Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.15.6 External Parameter Provisioning
4.15.6.1 General
4.15.6.2 NEF service operations information flow
4.15.6.3 Expected UE Behaviour parameters
4.15.6.3a Network Configuration parameters
4.15.6.3b 5G VN group data
4.15.6.3c 5G VN Group membership management parameters
4.15.6.3d ECS Address Configuration Information Parameters
4.15.6.3e DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters
4.15.6.3f Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameters
4.15.6.3g Network Slice Usage Control parameters for dedicated S-NSSAI to a single AF
4.15.6.3h CAG Information provisioning parameters
4.15.6.3i Static IP address assignment parameters
4.15.6.4 Set a chargeable party at AF session setup
4.15.6.5 Change the chargeable party during the session
4.15.6.6 Setting up an AF session with required QoS procedure
4.15.6.6a AF session with required QoS update procedure
...
...
4.15.6 External Parameter Provisioning p. 436
4.15.6.1 General p. 436
Provisioning capability allows an external party to provision the information, such as expected UE behaviour and service specific parameters or the 5G VN group information to 5G network functions. In the case of provisioning the expected UE behavioural information, the expected UE behavioural information consists of information on expected UE movement and communication characteristics. In the case of provisioning the 5G VN group information the provisioning information consists of information on 5G VN group. The service specific information consists of information to support the specific service in 5G system. Provisioned data can be used by the other NFs.
4.15.6.2 NEF service operations information flow p. 437
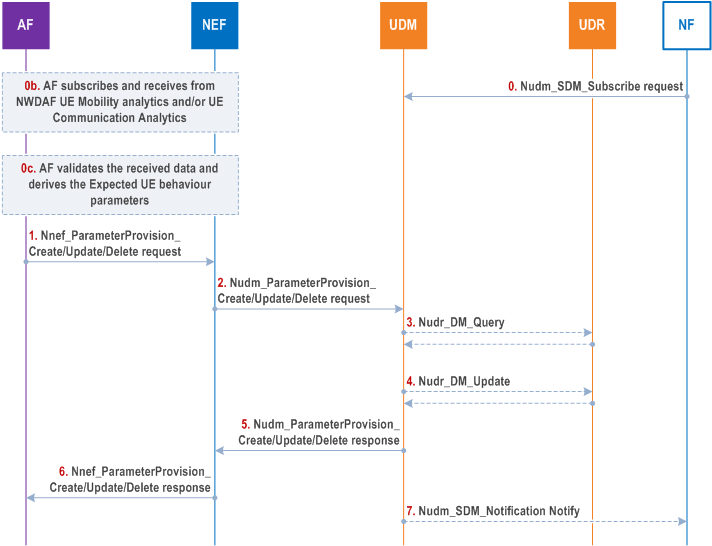
Step 0.
NF subscribes to UDM notifications of UE and/or Group Subscription data updates. In the UDM subscription, the NF may request to be notified about expected UE behaviour parameter(s) in Table 4.15.6.3-1 or Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameter(s) in Table 4.15.6.3f-1 or CAG Information provisioning parameters in Table 4.15.6.3h-1 that may have been externally provisioned by an AF.
If an expected UE behaviour parameter subscription is provided by the NF, the subscription may include a threshold indicating that certain confidence and/or accuracy levels must be met for the parameter(s) to be notified by the UDM to the NF. Meeting the threshold condition may mean that the confidence and/or accuracy levels of a parameter are equal to certain threshold, or less than certain threshold, or greater than certain threshold, or less than or equal to certain threshold, or greater than or equal to certain threshold. The threshold may be in the form of a range (e.g. minimum value to maximum value, where each may be inclusive or exclusive) or a specific value.
Step 0b.
[Conditional, on using NWDAF-assisted values] The AF may subscribe to NWDAF via NEF in order to learn the UE mobility analytics and/or UE Communication analytics for a UE or group of UEs by applying the procedure specified in clause 6.1.1.2 of TS 23.288. The Analytics ID is set to any of the values specified in clause 6.7.1 of TS 23.288.
Step 0c.
[Conditional, on using NWDAF-assisted values] AF validates the received data and derives any of the Expected UE behaviour parameters defined in clause 4.15.6.3 for a UE or group of UEs.
Step 1.
The AF provides one or more parameter(s) to be created or updated, or deleted in a Nnef_ParameterProvision_Create or Nnef_ParameterProvision_Update or Nnef_ParameterProvision_Delete Request to the NEF. The parameters(s) may include corresponding confidence and/or accuracy levels.
The AF provides target UE identifier (e.g. GPSI or External Group ID) as described in clause 5.2.6.4. The Transaction Reference ID identifies the transaction request between NEF and AF. For the case of Nnef_ParameterProvision_Create , The NEF assigns a Transaction Reference ID to the Nnef_ParameterProvision_Create request.
NEF checks whether the requestor is allowed to perform the requested service operation by checking requestor's identifier (i.e. AF Identifier).
For a Create request associated with a 5G VN group, the External Group ID identifies the 5G VN Group.
The payload of the Nnef_ParameterProvision_Update Request includes one or more of the following parameters:
ParameterProvision_Delete to the NEF.
Step 2.
- Expected UE Behaviour parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3); or
- Network Configuration parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3a); or
- 5G VN group data (i.e. 5G VN configuration parameters) (see clause 4.15.6.3b), or
- 5G VN group membership management parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3c); or
- Location Privacy Indication parameters of the "LCS privacy" Data Subset of the Subscription Data (see clause 5.2.3.3.1 of the present document and clause 7.1 of TS 23.273); or
- Ranging/Sidelink Positioning Indication parameters of the "Ranging/Sidelink Positioning privacy" Data Subset of the Subscription Data (see clause 5.2.3.3.1 of the present document and Annex B of TS 33.533); or
- MTC Provider Information; or
- AF provided ECS Address Configuration Information (see clause 4.15.6.3d); or
- DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3e); or
- Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3f); or
- CAG Information provisioning parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3h); or
- Static IP address assignment parameters (see clause 4.15.6.3i).
If the AF is authorised by the NEF to provision the parameters, the NEF requests to create, update and store, or delete the provisioned parameters as part of the subscriber data via Nudm_ParameterProvision_Create , Nudm_ParameterProvision_Update or Nudm_ParameterProvision_Delete Request message, the message includes the provisioned data and NEF reference ID and optionally MTC Provider Information.
If the AF is not authorised to provision the parameters, then the NEF continues in step 6 indicating the reason to failure in Nnef_ParameterProvision_Create /Update/Delete Response message. Step 7 does not apply in this case.
If the NEF did not receive DNN and/or S-NSSAI from the AF and such information is configured as needed within 5GC, the NEF determines the DNN and/or S-NSSAI from the AF Identifier.
If the AF provides the DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters, the AF shall indicate the External Group ID, targeted DNN and S-NSSAI in the request.
If the AF provides the service area in the form of geographical information, the NEF maps the geographical information to the list of TAs.
Step 3.
UDM may read from UDR, by means of Nudr_DM_Query , corresponding subscription information in order to validate required data updates and authorize these changes for this subscriber or Group for the corresponding AF.
Based on local configuration, UDM may determine if there is any requirement in terms of threshold conditions that need to be met by the provisioned parameter before storing the parameter in UDR. If there are no such requirement(s) or the requirement(s) are satisfied, UDM may proceed seamlessly. If not satisfied, step 5 is triggered as a failed procedure and a related cause value is provided, e.g. "confidence level not sufficient". In that case step 4 is skipped.
Step 4.
If the AF is authorised by the UDM to provision the parameters for this subscriber, the UDM resolves the GPSI to SUPI and requests to create, update or delete the provisioned parameters as part of the subscriber data via Nudr_DM_Create /Update/Delete Request message, the message includes the provisioned data.
If a new 5G VN group is created, the UDM shall assign a unique Internal Group ID for the 5G VN group and include the newly assigned Internal Group ID in the Nudr_DM_Create Request message. If the list of 5G VN group members is changed or if 5G VN group data has changed, the UDM updates the UE and/or Group subscription data according to the AF/NEF request.
When the service area is configured or updated for a group, the UDM authorises the request.
If the Default QoS is configured or updated for a group, the UDM authorises the request and uses such Default QoS to set 5GS Subscribed QoS profile in Session Management Subscription data for each UE within the group. The 5GS Subscribed QoS profile in Session Management Subscription data will be considered by SMF as described in clause 5.7.2.7 of TS 23.501.
If the Static IP address assignment parameters is created, updated or removed by the AF, the UDM authorises the request and adds, updates or removes such static IP address/prefix in Session Management Subscription data for the UE. The static IP address information in Session Management Subscription data will be considered by SMF as described in clause 5.8.2.2.1 of TS 23.501.
UDR stores the provisioned data as part of the UE and/or Group subscription data and responds with Nudr_DM_Create /Update/Delete Response message.
If the Maximum Group Data Rate is configured or updated for a 5G VN group, the UDM authorises the request and the Maximum Group Data Rate is applied as described in clause 5.29.2 of TS 23.501.
When the 5G VN group data (as described in clause 4.15.6.3b) or 5G VN group membership is updated, the UDR notifies to the subscribed PCF by sending Nudr_DM_Notify as defined in clause 4.16.12.2.
If CAG Information is created, updated or removed by the AF as described in clause 4.15.6.3h, the UDM authorises the request and adds, updates or removes such CAG information in Access and Mobility Subscription data for the UE.
If the AF is not authorised to provision the parameters, then the UDM continues in step 5 indicating the reason to failure in Nudm_ParameterProvision_Update Response message and step 7 is not executed.
The UDM classifies the received parameters (i.e. Expected UE Behaviour parameters or Suggested Number of Downlink Packets or the 5G VN configuration parameters or DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters or Location Privacy Indication parameters or ECS Address Configuration Information or Static IP address assignment parameters or CAG Information provisioning parameters), into AMF associated and SMF associated parameters. The UDM may use the AF Identifier received from the NEF in step 2 to relate the received parameter with a particular subscribed DNN and/or S-NSSAI. The UDM stores the SMF-Associated parameters under corresponding Session Management Subscription data type.
Each parameter or parameter set may be associated with a validity time. The validity time is stored at the UDM/UDR and in each of the NFs, to which parameters are provisioned (e.g. in AMF or SMF). Upon expiration of the validity time, each node deletes the parameters autonomously without explicit signalling.
If the ECS Address Configuration Information is provided to any UE in AF request, the UDM shall make use of the shared data mechanism defined in TS 29.503 and notify all NFs (SMFs) that have subscribed to receiving such shared data change notifications.
Step 5.
UDM responds the request with Nudm_ParameterProvision_Create /Update/Delete Response. If the procedure failed, the cause value indicates the reason.
Step 6.
NEF responds the request with Nnef_ParameterProvision_Create /Update/Delete Response. If the procedure failed, the cause value indicates the reason.
Step 7.
[Conditional this step occurs only after successful step 4] UDM notifies the subscribed Network Function of the updated UE and/or Group subscription data via Nudm_SDM_Notification Notify message.
-
If the subscribed NF is AMF, the UDM performs Nudm_
SDM_ (SUPI or Internal Group Identifier, AMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameters, Subscribed Periodic Registration Timer, subscribed Active Time, 5G VN group data or DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters, UE allowed CAG list and its validity timer, etc.) service operation. If the AMF receives confidence and/or accuracy levels along the Expected UE behaviour parameter(s), the AMF may use the associated confidence level and/or accuracy level when handling the expected UE behaviour parameter(s). The AMF uses the received parameters to derive the appropriate UE configuration of the NAS parameters and to derive Core Network assisted RAN parameters. The AMF may determine a Registration area based on parameters Stationary indication or Expected UE Moving Trajectory. If the AMF obtains service area for a group or SUPI, the AMF configures the DNN for the group as LADN DNN and applies the LADN per DNN and S-NSSAI taking into account the service area for the group as described in clause 5.6.5a of TS 23.501.Notification -
If the subscribed NF is SMF, the UDM performs Nudm_
SDM_ (SUPI or Internal Group Identifier, SMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameter set, DNN/S-NSSAI, Suggested Number of Downlink Packets, 5G VN group data, Session Management Subscription data, etc.) service operation. The SMF stores the received parameters and associates them with a PDU Session based on the DNN and S-NSSAI included in the message from UDM. If the SMF is notified by UDM that the subscription data has changed, and SMF detects that the static IP address/prefix is added, removed or updated, the SMF may perform the PDU Session release procedure and includes a cause value indicating that a PDU Session re-establishment is requested, as described in clause 4.3.4 and in clause 5.8.2.2.1 of TS 23.501. If the SMF receives confidence and/or accuracy levels along the Expected UE behaviour parameter(s), the SMF may use the associated confidence level and/or accuracy level when handling the expected UE behaviour parameter(s). The SMF may use the parameters as follows:Notification - SMF configures the UPF accordingly. The SMF can use the Scheduled Communication Type parameter or Suggested Number of Downlink Packets parameter to configure the UPF with how many downlink packets to buffer. The SMF may use Communication duration time parameter and/or Expected Inactivity Time parameter and/or Battery Indication parameter combined with their confidence and/or accuracy levels to set the inactivity timer for a PDU Session. The SMF then waits for a UP inactivity report to be received from UPF. Based on the received UP inactivity report, the SMF may determine to deactivate the corresponding UP connection associated to the PDU Session of a single UE or determine a collective pattern of deactivating UP connections for multiple UEs (e.g. for a group of UEs receiving application AI/ML traffic during FL operation) and perform CN-initiated selective deactivation of UP connection of an existing PDU Session.
- The SMF may derive SMF derived CN assisted RAN information for the PDU Session. The SMF provides the SMF derived CN assisted RAN information to the AMF as described in PDU Session establishment procedure or PDU Session modification procedure.
4.15.6.3 Expected UE Behaviour parameters p. 441
These Expected UE Behaviour parameters characterise the foreseen behaviour of a UE or a group of UEs. Sets of these parameters may be provided via the NEF to be stored as part of the subscriber data. Each parameter within the Expected UE Behaviour shall have an associated validity time. The validity time indicates when the Expected UE Behaviour parameter expires and shall be deleted by the related NFs. The validity time may be set to indicate that the particular Expected UE Behaviour parameter has no expiration time. When the validity time expires, the related NFs delete their local copy of the associated Expected UE Behaviour parameter(s). In addition, each parameter within the Expected UE Behaviour may have a confidence and/or accuracy level associated with it. The confidence level indicates a probability assertion for the associated Expected UE Behaviour parameter and the accuracy level indicates the performance of the estimator (e.g. AI/ML model) used for the prediction. The provision procedure of the Expected UE Behaviour is realized by external parameter provision procedure defined in clause 4.15.6.2.
The Expected UE Behaviour parameters stored as AMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameters which is per UE level and SMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameters which is per PDU session level in UDM. AMF retrieves the AMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameters from UDM which may related to both PDU session(s) and SMS transmission. SMF retrieves the SMF-Associated Expected UE Behaviour parameters from UDM for the specific PDU session. AMF and SMF uses the Expected UE Behaviour parameters as described in clause 5.4.6.2 of TS 23.501.
| Expected UE Behaviour parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Expected UE Moving Trajectory | Identifies the UE's expected geographical movement Example: A planned path of movement |
| Stationary Indication | Identifies whether the UE is stationary or mobile [optional] |
| Communication Duration Time | Indicates for how long the UE will normally stay in CM-CONNECTED for data transmission. Example: 5 minutes. [optional] |
| Periodic Time | Interval Time of periodic communication Example: every hour. [optional] |
| Scheduled Communication Time | Time and day of the week when the UE is available for communication. Example: Time: 13:00-20:00, Day: Monday. [optional] |
| Battery Indication | Identifies power consumption criticality for the UE: if the UE is battery powered with not rechargeable/not replaceable battery, battery powered with rechargeable/replaceable battery, or not battery powered. [optional] |
| Traffic Profile | Identifies the type of data transmission: single packet transmission (UL or DL), dual packet transmission (UL with subsequent DL or DL with subsequent UL), multiple packets transmission [optional] |
| Scheduled Communication Type | Indicates that the Scheduled Communication Type is Downlink only or Uplink only or Bi-directional [To be used together with Scheduled Communication Time] Example: <Scheduled Communication Time>, DL only. [optional] |
| Expected Time and Day of Week in Trajectory | Identifies the time and day of week when the UE is expected to be at each location included in the Expected UE Moving Trajectory. [optional] |
The Expected UE Moving Trajectory and the Expected Time and Day of Week in Trajectory may be used by the AMF. All other parameters may be used by the AMF and by the SMF.The Scheduled Communication Type and the Traffic Profile should not be used by the AMF to release the UE when NAS Release Assistance Information from the UE is available.
In the case of NB-IoT UEs, the parameters may be forwarded to the RAN to allow optimisation of Uu resource allocation for NB-IoT UE differentiation.
4.15.6.3a Network Configuration parameters |R16| p. 442
The Network Configuration parameters are the parameters sent from an AF by invoking the Nnef_ParameterProvision Service as described in clause 4.15.6.2.
The Network Configuration parameters are described in Table 4.15.6.3a-1.
| Network Configuration parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Response Time | Identifies the time for which the UE stays reachable to allow the AF to reliably deliver the required downlink data. [optional] |
| Maximum Latency | Identifies maximum delay acceptable for downlink data transfers. Example: in order of 1 minute to multiple hours. [optional] |
| Suggested Number of Downlink Packets | Identifies the number of packets that the core network is suggested to buffer if the UE is not reachable. Example: 5 packets. [optional] |
| MPS for Messaging indication | Sets(Enables)/Clears(Disables) the MPS priority handling for Messaging service of the UE. |
The parameters Maximum Response Time and Maximum Latency are stored in the UDM and the Maximum Response Time is sent to the AMF for event monitoring as specified in clause 4.15.3.2.3b.
The AMF may use the Maximum Response Time parameter as guide to configure:
SDM_Notification message. If there is a deletion of Network Configuration request, the UDM re-calculates the values (see step 2 in clause 4.15.3.2.3b) and notify the AMF if needed.
The Suggested Number of Downlink Packets is classified as SMF associated subscription data. If the NEF is providing DNN and S-NSSAI as specified in clause 4.15.3.2.3, then the UDM is able to associate the parameters with subscribed DNN and S-NSSAI and provides the Suggested Number of Downlink Packets consolidated as specified in 4.15.3.2.3b to the SMF for the PDU Session associated with the specific DNN and S-NSSAI as specified in clause 4.15.6.2. The SMF may use the Suggested Number of Downlink Packets parameter to configure the number of packets to buffer in the SMF/UPF (in the case of UPF anchored PDU sessions) or in the NEF (in the case of NEF anchored PDU session) when the UE is not reachable and extended buffering of downlink data is activated.
The MPS for Messaging indication sets(enables)/clears(disables) the MPS treatment of messaging service for MPS-subscribed UE. The parameter is stored in UDM/UDR and provided to NFs and entities involved in the messaging service (i.e. SMS over NAS, SMS over IP and messaging over IMS are all controlled by one indication) as part of the subscription data. The MPS for Messaging indication is used in communications between NFs and network entities in CN and is not delivered to UE. The detailed MPS for Messaging indication handling is further specified in clause 4.13 for SMS over NAS, in TS 23.204 for SMS over IP, and in TS 23.228 for messaging over IMS.
A Validity Time may be associated with any of the Network Configuration parameters. When the validity time expires, the related NFs delete their local copy of the associated Network Configuration parameter(s). If the deletion results in subscribed value change, the UDM shall notify the AMF or SMF of the changed value.
- Extended Connected time for MICO mode;
- when to send reachability notifications to AF relative to expected reachability events (e.g. paging occasions).
4.15.6.3b 5G VN group data |R16| p. 443
The 5G VN group data is described in Table 4.15.6.3b-1.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| DNN | DNN for the 5G VN group. |
| S-NSSAI | S-NSSAI for the 5G VN group. |
| PDU Session Type | PDU Session Types allowed for 5G VN group. |
| Application descriptor | There may be multiple instances of this information; this information may be used to build URSP sent to 5G VN group members (NOTE 1). |
| Information related with secondary authentication / authorization |
This may indicate:
|
| 5G VN group communication indication | Indicates that the 5G VN group is associated with 5G VN group communication. |
| Maximum Group Data Rate |
This limits the total bit rate that is expected to be provided across all sessions of a 5G VN group.
[optional]. |
| User Plane Security Policy | User Plane Security Policy for PDU sessions associated with the 5G VN group. |
|
NOTE 1:
As described in TS 23.503, the PCF may be configured with a mapping from Application Descriptor to other information required to construct the URSP rules, e.g. IP filters and SSC mode.
|
|
The information described in Table 4.15.6.3b-1 corresponds to 5G VN group data that an AF may provide together with External Group ID.
4.15.6.3c 5G VN Group membership management parameters |R16| p. 444
5G VN group membership management parameters that an AF may provide are described in Table 4.15.6.3c-1.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| List of GPSI | List of 5G VN Group members, each member is identified by GPSI |
| External Group ID | A identifier for 5G VN group |
4.15.6.3d ECS Address Configuration Information Parameters |R17| p. 444
AF provided ECS Address Configuration Information that an AF may provide to the 5GC is described in Table 4.15.6.3d-1. The AF may associate ECS Address Configuration Information with a group of UE or with any UE.
Multiple AF may configure 5GC with AF provided ECS Address Configuration Information.
The Subscription provided ECS Address Configuration Information that a SMF may receive is described in Table 4.15.6.3d-2
For non-roaming and LBO cases, the ECS Address Configuration Information is provided to SMF as Session Management Subscription data. The ECS Address Configuration Information is associated with a DNN and S-NSSAI included in the message from UDM.
For HR cases:
- When the HPLMN has the knowledge of EACI in the VPLMN, the ECS Address Configuration Information is provided to H-SMF as Session Management Subscription data. The ECS Address Configuration Information is associated with a DNN, S-NSSAI and PLMN ID included in the message from UDM.
- When the HPLMN does not have the knowledge of EACI in the VPLMN, for this scenario, as defined in clauses 6.5.2.6.2 and 6.5.2.6.3 of TS 23.548, V-NEF stores the VPLMN EACI received from AF deployed in the VPLMN in V-UDR as Application data. The ECS Address Configuration Information for this case is associated with DNN, S-NSSAI and any UE.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| ECS Address Configuration Information | One or more ECS Configuration Information as defined in clause 8.3.2.1 of TS 23.558. |
| Target | This may correspond to one of:
|
| PLMN ID | The ECS Address Configuration Information is applied to the UE roaming in target PLMN. |
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| ECS Address Configuration Information | As defined in Table 4.15.6.3d-1. The SMF is not expected to understand the internal structure of ECS Address Configuration Information. |
4.15.6.3e DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters |R18| p. 445
The DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters are the parameters sent from an AF by invoking the Nnef_ParameterProvision Service as described in clause 4.15.6.2.
The DNN and S-NSSAI specific Group Parameters are described in Table 4.15.6.3e-1.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Default QoS (NOTE 1) | Identifies the requested default QoS parameters (as defined in clause 5.7.2.7 of TS 23.501) applicable to each UE within a group. [optional] |
| Service Area (NOTE 1) | Identifies the AF-requested Service Area applicable to each UE within a group. [optional] |
|
NOTE 1:
These parameters are applicable per DNN and S-NSSAI.
|
|
4.15.6.3f Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameters |R18| p. 445
The Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameters characterise the foreseen behaviour of a UE for a specific application. When AF provisions the Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour parameters, the AF shall provide application traffic descriptors (i.e. the corresponding Packet Filters or Application ID). Each parameter within the Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour shall have an associated validity time and may have a confidence and/or accuracy level associated with it as defined in the clause 4.15.6.2 and clause 4.15.6.3.
| Application-Specific Expected UE Behaviour Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Expected PDU session Inactivity Time | Identifies the expected PDU Session Inactivity time during which the UE will not have traffic related to the application. |
4.15.6.3g Network Slice Usage Control parameters for dedicated S-NSSAI to a single AF |R18| p. 446
An AF having a S-NSSAI dedicated to it may be authorized, to control the parameters to remove the S-NSSAI from the Allowed NSSAI or release a PDU Session associated with the S-NSSAI. In this case, these parameters may be provided by an authorized AF via the NEF and be stored as part of the subscriber data. The provision procedure of the Network Slice Usage Control Parameters is realized by external parameter provision procedure as described in clause 4.15.6.2. The AMF and SMF use the Network Slice Usage Control parameter as described in clause 5.15.15 of TS 23.501.
| Network Slice Usage Control parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| For each indicated S-NSSAI | |
| S-NSSAI | S-NSSAI for which the inactivity-based slice control applies (NOTE 1) |
| slice deregistration inactivity timer value | For network slice usage control, this timer identifies the wait time before deregistering the UE from the S-NSSAI by removing the S-NSSAI from the Allowed NSSAI when no associated PDU Session is established with the indicated S-NSSAI.
[optional] |
| PDU Session inactivity timer value | Identifies the wait time to release the PDU Session associated with the indicated S-NSSAI when there is no data transmission
[optional] |
|
NOTE 1:
This slice is solely dedicated for one authorized AF and not shared with other AFs.
|
|
According to the received network slice usage control parameter, the UDM updates all related UE subscription data which includes the indicated S-NSSAI.
Only in this case and for subscribers having such an S-NSSAI as a subscribed S-NSSAI, the slice deregistration inactivity timer value and/or PDU Session inactivity timer value is obtained by the AMF or SMF as part of the subscription data respectively as specified in clauses 4.2.2.2.2 and 4.3.2.2.1.
4.15.6.3h CAG Information provisioning parameters |R19| p. 446
The CAG Information provisioning parameters are the parameters sent from an AF by invoking the Nnef_ParameterProvision Service as described in clause 4.15.6.2. The AF request can be driven by the CAG owner or an authorized administrator. The CAG Information provisioning includes the parameters listed in Table 4.15.6.3h-1. According to the received CAG Information provisioning parameters at NEF, the NEF updates the UDM with the provided information. The UDM updates the allowed CAG list of the given UE(s) and notifies AMF via Nudm_SDM_Notification Notify message as defined in clause 4.15.6.2. Then, AMF initiates UE Configuration Update procedure to the UE(s) to update the allowed CAG list of the UE(s) along with the provided validity timer as described in clause 4.2.4.2.
| CAG Information provisioning parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| UE ID(s) | Indicates the unique identifier for the user to be updated with provided CAG information. It can be GPSI. |
| CAG ID(s) | Indicates the CAG ID(s) to be included to the existing UE Allowed CAG list. |
| Time validity information | Indicates the expiry time if the CAG information is only valid temporarily. If no expiry time is present, the provided CAG information will be valid until the next update is performed. |
4.15.6.3i Static IP address assignment parameters |R19| p. 447
An AF may be authorized to provide static IP address(es) per subscriber for a given DNN and S-NSSAI. In this case, the static IP address for a GPSI may be provided by an authorized AF via the NEF and be stored as part of the UE subscriber data. The provision procedure for static IP addresses is realized by external parameter provision procedure as described in clause 4.15.6.2. The AF may provide a GPSI and include the static IP address/prefix for that GPSI, as described in Table 4.15.6.3i-1. The SMF uses the static UE IP address as described in clause 5.8.2.2 of TS 23.501.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| GPSI | GPSI for which the IP address/prefix applies. |
| DNN | DNN for which the IP address information applies. |
| S-NSSAI | S-NSSAI for which the IP address information applies. |
4.15.6.4 Set a chargeable party at AF session setup p. 447
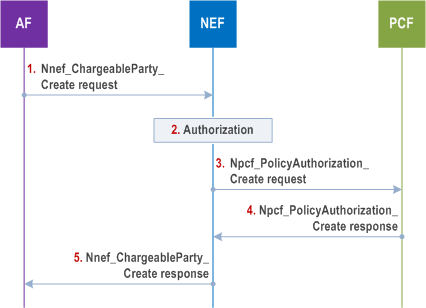
Step 1.
When setting up the connection between an ASP sponsoring a session and the UE, the ASP may communicate with the AF to request to become the chargeable party for the session to be set up by sending a Nnef_ChargeableParty_Create request message (AF Identifier, UE address, Flow description information or External Application Identifier, Sponsor Information, Sponsoring Status, Background Data Transfer Reference ID, DNN, S-NSSAI) to the NEF. The Sponsoring Status indicates whether sponsoring is started or stopped, i.e. whether the 3rd party service provider is the chargeable party or not. The Background Data Transfer Reference ID parameter identifies a previously negotiated transfer policy for background data transfer as defined in clause 4.16.7. The NEF assigns a Transaction Reference ID to the Nnef_ChargeableParty_Create request.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the AF request to sponsor the application traffic and stores the sponsor information together with the AF Identifier and the Transaction Reference ID. If the authorisation is not granted, step 2 is skipped and the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
The NEF interacts with the PCF by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create request message and provides IP filter information or Ethernet filter information, sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503), Background Data Transfer Reference ID (if received from the AF) and Sponsoring Status (if received from the AF) to the PCF.
Step 4.
The PCF determines whether the request is allowed and notifies the NEF if the request is not authorized. If the request is not authorized, NEF responds to the AF in step 5 with a Result value indicating that the authorization failed.
Step 5.
The NEF sends a Nnef_ChargeableParty_Create response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the AF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
4.15.6.5 Change the chargeable party during the session p. 448
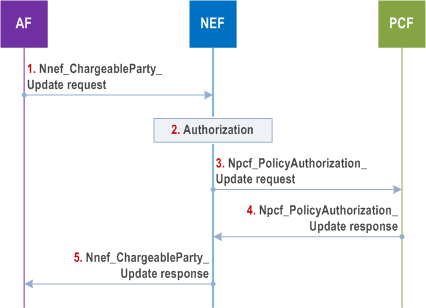
Step 1.
For the ongoing AF session, the AF may send a Nnef_ChargeableParty_Update request message (AF Identifier, Transaction Reference ID, Sponsoring Status, Background Data Transfer Reference ID) to the NEF. The Sponsoring Status indicates whether sponsoring is enabled or disabled, i.e. whether the 3rd party service provider is the chargeable party or not. The Background Data Transfer Reference ID parameter identifies a previously negotiated transfer policy for background data transfer as defined in clause 4.16.7. The Transaction Reference ID provided in the Change chargeable party request message is set to the Transaction Reference ID that was assigned, by the NEF, to the a Nnef_ChargeableParty_Create request.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the AF request of changing the chargeable party. If the authorisation is not granted, step 3 is skipped and the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
The NEF interacts with the PCF by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request and provides IP filter information or Ethernet filter information, sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503), Background Data Transfer Reference ID (if received from the AF) and Sponsoring Status (if received from the AF) to the PCF.
Step 4.
The PCF determines whether the request is allowed and notifies the NEF if the request is not authorized. If the request is not authorized, NEF responds to the AF in step 5 with a Result value indicating that the authorization failed.
Step 5.
The NEF sends a Nnef_ChargeableParty_Update response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the AF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
4.15.6.6 Setting up an AF session with required QoS procedure p. 449
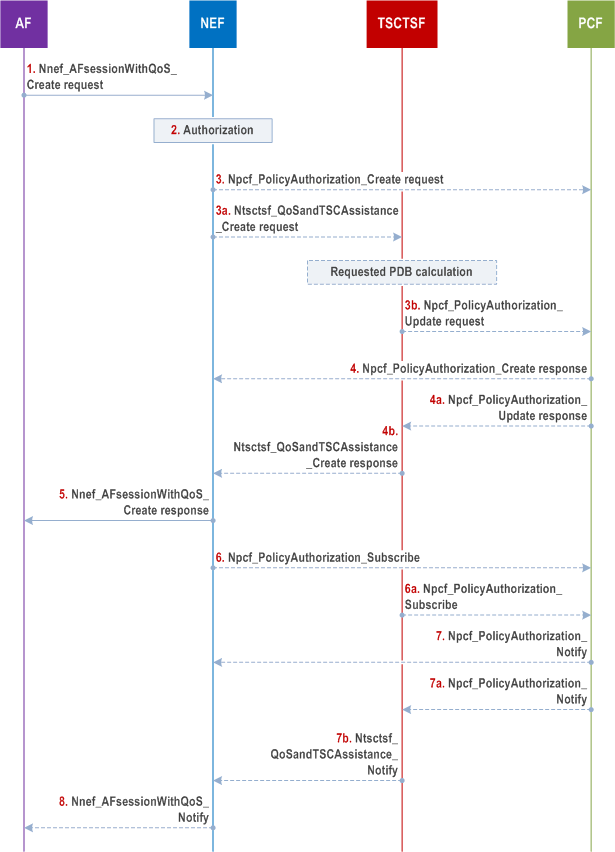
Step 1.
The AF may send Nnef_
The AF sends a request to reserve resources for an AF session using Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create request message (UE address, AF Identifier, Flow description information or External Application Identifier, QoS Reference or individual QoS parameters, Alternative Service Requirements (as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503), DNN, S-NSSAI) to the NEF. Optionally, QoS monitoring requirements, Indication of ECN marking for L4S, Data Burst Size Marking Support Indication, Time to Next Burst Support Indication, PDU Set QoS Parameters (as described in clause 5.7.7 of TS 23.501) and Protocol Description (as described in clause 5.37.5, 5.37.8.3 and other (sub)clauses in clause 5.37 of TS 23.501) can be included in the AF request. For a Multi-modal service, the AF may provide a Multi-modal Service ID together with Multi-modal Service Requirements information for each data flow, as described in clause 6.1.3.27.3 of TS 23.503. Optionally, a period of time or a traffic volume for the requested QoS can be included in the AF request. The AF may, instead of a QoS Reference, provide one or more of the following individual QoS parameters: Requested 5GS Delay (optional), Requested Priority (optional), Requested Guaranteed Bitrate, Requested Maximum Bitrate, Maximum Burst Size and Requested Packet Error Rate. The AF may also provide an Averaging Window value for deriving such parameters for GBR QoS Flows. Regardless of whether the AF request is formulated using a QoS Reference or individual QoS parameters, the AF may also provide one or more of the following parameters that describe the traffic characteristics: flow direction, Burst Arrival Time at UE (uplink) or UPF (downlink), Periodicity, Time domain, Survival Time, Capability for BAT adaptation or BAT Window, Periodicity Range. The AF may also provide an RT Latency Indication. The optional Alternative Service Requirements provided by the AF shall either contain QoS References or Requested Alternative QoS Parameter Set(s) in a prioritized order as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503. Optionally, Packet Delay Variation requirements can be included in the AF request as described in clause 6.1.3.26 of TS 23.503. Optionally, the AF may provide QoS duration and QoS inactivity interval in order to indicate PCF the time period when the QoS should be applied.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the AF request that contains a single UE address and may apply policies to control the overall amount of QoS authorized for the AF. If the authorisation is not granted, all steps (except step 5) are skipped and the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed. The NEF assigns a Transaction Reference ID to the Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create request.
The NEF determines whether to invoke the TSCTSF or to directly contact the PCF based on operator configuration. This determination may use the presence of a QoS Reference or individual QoS parameters in the AF request. The determination may also use the AF identifier or the presence of AF provided parameters that describe the traffic characteristics in the AF request.
If the NEF determines not to invoke the TSCTSF, then steps 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 are executed, otherwise, steps 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b, 5, 6a, 7a, 7b, 8 are executed.
Step 3.
If the NEF determines to contact the PCF directly without invoking the TSCTSF, the NEF uses the UE address to discover the PCF from the BSF. The NEF forwards received parameters to the PCF in the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create request. Any optionally received period of time or traffic volume mapped and forwarded as sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503).
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the AF uses the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create request message to interact directly with PCF to request reserving resources for an AF session.
Step 3a.
If the NEF determines to invoke the TSCTSF, the NEF forwards received parameters in the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Create request message to the TSCTSF. Any optionally received period of time or traffic volume is mapped and forwarded as sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503).
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the AF uses the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Create request message to interact directly with TSCTSF to request reserving resources for an AF session.
A TSCTSF address may be locally configured (a single TSCTSF per DNN/S-NSSAI) in the NEF, PCF and trusted AF. Alternatively, the NEF uses the AF Identifier to determine the DNN/S-NSSAI and uses the DNN/S-NSSAI to discover the TSCTSF from the NRF.
Step 3b.
The TSCTSF determines whether it has an AF session with a PCF for the given UE address. In this case the TSCTSF sends a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request message to the PCF and forwards the received parameters after executing the adjustment and mapping actions described below.
If the TSCTSF does not have an AF-session for a given UE address, the TSCTSF discovers the PCF and a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create request message to the PCF.
If the TSCTSF receives a Requested 5GS Delay, the TSCTSF calculates a Requested PDB by subtracting the UE-DS-TT Residence Time (either provided by the PCF or pre-configured at TSCTSF) from the Requested 5GS Delay and sends the Requested PDB to the PCF instead of the Requested 5GS Delay. If the TSCTSF receives any of the following parameters: flow direction, Burst Arrival Time, Periodicity, Time domain, Survival Time, Capability for BAT adaptation or BAT Window, Periodicity Range from the NEF, the TSCTSF determines the TSC Assistance Container and sends it to the PCF instead of these parameters.
Step 4.
If the request is authorized, the PCF derives the required QoS parameters of the PCC rule based on the information provided by the NEF and determines whether this QoS is allowed (according to the PCF configuration) and notifies the result to the NEF. If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the PCF sends the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create response message directly to AF.
If the PCF receives the individual QoS parameters instead of QoS Reference, the PCF determines a 5QI that matches the individual QoS parameters as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503. It also sets the GBR and MBR for the PCC rule according to the requested values. The PCF may use the Requested Priority from the AF to determine Priority Level as defined in clause 5.7.3.3 of TS 23.501. Requested individual QoS parameter values supersede default values for the 5QI.
If the PCF receives the RT Latency Indication described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503, the PCF executes Uplink-Downlink Transmission Coordination as described in clause 5.37.7 of TS 23.501 and the associated QoS monitoring for the two correlated QoS Flows as described in clause 6.1.3.27.2 of TS 23.503.
If the PCF receives PDU Set QoS parameters described in clause 5.7.7 of TS 23.501, the PDU Set QoS parameters are applied as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503.
If the PCF receives an explicit indication (i.e. Indication of ECN marking for L4S) as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503, PCF decides that the service data flow supports ECN marking for L4S. PCF then indicates to the SMF to enable ECN marking for L4S for that QoS flow.
In addition, if the Alternative Service Requirements are provided, the PCF derives the Alternative QoS parameter set(s) in the same way from the one or more QoS Reference parameters or the Requested Alternative QoS Parameter Set(s) contained in the Alternative Service Requirements keeping the same prioritized order (as defined in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503).
For multi-modal flows, the PCF derives the required QoS parameters in the PCC rules and generates the QoS monitoring requirements policy for each media flow, based on the information provided by the NEF.
If the PCF determines that the SMF needs updated policy information, the PCF issues a Npcf_SMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify request with updated policy information about the PDU Session as described in the PCF initiated SM Policy Association Modification procedure in clause 4.16.5.2.
Step 4a.
For requests received from the TSCTSF in step 3b, the PCF determines whether the request is authorized and notifies the TSCTSF if the request is not authorized.
If the request is authorized, the PCF derives the required QoS parameters of the PCC rule in the same way it is described in step 4 based on the information provided by the TSCTSF and determines whether this QoS is allowed (according to the PCF configuration) and notifies the result to the TSCTSF.
If the PCF determines that the SMF needs updated policy information, the PCF issues a Npcf_SMPolicyControl_UpdateNotify request with updated policy information about the PDU Session as described in the PCF initiated SM Policy Association Modification procedure in clause 4.16.5.2.
If the PCF receives a subscription for the 5GS Bridge/Router information from the TSCTSF, if the PCF does not have the 5GS Bridge/Router information for the PDU Session, the PCF uses the PCF initiated SM Policy Association Modification procedure as described in clause 4.16.5.2 to subscribe for 5GS Bridge/Router information event from the SMF. Once the PCF has the 5GS Bridge/Router information, the PCF notifies the TSCTSF for the 5GS Bridge/Router information (including the UE-DS-TT Residence Time).
Step 4b.
The TSCTSF sends a Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Create response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the NEF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the TSCTSF sends the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Create response message directly to AF.
Step 5.
The NEF sends a Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the AF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
Step 6.
The NEF shall send a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Subscribe message to the PCF to subscribe to notifications of Resource allocation status and may subscribe to other events described in clause 6.1.3.18 of TS 23.503.
Step 6a.
The TSCTSF shall send a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Subscribe message to the PCF to subscribe to notifications of Resource allocation status and may subscribe to other events described in clause 6.1.3.18 of TS 23.503.
The TSCTSF that receives Capability for BAT adaptation or BAT Window in step 3a shall subscribe to notification on BAT offset via sending a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Subscribe request message to the PCF.
Step 7.
When the event condition is met, e.g. that the establishment of the transmission resources corresponding to the QoS update succeeded or failed, the PCF sends Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message to the NEF notifying about the event.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the PCF sends the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message directly to AF.
Step 7a.
When the event condition is met, e.g. that the establishment of the transmission resources corresponding to the QoS update succeeded or failed, the PCF sends Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message to the TSCTSF notifying about the event.
Step 7b.
The TSCTSF sends Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Notify message with the event reported by the PCF to the NEF.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the TSCTSF sends the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Notify message directly to AF.
Step 8.
The NEF sends Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Notify message with the event reported by the PCF to the AF.
4.15.6.6a AF session with required QoS update procedure |R16| p. 453
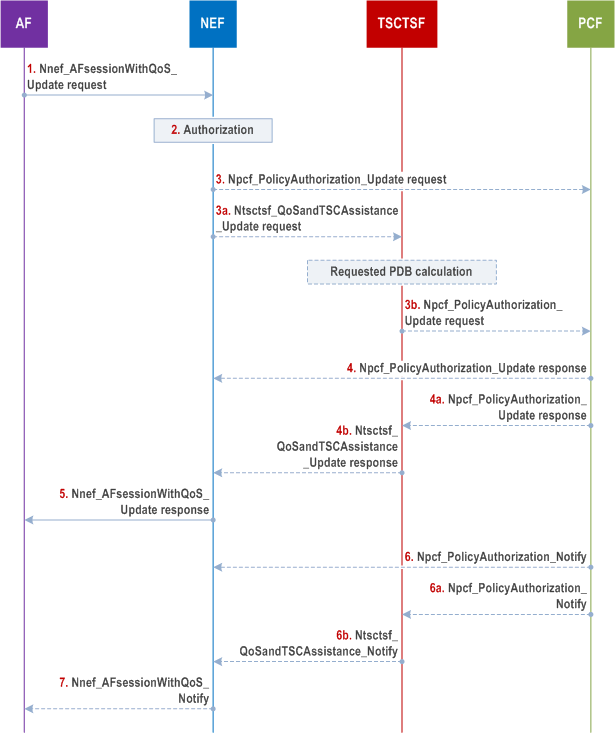
Step 1.
For an established AF session with required QoS, the AF may send a Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Update request message (AF Identifier, Transaction Reference ID, [Flow description information], [QoS Reference or individual QoS parameters], [Alternative Service Requirements (as described in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503)]) to NEF for updating the reserved resources. Optionally, Indication of ECN marking for L4S, Data Burst Size Marking Support Indication, Time to Next Burst Support Indication, PDU Set QoS Parameters (as described in clause 5.7.7 of TS 23.501) and Protocol Description (as described in clause 5.37.5, 5.37.8.3 and other (sub)clauses in clause 5.37 of TS 23.501) can be included in the AF request. For a Multi-modal service, the AF may provide/update Multi-modal Service Requirements information of the existing data flows as described in clause 6.1.3.27.3 of TS 23.503. Optionally, a period of time or a traffic volume for the requested QoS can be included in the AF request. The Transaction Reference ID provided in the AF session with required QoS update request message is set to the Transaction Reference ID that was assigned, by the NEF, to the Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create request message. The AF may, instead of a QoS Reference, provide one or more of the following individual QoS parameters: Requested 5GS Delay (optional), Requested Priority (optional), Requested Guaranteed Bitrate, Requested Maximum Bitrate, Maximum Burst Size and Requested Packet Error Rate. The AF may also provide an Averaging Window. Regardless whether the AF request is formulated using a QoS Reference or individual QoS parameters, the AF may also provide one or more of the following parameters that describe the traffic characteristics: flow direction, Burst Arrival Time at UE (uplink) or UPF (downlink), Periodicity, Time domain, Survival Time, Capability for BAT adaptation or BAT Window, Periodicity Range. The optional Alternative Service Requirements provided by the AF shall either contain QoS References or Requested Alternative QoS Parameter Set(s) in a prioritized order as specified in clause 6.1.3.22 of TS 23.503. Optionally, Packet Delay Variation requirements can be included in the AF request as described in clause 6.1.3.26 of TS 23.503.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the AF request of updating AF session with required QoS and may apply policies to control the overall amount of QoS authorized for the AF. If the authorisation is not granted, all steps (except step 5) are skipped and the NEF replies to the AF with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
The NEF shall contact the same NF type (i.e. TSCTSF or PCF) as with the initial Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create request during the establishment procedure in clause 4.15.6.6. If the NEF determined not to invoke the TSCTSF, then steps 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 are executed, otherwise, steps 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b, 5, 6a, 6b, 7 are executed. If the Nnef_AfsessionWithQoS_Update adds any parameters that would require the NEF to invoke TSCTSF while the NEF determined not to invoke the TSCTSF for the initial Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Create request, the NEF shall reject the Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Update request with a cause value indicating the reason of failure.
If the NEF does not invoke the TSCTSF, the NEF interacts with the PCF by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request and forwards received parameters to the PCF. Any optionally received period of time or traffic volume is mapped and forwarded as sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503).
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the AF uses the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request message to interact directly with PCF to update the reserving resources for an AF session.
Step 3a.
If the NEF decided to contact the TSCTSF when the session was established, the NEF forwards received parameters in the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Update request message to the TSCTSF. Any optionally received period of time or traffic volume is mapped and forwarded as sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.503).
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the AF uses the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Update request message to interact directly with TSCTSF to update the reserving resources for an AF session.
Step 3b.
The TSCTSF interacts with the PCF by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request and forwards the received parameters after executing the adjustment and mapping actions described in step 3b of clause 4.15.6.6.
Step 4.
The PCF processes the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request according to the actions described in step 4 of clause 4.15.6.6.
Step 4a.
The PCF processes the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request according to the actions described in step 4a of clause 4.15.6.6. If the PCF has received a request to unsubscribe for 5GS Bridge/Router information Notification, the PCF uses the PCF initiated SM Policy Association Modification procedure as described in clause 4.16.5.2 to unsubscribe for 5GS Bridge/Router information event from the SMF.
Step 4b.
The TSCTSF sends a Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Update response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the NEF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the TSCTSF sends the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Update response message directly to AF.
Step 5.
The NEF sends a Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Update response message (Transaction Reference ID, Result) to the AF. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
Step 6.
The PCF sends Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message to the NEF when the modification of the transmission resources corresponding to the QoS update succeeded or failed, or when an Alternative Service Requirement is being applied.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the PCF sends the Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message directly to AF.
Step 6a.
The PCF sends Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify message to the TSCTSF when the modification of the transmission resources corresponding to the QoS update succeeded or failed, or when an Alternative Service Requirement is being applied.
Step 6b.
The TSCTSF sends Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Notify message with the event reported by the PCF to the NEF.
If the AF is considered to be trusted by the operator, the TSCTSF sends the Ntsctsf_QoSandTSCAssistance_Notify message directly to the AF.
Step 7.
The NEF sends Nnef_AFsessionWithQoS_Notify message with the event reported by the PCF to the AF.