Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
6.15 IPv4 Home Address Release Procedure for S2c
6.16 Enhanced security support for S2c
6.16.1 General
6.16.2 Activation of enhanced security for S2c
6.16.3 De-activation of enhanced security for S2c
...
...
6.15 IPv4 Home Address Release Procedure for S2c p. 153
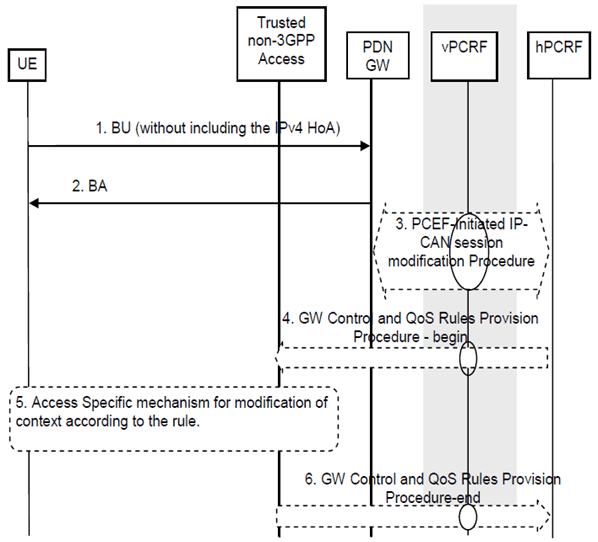
This procedure is initiated by the UE to release an IPv4 Home Address previously registered at the PDN-GW.
The optional interaction steps between the gateways and the PCRF in the procedures only occur if dynamic policy provisioning is deployed. Otherwise policy may be statically configured in the gateway.
The roaming (Figure 4.2.3-1), Local Breakout (Figure 4.2.3-4) and non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-1) scenarios are depicted in the Figure. In the roaming case, the vPCRF acts as an intermediary, relaying the PCC messages between the hPCRF in the HPLMN to the BBERF/PCEF in the VPLMN. In the non-roaming case, the vPCRF is not involved at all. In the Roaming and LBO cases, the 3GPP AAA Proxy serves as an intermediary between the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access and the 3GPP AAA Server in the HPLMN.
Step 1.
If the UE has previously registered IPv4 home address and wants to release it, the UE sends a Binding Update (IPv6 HoA, lifetime) message to the PDN-GW without including the IPv4 HoA, indicating de-registration for the IPv4 Home Address only.
Step 2.
The PDN-GW modifies the existing entry to delete the IPv4 home address implied in the Binding Update message from its Binding Cache and releases all associated resources, and then sends a Binding Ack message to the UE.
Step 3.
The PDN-GW initiates the PCEF initiated IP-CAN session modification procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the PCRF of the deleted IPv4 address. If PCC rules have changed the PCRF provides the updated PCC rules to the PDN-GW as part of this procedure.
Step 4.
In case QoS rules have to be modified, e.g. change of SDF filters, the PCRF initiates a GW Control and QoS rules provision procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the S-GW of the updated QoS rules.
Step 5.
An IP-CAN specific or resource release procedure may be triggered by the enforcement of the received policy rules.
Step 6.
The Trusted non-3GPP access informs the PCRF of the success of the QoS rules enforcement, thus ending the GW Control and QoS rules provision procedure described in TS 23.203.
6.16 Enhanced security support for S2c |R10| p. 155
6.16.1 General p. 155
Optionally UE and PDN-GW may support integrity protection and/or confidentiality protection of user plane traffic exchanged over the S2c tunnel when the UE is in a trusted non-3GPP access.
6.16.2 Activation of enhanced security for S2c p. 155
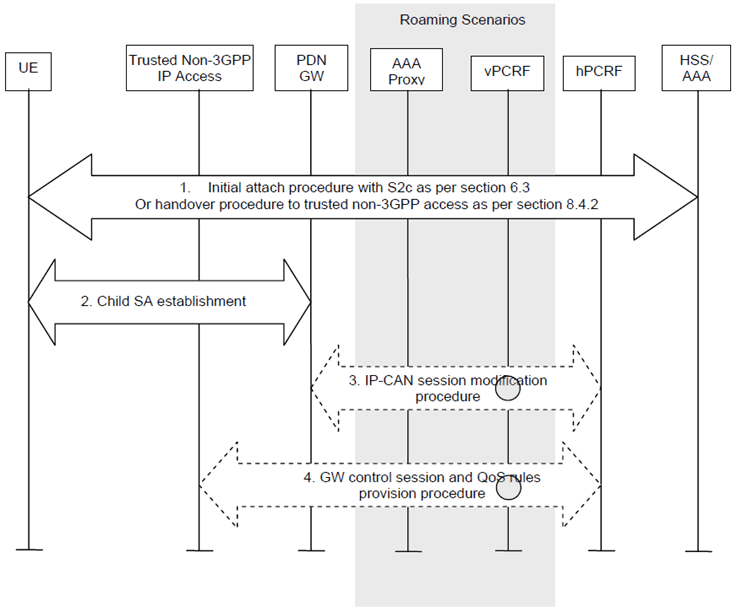
Step 1.
The UE performs an initial attach procedure to a trusted non-3GPP access with S2c as described in clause 6.3 or performs a handover procedure to a trusted non-3GPP access as specified in clause 8.4.2. At the end of this step the UE is connected to a trusted non-3GPP access via S2c.
Step 2.
At any time when the UE is connected to a trusted non-3GPP access the UE or the PDN-GW may trigger the creation of a child IPsec Security Association for protecting the traffic sent via the S2c reference point. The child SA is created as specified in RFC 4877. The child SA may provide user plane integrity protection. Additionally, the same child SA may be used also for user plane confidentiality protection.
Step 3.
The PDN-GW initiates an IP-CAN session modification procedure to provide to the PCRF new tunnel information.
Step 4.
Based on the tunnel information provided by the PDN-GW, the PCRF initiates a QoS rules provision procedure to the trusted non-3GPP access indicating the new tunnel information.
6.16.3 De-activation of enhanced security for S2c p. 156
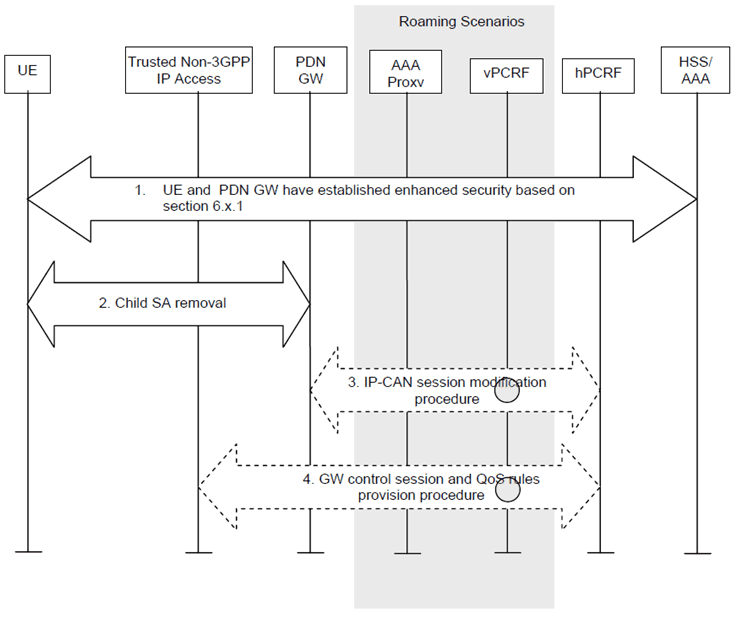
Step 1.
The UE and the PDN-GW have established enhanced security based on clause 6.16.1. As a result user plane traffic exchanged through S2c is integrity protected and/or confidentiality protected.
Step 2.
At any time the UE or the PDN-GW may trigger the removal of a child IPsec Security Association for protecting the traffic sent via the S2c reference point. The child SA is removed as specified in RFC 4877.
Step 3.
The PDN-GW initiates an IP-CAN session modification procedure to provide to the PCRF new tunnel information.
Step 4.
Based on the tunnel information provided by the PDN-GW, the PCRF initiates a QoS rules provision procedure to the trusted non-3GPP access indicating the new tunnel information.