Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
16.4 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on S2a
16.4.1 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on GTP S2a
16.4.2 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on PMIP S2a
16.5 Dedicated bearer activation in WLAN on GTP S2a
16.6 Network-initiated bearer modification in WLAN on GTP S2a
16.6.1 PDN GW Initiated Bearer Modification
16.6.2 HSS Initiated Bearer Modification
...
...
16.4 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on S2a p. 277
16.4.1 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on GTP S2a p. 277
This procedure depicted in Figure 16.4.1-1 can be used to deactivate an S2a dedicated bearer or deactivate all S2a bearers belonging to a PDN address, for e.g., due to IP-CAN session modification requests from the PCRF. If the default S2a bearer belonging to a PDN connection is deactivated, the PDN-GW deactivates all S2a bearers belonging to the PDN connection.
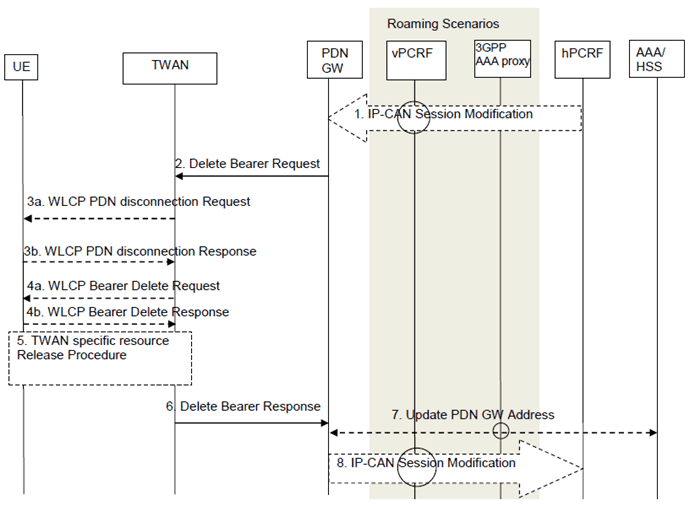
Figure 16.4.1-1: PDN-GW Initiated Bearer Deactivation with GTP on S2a
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
This procedure applies to the Non-Roaming, Roaming and Local Breakout cases. In the Local Breakout case, the vPCRF forwards messages between the PDN-GW and the hPCRF. In the non-roaming and home routed roaming cases, the vPCRF is not involved at all.
The optional interaction steps between the PDN-GW and the PCRF in the procedures in Figure 16.4.1-1 only occur if dynamic policy provisioning is deployed. Otherwise policy may be statically configured within the PDN-GW.
Step 1.
Steps 3-4 only apply in multi-connection mode:
If dynamic PCC is deployed, the PDN-GW initiated Bearer Deactivation procedure may for example be triggered due to 'IP-CAN session Modification procedure', as defined in TS 23.203. In this case, the resources associated with the PDN connection in the PDN-GW are released. If requested by the Application Function (e.g. P-CSCF), the PCRF may also include a request to provide the User Location Info and/or the Time zone to the PDN-GW.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW sends a Delete Bearer Request message (EPS Bearer Identity, Cause) to the TWAN. This message can include an indication that all bearers belonging to that PDN connection shall be released.
Step 3.
In multi-connection mode, if all bearers belonging to a PDN connection are released, then the UE is informed of the PDN connection release by means of a WLCP PDN Disconnection Request (PDN Connection ID).
The UE acknowledges the disconnection request.
Step 4.
In multi-connection mode, if a dedicated bearer is marked for deletion in step 2 and multiple WLCP bearers are used, the TWAN sends a WLCP Bearer Delete message with a list of bearer identities to be deleted. The UE acknowledges the Bearer Delete Request.
Step 5.
If supported by the TWAN, the TWAN specific resources may be released in the TWAN. The details of this step are out of the scope of 3GPP.
Step 6.
The TWAN deletes the bearer contexts related to the Delete Bearer Request, and acknowledges the bearer deactivation to the PDN-GW by sending a Delete Bearer Response (EPS Bearer Identity) message. Additionally, the Delete Bearer Response includes the TWAN Identifier as described in clause 16.1.7, the Timestamp of this TWAN-Identifier and the UE Time Zone.
Step 7.
In the case where the resources corresponding to the PDN connection are released in PDN-GW, the PDN-GW informs the 3GPP AAA Server/HSS of the PDN disconnection.
Step 8.
The PDN-GW deletes the bearer context related to the deactivated S2a bearer. If the dedicated bearer deactivation procedure was triggered by receiving a PCC decision message from the PCRF, the PDN-GW indicates to the PCRF whether the requested PCC decision was successfully enforced by completing the PCRF-initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure or the PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203, proceeding after the completion of IP-CAN bearer signalling. If requested by the PCRF in step 1, the PDN-GW provides the User Location Information, that contains the TWAN Identifier and/or UE Time Zone that will be forwarded to the Application Function as defined in TS 23.203.
16.4.2 PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation in WLAN on PMIP S2a p. 278
The procedure is similar to GTP based S2a call flows in clause 16.4.1 when the resources corresponding to the PDN connection is released, with the following differences:
- Step 2 is a Binding Revocation Request. The details of the Binding Revocation message are described in step 2 in clause 6.12.1.
- Step 6 is a Binding Revocation Acknowledgement. The details of the Binding Revocation Acknowledgement message are described in step 5 in clause 6.12.1. Additionally, the Binding Revocation Acknowledgement includes the current TWAN Identifier as described in clause 16.1.7, the Timestamp of this TWAN-Identifier and the UE Time Zone.
16.5 Dedicated bearer activation in WLAN on GTP S2a p. 278
The dedicated bearer activation procedure for GTP based S2a is depicted in Figure 16.5-1.
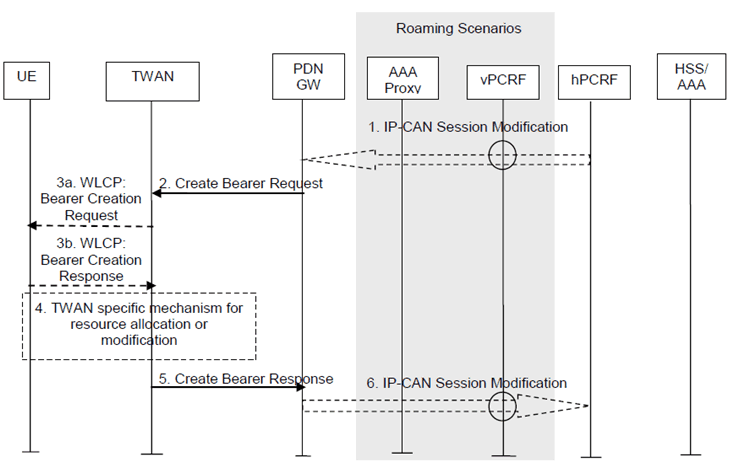
Figure 16.5-1: Dedicated S2a Bearer Activation Procedure with GTP on S2a
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
Steps 3 only applies in multi-connection mode:
If dynamic PCC is deployed, the PCRF sends a PCC decision provision (QoS policy) message to the PDN-GW. If the Application Function (e.g. P-CSCF) requests it, the PCRF may also include a request to provide the User Location Info and/or the Time zone. This corresponds to the initial steps of the PCRF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure or to the PCRF response in the PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203, up to the point that the PDN-GW requests IP-CAN Bearer Signalling. If dynamic PCC is not deployed, the PDN-GW may apply local QoS policy.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW uses this QoS policy to assign the S2a bearer QoS, i.e., it assigns the values to the bearer level QoS parameters QCI, ARP, GBR and MBR. If this dedicated bearer is created as part of the handover from 3GPP access with GTP-based S5/S8, then the PDN-GW applies the Charging ID already in use for the corresponding dedicated bearer while the UE was in 3GPP access (i.e. bearer with the same QCI and ARP as in 3GPP access). Otherwise, the PDN-GW generates a new Charging ID for the dedicated bearer. The PDN-GW sends a Create Bearer Request message (IMSI, EPS bearer QoS, TFT, PDN-GW Address for the user plane, PDN-GW TEID of the user plane, Charging Id, LBI) to the trusted WLAN access network. The Linked EPS bearer Identity (LBI) is the EPS bearer Identity of the default bearer.
Step 3.
The TWAN sends WLCP message Bearer Creation Request (PDN connection ID, Bearer ID, TFT, Bearer QoS information, User plane connection ID) to the UE if UE is capable of multiple WLCP bearers per PDN connection. The user plane connection ID is assigned by the TWAG and shall be unique among all WLCP bearers for that UE. The UE stores the information on the new WLCP bearer and responds with WLCP Bearer Creation Response to the TWAN. For uplink packets that match bearer TFT according to same principles as for 3GPP access, the UE applies Bearer QoS and send packet on that bearer i.e. on the user plane connection ID (MAC address) associated with the bearer. A TWAN specific resource allocation/modification procedure may be executed in this step. The details of this step are out of the scope of 3GPP.
Step 4.
A TWAN specific resource allocation/modification procedure may be executed in this step. The details of this step are out of the scope of 3GPP.
Step 5.
The TWAN selects an EPS bearer Identity, which has not yet been assigned to the UE. The TWAN then stores the EPS bearer Identity and links the dedicated bearer to the default bearer indicated by the Linked Bearer Identity (LBI). The TWAN uses the uplink packet filter (UL TFT) to determine the mapping of uplink traffic flows to the S2a bearer. The TWAN then acknowledges the S2a bearer activation to the PGW by sending a Create Bearer Response (EPS bearer Identity, TWAN Address for the user plane, TWAN TEID of the user plane) message. Additionally, the Create Bearer Response includes the current TWAN Identifier as described in clause 16.1.7 and the UE Time Zone.
Step 6.
If the dedicated bearer activation procedure was triggered by a PCC Decision Provision message from the PCRF, the PDN-GW indicates to the PCRF whether the requested PCC decision (QoS policy) could be enforced or not, allowing the completion of the PCRF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure or the PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203, after the completion of IP-CAN bearer signalling. If requested by the PCRF in step 1, the PDN-GW provides the User Location Information that contains the TWAN identifier and/or UE Time Zone that will be forwarded to the Application Function as defined in TS 23.203.
16.6 Network-initiated bearer modification in WLAN on GTP S2a p. 280
16.6.1 PDN GW Initiated Bearer Modification p. 280
The PDN-GW initiated bearer modification procedure for a GTP based S2a is depicted in Figure 16.6.1-1. This procedure is used to update the TFT for an active default or dedicated S2a bearer, or in cases when one or several of the S2a bearer QoS parameters QCI, GBR, MBR or ARP are modified (including the QCI or the ARP of the default S2a bearer e.g. due to the HSS Initiated Subscribed QoS Modification procedure, as described in clause 16.6.2).
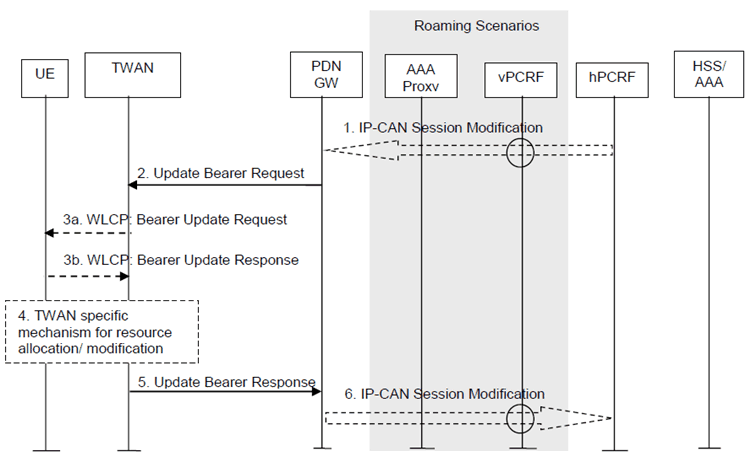
Figure 16.6.1-1: PDN-GW-initiated S2a Bearer Modification Procedure with GTP on S2a
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
Steps 3 only applies in multi-connection mode:
If dynamic PCC is deployed, the PCRF sends a PCC decision provision (QoS policy) message to the PDN-GW. If the Application Function (e.g. P-CSCF) requests it, the PCRF may also include a request to provide the User Location Information and/or the Time zone. This corresponds to the initial steps of the PCRF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure or to the PCRF response in the PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203, up to the point that the PDN-GW requests IP-CAN Bearer Signalling. If dynamic PCC is not deployed, the PDN-GW may apply local QoS policy.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW uses this QoS policy to determine that a service data flow shall be aggregated to or removed from an active S2a bearer or that the authorized QoS of a service data flow has changed. The PDN-GW generates the TFT and updates the S2a bearer QoS to match the traffic flow aggregate. The PDN-GW then sends the Update Bearer Request (EPS bearer Identity, EPS bearer QoS, TFT) message to the trusted WLAN access network.
Step 3.
The TWAN sends WLCP Bearer Update Request with a list of modified bearers (Bearer ID, TFT, Bearer QoS information) to the UE if multiple WLCP bearers are used between the UE and TWAG. The UE stores and uses the updated TFT or Bearer QoS information for each Bearer Id. The UE acknowledges the WLCP Bearer Update Request by sending WLCP Bearer Update Response.
Step 4.
A TWAN specific resource allocation/modification procedure may be executed in this step. The details of this step are out of the scope of 3GPP.
Step 5.
The TWAN uses the uplink packet filter (UL TFT) to determine the mapping of traffic flows to the S2a bearer and acknowledges the S2a bearer modification to the PGW by sending an Update Bearer Response (EPS bearer Identity) message. Additionally, the Update Bearer Response includes the current TWAN Identifier as described in clause 16.1.7 and the UE Time Zone.
Step 6.
If the Bearer modification procedure was triggered by a PCC Decision Provision message from the PCRF, the PDN-GW indicates to the PCRF whether the requested PCC decision (QoS policy) could be enforced or not by sending a Provision Ack message allowing the completion of the PCRF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure or the PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203, after the completion of IP-CAN bearer signalling. If requested by the PCRF in step1, the PDN-GW provides the User Location Information that contains the TWAN identifier and/or UE Time Zone that will be forwarded to the Application Function as defined in TS 23.203.
16.6.2 HSS Initiated Bearer Modification p. 281
The HSS Initiated Subscribed QoS Modification for a GTP-based S2a is depicted in Figure 16.6.2-1.
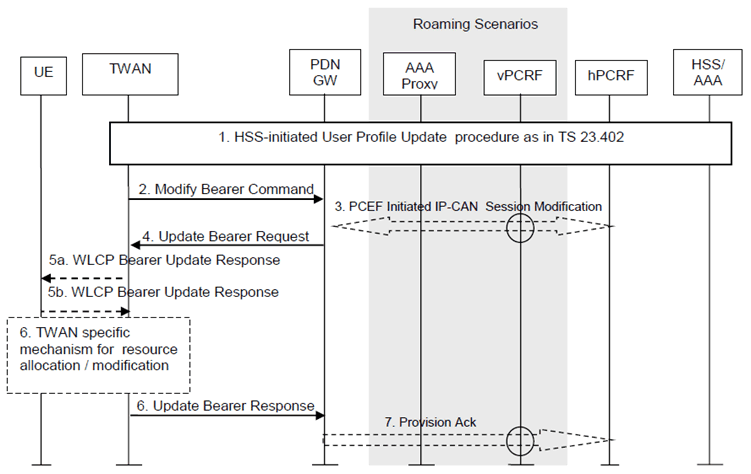
Step 1.
Steps 5 only applies in multi-connection mode:
The HSS updates the User Profile as specified in clause 12.2.1.
Step 2.
If the QCI and/or ARP and/or subscribed APN-AMBR has been modified and there is a related active PDN connection with the modified QoS Profile, the trusted WLAN access network sends the Modify Bearer Command (EPS bearer Identity, EPS bearer QoS, APN AMBR) message to the PDN-GW. The EPS bearer Identity identifies the default bearer of the affected PDN connection. The EPS bearer QoS contains the EPS subscribed QoS profile to be updated.
Step 3.
If PCC infrastructure is deployed, the PDN-GW informs the PCRF about the updated EPS bearer QoS. The PCRF sends the new updated PCC decision to the PDN-GW. This corresponds to the PCEF-initiated IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203.
The PCRF may modify the APN-AMBR and the QoS parameters (QCI and ARP) associated with the default bearer in the response to the PDN-GW as defined in TS 23.203.
Step 4.
The PDN-GW modifies the default bearer of each PDN connection corresponding to the APN for which subscribed QoS has been modified. If the subscribed ARP parameter has been changed, the PDN-GW shall also modify all dedicated S2a bearers having the previously subscribed ARP value unless superseded by PCRF decision. The PDN-GW then sends the Update Bearer Request (EPS bearer Identity, EPS bearer QoS, TFT, APN AMBR) message to the TWAN.
Step 5.
The TWAN sends WLCP Bearer Update Request with a list of modified bearers (Bearer ID, TFT, Bearer QoS information) to the UE if multiple WLCP bearers are used between the UE and TWAG. The UE stores and uses the updated TFT or Bearer QoS information for each Bearer Id. The UE acknowledges the WLCP Bearer Update Request by sending a WLCP Bearer Update Response.
Step 6.
A TWAN specific resource allocation/modification procedure may be executed in this step. The details of this step are out of the scope of 3GPP.
Step 7.
The TWAN acknowledges the bearer modification to the PDN-GW by sending an Update Bearer Response (EPS bearer Identity) message. If the bearer modification fails the PDN-GW deletes the concerned S2a Bearer.
Step 8.
The PDN-GW indicates to the PCRF whether the requested PCC decision was enforced or not by sending a Provision Ack message.