Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.15.9 Time Synchronization exposure
4.15.9.1 General
4.15.9.2 Exposure of UE availability for Time Synchronization service
4.15.9.3 Time Synchronization activation, modification and deactivation
4.15.9.3.1 General
4.15.9.3.2 Time synchronization service activation
4.15.9.3.3 Time synchronization service modification
4.15.9.3.4 Time synchronization service deactivation
...
...
4.15.9 Time Synchronization exposure |R17| p. 477
4.15.9.1 General p. 477
Time synchronization exposure allows an AF to configure time synchronization in 5GS. For (g)PTP operation, the Time synchronization service allows an AF to subscribe to the UE and 5GC capabilities and availability for time synchronization service (as described in clause 4.15.9.2), to configure the (g)PTP instance in 5GS as described in clause 4.15.9.3 and monitor service status as described in clause 4.15.9.5. For 5G access stratum based time distribution, the AF can influence the 5G access stratum time distribution as described in clause 4.15.9.4 and monitor service status as described in clause 4.15.9.5. The time synchronization exposure is provided by NEF that uses the service provided by TSCTSF. The AF that is part of operator's trust domain may invoke the services directly with TSCTSF and TSCTSF responds/notifies directly to the AF, accordingly.
4.15.9.2 Exposure of UE availability for Time Synchronization service p. 477
The procedure is used by the AF to subscribe to notifications and to explicitly cancel a previous subscription for UE availability for time synchronization service. Cancelling is done by sending Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsUnsubscribe request identifying the subscription to cancel with Subscription Correlation ID.
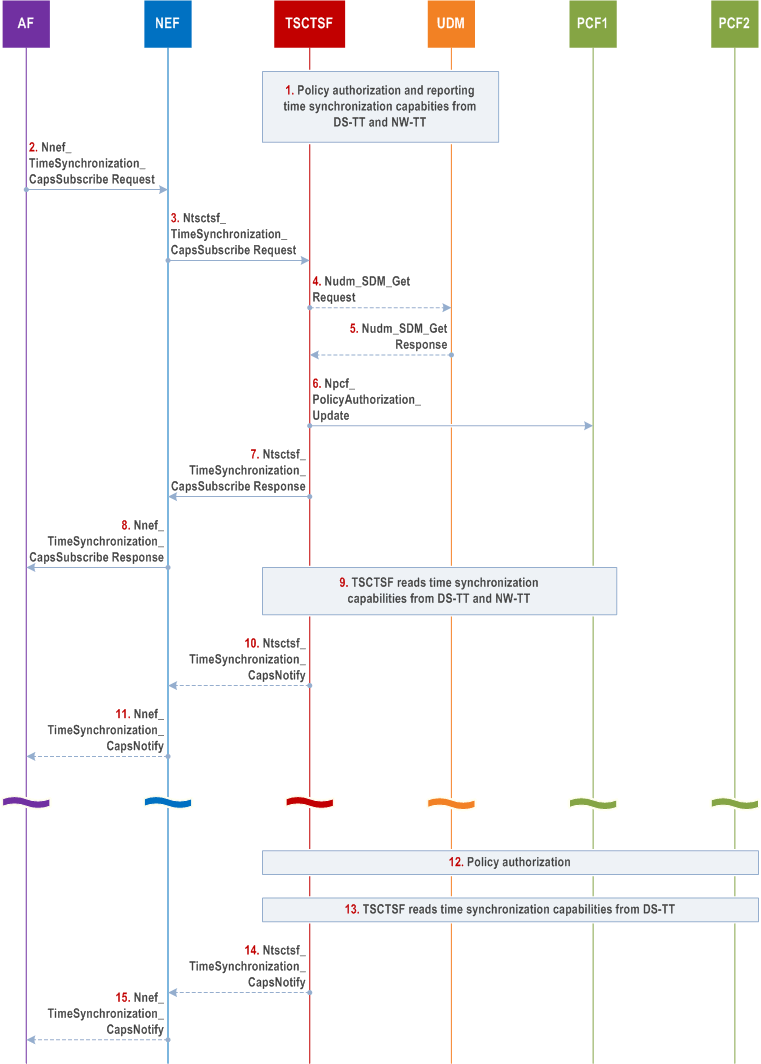
Step 1.
Upon PDU Session establishment, the PCF determines if the PDU Session is potentially impacted by time synchronization service (based on local configuration or 5GS Bridge/Router information event from SMF as described in SM Policy Association Establishment procedure in clause 4.16.4). In this case the PCF invokes Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify service operation to the TSCTSF discovered and selected as described in clause 6.3.24 of TS 23.501. The Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify service operation includes the UE address of the PDU Session and DNN/S-NSSAI.
The PCF registers to BSF as described in TS 23.503. TSCTSF invokes a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Create request message to the PCF and stores the DNN, S-NSSAI and IP address as received from PCF and SUPI as received from BSF and associates them with the AF-session.
If PMIC/UMIC information from the DS-TT or NW-TT is available at the PCF, the PCF reports it to the TSCTSF invoking Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Notify .
Step 2.
The AF subscribes to the UE availability for time synchronization service and provides the associated Notification Target Address of the AF by sending Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe request.
Report Type defines the type of reporting requested (e.g. one-time reporting, periodic reporting or event based reporting).
The request may include DNN and slicing information (S-NSSAI) and shall include an AF-Service-Identifier. If the DNN and S-NSSAI are omitted in the request, the NEF uses the AF-Service-Identifier to determine the target DNN and slicing information (S-NSSAI).
The Event Filter may include a list of UE identities (GPSIs) or Groups of UEs identified by an External Group Identifier that further define the subset of the target UEs. If the request does not include UE identities nor External Group Identifier, the request is targeted to any UE with a PDU Session using the DNN and S-NSSAI. The NEF forwards the GPSIs or the External Group Identifier to the TSCTSF by including them/it inside the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe request.
Additionally, the Event Filter may include one or more of the requested PTP instance type, requested transport protocol for PTP, or requested PTP Profile as described in Table 5.2.6.25.6-1.
When the NEF processes the AF request the AF-Service-Identifier may be used to authorize the AF request.
Depending on the AF-Service-Identifier and/or DNN/S-NSSAI, the NEF may reject the request if the list of UE identities or External Group Identifier is not included in the request.
To unsubscribe to the UE availability for time synchronization for a list of UE(s), the AF invokes Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsUnsubscribe service operation and provides the Subscription Correlation ID.
Step 3.
(In the case of Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe ): The NEF discovers the TSCTSF as described in clause 6.3.24 of TS 23.501. The NEF invokes the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe request service operation to the selected TSCTSF.
(In the case of Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsUnsubscribe ): The NEF uses the Subscription Correlation ID to determine the TSCTSF and interacts with the TSCTSF by triggering a Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsUnsubscribe request message.
The AF that is part of operator's trust domain may invoke the services directly with TSCTSF.
Step 4.
If the Event Filter includes GPSI(s), an External Group Identifier or an Internal Group Identifier, the TSCTSF uses the Nudm_SDM_Get request to retrieve the subscription information (SUPI(s)) from the UDM using each GPSI or the External Group Identifier as received from the NEF or an Internal Group Identifier as provided directly by the AF (in the case when the AF is within the operator's domain).
The TSCTSF requests the Time Synchronization Subscription data from the UDM. The TSCTSF may also use stored Time Synchronization Subscription data which it retrieved from the UDM when the UE established PDU session, see clause 4.28.3.1.
Step 5.
The UDM provides the Nudm_SDM_Get response containing SUPI that are mapped from each received GPSI or a list of SUPIs mapped from the External/Internal Group Identifier and identify UEs targeted by the AF request.
Step 6.
(in the case of Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe ): The TSCTSF uses the parameters received in step 3 and step 5 (i.e. DNN, S-NSSAI and the list of SUPIs if present) to find matching AF-session(s).
If the Time Synchronization Subscription data is available, the subscription data returned by the UDM includes the AF request authorization that indicates whether the AF is allowed to request (g)PTP-based time distribution for DNN/S-NSSAI. If the subscription data indicates that the AF is not allowed to request (g)PTP-based time synchronization, the AF-session is excluded from the list of matching AF-sessions.
For any such matching AF-session, the TSCTSF interacts with the PCF by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request message.
(in the case of Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsUnsubscribe ): The TSCTSF uses the Subscription Correlation ID to determine the AF sessions and interacts with the PCF(s) by triggering a Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Delete request message. Steps 10-15 are skipped.
Step 7.
TSCTSF acknowledges the execution of Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe to the requester that initiated the request. The acknowledgement contains a Subscription Correlation ID that the requester can use to cancel or modify the subscription.
Step 8.
NEF acknowledges the execution of Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe to the requester that initiated the request. The acknowledgement contains a Subscription Correlation ID that the AF can use to cancel or modify the subscription.
Step 9.
As part of Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update request, the TSCTSF uses the procedures as described in clause K.2.1 of TS 23.501 to determine the (g)PTP capabilities from the DS-TT. If the TSCTSF has not determined the (g)PTP capabilities from the NW-TT, the TSCTSF determines the capabilities using the procedures as described in clause K.2.1 of TS 23.501.
The TSCTSF composes the time synchronization capabilities for the DS-TT/UE(s) connected to the NW-TT based on the capability information received from the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT. If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe request include an Event Filter with one or more of the requested PTP instance type, requested transport protocol for PTP, or requested PTP Profile, the TSCTSF considers only the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT(s) with these capabilities as part of the time synchronization capability set that is reported to the NEF (or AF).
The TSCTSF maintains association between the user-plane Node ID, the time synchronization capabilities, the reference to the capabilities (as identified by the Subscription Correlation ID), the Event Filter (if available), the NEF or AF Notification Target Address and list of the AF sessions with PCFs with this user-plane Node ID. If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe request includes one or more Event Filter(s), the TSCTSF considers only the matching UE identities and the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT(s) with the matching capabilities to be included in the associated AF sessions.
Step 10.
The TSCTSF sends Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify (as described in clause 5.2.27.2.8) to the NEF. The message includes the time synchronization capabilities as composed in step 9. The message contains one or more user-plane Node ID(s) and a list of UE identities associated to each user-plane Node ID and time synchronization capabilities for each set of DS-TTs connected to given user-plane Node ID, as described in Table 5.2.6.25.8-1. The user-plane Node ID identifies the NW-TT to where the UE/DS-TT(s) are connected to.
Step 11.
The NEF sends Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify with Time Synchronization capability event (as described in Table 5.2.6.25.8-1) to the AF.
Step 12-13.
Upon PDU Session Establishment as defined clause 4.3.2.2.1, steps 1, 9, 10 and 11 are repeated for the new PDU Session.
Step 14.
If necessary, e.g. upon PDU Session establishment or release, the TSCTSF may update the time synchronization capabilities for the DS-TT/UE(s) connected to the NW-TT(s). The TSCTSF sends Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify with Time Synchronization capability event (as described in Table 5.2.6.25.8-1) containing the updated capabilities to the NEF.
Step 15.
The NEF sends Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify containing the updated capabilities to the AF.
4.15.9.3 Time Synchronization activation, modification and deactivation p. 480
4.15.9.3.1 General p. 480
This procedure can be used by the AF to activate, modify or deactivate the (g)PTP instances in 5GS.
The AF may activate the time synchronization service using the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate service operation. The service operation creates a time synchronization configuration based on the service parameters as indicated in the create request. The AF may update the time synchronization configuration using the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate service operation. The AF may deactivate the time synchronization service using the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete service operation, which deletes the corresponding time synchronization service configuration. The AF may subscribe to time synchronization status report by providing clock quality acceptance criteria via Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate service operation. The AF may receive time synchronization service status update via Nnef_TimeSynchronization_UpdateNotify service operation. 5GS may provide a time synchronization status report to the AF in case of a PTP port is activated or deactivated due to a detected failure, degradation, or improvement of the service.
The Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate and Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request may contain the parameters as described in Table 4.15.9.3-1.
| Time Synchronization Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| PTP instance type | Identifies the requested PTP instance type as described in clause 5.27.1.4 of TS 23.501. |
| Transport protocol | Identifies the requested transport protocol for PTP instance as described in clause 5.27.1.4 of TS 23.501. This is applicable for IEEE Std 1588 [76] Boundary Clock and Transparent Clock operation. |
| PTP Profile | Identifies the PTP profile for the PTP instance as requested by AF. |
| Grandmaster enabled | Indicates whether the AF requests the PTP instance in 5GS to be able to act as a grandmaster for PTP or gPTP (depending on the requested PTP instance type). This is applicable for IEEE Std 1588 [76] Boundary Clock or IEEE Std 802.1AS [75] operation. [optional] |
| Grandmaster priority | Indicates a priority used as defaultDS.priority1 when generating Announce message when 5GS acts as (g)PTP GM. Applicable only if the Grandmaster enabled = TRUE. If omitted, the default value as described in the PTP Profile is used. [optional] |
| Time Domain | (g)PTP domain of the PTP instance as defined in IEEE Std 1588 [76]. |
| Temporal Validity Condition | Indicates start-time and stop-time attributes that describe the time period when the time synchronization service for a PTP instance is active. [optional] |
| Spatial Validity Condition | Indicates a geographical area (e.g. a civic address or shapes) or a TA list in which time synchronization service is enabled (NOTE 1). [optional] |
| Time synchronization error budget | Indicates the time synchronization budget for the time synchronization service (as described in clause 5.27.1.9 of TS 23.501). [optional] |
| Clock quality detail level | For (g)PTP services, its value, if provided, shall be set to "acceptable/not acceptable indication" (NOTE 2). [optional] |
| Clock quality acceptance criteria | It indicates the acceptable criteria for the UE. It is defined based on the attributes specified in Table 5.27.1.12-1 of TS 23.501. The parameter shall be included if the "clock quality detail level" is present. The parameter shall be included if the "clock quality detail level" is present. [conditional] |
| For each PTP port in the PTP instance | |
| Either UE identity (for a DS-TT port), or "N6 interface" indication | Identifies the UE/DS-TT which the parameters below apply. "N6 interface" indicates that the parameters below apply to the N6 interface. If the "PTP port" needs to be identified, this field refers to the UE identity (GPSI or SUPI). If the N6 termination needs to be identified, then this field indicates "N6 interface" flag, instead of SUPI or GPSI. |
| PTP enabled | TRUE/FALSE. This is used to set the portDS.portEnable. If omitted, the default value as described in the PTP Profile is used. [optional] |
| Log Sync Interval | Specifies the mean time interval between successive Sync messages. This is applicable for IEEE Std 1588 [76] Boundary Clock or IEEE Std 802.1AS [75] operation. If omitted, the default value as described in the PTP Profile is used. [optional] |
| Use management settable Log Sync Interval | TRUE/FALSE. This is applicable if the PTP Profile is IEEE Std 802.1AS [75]. When set to FALSE, the Log Sync Interval is used to set the initialLogSyncInterval as described in IEEE Std 802.1AS [75]. When set to TRUE, the Log Sync Interval is used to set the mgtSettableLogSyncInterval as described in IEEE Std 802.1AS [75]. If omitted, the default value as described in the IEEE Std 802.1AS [75] is used. [optional] |
| Log Announce Interval | Specifies the mean time interval between successive Announce messages. This is applicable for IEEE Std 1588 [76] Boundary Clock or IEEE Std 802.1AS [75] operation. If omitted, the default value as described in the PTP Profile is used. [optional] |
| Use management settable Log Announce Interval | TRUE/FALSE. This is applicable if the PTP Profile is IEEE Std 802.1AS [75]. When set to FALSE, the Log Announce Interval is used to set the initialLogAnnounceInterval as described in IEEE 802.1AS. When set to TRUE, the Log Announce Interval is used to set the mgtSettableLogAnnounceInterval as described in IEEE Std 802.1AS [75]. If omitted, the default value as described in the IEEE Std 802.1AS [75] is used. [optional] |
|
NOTE 1:
A geographical area requested by an AF includes at least one tracking area (TA), i.e. the granularity is restricted to a TA level in this release of the specifications.
NOTE 2:
UE/DS-TT retrieves detailed information about (g)PTP services status from Announce messages, i.e. setting Clock Quality Detail Level to "Acceptable/Not Acceptable" indication can be used to specify Clock Quality Acceptance Criteria for Timing Synchronization Status (TSS) reporting towards the AF.
|
|
The AF may use Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsSubscribe service operation as described in clause 4.15.9.2 to learn the UE capabilities for time synchronization service. The Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify service operation indicates the list of UE identities, User-plane Node ID and the Subscription Correlation ID. The AF can use the Subscription Correlation ID and the user-plane node ID received in the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_CapsNotify service operation as a target of the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request. The NEF uses the Subscription Correlation ID and user-plane node ID to determine the list of UEs and list of AF-sessions to which the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate service operation is targeted to.
4.15.9.3.2 Time synchronization service activation p. 485
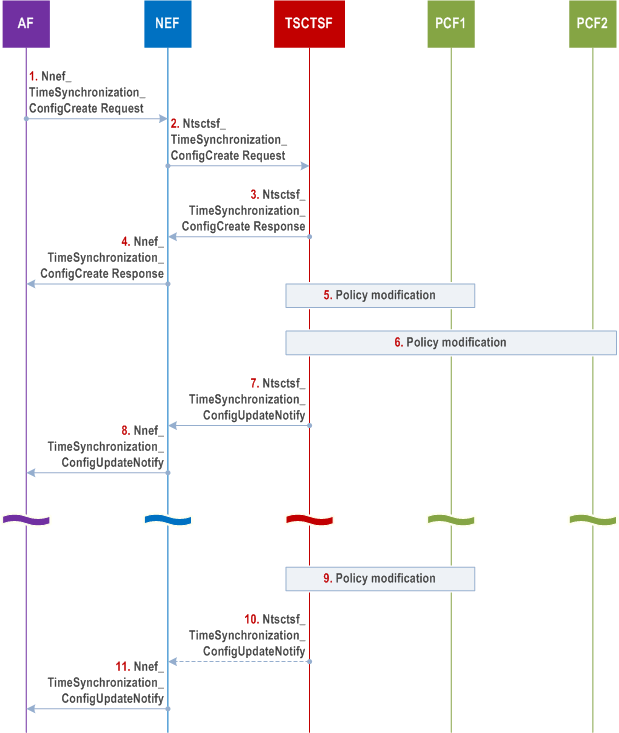
Step 1.
The AF creates a time synchronization service configuration for a PTP instance by invoking Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate service operation. The request includes the parameters as described in Table 4.15.9.3-1. The request contains a Subscription Correlation ID and user-plane node ID as a reference to the target of the UEs and AF-sessions.
The create request creates also a subscription for the changes in the time synchronization service configuration. The AF may subscribe to receiving network time synchronization status report(s) as specified in clause 4.15.9.5.1.
Step 2.
The NEF authorizes the request. After successful authorization, the NEF invokes the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate service operation with the corresponding TSCTSF, with the parameters as received from the AF.
If the request includes a spatial validity condition and if the AF uses a geographical area as a spatial validity condition, the NEF transforms this information into 3GPP identifiers (e.g. TAI(s)) based on pre-configuration.
The AF that is part of operator's trust domain may invoke the services directly with TSCTSF.
If the request includes a spatial validity condition and if the AF is within the operator's domain, the spatial validity condition shall comprise of a list of TA(s).
Step 3.
TSCTSF checks whether the AF requested parameters comply with the stored Time Synchronization Subscription data as defined in clause 5.27.1.11 of TS 23.501, for that, the TSCTSF retrieves the Time Synchronization Subscription data from the UDM (as defined in clause 4.15.9.2). The TSCTSF determines the Time Synchronization Coverage Area and responds with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate response as specified in clause 5.27.1.11 of TS 23.501. The Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate response includes a PTP instance reference.
Step 4.
The NEF responds with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate response, including a reference to the time synchronization service configuration (PTP instance reference).
Step 5-6.
The TSCTSF uses the Subscription Correlation ID and user-plane node ID in Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate to determine the target UEs and corresponding AF-sessions. The TSCTSF uses the parameters (e.g. requested PTP instance type, transport protocol and PTP profile) in the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request to determine suitable DS-TT(s) and corresponding AF-sessions among all AF-sessions that are associated with the Subscription Correlation ID and user-plane node ID in the request.
The TSCTSF maintains association between list of suitable AF-sessions, corresponding time synchronization configuration, the PTP instance reference in 5GS, PTP instance references in each involved DS-TT and NW-TT and Subscription Correlation ID and user-plane node ID as given in step 1.
The TSCTSF uses the procedures described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501 to configure and initialize the PTP instance in the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT. The TSCTSF constructs a PMIC to each DS-TT/UE to activate the time synchronization service in DS-TT in respect to the service parameters in the request in step 2. The TSCTSF constructs PMIC(s) and UMIC to NW-TT to activate the time synchronization service in NW-TT in respect to the service parameters in the request in step 2.
Upon reception of responses from each DS-TT and NW-TT, the TSCTSF determines the state of the time synchronization configuration.
The TSCTSF constructs a PMIC to each DS-TT/UE to subscribe for the port management information changes in the DS-TT. The TSCTSF constructs PMIC(s) and UMIC to NW-TT to subscribe for the port management and user-plane management information changes in NW-TT. The TSCTSF retrieves the PMIC(s) and UMIC via means of Npcf_PolicyAuthorization service operations.
The create request creates also a subscription for notifications for the changes in the time synchronization service configuration. If the AF provided clock quality acceptance criteria in step 1, the TSCTSF subscribes for notifications for changes in the NG-RAN and UPF/NW-TT timing synchronization status, as described in clause 4.15.9.5.1:
TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request contains a temporal validity condition with a start-time and/or the stop-time that is in the future, the TSCTSF maintains the start-time and stop-time for the time synchronization service for the corresponding time synchronization configuration. If the start-time is in the past, the TSCTSF treats the request as if the time synchronization service was activated immediately. When the start-time is reached, the TSCTSF proceeds as described in this step above. When the stop-time is reached for active time synchronization service configuration, the TSCTSF proceeds as Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete was received as described in clause 4.15.9.3.4.
If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request contains a spatial validity condition, then the TSCTSF performs the following operations:
Step 7.
- To determine the impacted UEs due to a timing synchronization status update reported by the NG-RAN, the TSCTSF follows the operation described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501.
- To determine the impacted UEs due to a timing synchronization status update reported by the UPF/NW-TT, the TSCTSF verifies if the UPF/NW-TT is configured to send (g)PTP messages to the UEs/DS-TTs.
-
TSCTSF determines whether the TSCTSF has subscribed for the UE presence in Area of Interest composed by the TA(s) in the Time Synchronization Coverage Area. If not, the TSCTSF may either discover the AMF(s) serving the TA(s) comprising the Time Synchronization Coverage Area or discover the serving AMF(s) for each UE identified by a GPSI/SUPI as described in clause 5.27.1.10 of TS 23.501.
Then the TSCTSF subscribes to the AMF(s) to receive notifications about the UE presence in Area of Interest using Namf_
EventExposure operation with the corresponding event filters as described in clause 5.2.2.3 and in clause 5.3.4.4 of TS 23.501. The subscribed area of interest may be the same as the Time Synchronization Coverage Area or may be a subset of the Time Synchronization Coverage Area (e.g. a list of TAs) based on the latest known UE location. -
In order to ensure that a TAI list specifying the AoI for the AMF is aligned with UE's Registration Area (RA), the following steps shall be performed:
- When invoking the subscription with the AMF(s), the TSCTSF may provide an indication, a new Parameter Type = "Adjust AoI based on RA", that the AMF may adjust the received AoI depending on UE's RA.
-
After receiving the Namf_
EventExposure_ request from the TSCTSF with the Parameter Type = "Adjust AoI based on RA" and specified AoI, the AMF compares TAs from the AoI with the UE's Registration Area (RA). If the AoI includes one or more TA(s) that are part of UE's current RA, the AMF reports the UE is inside the Area Of Interest, otherwise the AMF reports the UE is outside the Area Of Interest, as described in Annex D.Subscribe -
The AMF notifies the TSCTSF about the UE's presence in the AoI using the Namf_
EventExposure_ service operation.Notify
-
Based on the notification from the AMF and the Time Synchronization Coverage Area determined in step 3, the TSCTSF determines whether to activate time synchronization service for this UE:
- If the UE location is within the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, the TSCTSF determines to activate time synchronization service for the UE/DS-TT creating the PTP port in DS-TT and adding it to the PTP instance. The TSCTSF uses the procedures described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501 to configure and initialize the PTP instance in the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT.
- If the UE location is outside the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, the TSCTSF determines not to activate time synchronization service and not to create a PTP port in a DS-TT.
The TSCTSF notifies the NEF (or AF) with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the PTP instance reference and the current state of the time synchronization service configuration.
If TSCTSF received spatial validity condition as part of the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request, the TSCTSF notifies the NEF (or AF) with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, whenever the UE moves in or out of the Area of Interest. The notification contains the PTP instance reference and the current state of the time synchronization service configuration.
Step 8.
The NEF notifies the AF with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the PTP instance reference and the current state of the time synchronization service configuration.
Step 9.
Upon a change in the PTP instance in the DS-TT or NW-TT, the DS-TT or NW-TT report the change via PMIC or UMIC to the TSCTSF as described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501.
Upon PDU Session release indication from a PCF, the TSCTSF removes the corresponding AF-session from the list of AF-sessions associated with the time synchronization configuration. The TSCTSF uses the procedure in clause 4.15.9.4 to remove the 5G access stratum time distribution parameters for the UE that is removed from the impacted PTP instance.
Upon PDU Session Establishment as defined clause 4.3.2.2.1, steps 10-13 in Figure 4.15.9.2-1 are repeated for the new PDU Session and the TSCTSF may notify the NEF (or AF) for the Time Synchronization capability event, optionally with the updated time synchronization capabilities, as described in step 12 in Figure 4.15.9.2-1.
If TSCTSF received spatial validity condition as part of the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigCreate request, upon a change in the UE presence in Area of Interest, the TSCTSF determines if the spatial validity condition shall trigger an activation or deactivation of the time synchronization service:
Step 10.
-
If the UE has moved outside the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, then the TSCTSF temporarily removes the UE/DS-TT port from the PTP instance:
- If the DS-TT is configured to send Sync, Follow_Up and Announce messages for the related PTP instance, then TSCTSF deactivates the Grandmaster functionality in the DS-TT using PMIC (see also clause K.2.2.4 of TS 23.501).
- If NW-TT is configured to send Sync, Follow_Up and Announce messages on behalf of the DS-TT, then TSCTSF deactivates the Grandmaster functionality on behalf of the DS-TT in NW-TT using UMIC (see also clause K.2.2.4 of TS 23.501).
- If the UE has moved inside the Time Synchronization Coverage Area, then the TSCTSF adds the DS-TT PTP port to the PTP instance and also (re-)activates the Grandmaster functionality (described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501).
- If the clock quality acceptance criteria can still be met, then TSCTSF may update the clockQuality information sent in Announce messages for the PTP instance using PMIC/UMIC reporting. The handling of Announce messages follows existing procedures as described in TS 23.501.
- If the clock quality acceptance criteria cannot be met or can be met again, then TSCTSF informs the AF about the acceptance criteria result (e.g. acceptable/not acceptable).
The TSCTSF updates the state of the time synchronization configuration and may notify the NEF (or AF) with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the PTP instance reference and the updated state of the time synchronization service configuration, including whether there was a change in the UE's presence in the Time Synchronization Coverage Area (in cases when the AF has requested the service for a specific spatial validity condition), or the clock quality acceptance criteria result (in cases when the AF has requested the service with a clock quality acceptance criteria condition).
Step 11.
The NEF notifies the AF with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the reference to the time synchronization service configuration (PTP instance reference) and the updated state of the time synchronization service configuration.
If the AF receives a clock quality acceptance criteria result, the AF may update the configuration of the PTP instance by updating the PTP instance sending a Nnef/Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate or Nnef/Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete request, as described in clauses 4.15.9.3.3 and 4.15.9.3.4.
4.15.9.3.3 Time synchronization service modification p. 489
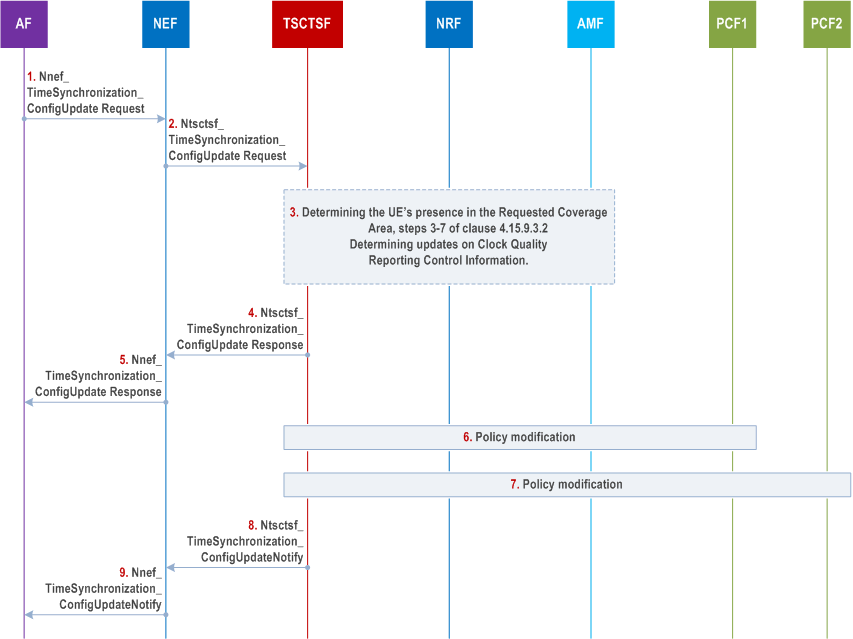
Step 1.
To update an existing time synchronization service configuration of the PTP instance, the AF invokes a Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate service operation providing the corresponding PTP instance reference.
Step 2.
The NEF invokes the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate service operation with the corresponding TSCTSF.
The AF that is part of the operator's trust domain may invoke the services directly with the TSCTSF.
Step 3.
The TSCTSF checks whether the AF requested parameters in the update request comply with the stored Time Synchronization Subscription data as defined in clause 5.27.1.11 of TS 23.501, for that, the TSCTSF retrieves the Time Synchronization Subscription data from UDM as defined in clause 4.15.9.2. If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request includes or updates the Spatial validity condition and the Spatial validity condition is allowed per the subscription, the TSCTSF determines the UE's presence in the updated Spatial validity condition as specified in steps 3-7 of the time synchronization activation procedure in clause 4.15.9.3.2.
If the AF updates the clock quality acceptance criteria in step 1, the TSCTSF determines the clock acceptance criteria upon a time synchronization failure/degradation/improvement as specified in step 9 of the time synchronization activation procedure in clause 4.15.9.3.2. If AF provides clock quality acceptance criteria in step 1, and it was not available when the service was activated, the TSCTSF subscribes for notifications for changes in the NG-RAN and UPF/NW-TT timing synchronization status, as described in clause 4.15.9.5.1:
Step 4.
- To determine the impacted UEs due to a timing synchronization status update reported by the NG-RAN, the TSCTSF follows the operation described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501.
- To determine the impacted UEs due to a timing synchronization status update reported by the UPF/NW-TT, the TSCTSF verifies if the UPF/NW-TT is configured to send (g)PTP messages to the UEs/DS-TTs.
The TSCTSF responds with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate response where the AF may include an indication that the UE(s) are (not) present in the Requested Coverage Area (in cases when the AF has requested the service for a specific area).
Step 5.
The NEF responds with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate .
Step 6-7.
The TSCTSF uses the PTP instance reference included in the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request to identify the time synchronization service configuration and the corresponding AF sessions.
If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request includes updated service parameters for the PTP instance and if the corresponding DS-TT(s) and NW-TT are suitable with the parameters (e.g. requested PTP instance type, transport protocol and PTP profile), the TSCTSF uses the procedures described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501 to update the PTP instance(s) in the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT.
If the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request includes one or more UE identities to be added to the PTP instance, if the corresponding DS-TT(s) are suitable with the parameters (e.g. requested PTP instance type, transport protocol and PTP profile) in the time synchronization service configuration as identified by the PTP instance reference in the request:
TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate request includes one or more UE identities to be removed to the PTP instance, the TSCTSF removes the corresponding AF-sessions from the list of AF-sessions associated with the time synchronization configuration. The TSCTSF uses the procedure in clause 4.15.9.4 to remove the 5G access stratum time distribution parameters for the UEs that are removed from the impacted PTP instance.
Step 8.
- the TSCTSF adds the suitable AF-sessions to the list of AF-sessions that are associated with the time synchronization service configuration; and
- the TSCTSF uses the procedures described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501 to initialize and activate the PTP instance(s) in the corresponding DS-TT(s).
- the TSCTSF uses the procedure in clause 4.15.9.4 to modify or activate the 5G access stratum time distribution for the UEs that are added to the impacted PTP instance.
The TSCTSF notifies the NEF (or AF) with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the PTP instance reference and the current state of the time synchronization service configuration, including and whether there was a change in the UE's presence in the Spatial validity condition (in cases when the AF has requested the service for a specific area) and/or whether there was a change in network's timing synchronization status as described in clause 5.27.1.12 of TS 23.501 including the clock quality acceptance criteria result.
Step 9.
The NEF notifies the AF with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify service operation, containing the PTP instance reference, the current state of the time synchronization service configuration, network's time synchronization status and clock quality acceptance criteria result, if provided by Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdateNotify . Based on the notification, the AF decides whether to modify the service configured for the UE of a PTP instance using Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigUpdate service, or whether to deactivate it using Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete service.
4.15.9.3.4 Time synchronization service deactivation p. 491
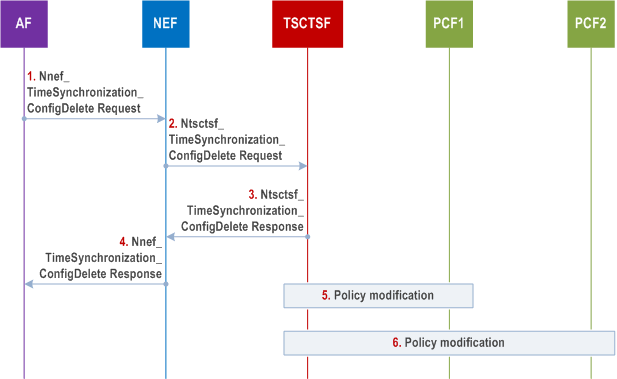
Step 1.
To remove an existing time synchronization service configuration of the PTP instance, the AF invokes a Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete service operation providing the corresponding PTP instance reference.
Step 2.
The NEF invokes the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete service operation with the corresponding TSCTSF.
The AF that is part of operator's trust domain may invoke the services directly with TSCTSF.
The TSCTSF may also invoke the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete service operation when it determines (based on notifications from the AMF(s), see steps 3-7 of clause 4.15.9.3.2) that the UE(s) are outside the Spatial validity condition.
Step 3.
The TSCTSF responds with the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete response.
Step 4.
The NEF responds with the Nnef_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete response.
Step 5-6.
The TSCTSF uses the PTP instance reference included in the Ntsctsf_TimeSynchronization_ConfigDelete request to identify the time synchronization service configuration and the corresponding AF sessions. The TSCTSF uses the procedures described in clause K.2.2 of TS 23.501 to disable the corresponding PTP instance(s) in the DS-TT(s) and NW-TT. The TSCTSF deletes the time synchronization service configuration for the respective PTP instance.
The TSCTSF uses the procedure in clause 4.15.9.4 to deactivate the 5G access stratum time distribution for the UEs that are part of the impacted PTP instance.