Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.4.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
8.3 ECS Discovery and Service provisioning
8.3.1 General
8.3.2 ECS Discovery
8.3.2.1 General
8.3.2.2 Procedures
8.3.2.3 Information flows
8.3.2.4 APIs
...
...
8.3 ECS Discovery and Service provisioning p. 61
8.3.1 General p. 61
Service provisioning allows configuring the EEC with information about available Edge Computing services, based on the hosting UEs location, service requirements, service preferences and connectivity. This configuration includes the necessary address information for the EEC to establish connection with the EES(s).
If the ECS deployed by MNO is contracted with one or more ECSP(s), the ECS provides EES configuration information of MNO owned and ECSP owned EESs via MNO ECS as described in clause 8.3.3.3.3.
If the ECS is deployed by a non-MNO ECSP, the ECS endpoint address may be configured with the EEC. An EEC that is aware of multiple ECSP's ECS endpoint addresses may perform the service provisioning procedure per ECS of each ECSP multiple times.
Figure 8.3.1-1 illustrates an overview of service provisioning. Service provisioning procedures support the following models:
- Request/ Response model; and
- Subscribe/ Notify model.
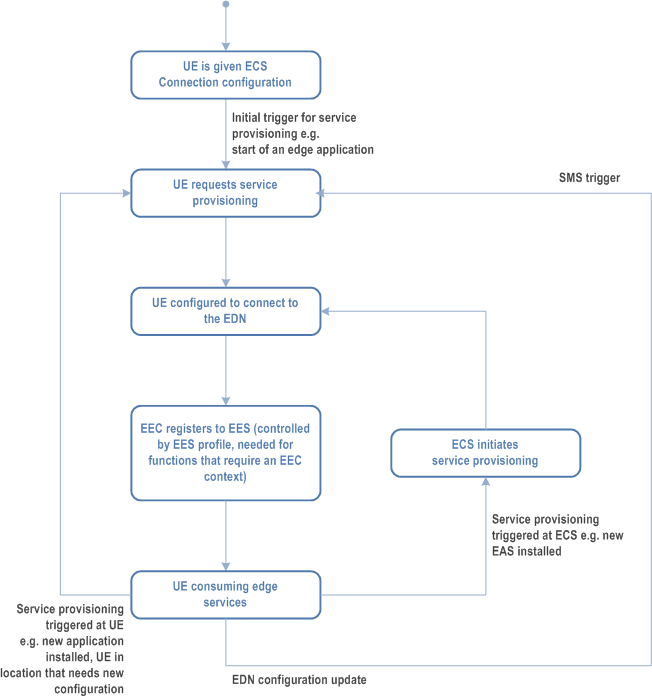
The UE is given configuration information enabling it to connect to the ECS. The UE can then request initial provisioning from the ECS to obtain configuration required to connect to the EDN. Once provisioned, the EEC of the UE registers with the selected EES(s) from the list of provisioned EES(s) it received from the ECS(s), if the EEC registration configuration in EES profile indicates that EEC registration is required. The UE further consumes the edge computing services and performs various operations such as EAS discovery, Edge application communications, ACR, etc. While the UE is consuming the edge computing services, the UE or ECS may be triggered to re-request service provisioning.
The triggers for service provisioning are classified as:
-
Triggers at UE - Some examples are:
- AC related updates available at the EEC due to AC installation/re-installation, AC requesting application server access (e.g. via internet browser);
- EEC supporting one or more ACs may be updated due to EEC re-installation; and
- Lifetime of EDN Configuration Information is expired or the EEC detects that the UE moves out of EDN Service Area in the EDN Configuration Information.
-
Triggers at ECS - Some examples are:
- EES updates received due to EAS installation/re-installation/re-location; and
- ECS receives the EDN/DNAI change notification of the UE from 5GC when the ECS subscribes to the user plane path management events as specified in clause 8.10.2.
8.3.2 ECS Discovery p. 63
8.3.2.1 General p. 63
ECS configuration information consists of one or more endpoint information (e.g. URI(s), FQDN(s), IP address(es)) of ECS(s), and optionally the corresponding ECS Provider Identifier. ECS configuration information can be
- pre-configured with the EEC;
- configured by an edge-aware AC;
- configured by the user;
- provisioned by MNO through 5GC procedure if the UE has the capability to deliver the ECS configuration information to the EEC on the UE (see clause 6.5.2 of TS 23.548);
- derived from HPLMN identifier for non-roaming scenario or from VPLMN identifier for roaming scenario; or
- derived from serving SNPN identifier.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ECS address | M | Endpoint information of ECS (e.g. URI, FQDN, IP address) |
| ECSP Identifier (NOTE 1) | O | The identifier of the ECSP (e.g., the MNO or a 3rd party service provider) that provides the ECS. |
| Spatial Validity Conditions | O | Spatial validity condition, as described in TS 23.548. |
| Security Parameters | O | The security parameters (as specified in clause 6.2 of TS 33.558) are used by EEC to communicate with the ECS. |
| List of supported PLMN(s) | O | The List of PLMNs and associated ECSPs for which EDN configuration information can be provided by the ECS. |
| > PLMN ID | O | The identifier of a PLMN for which EDN configuration information can be provided by the ECS. |
| > List of supported ECSP(s) (NOTE 2) | O | The identifier of the ECSP(s) associated with the PLMN and whose information is available at the ECS. |
| >> ECSP ID | M | Identifier of an ECSP. |
|
NOTE 1:
This IE shall be included when the ECS configuration information is provisioned by the MNO through the 5GC procedure.
NOTE 2:
This IE may not be included if the ECSP does not want to expose its EES deployment information or business relationship-related information.
|
||
8.3.2.2 Procedures p. 64
8.3.2.2.1 General p. 64
There is no additional information about procedures for ECS Discovery.
8.3.2.3 Information flows p. 64
8.3.2.3.1 General p. 64
There is no additional information about information flows for ECS Discovery
8.3.2.4 APIs p. 64
8.3.2.4.1 General p. 64
There is no additional information about APIs for ECS Discovery