Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
8 Handovers without Optimizations Between 3GPP Accesses and Non-3GPP IP Accesses
8.1 Common Aspects for Handover without Optimizations for Multiple PDNs
8.2 Handovers between non-3GPP IP access with PMIPv6 on S2a/S2b and 3GPP Access
8.2.1 Handover from Trusted or Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access with PMIPv6 on S2a/S2b to 3GPP Access
8.2.1.1 General Procedure for GTP based S5/S8 for E-UTRAN Access
...
...
8 Handovers without Optimizations Between 3GPP Accesses and Non-3GPP IP Accesses p. 186
8.1 Common Aspects for Handover without Optimizations for Multiple PDNs p. 186
This clause describes the common aspects of handover for connectivity with multiple PDNs.
The support of multiple PDNs has the following impacts on the handover procedures for single PDN connectivity:
- Upon handover from 3GPP access to non-3GPP access, and from non-3GPP access to 3GPP access, if the UE has multiple PDN connections to different APNs in the source access and the UE is capable of routing different simultaneously active PDN connections through different access networks, the UE may transfer from the source to the target access all the PDN connections that were active in source access before handover or only a subset of them, with the restriction that multiple PDN connections to the same APN shall be kept in one access.
- Upon handover from 3GPP access to non-3GPP access, and from non-3GPP access to another non-3GPP access, using S2a or S2b, during the access authentication the HSS/AAA returns to the Trusted Non-3GPP Access or the ePDG the PDN-GW identity and the associated APN for each PDN the UE is connected to. For non-3GPP accesses that support UE to establish connectivity to PDNs after attach, the UE performs an attach to the target non-3GPP access indicating that it is a handover, resulting in the UE being connected to one PDN, and the UE establishes connectivity with the remaining PDNs that are being transferred from the 3GPP system using the UE-initiated Connectivity to Additional PDN procedure.
-
If the UE hands over between 3GPP access and a non-3GPP access and the UE has more than one PDN connection to a given APN in the source access and multiple PDN connections to a single APN are not supported via the target access, only one PDN connection to the given APN will be established in the target access. In this case, the following applies:
- If dynamic PCC is deployed and the PCRF receives a Gateway Control Session Establishment Request from the target BBERF indicating an IP-CAN type different from 3GPP access, the PCRF shall select one of the IP-CAN sessions for this APN and continue with the BBERF relocation procedure for that PDN connection.
- When the PDN-GW receives a PBU over PMIP-based S2a or S2b or S5/S8, the PDN-GW shall select one of the PDN connections for this APN and continue with the handover procedure for that PDN connection. The PDN-GW shall terminate the remaining PDN connections for that APN without removing the PDN-GW information in HSS. If dynamic PCC is deployed, the PDN-GW informs the PCRF about the deactivated PDN connections using the PCEF initiated IP-CAN session termination procedure as described in TS 23.203.
- Whenever the PDN-GW receives a PBU containing an IPv6 prefix or an IPv4 address associated to one of the PDN connections and the IPv6 prefix or the IPv4 address is valid, the PDN-GW shall use the IPv6 prefix or the IPv4 address to select the PDN connection out of the active PDN connections. When the information is not included in the PBU, the PDN-GW and PCRF shall select the latest PDN connection out of the active PDN connections for the given APN (i.e. the PDN connection that was activated last out of the active PDN connections for the given APN).
-
If the UE hands over between 3GPP access and a non-3GPP access and the UE has more than one PDN connection to a given APN in the source access and multiple PDN connections to a single APN is supported in the target access the following applies:
- All PDN connections to the same APN shall be handed over.
- When the PDN-GW receives the request to establish a PDN connection to the given APN, the PDN-GW shall select one of the PDN connections for this APN and continue with the handover procedure for that PDN connection.
- When S2c is used and it is bootstrapped before the handover to a foreigner link the home address identifies the PDN connection and the PDN-GW shall select the PDN connection accordingly.
- Upon handover from non-3GPP access to 3GPP access, if the MME has changed since the last detach or if there is no valid Subscriber context for the UE in the MME, or if the ME identity has changed, during the access authentication the HSS returns the Subscriber Data to the MME, including the PDN-GW identity and the associated APN for each PDN the UE is connected to before the handover. The UE performs an attach to the 3GPP access with and indication for "handover" and then establishes connectivity with the remainder of PDNs that it was connected with over the non-3GPP system before the handover, using UE requested PDN connectivity specified in TS 23.401. The UE provides an indication of "handover" by providing Request Type indicating "handover" in the PDN connectivity request message as specified in TS 23.401.
-
For connectivity based on S2c:
- Upon handover from 3GPP access to non-3GPP access, and from non-3GPP access to another non-3GPP access, the UE performs DSMIPv6 bootstrapping (if not yet performed) and binding procedures for each PDN connection that is being transferred from the source to the target access.
- Upon handover from non-3GPP access, the UE de-registers the DSMIPv6 binding for each PDN connection that is being transferred from the source to the target access.
8.2 Handovers between non-3GPP IP access with PMIPv6 on S2a/S2b and 3GPP Access p. 187
8.2.1 Handover from Trusted or Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access with PMIPv6 on S2a/S2b to 3GPP Access p. 187
8.2.1.1 General Procedure for GTP based S5/S8 for E-UTRAN Access p. 187
The steps involved in the handover from a trusted or untrusted non-3GPP IP access to E-UTRAN connected to EPC are depicted below for both the non-roaming and roaming cases and when PMIPv6 is used on S2a or S2b. It is assumed that while the UE is served by the trusted or untrusted non-3GPP IP access, a PMIPv6 tunnel is established between the non-3GPP access network and the PDN-GW in the EPC.
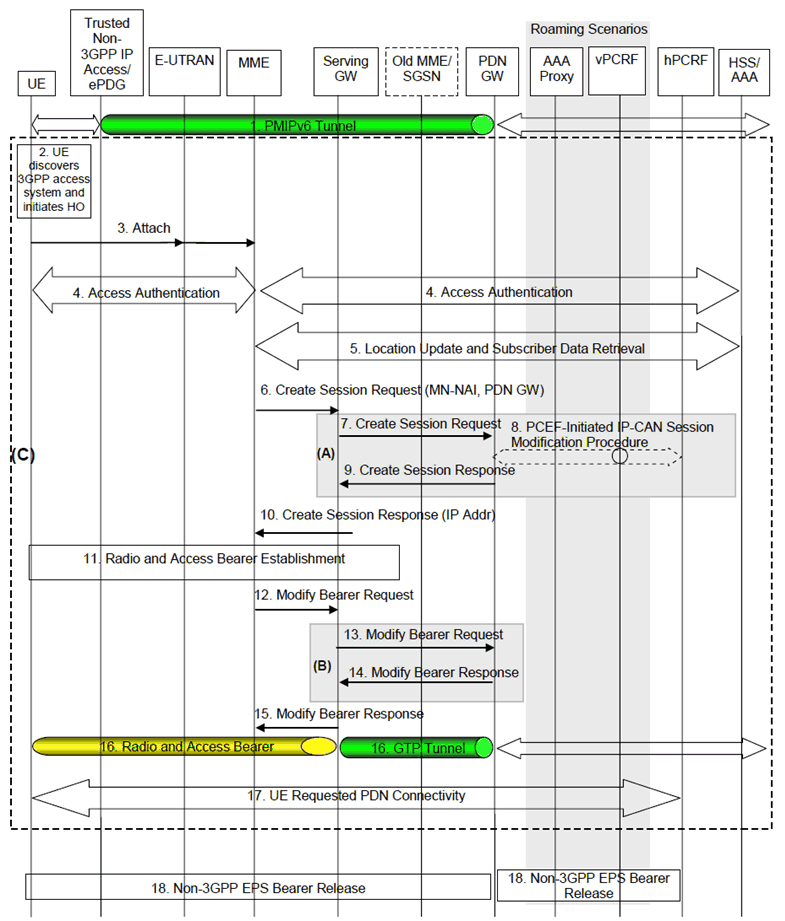
Figure 8.2.1.1-1: Handover from Trusted or Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access to E-UTRAN with PMIPv6 on S2a or S2b and GTP on S5/S8 interfaces
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
In case of connectivity to multiple PDNs the following applies:
- If the UE is connected to both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, steps 2 to 16 shall be skipped and the UE shall only perform step 17 for each PDN connection that is being transferred from non-3GPP access.
- If the UE is connected only to non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, steps 2 to 16 shall be performed. In step 3 the UE should provide the APN corresponding to one of the PDN connections that are being transferred from non-3GPP access. If the APN is not provided, and the subscription context from HSS contains a PDN-GW identity corresponding to the default APN, the MME shall use the PDN-GW corresponding to the default APN as specified in TS 23.401. The UE shall then repeat step 17 for each of the remaining PDN connections that are being transferred from non-3GPP access.
- Step 18 shall be repeated for each PDN connection that is being transferred from non-3GPP access.
Step 1.
The UE uses a trusted or untrusted non-3GPP access system and is being served by PDN-GW (as PMIPv6 LMA).
Step 2.
The UE discovers the E-UTRAN access and determines to transfer its current sessions (i.e. handover) from the currently used non-3GPP access system to E-UTRAN. The mechanisms that aid the UE to discover the 3GPP Access system, are specified in clause 4.8 (Network Discovery and Selection).
Step 3.
The UE sends an Attach Request to the MME with Request Type indicating "Handover" Attach. The message from the UE is routed by E-UTRAN to the MME as specified in TS 23.401 (E-UTRAN). The UE should include any one of the APNs, corresponding to the PDN connections in the source non-3GPP access. The APN is provided as specified in TS 23.401.
Step 4.
The MME may contact the HSS and authenticate the UE as described in TS 23.401.
Step 5.
After successful authentication, the MME may perform location update procedure and subscriber data retrieval from the HSS as specified in TS 23.401. Since theRequest Type is "Handover", the PDN-GW identity conveyed to the MME will be stored in PDN subscription context. The MME receives information on the PDNs the UE is connected to over the non-3GPP access in the Subscriber Data obtained from the HSS.
Step 6.
The MME selects an APN, a serving GW and PDN-GW as described in TS 23.401. The MME sends a Create Session Request (including IMSI, MME Context ID (SGSN equivalent is TBD), PDN-GW address, Handover Indication, APN) message to the selected Serving-GW. Since the Request Type is "Handover", a Handover Indication information is included.
Step 7.
The Serving-GW sends a Create Session Request (Handover Indication) message to the PDN-GW in the VPLMN or HPLMN as described in TS 23.401. Since the MME includes Handover Indication information in Create Session Request message, the Serving-GW includes this information in Create Session Request message.
Since Handover Indication is included, the PDN-GW should not switch the tunnel from non-3GPP IP access to 3GPP access system at this point.
Step 8.
Since Handover Indication is included, the PDN-GW may execute a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203 to report e.g. change in IP-CAN type. If the UE had disconnected from the default PDN before handover then the PDN-GW executes a PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Establishment procedures as described in TS 23.203.
Since Handover Indication is included in step 7, the PDN-GW defers any modification to the PCC Rules (due to changes received from the PCRF, if there is PCRF interaction) and still applies the existing PCC Rules for charging and policy until step 13.
Depending on the active PCC rules, the establishment of dedicated bearers for the UE may be required. The establishment of dedicated bearers in combination with the default takes place as described in Annex F of TS 23.401.
Step 9.
The PDN-GW responds with a Create Session Response message to the Serving-GW as described in TS 23.401.The Create Session Response contains the IP address or the prefix that was assigned to the UE while it was connected to the non-3GPP IP access. It also contains the Charging Id previously assigned to the PDN connection in the non-3GPP access although the Charging Id still applies to the non-3GPP access.
Step 10.
The Serving-GW returns a Create Session Response message to the MME as specified in TS 23.401. This message also includes the IP address of the UE. This message also serves as an indication to the MME that the S5 bearer setup and update has been successful. At this step the PMIPv6 or GTP tunnel(s) over S5 are established.
Step 11.
Radio and Access bearers are established at this step in the 3GPP access as specified in TS 23.401.
Step 12.
The MME sends a Modify Bearer Request (eNodeB address, eNodeB TEID, Handover Indication) message to the Serving-GW.
Step 13.
Since the Handover Indication is included in step 12), the Serving-GW sends a Modify Bearer Request message to the PDN-GW to prompt the PDN-GW to tunnel packets from non 3GPP IP access to 3GPP access system and immediately start routing packets to the Serving-GW for the default and any dedicated EPS bearers established.
In this step, the PDN-GW applies any modification to the PCC Rules received from the PCRF, if there is PCRF interaction in step 8. The Charging Id previously in use for the PDN connection in the non-3GPP access now only applies to the default bearer in use in E-UTRAN access. If dedicated bearers are created, a new Charging Id is assigned by the PGW for each of them according to TS 23.401.
Step 14.
The PDN-GW acknowledges by sending Modify Bearer Response to the Serving-GW.
Step 15.
The Serving-GW acknowledges by sending Modify Bearer Response (EPS Bearer Identity) message to the MME.
Step 16.
The UE sends and receives data at this point via the E-UTRAN system.
Step 17.
For connectivity to multiple PDNs, the UE establishes connectivity to each PDN that is being transferred from non-3GPP access, besides the PDN connection established in steps 3-15, by executing the UE requested PDN connectivity procedure specified in TS 23.401.
Step 18.
The PDN-GW shall initiate resource allocation deactivation procedure in the trusted/untrusted non-3GPP IP access as defined in clause 6.12 or clause 7.9.