Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
10 Handovers with Optimizations Between 3GPP Accesses and Mobile WiMAX
11 Handover Optimizations Applicable to All Non-3GPP Accesses
12 Interactions Between HSS and AAA Server
12.0 General
12.1 Location Management Procedures
12.2 Subscriber Profile Management Procedures
12.3 Authentication Procedures
...
...
10 Handovers with Optimizations Between 3GPP Accesses and Mobile WiMAX p. 237
10.1 Optimizations for network-controlled dual radio handover p. 237
10.1.1 General Principles p. 237
The solution for network-controlled dual radio handover between 3GPP accesses (GERAN, UTRAN, E-UTRAN) and Mobile WiMAX is based on the concepts of clause 4.1.2 In addition, the following principles apply when the ANDSF functionality is supported by the network and by the UE:
- The EPS shall support mechanisms for delivery of inter-system mobility policies and access network discovery information over the S14 interface, as described in clause 4.8.
-
The inter-system mobility policies shall contain operator-defined rules and preferences that help the UE:
- determine when mobility between mobile WiMAX and 3GPP accesses is restricted or allowed; and
- determine when a 3GPP or mobile WiMAX access is more preferable than the currently used radio access.
- The access network discovery information shall contain information about mobile WiMAX access networks that are available in the vicinity of the UE, if the UE's location is known and if such information is available in the network and allowed by the operator.
-
If a UE discovers a neighbour mobile WiMAX access and determines (based on the inter-system mobility policies and user preferences) that:
- the discovered mobile WiMAX access is more preferable to the currently used 3GPP access; and
- mobility from 3GPP access to mobile WiMAX access is allowed, then the UE shall attempt to handover to the discovered mobile WiMAX access;
-
If a UE discovers one or more neighbour 3GPP accesses and determines (based on the inter-system mobility policies and user preferences) that:
- 3GPP access is more preferable to mobile WiMAX access; and
- mobility from mobile WiMAX access to 3GPP access is allowed, then the UE shall select a neighbour 3GPP access (e.g. based on 3GPP access selection rules) and shall attempt to handover to the selected 3GPP access;
11 Handover Optimizations Applicable to All Non-3GPP Accesses p. 237
<This clause describes handover optimization procedures that are generic and applicable to all non-3GPP accesses.>
12 Interactions Between HSS and AAA Server p. 238
12.0 General p. 238
The interaction between the 3GPP AAA Server and the HSS is not explicitly presented in several Figures of this specification. Though these entities are depicted as "AAA/HSS" in these Figures, these functions are distinct and interact over the SWx reference point.
12.1 Location Management Procedures p. 238
The location management procedures between HSS and 3GPP AAA Server is described in this clause.
Non-3GPP access location management procedures define the process in which the 3GPP AAA Server interacts with the HSS for the following purposes:
- To register the current 3GPP AAA Server address in the HSS for a given 3GPP user. This procedure is invoked by the 3GPP AAA Server after a new subscriber has been authenticated by the 3GPP AAA Server (either at attach and handover). As part of the response, the HSS returns the subscriber's user profile data (QoS profile, user capabilities, etc.) to the 3GPP AAA Server.
- To register the current PDN-GW identity and its association with the UE and APN in the HSS for a given user. This information is provided by the AAA Server to the HSS at attachment to a particular PDN via non-3GPP access.
- To acquire the PDN-GW identity for each of the already allocated PDN Gateway(s) with the corresponding PDN information from the HSS over the SWx reference point for a given UE. This is for the case when the UE has already been assigned PDN Gateway(s) due to a previous attach in a 3GPP access (when the UE is handed over from a 3GPP access to a non-3GPP access).
- To de-register the currently registered 3GPP AAA Server-address in the HSS for a given user and purge any related non-3GPP user status data in the HSS. The 3GPP AAA Server de-registers its address and purges user status data when e.g. the UE has disappeared from non-3GPP access coverage, when another EPC core network entity (e.g. charging system) has initiated a disconnection, when a re-authentication failure in the 3GPP AAA Server occurs, etc. If a UE has changed to a 3GPP access RAT, the 3GPP AAA Server initiated De-Registration procedure should not affect any currently selected PDN-GW identity and APN associated with the UE's PDN Connection stored in the HSS and in use in the 3GPP access.
- HSS-initiated de-registration procedure to purge the UE from the 3GPP AAA server. This happens when the user's subscription has been cancelled or other operator-determined reasons. As a result, the 3GPP AAA server should deactivate any UE tunnel in the PDN-GW and/or detach the UE from the access network.
12.1.1 UE Registration Notification p. 238
After a UE has successfully been authenticated and authorised by the 3GPP AAA Server to make use of a given non-3GPP access (over SWa/STa), ePDG (over SWm) or PDN-GW (over S6b for S2c), the 3GPP AAA Server registers its address to the HSS, unless already done. In turn, the HSS should store the address of the registered 3GPP AAA server for the given user and mark the user as registered in the 3GPP AAA Server. In the response, the HSS returns user profile data.
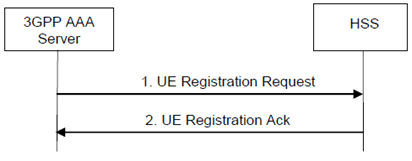
Step 1.
Once the UE has been successfully authenticated by the 3GPP AAA server, the 3GPP AAA Server sends a UE Registration Request (User Identity, Mobile Equipment Identity, 3GPP AAA Server address) to the HSS.
Step 2.
The HSS checks that the user is known and that the stored 3GPP AAA Server address is the same one stored for the user and that it is the same 3GPP AAA Server that previously requested authentication vectors for this same user. If this is successful, the HSS marks the 3GPP AAA Server as the registered 3GPP AAA Server for user. The HSS responds with a UE Registration Ack (User Identity, Subscription Data). The subscription data includes information to be used by the PDN GW selection function or an already selected PDN GW identity and APN if present. The subscription data shall also include an indication of MPS subscription, if the user has an MPS subscription.
12.1.2 AAA-initiated UE De-registration Notification p. 239
The 3GPP AAA Server requests the HSS to De-Register the currently registered UE. In doing so, the 3GPP AAA Server is notifying the HSS that the UE no longer has any context in the 3GPP AAA Server. The HSS should in turn delete the registered 3GPP AAA Server address.
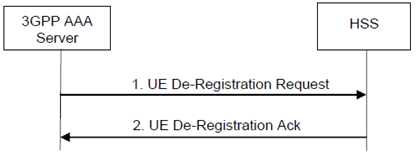
Step 1.
The 3GPP AAA Server sends a UE De-Registration Request (User Identity, Cause) to the HSS. The "Cause" field may take values such as Authentication-Failure, UE-Detached, Charging-System-Request, etc.
Step 2.
The HSS marks the UE as not-registered, removes the 3GPP AAA Server address previously stored for the UE and responds with a UE De-Registration Ack.
12.1.3 HSS-initiated UE De-registration Notification p. 239
The HSS requests the 3GPP AAA Server to de-register a UE, for instance, when a subscription is withdrawn or other operator determined reasons. The 3GPP AAA Server should purge user data, set the user to not-registered and detach the UE and/or deactivate any network resources allocated to the user.
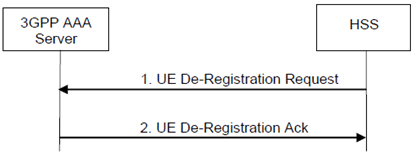
Step 1.
The HSS server sends a UE De-Registration Request (User Identity, Cause) to the 3GPP AAA Server. The "Cause" field may take values such as Subscription Withdrawn, Administrative-Reason, etc.
Step 2.
The 3GPP AAA Server marks the user as not-registered and purges any user data. It responds with a UE De-Registration Ack. In addition, the 3GPP AAA Server should initiate detach of the UE or de-activation of any network resources.
12.1.4 PDN-GW Identity Notification from AAA Server p. 240
For non-emergency services, the 3GPP AAA Server updates the HSS with the PDN-GW identity of the selected PDN-GW and the APN associated with the UE's PDN Connection. For emergency services, the 3GPP AAA server may update the HSS with the PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services. This procedure only occurs when the 3GPP AAA Server has in turn successfully received the PDN-GW identity and APN (or the PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services in case of emergency services) from the PDN-GW the UE is attached to. The 3GPP AAA server should subsequently always update the HSS with the PDN-GW identity in the above-mentioned manner. This procedure is used for PDN-GW registration.
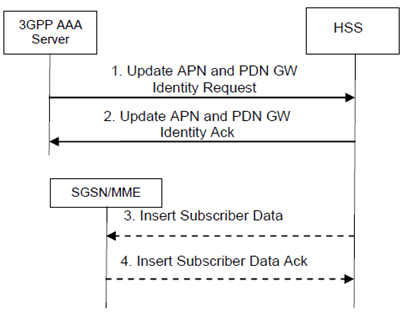
Step 1.
The 3GPP AAA Server sends a Update PDN-GW Identity Request (PDN-GW Identity, APN, User Identity) or a Update PDN-GW Identity Request (PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services) to the HSS.
The PDN-GW identity (or the PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services) is either the IP address (e.g. if the PDN-GW has a single IP address for all the mobility protocols it supports or if it only supports one mobility protocol) or the FQDN (e.g. if the PDN-GW has multiple IP addresses for the mobility protocols it supports).
Step 2.
The HSS checks that the user is known and that the stored 3GPP AAA Server name is the currently registered 3GPP AAA server for this same user. If this is successful, the HSS returns a Update PDN-GW Identity Acknowledgement.
Step 3.
Steps 3-4 are only performed if the PDN-GW identity (or the PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services) information was successfully modified in the HSS and an SGSN or MME is registered in the HSS for the same UE. In this case the HSS sends an Insert Subscriber Data message to the SGSN or MME to update the change in the SGSN or MME. If both an SGSN and an MME is registered in the HSS, and Insert Subscriber Data message is sent to each of them.
Step 4.
The SGSN or MME acknowledges by sending an Insert Subscriber Data Ack message.
12.1.5 PDN-GW Identity Notification from MME/SGSN |R10| p. 241
In case of initial attach, or UE requested PDN connectivity in the 3GPP access, if the Request Type of the UE requested connectivity procedure does not indicate "Emergency", the SGSN/MME updates the HSS with the PDN-GW identity of the selected PDN-GW and the APN associated with the UE's PDN connection. If a 3GPP AAA Server is registered in the HSS for the same UE, the HSS provides the updated APN and PDN-GW identity information to the 3GPP AAA Server.
If, in the case of initial attach or UE requested PDN connectivity in the 3GPP access, the Request Type of the UE requested connectivity procedure indicates "Emergency", the SGSN/MME may update the HSS with the "PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services". If a 3GPP AAA Server is registered in the HSS for the same UE, the HSS provides the "PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services" to the 3GPP AAA Server.
If NBM is used for establishing connectivity in the non-3GPP access, the 3GPP AAA Server notifies the changes to the non-3GPP access network. This procedure is used for PDN-GW registration.
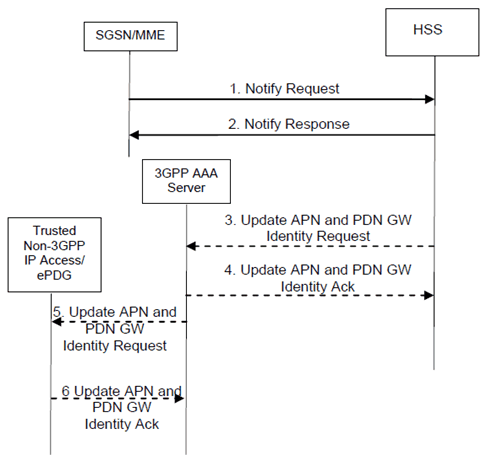
Step 1.
The SGSN/MME sends a Notify Request (PDN-GW Identity, APN, User Identity) or a Notify Request (PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services, User Identity) to the HSS.
Step 2.
The HSS checks that the user is known and that the stored SGSN/MME is the currently registered SGSN/MME for this same user. If this is successful, the HSS returns a Notify Response.
Step 3.
Steps 3-4 are only performed if the PDN-GW identity (or the PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services) information was successfully modified in the HSS and a 3GPP AAA Server is registered in the HSS for the same UE. In this case the HSS sends Update APN and PDN-GW Identity Request message to the 3GPP AAA Server.
Step 4.
The 3GPP AAA Server acknowledges by sending a Update APN and PDN-GW Identity Ack message.
Step 5.
If NBM is used for establishing connectivity in the non-3GPP IP access, the 3GPP AAA Server updates the ePDG/trusted non-3GPP IP access network with the new APN and PGW Identity data by sending Update APN and PDN-GW Identity message.
Step 6.
The ePDG/trusted non-3GPP IP access network acknowledges by sending Update APN and PDN-GW Identity Ack message.
12.2 Subscriber Profile Management Procedures p. 242
The subscriber profile management procedures between HSS and 3GPP AAA Server is described in this clause.
The procedure is invoked by the HSS when the subscriber profile has been modified and needs to be sent to the 3GPP AAA Server. This may happen due to a modification of user profile data in the HSS.
The 3GPP AAA Server may also request the user profile data from the HSS. This procedure is invoked when for some reason the subscription profile of a subscriber is lost or needs to be updated.
12.2.1 HSS-initiated User Profile Update Procedure p. 242
The HSS may send a User Profile Update request to the 3GPP AAA Server whenever the subscriber profile in the HSS is modified since it was previously sent to the 3GPP AAA Server. The User Profile Update procedure is depicted in the following Figure.
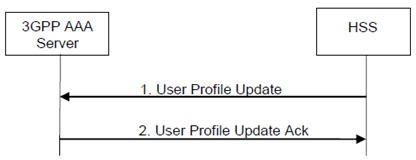
Step 1.
The HSS sends a User Profile Update (User Identity, Subscription Data) message to the 3GPP AAA Server. If the HSS is aware of the non-3GPP access type it may return only the subscription data that affects the non-3GPP access.
Step 2.
The 3GPP AAA Server updates its subscription data and acknowledges the User Profile Update message by returning a User Profile Update Ack (User Identity) message. As a result, the 3GPP AAA Server may need to update the non-3GPP access network and the PDN-GW with new authorisation data, new service authorisation data and new subscribed QoS data.
12.2.2 AAA-initiated Provide User Profile Procedure p. 242
The 3GPP AAA Server may send a Provide User Profile request to the HSS when the user subscription profile of a subscriber is lost or is corrupt or for any other reason.
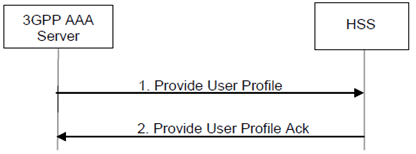
Step 1.
The 3GPP AAA Server sends a Provide User Profile (User Identity) to the HSS.
Step 2.
The HSS checks that the user is known and that the stored 3GPP AAA Server address is the same one stored for the user and that it is the same server that previously requested authentication of the same user. If this is successful, the HSS returns a Provide User Profile Ack (user identity, subscription data). If the HSS is aware of the non-3GPP access type it may return only the subscription data that affects the non-3GPP access.
12.3 Authentication Procedures p. 243
The authentication procedures between HSS and 3GPP AAA Server are described in TS 33.402.
The authentication procedures define the process in which the 3GPP AAA Server interacts with the HSS to acquire necessary data (i.e. Authentication Vectors for EAP-AKA or EAP-AKA') from the HSS to successfully authenticate the user for accessing the non-3GPP system.