Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.11.1.2.2 EPS to 5GS handover using N26 interface p. 288
4.11.1.2.2.1 General p. 288
N26 interface is used to provide seamless session continuity for single registration mode.
The procedure involves a handover to 5GS and setup of QoS Flows in 5GS.
In the home routed roaming case, the PGW-C+ SMF in the HPLMN always receives the PDU Session ID from UE and provides PDN Connection associated 5G QoS parameter(s) and S-NSSAI to the UE. This also applies in the case that the HPLMN operates the interworking procedure without N26.
In the case of handover to a shared 5GS network, the source E-UTRAN determines a PLMN to be used in the target network as specified by clause 5.2a of TS 23.251 for eNodeB functions. A supporting MME may provide the AMF via N26 with an indication that source EPS PLMN is a preferred PLMN when that PLMN is available at later change of the UE to an EPS shared network.
If the PDN Type of a PDN Connection in EPS is non-IP and is locally associated in UE and SMF to PDU Session Type Ethernet or Unstructured, the PDU Session Type in 5GS shall be set to Ethernet or Unstructured respectively.
In order to support the E-UTRAN NTN enhancements defined in TS 36.300, for handover from EPS to 5GS, the following applies related to handling of UE's radio capabilities:
- If the target NG-RAN node knows (e.g. by configuration) that the UE's E-UTRA radio capabilities applicable to the target NG-RAN node may be different to the E-UTRA radio capabilities stored in the source eNodeB (e.g. for handover from an eNodeB that supports the NTN enhancements as defined in TS 36.300), then the target NG-RAN node shall trigger retrieval of the E-UTRA radio capability information again from the UE. In order to support the E-UTRAN NTN enhancements defined in TS 36.300, for handover from 5GS to EPS, the following applies related to handling of UE's radio capabilities:
- If the target eNodeB node knows (e.g. by configuration) that the UE's E-UTRA radio capabilities applicable to the target eNodeB may be different to the E-UTRA radio capabilities stored in the source NG-RAN node (e.g. for handover to eNodeB that supports the NTN enhancements as defined in TS 36.300), then the target eNodeB shall trigger retrieval of the E-UTRA radio capability information again from the UE.
4.11.1.2.2.2 Preparation phase p. 286
Figure 4.11.1.2.2.2-1 shows the preparation phase of the Single Registration-based Interworking from EPS to 5GS procedure.
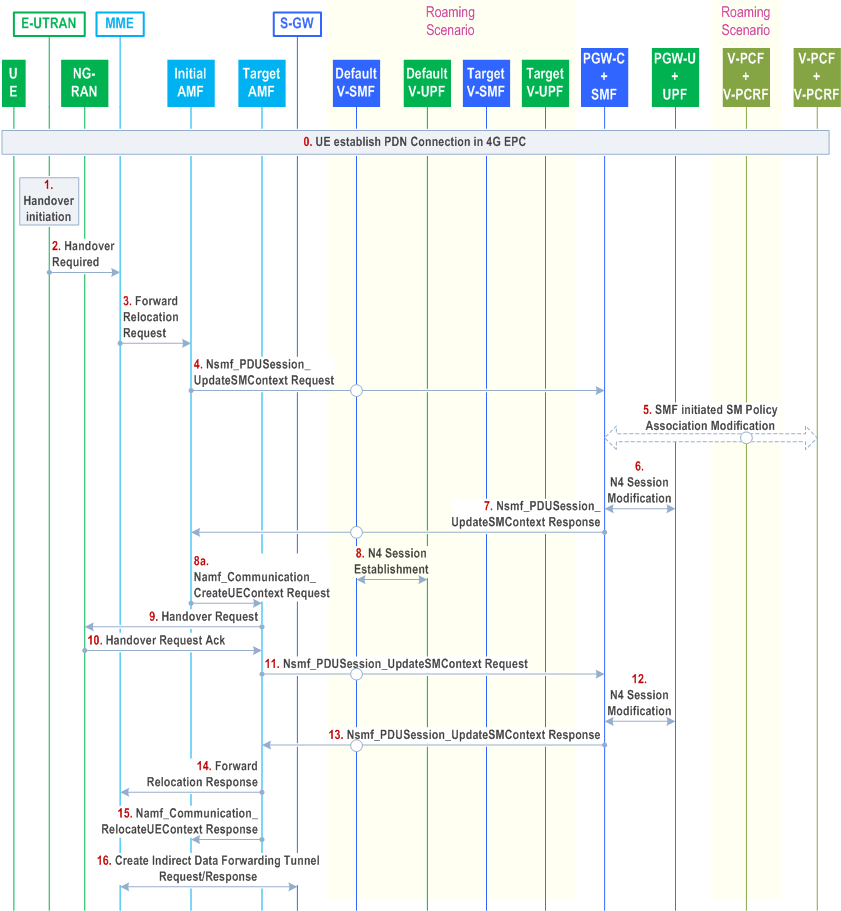
This procedure applies to the Non-Roaming (TS 23.501 Figure 4.3.1-1), Home-routed roaming (TS 23.501 Figure 4.3.2-1) and Local Breakout roaming Local Breakout (TS 23.501 Figure 4.3.2-2) cases.
- For non-roaming scenario, V-SMF, v-UPF and v-PCF are not present
- For home-routed roaming scenario, the SMF+PGW-C and UPF+PGW-U are in the HPLMN. v-PCF are not present
- For local breakout roaming scenario, V-SMF and v-UPF are not present. SMF+PGW-C and UPF+PGW-U are in the VPLMN.
Step 1 - 2.
Upon completion of the handover procedure, based on the PDU Set Based Handling Support Indication received in step 10 as described in clause 5.37.5.3 of TS 23.501, the SMF may initiate the PDU Session modification procedure to provide PDU Set QoS parameters to NG-RAN and configure the PSA UPF to activate/deactivate the PDU Set identification and marking for DL.
Step 1 - 2 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401.
Step 3.
Step 3 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401 with the following modifications:
An additional optional parameter Return preferred. Return preferred is an optional indication provided by the MME to indicate a preferred return of the UE to the last used EPS PLMN at a later access change to an EPS shared network. Based on the Return Preferred indication, the initial AMF may store the last used EPS PLMN ID in the UE Context.
The initial AMF converts the received EPS MM Context into the 5GS MM Context. This includes converting the EPS security context into a mapped 5G security context as described in TS 33.501. The MME UE context includes IMSI, ME Identity, UE security context, UE Network Capability and EPS Bearer context(s) and may also include LTE-M Indication. The MME EPS Bearer context(s) include for each EPS PDN connection the IP address and FQDN for the S5/S8 interface of the SMF+PGW-C and APN and for each EPS bearer the IP address and CN Tunnel Info at the UPF+PGW-U for uplink traffic. If the AMF received the LTE-M indication in the EPS MM Context, then it considers that the RAT Type is LTE-M.
The initial AMF queries the (PLMN level) NRF in serving PLMN by issuing the Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request including the FQDN for the S5/S8 interface of the SMF+PGW-C and the NRF provides the IP address or FQDN of the N11/N16 interface of the SMF+PGW-C.
If the initial AMF cannot retrieve the address of the corresponding SMF for a PDN connection, it will not move the PDN connection to 5GS.
Step 4.
The initial AMF invokes the Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext service operation (UE EPS PDN Connection, initial AMF ID, data Forwarding information, Target ID) on the SMF identified by the SMF+PGW-C address and indicates HO Preparation Indication (to avoid switching the UP path). The initial AMF ID uniquely identifies the initial AMF serving the UE. This step is performed for each PDN Connection and the corresponding SMF+PGW-C address/ID in the UE context the initial AMF received in step 3. The SMF finds the corresponding PDU Session based on EPS Bearer Context(s).
Based on configuration and the Direct Forwarding Flag received from the MME, the initial AMF determines the applicability of data forwarding and indicates to the SMF whether the direct data forwarding or indirect data forwarding is applicable.
Target ID corresponds to Target ID provided by the MME in step 3.
For home-routed roaming scenario, the initial AMF selects a default V-SMF per PDU Session and invokes the Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext service operation (UE PDN Connection Contexts, initial AMF ID, SMF + PGW-C address, S-NSSAI). The S-NSSAI is the S-NSSAI configured in initial AMF for interworking, which is associated with default V-SMF.
The default V-SMF selects the SMF+PGW-C using the received H-SMF address as received from the initial AMF and initiates a Nsmf_PDUSession_Create service operation with the SMF+PGW-C and indicates HO Preparation Indication. The V-SMF provides the QoS constraints of the VPLMN to the H-SMF.
Step 5 and step 6 are skipped if the SMF+PGW-C (H-SMF+PGW-C in the case of home-routed scenario) determines that session continuity from EPS to 5GS is not supported for the PDU Session (e.g. PDU Session ID was not received for the PDN connection in EPS, or PDU Session ID was received but mapped 5GS parameters were not provided to the UE due to 5GC interworking restricted).
Step 5.
If dynamic PCC is deployed, the SMF+ PGW-C (H-SMF for home-routed scenario) may initiate SMF initiated SM Policy Modification towards the PCF.
Step 6.
The SMF+PGW-C requests the PGW-U+UPF to allocate the CN Tunnel Info for PDU Session. The SMF+PGW-C send N4 Session modification to PGW-U+UPF to establish the CN tunnel for PDU Session at PGW-U+UPF. The PGW-U+UPF is ready to receive the uplink packets from NG-RAN. The PGW-U+UPF allocates the PGW-U CN Tunnel Info for PDU Session and sends it to the SMF+PGW-C. This step is performed at all SMF+PGW-Cs allocated to the UE for each PDU Session of the UE.
Step 7.
The SMF+PGW-C (default V-SMF in the case of home-routed roaming scenario only) sends a Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (PDU Session ID, S-NSSAI, allocated EBIs, N2 SM Information (QoS Profile(s), EPS Bearer Setup List, Mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s), CN Tunnel-Info, cause code)) to the initial AMF.
For home-routed roaming scenario the step 8 need be executed first. The CN Tunnel-Info provided to the initial AMF in N2 SM Information is the V-CN Tunnel-Info.
The SMF includes mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s) as part of N2 SM Information container. If the P-GW-C+SMF (H-SMF in the case of home-routed scenario) determines that seamless session continuity from EPS to 5GS is not supported for the PDU Session (e.g. PDU Session ID was not received for the PDN connection in EPS), then it does not provide SM information for the corresponding PDU Session but includes the appropriate cause code for rejecting the PDU Session transfer within the N2 SM Information and release the PDN connection locally in the SMF+PGW-C. If neither indirect forwarding nor direct forwarding is applicable, the SMF shall further include a "Data forwarding not possible" indication in the N2 SM information container. If SMF is indicated that Direct Forwarding is applicable in step 4, the SMF shall further include a "Direct Forwarding Path Availability" indication in the N2 SM information container. In home routed roaming case, the S-NSSAI included in N2 SM Information container is the S-NSSAI received in step 4.
The initial AMF stores an association of the PDU Session ID, S-NSSAI and the SMF ID. The AMF stores also the allocated EBI(s) associated to the PDU Session ID.
If the PDN Type of a PDN Connection in EPS is non-IP and is locally associated in SMF to PDU Session Type Ethernet, the PDU Session Type in 5GS shall be set to Ethernet. If the PDN type of a PDN Connection in EPS is non-IP and is locally associated in UE and SMF to PDU Session Type Unstructured, the PDU Session Type in 5GS shall be set to Unstructured.
In the case of PDU Session Type Ethernet, that was using PDN type non-IP in EPS, the SMF creates QoS rules and QoS Flow level QoS parameters for the QoS Flow(s) associated with the QoS rule(s) based on the PCC Rules received from PCF.
In the case of home-routed roaming scenario, the V-SMF may apply VPLMN policies as described in clause 5.17.1.3 of TS 23.501.
The SMF includes the User Plane Security Policy as part of N2 SM Information container. The SMF determines the User Plane Security Policy as described in clause 5.10.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 8.
For home-routed roaming scenario only: The default V-SMF selects a default v-UPF and initiates an N4 Session Establishment procedure with the selected default v-UPF. The default V-SMF provides the default v-UPF with packet detection, enforcement and reporting rules to be installed on the UPF for this PDU Session, including H-CN Tunnel Info.
The default v-UPF acknowledges by sending an N4 Session Establishment Response message. The V-CN Tunnel Info is allocated by the v-UPF and provided to the default V-SMF in this step.
Step 8a.
Based on the received S-NSSAI from the SMF+PGW-C, the Initial AMF may reselect a target AMF as described in clause 5.15.5.2.1 of TS 23.501 and invokes Namf_Communication_RelocateUEContext request (SUPI, Target 5GAN Node ID, PDU session ID and the S-NSSAI associated with N2 SM Information received in step 7, Source to Target Transparent Container, 5GS MM Context, MME Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, MME Address for Control plane, PDU Session ID and its associated S-NSSAI of the VPLMN value for each PDU Session, the corresponding S-NSSAI of HPLMN value for home routed PDU Session(s), SMF+PGW-C ID of each PDU Session, default V-SMF ID and SM Context ID of each PDU Session, allocated EBIs of each PDU Session, Allowed NSSAI received from NSSF) to the selected target AMF.
Step 9.
The target AMF sends a Handover Request (Source to Target Transparent Container, Allowed NSSAI, PDU session ID and the S-NSSAI received from Source AMF associated with the corresponding N2 SM Information (QFI(s), QoS Profile(s), EPS Bearer Setup List, V-CN Tunnel Info, Mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s)), Mobility Restriction List, UE Radio Capability ID) message to the NG-RAN.
If available, the target AMF provides NG-RAN with a PLMN list in the Mobility Restriction List containing at least the serving PLMN, which may also include the last used EPS PLMN ID if it is the preferred PLMN for subsequent mobility to EPS. See clause 9.3.1.85 of TS 38.413 for details about the Mobility Restriction List.
NG-RAN can use the source to target transparent container and N2 SM Information container to determine which QoS flows have been proposed for forwarding and decide for which of those QoS flows it accepts the data forwarding or not.
The target AMF provides the UE Radio Capability ID to NG-RAN if RACS is supported. If the UE Radio Capability ID is included in the Handover Request message, when there is no corresponding UE radio capabilities set for UE Radio Capability ID at NG-RAN and no UE radio access capabilities are provided in the Source to Target transparent container, NG-RAN shall request the T-AMF to provide the UE radio capabilities set corresponding to UE Radio Capability ID to the NG-RAN. If the Source to Target transparent container contains the UE radio access capabilities and the T-RAN did not receive the UE Radio Capability ID from the T-AMF, NG-RAN shall proceed with handover using the received UE access radio capabilities. If the T-RAN received both the UE radio access capabilities and the UE Radio Capability ID, then the T-RAN shall use any locally stored UE radio access capability information corresponding to the UE Radio Capability ID. If none are stored locally, the T-RAN may request the full UE radio access capability information from the core network. If the full UE radio access capability information is not promptly received from the core network, or the T-RAN chooses not to request them, then the T-RAN shall proceed with the UE radio access capabilities sent by the source RAN node. The T-RAN shall not use the UE radio access capability information received from the source RAN node for any other UE with the same the UE Radio Capability ID.
Step 10.
The NG-RAN sends a Handover Request Acknowledge (Target to Source Transparent Container, List of PDU Sessions to Hand-over with N2 SM response (PDU Session ID, list of accepted QFI(s), AN Tunnel Info, Data Forwarding Tunnel Info), List of PDU Sessions that failed to be established with the failure cause given in the N2 SM information element, PDU Set Based Handling Support Indication included in the N2 SM information) message to the target AMF.
If indirect data forwarding is applied, the NG-RAN includes one assigned TEID/TNL address per PDU Session (for which there is at least one QoS flow for which it has accepted the forwarding) within the SM Info container. It also includes the list of QoS flows for which it has accepted the forwarding. According to the mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s), if one EPS bearer in EPS is mapped to multiple QoS flows in 5GS, all such QoS flows need to be accepted to support indirect data forwarding during EPS to 5GS mobility. Otherwise, the NG RAN rejects the indirect data forwarding for the QoS flows which are mapped to the EPS bearer.
If direct data forwarding is applied, the NG-RAN includes one assigned TEID/TNL per E-RAB accepted for direct data forwarding.
When the target NG-RAN rejects the handover with a Handover Failure, steps 11-13 and step 16 are not executed.
The NG-RAN includes the PDU Set Based Handling Support Indication in N2 SM information as described in clause 5.37.5.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 11.
The target AMF sends an Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (PDU Session ID, N2 SM response received from NG-RAN in step 10) message to the SMF for updating N3 tunnel information. In home routed roaming case, the Data Forwarding Tunnel Info is handled by the default V-SMF and will not be sent to the SMF+PGW-C.
Step 12.
SMF+PGW-C (default V-SMF in home-routed roaming scenario) performs preparations for N2 Handover by indicating N3 UP address and Tunnel ID of NG-RAN to the UPF if N2 Handover is accepted by NG-RAN. If indirect data forwarding is applied, SMF+PGW-C indicates the mapping between the TEID where the UPF receives data forwarded by the source SGW and the QFI(s) and N3 Tunnel Info for data forwarding where the UPF is selected to forward such data (e.g. an intermediate UPF). If the EPS bearer is mapped to multiple QoS flows and an intermediate UPF is selected for data forwarding, only one QFI is selected by the SMF+PGW-C from QFIs corresponding to the QoS flows.
If indirect data forwarding is applied in home routed roaming case, the default V-SMF sends a default V-UPF for data forwarding the mapping between the TEID where the UPF receives data forwarded by the source SGW and the QFI and N3 Tunnel Info for data forwarding. If the EPS bearer is mapped to multiple QoS flows and an intermediate UPF is selected for data forwarding, only one QFI is selected by the SMF+PGW-C from QFIs corresponding to the QoS flows.
If N2 Handover is not accepted by NG-RAN, SMF+PGW-C deallocates N3 UP address and Tunnel ID of the selected UPF.
The EPS Bearer Setup list is a list of EPS bearer Identifiers successfully handover to 5GC, which is generated based on the list of accepted QFI(s).
If a PDU Session is rejected by the Target NG-RAN with an indication that the PDU session was rejected because User Plane Security Enforcement is not supported in the Target NG-RAN and the User Plane Enforcement Policy indicates "Required" as described in clause 5.10.3 of TS 23.501, the SMF triggers the release of this PDU Session. In all other cases of PDU Session rejection, the SMF can decide whether to release the PDU Session or to deactivate the UP connection of this PDU Session.
If some of the QoS Flows of a PDU Session are not accepted by the Target NG-RAN, the SMF shall initiate the PDU Session Modification procedure to remove the non-accepted QoS Flows from the PDU Session(s) after the handover procedure is completed.
Step 13.
SMF+PGW-C (default V-SMF in home-routed roaming scenario) to target AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (PDU Session ID, EPS Bearer Setup List). The data forwarding information is included in the EPS Bearer Setup List. In home routed roaming case, the default V-SMF provides the tunnel information for data forwarding.
This message is sent for each received Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext_Request message.
Step 14.
The target AMF sends the message Forward Relocation Response (Cause, Target to Source Transparent Container, Serving GW change indication, EPS Bearer Setup List, target AMF Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, Addresses and TEIDs) to MME. The EPS Bearer Setup list is the combination of EPS Bearer Setup list from different SMF+PGW-C(s).
In the case of Handover Failure in step 10, the target AMF provides to the MME the failure related information such as the Target RAN to Source RAN Failure Information.
Step 15.
The target AMF invokes Namf_Communication_RelocateUEContext response (Cause) to the initial AMF if step 8a had been performed. The target AMF indicates whether the Relocate UE Context (hand-Over) succeeded or failed.
If the target NG RAN has rejected the Handover Request in step 10, the Namf_Communication_RelocateUEContext response indicates a failure due to RAN rejection. Then the initial AMF invokes the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext request towards the SMF+PGW-C(s) contacted at step 4 indicating . The Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext request contains an indication that this is due to a handover rejected by the target RAN.
Step 16.
Step 8 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401 is executed if the source MME determines that indirect data forwarding applies.
4.11.1.2.2.3 Execution phase p. 289
Figure 4.11.1.2.2.3-1 shows the Single Registration-based Interworking from EPS to 5GS procedure.
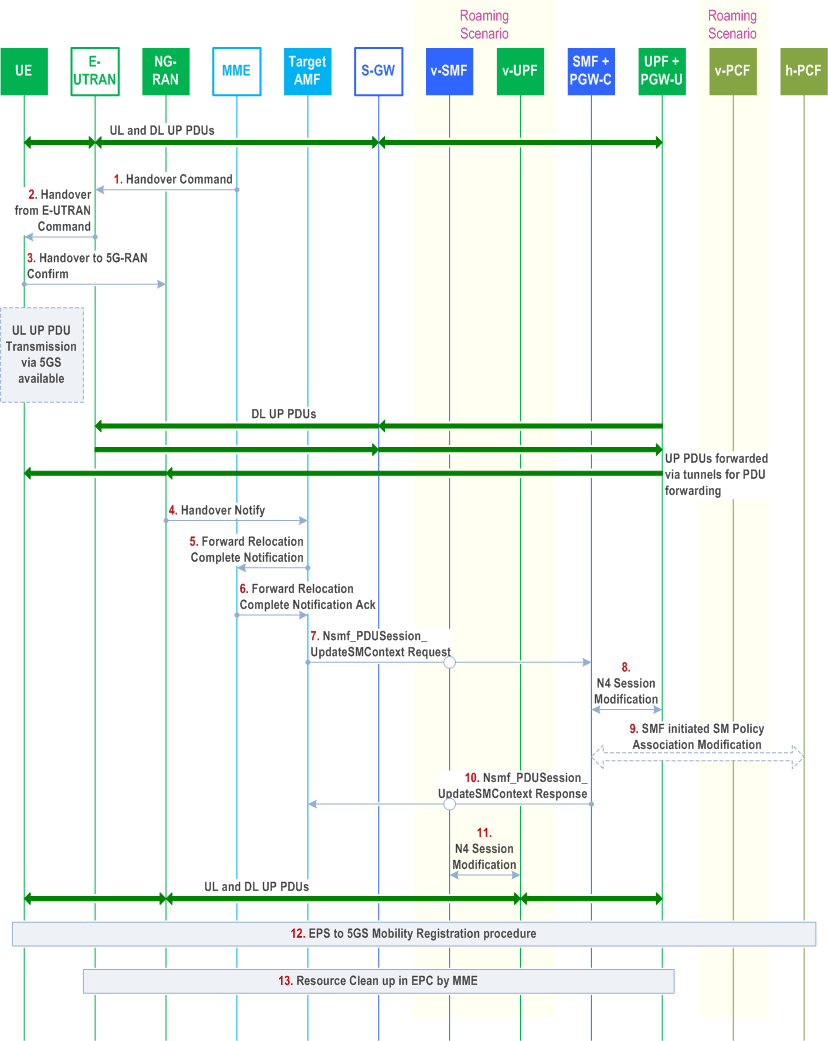
Step 1 - 2.
Step 9 - 11 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401. Different from step 9a of clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401, upon reception of Handover Command, the UE will keep the QoS Flow context for which it did not receive the corresponding radio resources in the NG-RAN until the QoS Flow is released by the network using PDU Session Modification procedure in clause 4.3.3. If the QoS Flow with a default QoS Rule of a PDU Session does not have the corresponding radio resources in the NG-RAN, UE considers that the user plane of this PDU Session is deactivated.
Step 3.
Handover Confirm: the UE confirms handover to the NG-RAN.
The UE moves from the E-UTRAN and synchronizes with the target NG-RAN. The UE may resume the uplink transmission of user plane data only for those QFIs and Session IDs for which there are radio resources allocated in the NG-RAN.
The E-UTRAN sends DL data to the Data Forwarding address received in step 1. If the indirect data forwarding is applied, the E-UTRAN forward the DL data to NG-RAN via the SGW and the v-UPF. The v-UPF forwards the data packets to the NG-RAN using the N3 Tunnel Info for data forwarding, adding the QFI information. The target NG-RAN prioritizes the forwarded packets over the fresh packets for those QoS flows for which it had accepted data forwarding.
If Direct data forwarding is applied, the E-UTRAN forwards the DL data packets to the NG-RAN via the direct data forwarding tunnel.
Step 4.
Handover Notify: the NG-RAN notifies to the target AMF that the UE is handed over to the NG-RAN.
Step 5.
Then the target AMF knows that the UE has arrived to the target side and informs the MME by sending a Forward Relocation Complete Notification message.
Step 6.
Step 14 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401.
Step 7.
Target AMF to SMF +PGW-C (V-SMF in the case of roaming and Home-routed case): Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (Handover Complete Indication for PDU Session ID). In the Home-routed roaming case, the V-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_Update Request (V-CN Tunnel Info, Handover Complete Indication) to SMF+PGW-C.
Handover Complete Indication is sent per each PDU Session to the corresponding SMF +PGW-C (sent by V-SMF in the roaming and Home-routed case) to indicate the success of the N2 Handover.
If indirect forwarding is used, a timer in SMF+PGW-C (V-SMF in the case of roaming and Home-routed case) is started to supervise when resources in UPF (for indirect data forwarding) shall be released.
Step 8.
The SMF + PGW-C updates the UPF + PGW-U with the V-CN Tunnel Info, indicating that downlink User Plane for the indicated PDU Session is switched to NG-RAN or V-UPF in the case of roaming in Home-routed case and the CN tunnels for EPS bearers corresponding to the PDU session can be released.
For each EPS Bearer one or more "end marker" is sent to Serving GW by the UPF+PGW-U immediately after switching the path. The UPF + PGW-U starts sending downlink packets to the V-UPF.
Step 9.
If PCC infrastructure is used, the SMF + PGW-C informs the PCF about the change of, for example, the RAT type and UE location.
Step 10.
SMF +PGW-C to target AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (PDU Session ID).
SMF +PGW-C confirms reception of Handover Complete.
Step 11.
-
If the SMF has not yet registered for this PDU Session ID, then the SMF registers with the UDM using Nudm_
UECM_ (SUPI, DNN, PDU Session ID) for a given PDU Session as in step 4 of PDU Session Establishment Procedure in clause 4.3.2.Registration
For home-routed roaming scenario: The V-SMF provides to the v-UPF with the N3 DL AN Tunnel Info. This step is executed after step 7.
Step 12.
The UE performs the EPS to 5GS Mobility Registration Procedure from step 2 in clause 4.11.1.3.3. The UE includes the UE Policy Container containing the list of PSIs, indication of UE support for ANDSP and OSId if available. If the UE holds a native 5G-GUTI it also includes the native 5G-GUTI as an additional GUTI in the Registration Request. The UE shall select the 5G-GUTI for the additional GUTI as follows, listed in decreasing order of preference:
Step 13.
- a native 5G-GUTI assigned by the PLMN to which the UE is attempting to register, if available;
- a native 5G-GUTI assigned by an equivalent PLMN to the PLMN to which the UE is attempting to register, if available;
- a native 5G-GUTI assigned by any other PLMN, if available.
Step 19 from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401. Step 20a - 20b from clause 5.5.1.2.2 (S1-based handover, normal) in TS 23.401, with the following modification:
For the PDN connections that are not possible to be transferred to 5GS (e.g. PDN connections are anchored in a standalone PGW), the MME initiates PDN connection release procedure as specified in TS 23.401.
Step 14.
If indirect forwarding was used, then the expiry of the timer started at step 7 triggers the SMF+PGW-C (V-SMF in the case of roaming and Home-routed case) to release temporary resources used for indirect forwarding that were allocated at steps 11 to 13 in clause 4.11.1.2.2.2.