and EPS Bearer ID revocation procedure are perfomed as described for the home-routed roaming case in clause 4.11.1.4, with the following differences:
- H-SMF is replaced by SMF.
- V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF.
- In step 8 of clause 4.11.1.4.1, in addition to home routing roaming scenario, for scenario of deployments topologies with specific SMF Service Areas, if EBI is assigned successfully, the SMF+PGW-C also prepares CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer and provides this information to the I-SMF.
4.23.12.5 EPS to 5GS mobility registration procedure (Idle) using N26 interface with AMF reallocation and I-SMF insertion p. 659
For EPS to 5GS Mobility registration procedure using N26 with AMF reallocation and I-SMF insertion, the procedure "EPS to 5GS Mobility Registration Procedure (Idle) using N26 interface with AMF reallocation" defined in clause 4.11.1.3.4 are re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-SMF selection is replaced by the I-SMF selection.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA).
4.23.12.6 5GS to EPS handover using N26 interface with I-SMF removal p. 659
The procedure "5GS to EPS handover using N26 interface" in clause 4.11.1.2.1 for the home routed-roaming case is applied to handover from 5GS to EPS using N26 interface with I-SMF removal with the following changes:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
4.23.12.7 EPS to 5GS handover using N26 interface with I-SMF insertion p. 659
4.23.12.7.1 Preparation phase p. 659
For handover from EPS to 5GS using N26 interface, if I-SMF needs to be inserted, the preparation procedure defined in clause 4.11.1.2.2.1 for the home routed-roaming case are re-used, with the following changes:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-SMF selection is replaced by the I-SMF selection.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA).
4.23.12.7.2 Execution phase p. 660
For handover from EPS to 5GS using N26 interface, if I-SMF needs to be inserted, the execution procedure defined in clause 4.11.1.2.2.2 for the home routed-roaming case are re-used, with the following change:
- The V-SMF is replaced by I-SMF and H-SMF is replaced by SMF, V-UPF is replaced by I-UPF.
- The V-SMF selection is replaced by the I-SMF selection.
- The V-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at I-UPF, H-CN Tunnel Info is replaced by Tunnel Info at UPF(PSA).
4.23.12.8 Impact to 5GC procedures p. 660
4.23.12.8.1 General p. 660
This clause captures impact to 5GC procedures in other clauses of clause 4.23 to support interworking with N26.
4.23.12.8.2 UE Triggered Service Request with I-SMF insertion/change/removal p. 660
The following impact is applicable for UE triggered Service Request with I-SMF insertion in clause 4.23.4.3:
- In step 8a, when an I-SMF is inserted, if EBI(s) have been allocated before but the SMF+PGW-C has not prepared the CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer, the SMF+PGW-C requests the PGW-U+UPF to allocate the CN Tunnel for each EPS bearer for PDU Session(s). PGW-U+UPF allocates the PGW-U tunnel info for the EPS bearer and sends it to the SMF+PGW-C.
- In step 8c, the SMF+PGW-C provides also CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer to the I-SMF.
4.23.12.8.3 PDU Session establishment procedure p. 660
The following impact is applicable for PDU Session establishment in clause 4.23.5.1:
- If I-SMF is involved in the PDU Session establishment, after EBI has been successfully allocated, the SMF+PGW-C also prepares CN tunnel info for each EPS bearer and provides it to the I-SMF, see clause 4.23.12.4.
4.23.12.8.4 PDU Session modification procedure p. 660
The following impact is applicable for PDU Session modification in clause 4.23.5.3:
- If I-SMF is involved in the PDU Session modification, if EBI needs to be allocated and the allocation is successful, the SMF+PGW-C also prepares CN tunnel info for each EPS bearer and provides it to the I-SMF, see clause 4.23.12.4.
4.23.12.8.5 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover with I-SMF insertion/change/removal p. 660
The following impact is applicable for Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover with I-SMF insertion in clause 4.23.7.3.2:
- In step 7c, at I-SMF insertion, if EBI(s) have been allocated before but the SMF+PGW-C has not prepared the CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer, the SMF+PGW-C requests the PGW-U+UPF to allocate the CN Tunnel for each EPS bearer for PDU Session(s). PGW-U+UPF allocates the PGW-U tunnel info for the EPS bearer and sends it to the SMF+PGW-C.
- In step 7f, the SMF+PGW-C provides also the CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer to the I-SMF.
4.23.12.8.6 Xn based handover with insertion of I-SMF p. 661
The following impact is applicable Xn based handover with insertion of I-SMF in clause 4.23.11.2:
- In step 6, at I-SMF insertion, if EBI(s) have been allocated before but the SMF+PGW-C has not prepared the CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer, the SMF+PGW-C requests the PGW-U+UPF to allocate the CN Tunnel for each EPS bearer for PDU Session(s). PGW-U+UPF allocates the PGW-U tunnel info for the EPS bearer and sends it to the SMF+PGW-C.
- In step 9, the SMF+PGW-C provides also the CN Tunnel Info for each EPS bearer to the I-SMF.
4.23.13 Non N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF p. 661
4.23.13.1 General p. 661
When UE moves a PDU Session from EPS to 5GS, the AMF determines whether I-SMF needs to be inserted based on the UE location and the service area of the SMF+PGW-C.
This clause describes the non N26 based Interworking Procedures with I-SMF insertion when UE move a PDU Session from EPS to 5GS and I-SMF removal when UE moves a PDU Session from 5GS to EPS.
This may happen e.g. when the UE moves a PDU Session between an ePDG (over EPC) and 3GPP access over 5GC;
4.23.13.2 Mobility procedure without N26 interface from EPS to 5GS p. 661
At Mobility procedure from EPS to 5GS without N26 interface the procedure described in Figure 4.11.2.3-1 takes place, with following difference:
- During step 9 of Figure 4.11.2.3-1 "UE requested PDU Session Establishment according to clause 4.3.2.2", the mechanisms described in clause 4.23.5.1 apply
4.23.13.3 Mobility procedure without N26 interface from EPC/ePDG to 5GS p. 661
At Handover from EPC/ePDG to 5GS, the procedure described in Figure 4.11.4.1-1 takes place, with following difference:
- During step 2 of Figure 4.11.4.1-1 "UE requested PDU Session Establishment according to clause 4.3.2.2", the mechanisms described in clause 4.23.5.1 apply
4.23.13.4 Mobility procedure without N26 interface from 5GS to EPS p. 661
At Mobility procedure from 5GS to EPS without N26 interface, the procedure described in Figure 4.11.2.2-1 takes place, with following difference:
- During step 14 of Figure 4.11.2.2-1 (SMF+PGW-C initiates release of the PDU Session(s) in 5GS transferred to EPS), if an I-SMF was involved in the PDU Session, the same mechanisms than in Home Routed roaming apply (release according to Figure 4.3.4.3-1) with the SMF playing the role of the H-SMF and the I-SMF playing the role of the V-SMF.
4.23.13.5 Mobility procedure without N26 interface from 5GS to EPC/ePDG p. 661
At Handover from 5GS to EPC/ePDG, the procedure described in Figure 4.11.4.2-1 takes place, with following difference:
- During step 3 of Figure 4.11.4.2-1 (5GC and NG-RAN resource release), if an I-SMF was involved in the PDU Session, the same mechanisms than in Home Routed roaming apply (Figure 4.3.4.3-1 steps 3a-16b) with the SMF playing the role of the H-SMF and the I-SMF playing the role of the V-SMF.
4.23.14 Pause of charging p. 662
When I-SMF is involved for a PDU Session, the procedure for pause of charging in home routed roaming case defined in clause 4.4.4 is applied by replacing the H-SMF with SMF and V-SMF with I-SMF.
When a Local UPF (PSA) is involved, the SMF stops or starts the usage reporting including usage reporting at the Local UPF (PSA) via the I-SMF.
For a PDU Session, if charging has been paused previously, in addition to the conditions for stopping pause of charging as described in clause 4.4.4, the charging is unpaused in the following case:
-
When the SMF receives Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request from a new I-SMF or Nsmf_Create PDUSession_ request from AMF.CreateSMContext
4.23.15 PDU Session mobility between 3GPP and non-3GPP access p. 662
In this Release of the specification, deployments topologies with specific SMF Service Areas apply only for 3GPP access.
At PDU Session mobility from 3GPP to non-3GPP access, an I-SMF may need to be removed because an I-SMF had been inserted when the PDU Session was served over 3GPP access.
At PDU Session mobility from non-3GPP to 3GPP access, an I-SMF may need to be inserted because the TA associated with the UE location over 3GPP requires the AMF to insert an I-SMF.
4.23.16 Handover of a PDU Session procedure between 3GPP and untrusted non-3GPP access p. 662
4.23.16.1 Handover of a PDU Session procedure from untrusted non-3GPP to 3GPP access (non-roaming and roaming with local breakout) p. 662
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.9.2.1 when a PDU Session is handover from untrusted non-3GPP to 3GPP access (non-roaming and roaming with local breakout):
-
Step2: The UE performs a PDU Session Establishment procedure with the PDU Session ID of the PDU Session to be moved as specified clause 4.23.5.1 and an I-SMF and an I-UPF may be selected and inserted for this PDU. If I-SMF is selected, in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Response the SMF shall include all QoS information for the QoS Flow(s) applicable to the PDU Session for the target access so that when sending the PDU Session Establishment Accept, within the N1 SM container and in the N2 SM information, the I-SMF can include all QoS information (e.g. QoS Rule(s) in N1 SM container, QFI(s) and QoS Profile(s) in N2 SM information) for the QoS Flow(s).Create
4.23.16.2 Handover of a PDU Session procedure from 3GPP to untrusted non-3GPP access (non-roaming and roaming with local breakout) p. 662
When a PDU Session is handover from 3GPP access with an I-SMF to untrusted non-3GPP access (non-roaming and roaming with local breakout), the following steps take place:
- Step 1 of clause 4.9.2.2.
- Step 2 of clause 4.9.2.2.
-
The step 3 in clause 4.9.2.4.2 is executed involving I-SMF instead of V-SMF, with following differences:
- Figure 4.3.4.3-1 step 14 involving I-SMF instead of V-SMF.
-
Figure 4.3.4.3-1 step 16a: The SMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ (Release) indicating the release is due to a PDU Session Handover out of the I-SMF.StatusNotify -
Figure 4.3.4.3-1 step 16b: the I-SMF invoke the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ (Release) indicating the Release is due to a PDU Session Handover out of the I-SMF: the AMF determines that only the SMcontext with the I-SMF is to be released but that the PDU Session is not released.SMContexStatusNotify
4.23.16.3 Handover of a PDU Session procedure from untrusted non-3GPP to 3GPP access (home routed roaming) p. 663
4.23.16.3.1 The target AMF is in the PLMN of the N3IWF p. 663
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.9.2.3.1 when a PDU Session is handover from untrusted non-3GPP to 3GPP access (home routed roaming) and target AMF is in the PLMN of the N3IWF:
-
Step2: The UE performs a PDU Session Establishment procedure with the PDU Session ID of the PDU Session to be moved as specified clause 4.23.5.1. A different V-SMF and a different V-UPF may be selected for the PDU Session.
If a new V-SMF is selected, in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Response the H-SMF shall include all QoS information for the QoS Flow(s) applicable to the PDU Session for the target access so that when sending the PDU Session Establishment Accept, within the N1 SM container and in the N2 SM information, the V-SMF can include all QoS information (e.g. QoS Rule(s) in N1 SM container, QFI(s) and QoS Profile(s) in N2 SM information) for the QoS Flow(s) acceptable according to VPLMN policies.Create - (additional) Step 4: If a new V-SMF and a new V-UPF are selected for the PDU Session, the step 3a and 14 in clause 4.3.4.3 are performed to release the resource in the old V-SMF and old V-UPF.
4.23.16a Handover of a PDU Session procedure between 3GPP and trusted non-3GPP access p. 663
4.23.16a.1 General p. 663
The handover of a PDU Session between 3GPP access and trusted non-3GPP access shall be supported as specified in clause 4.23.16 for all types of handover of a PDU Session between 3GPP access and untrusted non-3GPP access, with the following modifications and clarifications:
- The untrusted non-3GPP access is substituted by a trusted non-3GPP access point (TNAP).
- The N3IWF is substituted by the TNGF.
- The reference to clause 4.9.2 is substituted by clause 4.9.3 specifying handover of a PDU Session procedure between 3GPP and trusted non-3GPP access.
4.23.17 Additional considerations for Home-routed roaming |R17| p. 663
As described in clause 4.23.1, the procedures in clause 4.23 apply for home-routed roaming scenarios with V-SMF insertion/removal/change (i.e. by replacing the I-SMF with V-SMF and SMF with H-SMF). Differences compared to the procedures for I-SMF are described below:
-
The Registration procedure as defined in clause 4.23.3 with the following additions:
- Step 8a of clause 4.23.4.3 (for cases d and e): the new V-SMF provides the QoS constraints of the VPLMN to H-SMF.
- Step 8c of clause 4.23.4.3 (for cases d and e): the new V-SMF may apply VPLMN QoS policies as described in clause 5.7.1.11 of TS 23.501.
-
Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover with V-SMF insertion/change as defined in clause 4.23.7.3 (i.e. by replacing the I-SMF with V-SMF) with the following additions:
- Preparation phase, step 4b (for case V-SMF change): the target V-SMF may apply VPLMN QoS policies as described in clause 5.7.1.11 of TS 23.501.
- Preparation phase, step 5d (for case V-SMF insertion): the target V-SMF may apply VPLMN QoS policies as described in clause 5.7.1.11 of TS 23.501.
- Execution phase, step 6 (for case V-SMF change/insertion): the target V-SMF provides the QoS constraints of the VPLMN to H-SMF.