Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
5.18 Network Sharing
5.18.1 General concepts
5.18.2 Broadcast system information for network sharing
5.18.2a PLMN list and SNPN list handling for network sharing
5.18.3 Network selection by the UE
5.18.4 Network selection by the network
5.18.5 Network Sharing and Network Slicing
...
...
5.18 Network Sharing p. 345
5.18.1 General concepts p. 345
A network sharing architecture shall allow multiple participating operators to share resources of a single shared network according to agreed allocation schemes. The shared network includes a radio access network. The shared resources include radio resources.
The shared network operator allocates shared resources to the participating operators based on their planned and current needs and according to service level agreements.
In this Release of the specification, the 5G Multi-Operator Core Network (5G MOCN) network sharing architecture, in which only the RAN is shared in 5G System, is supported. The 5G System may also support Indirect Network Sharing deployment between hosting operator (i.e. shared network operator) and participating operator (see clause 6.21 of TS 22.261, Figure 5.18.1-2 and Annex R), in which the RAN is shared. The communication between the shared RAN and the core network of the participating operator is routed through the core network of the hosting operator that connects to the shared RAN.
5G MOCN for 5G System, including UE, RAN and AMF, shall support operators' ability to use more than one PLMN ID (i.e. with same or different country code (MCC) some of which is specified in TS 23.122 and different network codes (MNC)) or combinations of PLMN ID and NID. 5G MOCN supports NG-RAN Sharing with or without multiple Cell Identity broadcast as described in TS 38.300. Indirect Network Sharing for 5G system, including UE, shared RAN and CP NFs of hosting operator, shall support each participating operator to use more than one PLMN ID.
For Indirect Network Sharing, the shared RAN broadcasts multiple PLMN IDs, including the PLMN ID which represents the hosting operator and the PLMN IDs which represent participating operators. Multiple PLMN IDs are supported by the serving AMF (i.e. the AMF in the core network of the hosting operator). A UE from a participating operator can select the PLMN ID representing the participating operator in the shared RAN area based on existing procedures specified in TS 23.122. The serving AMF selects core network functions in the PLMN of the participating operator for the UE, based on home routed roaming architecture principle as specified in clause 4.2.4. In addition, the serving AMF selects the SMF of participating operator possibly considering UE location information and also selects a V-SMF in its own network during the PDU session establishment procedure. The serving PLMN ID used in the procedures is determined as follows:
- For interaction between the Network Functions in the hosting operator network and the participating operator network (e.g. AUSF, UDM), the NF of hosting operator network sets the serving PLMN ID to the selected PLMN ID. This includes the cases when the interaction is via another NF (e.g. V-PCF for UE policy, V-SMF) in the hosting operator network.
- For interactions between the Network Functions only in the hosting operator network (e.g. V-PCF for AM policy), the NF of hosting operator network sets the serving PLMN ID to the PLMN ID of the hosting operator.
- one or multiple SNPNs;
- one or multiple PNI-NPNs (with CAG); or
- one or multiple PLMNs only.
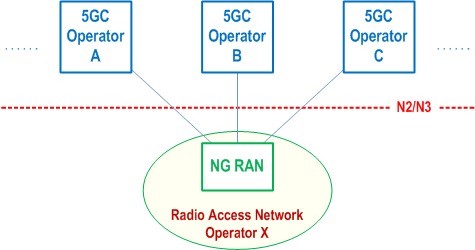
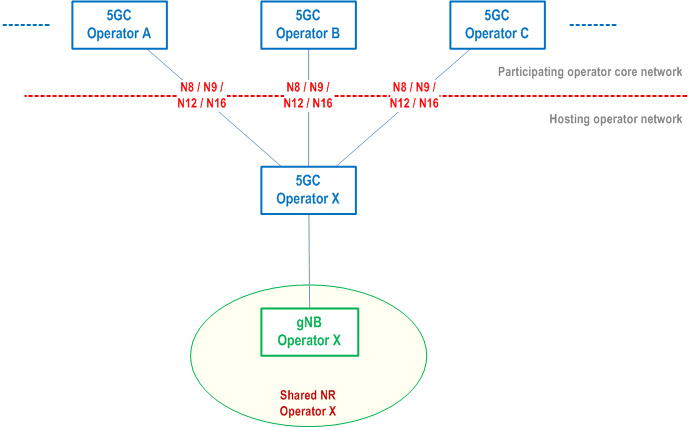
5.18.2 Broadcast system information for network sharing p. 347
If a shared NG-RAN is configured to indicate available networks (PLMNs and/or SNPNs) for selection by UEs, each cell in the shared radio access network shall in the broadcast system information include available core network operators in the shared network, including the PLMN IDs which represent the participating operators in case of Indirect Network Sharing as specified in clause 5.18.1.
The Broadcast System Information broadcasts a set of PLMN IDs and/or PLMN IDs and NIDs and one or more additional set of parameters per PLMN e.g. cell-ID, Tracking Areas, CAG Identifiers. All 5G System capable UEs that connect to NG-RAN support reception of multiple PLMN IDs and per PLMN specific parameters. All SNPN-enabled UEs support reception of multiple combinations of PLMN ID and NID and SNPN-specific parameters.
The available core network operators (PLMNs and/or SNPNs) shall be the same for all cells of a Tracking Area in a shared NG-RAN network.
UEs not set to operate in SNPN access mode decode the broadcast system information and take the information concerning available PLMN IDs into account in PLMN and cell (re-)selection procedures. UEs set to operate in SNPN access mode decode the broadcast system information and take the information concerning available PLMN IDs and NIDs into account in network and cell (re-)selection procedures. Broadcast system information is specified in TS 38.331 for NR, TS 36.331 for E-UTRA and related UE access stratum idle mode procedures in TS 38.304 for NR and TS 36.304 for E-UTRA.
5.18.2a PLMN list and SNPN list handling for network sharing p. 347
The AMF prepares lists of PLMN IDs or SNPN IDs suitable as target PLMNs or target SNPNs for use at idle mode cell (re)selection and for use at handover and RRC Connection Release with redirection. The AMF:
- provides the UE with the list of PLMNs or list of SNPNs that the UE shall consider as Equivalent to the serving PLMN or the serving SNPN (see TS 23.122); and
- provides the NG-RAN with a prioritised list of permitted PLMNs or a prioritized list of permitted SNPNs. When prioritising these PLMNs or SNPNs, the AMF may consider the following information: HPLMN of the UE or the subscribed SNPN of the UE, the serving PLMN or the serving SNPN, a preferred target PLMN (e.g. based on last used EPS PLMN) or a preferred target SNPN, or the policies of the operator(s).
5.18.3 Network selection by the UE p. 348
A UE that has a subscription to one of the sharing core network operators shall be able to select this core network operator while within the coverage area of the shared network and to receive subscribed services from that core network operator.
Each cell in shared NG-RAN shall in the broadcast system information include the PLMN IDs concerning available core network operators in the shared network.
When a UE performs an Initial Registration to a network, one of available PLMNs shall be selected to serve the UE. UE uses all the received broadcast PLMN IDs in its PLMN (re)selection processes which is specified in TS 23.122. UE shall inform the NG-RAN of the selected PLMN so that the NG-RAN can route correctly. The NG-RAN shall inform the core network of the selected PLMN.
In the case of Indirect Network Sharing, in this Release of the specifications, if hosting operator's network identifies that a UE is not from a participating operator when the UE selects a PLMN ID representing the participating operator, then the hosting operator network rejects the UE with an existing cause value during the registration procedure.
As per any network, after Initial Registration to the shared network and while remaining served by the shared network, the network selection procedures specified in TS 23.122 may cause the UE to perform a reselection of another available PLMN.
UE uses all of the received broadcast PLMN IDs in its cell and PLMN (re)selection processes.
5.18.4 Network selection by the network p. 348
The NG-RAN uses the selected PLMN/SNPN (provided by the UE at RRC establishment, or, provided by the AMF/source NG-RAN at N2/Xn handover) to select target cells for future handovers (and radio resources in general) appropriately. The network should not move the UE to another available PLMN/SNPN, e.g. by handover, as long as the selected PLMN/SNPN is available to serve the UE's location.
In the case of handover or network controlled release to a PLMN in a shared network:
- When multiple PLMN IDs are broadcasted in a cell selected by NG-RAN, NG-RAN shall select a target PLMN, taking into account the prioritized list of PLMN IDs provided via Mobility Restriction List from AMF.
- For Xn based HO procedure, Source NG-RAN indicates the selected PLMN ID to the target NG-RAN, see TS 38.300.
- For N2 based HO procedure, the NG-RAN indicates a selected PLMN ID to the AMF as part of the TAI sent in the HO required message. Source AMF uses the TAI information supplied by the source NG-RAN to select the target AMF/MME. The source AMF should forward the selected PLMN ID to the target AMF/MME. The target AMF/MME indicates the selected PLMN ID to the target NG-RAN/eNB so that the target NG-RAN/eNB can select target cells for future handover appropriately.
- For RRC connection release with redirection to E-UTRAN procedure, NG-RAN decides the target network by using PLMN information as defined in the first bullet.
- When multiple SNPN IDs are broadcasted in a cell selected by NG-RAN, NG-RAN shall select a target SNPN, taking into account the prioritized list of SNPN IDs provided via Mobility Restriction List from AMF.
- For Xn based HO procedure, Source NG-RAN indicates the selected SNPN ID to the target NG-RAN, see TS 38.300.
- For N2 based HO procedure, the NG-RAN indicates a selected SNPN ID to the AMF together with the TAI sent in the HO required message. Source AMF uses the selected SNPN ID together with the TAI information supplied by the source NG-RAN to select the target AMF. The source AMF should forward the selected SNPN ID to the target AMF. The target AMF indicates the selected SNPN ID to the target NG-RAN so that the target NG-RAN can select target cells for future handover appropriately.
5.18.5 Network Sharing and Network Slicing p. 349
As defined in clause 5.15.1, a Network Slice is defined within a PLMN or SNPN. Network sharing is performed among different PLMNs and/or SNPNs.
In the case of 5G MOCN, each PLMN or SNPN sharing the NG-RAN defines and supports its PLMN- or SNPN- specific set of slices that are supported by the common NG-RAN.
In the case of Indirect Network Sharing, the differences of Network Slicing handling is performed as the follows:
-
If, in an Indirect Network Sharing area, the selected PLMN ID which is broadcasted by shared RAN is the HPLMN ID or EHPLMN ID (which is not derived from UE's SUPI) of the UE, from the network side, the network slicing handling shall be performed as defined in clause 5.15.4 and clause 5.15.6. The changes compared to baseline operations are as follows:
- During Registration procedure, the UE includes S-NSSAI(s) of participating operator in the NAS Registration Request messages as described in TS 24.501. After receiving the Registration Request including the above information, the serving AMF determines the corresponding S-NSSAIs of hosting operator based on the Subscribed S-NSSAIs and slice mapping information from the HPLMN S-NSSAI(s) to the S-NSSAI(s) of the hosting operator locally or the slice mapping information received from the NSSF of hosting operator's network. The serving AMF further checks whether the corresponding S-NSSAIs of hosting operator are supported by the shared RAN. If none of the corresponding S-NSSAIs of hosting operator is supported, the serving AMF rejects the Registration Request. Otherwise the serving AMF continues the Registration procedure and sends to the UE Allowed NSSAI, Partially Allowed NSSAI, Rejected S-NSSAIs and Configured NSSAI only containing the S-NSSAI(s) of participating operator, i.e. HPLMN or EHPLMN S-NSSAI(s) without mapping information. The serving AMF creates a list of S-NSSAIs of the hosting operator corresponding to the S-NSSAIs included in the Allowed NSSAI sent to the UE and includes these S-NSSAIs in the Allowed NSSAI in the signalling to the shared RAN and to the PCF during the AM policy association establishment. The UE Context in the serving AMF shall retain the slice mapping information. The above AMF functionality is applied also during UE Configuration Update procedure.
- During PDU Session Establishment procedure, the UE includes the S-NSSAI(s) of participating operator in the PDU Session Establishment Request as described in TS 24.501. After receiving the S-NSSAI of participating operator from UE, the serving AMF uses the slice mapping information stored in the UE Context to determine the S-NSSAI of hosting operator (i.e. VPLMN S-NSSAI) to be used as "the S-NSSAI belonging to the Allowed NSSAI" as defined in clause 5.15.6. The serving AMF sends the serving PLMN ID (i.e. the selected PLMN ID representing the participating operator), VPLMN S-NSSAI (i.e. the corresponding S-NSSAI of the hosting operator) and HPLMN S-NSSAI to the V-SMF. The V-SMF can identify the Indirect Network Sharing case based on the serving PLMN ID and then it sends the HPLMN S-NSSAI in the PDU Session Establishment Accept message to the UE and uses the VPLMN S-NSSAI for the user plane handling (NG-RAN, V-UPF) in hosting operator's network.
- For other cases, i.e. the broadcast PLMN ID which represents the participating operator is different from HPLMN ID and EHPLMN IDs of UE, the network slicing handling including UE and network shall comply with the roaming case as defined in clause 5.15.6. The applied S-NSSAI values for the PLMN ID selected by UE (i.e. the broadcast PLMN ID) are the S-NSSAI values of hosting operator.