Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
13 Information Storage
13.0 General
13.1 HSS
13.2 MME
13.3 S-GW
13.4 Handling of Wild Card APN
13.5 ePDG
13.6 TWAN
15 Functional Description and Procedures for 3GPP Accesses with S2c
...
...
13 Information Storage p. 243
13.0 General p. 243
This clause describes the additional information stored in different nodes while the UE is in non-3GPP access.
The information provided in clauses 13.1, 13.2 and 13.3 is incomplete in this Release of the specification and intended only for information. Detailed information is available in corresponding stage 3 specifications.
13.1 HSS p. 243
The data held in the HSS when non 3GPP accesses are not used is defined in TS 23.401.
The additional data held in the HSS when non 3GPP accesses are used is defined in Table 13.1-1 below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| 3GPP AAA Server name | The Identity of the 3GPP AAA Server serving the UE currently. |
| QoS profile per access | The quality of service profile subscribed for a particular access for a specific APN |
| ODB | Indicates that the status of the operator determined barring for a specific access. |
| Access Restriction | Indicates the access restriction subscription information. |
13.2 MME p. 244
Information storage for the MME is described in TS 23.401. The additional data held in the MME when optimized interworking with CDMA2000 HRPD is used is defined in Table 13.2-1 below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| S101 HRPD access node IP address | The IP address of the HRPD AN used for the S101 tunnel for a UE. This is stored on a per UE basis. |
| S103 Forwarding Address | HS-GW IP address used for data forwarding to the HRPD access over S103 interface. This is stored on a per UE basis. |
| S103 GRE key(s) | GRE Key(s) used for the data forwarding tunnel to the HS-GW - one per PDN connection. This is stored on a per PDN connection basis. |
13.3 S-GW p. 244
Information storage for the S-GW is described in TS 23.401. The additional data held in the S-GW when optimized interworking with CDMA2000 HRPD is used is defined in Table 13.3-1 below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| S103 Forwarding Address | HS-GW IP address used for data forwarding to the HRPD access over S103 interface. This is stored on a per UE basis. |
| S103 GRE key(s) | GRE Key(s) used for the data forwarding tunnel to the HS-GW - one per PDN connection. This is stored on a per PDN connection basis. |
13.4 Handling of Wild Card APN p. 244
When the wild card APN is present in the subscription context, the UE is authorized to connect to APNs which are not present in the subscription context.
When a request is received for registering a PDN-GW ID for such an active APN which is not present in the subscription context, the nodes (HSS/MME/ S4 SGSN/AAA Server/Non-3GPP access) shall store the PDN-GW ID and the APN for the UE.
When a request is received for deregistering of PDN-GW ID, for such an active APN which is not present in the subscription context, the nodes (HSS/MME/ S4 SGSN/AAA Server/Non-3GPP access) shall delete the PDN-GW ID and the APN for the UE.
13.5 ePDG |R14| p. 244
Information storage for the ePDG required for emergency services is defined in Table 13.5-1 below.
The ePDG Emergency Configuration Data is used instead of UE subscription data received from the HSS, for all emergency bearer services that are established by an ePDG on UE request.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Access Point Name (em APN) | A label according to DNS naming conventions describing the access point used for Emergency PDN connection (wild card not allowed). |
| Emergency QoS profile | The bearer level QoS parameter values for Emergency APN's default bearer (QCI and ARP). The ARP is an ARP value reserved for emergency bearers. |
| Emergency APN-AMBR | The Maximum Aggregated uplink and downlink MBR values to be shared across all Non-GBR bearers, which are established for the Emergency APN, as decided by the PDN-GW. |
| Emergency PDN-GW identity | The statically configured identity of the PDN-GW used for emergency APN. The PDN-GW identity may be either an FQDN or an IP address. |
| Emergency fallback PDN-GW identity | Optional. The statically configured identity of the fallback PDN-GW used for emergency APN. The fallback PDN-GW identity may be either an FQDN or an IP address. |
13.6 TWAN |R14| p. 245
Information storage for the TWAN required for emergency services is defined in Table 13.6-1 below.
The TWAN Emergency Configuration Data is used instead of UE subscription data received from the HSS, for all emergency bearer services that are established by an TWAN on UE request.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Access Point Name (em APN) | A label according to DNS naming conventions describing the access point used for Emergency PDN connection (wild card not allowed). |
| Emergency QoS profile | The bearer level QoS parameter values for Emergency APN's default bearer (QCI and ARP). The ARP is an ARP value reserved for emergency bearers. |
| Emergency APN-AMBR | The Maximum Aggregated uplink and downlink MBR values to be shared across all Non-GBR bearers, which are established for the Emergency APN, as decided by the PDN-GW. |
| Emergency PDN-GW identity | The statically configured identity of the PDN-GW used for emergency APN. The PDN-GW identity may be either an FQDN or an IP address. |
| Emergency fallback PDN-GW identity | Optional. The statically configured identity of the fallback PDN-GW used for emergency APN. The fallback PDN-GW identity may be either an FQDN or an IP address. |
14 Void
15 Functional Description and Procedures for 3GPP Accesses with S2c p. 245
15.1 S2c Bootstrapping via DSMIPv6 Home Link p. 245
When connected over the UE home link (i.e. 3GPP access as defined in clause 4.1), the UE may trigger the establishment of S2c IKEv2 SA, e.g. to optimize future handovers to non-3GPP accesses using S2c. For each PDN connection, the S2c IKEv2 SA establishment has to be performed separately.
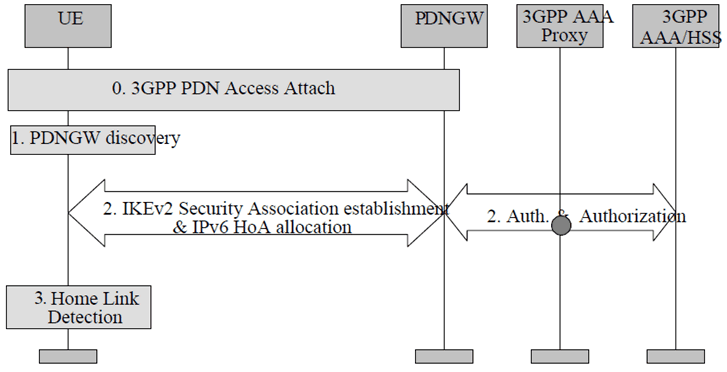
Step 0.
In this procedure it is assumed that UE is already attached to the PDN over the 3GPP access system as defined in TS 23.401. This step, according to TS 23.401 could be an initial attach to a default PDN or a UE initiated subsequent attach to another PDN.
Step 1.
The UE discovers the PDN-GW providing access to the PDN it connected to in Step 0, as defined in the clause 4.5.2. To ensure reachability of the PDN-GW, signalling associated with this step as well as step 2 below, should be performed over the connection established by step 0 above.
Step 2.
A security association is established between the UE and PDN-GW to secure the DSMIPv6 messages related to this PDN connection between the UE and the PDN-GW.
The UE initiates the establishment of the security association using IKEv2, RFC 5996; EAP, RFC 3748 is used over IKEv2 for authentication purposes. The PDN-GW communicates with the AAA infrastructure in order to complete the authentication.
During this step an IPv6 home prefix is assigned by the PDN-GW to the UE as defined in RFC 4877. During this step the UE shall include the IPv6 Home Address and may include the APN of the PDN it wants to access. The PDN-GW address and APN associated with the UE's PDN Connectivity are registered by the AAA server with the HSS as described in clause 12.
In this step, the PDN-GW may be either in the HPLMN or in the VPLMN. When the PDN-GW is in the VPLMN, the interaction between the PDN-GW in the VPLMN with the AAA/HSS in the HPLMN may involve a 3GPP AAA Proxy in the VPLMN.
Step 3.
UE confirms that it is located in its DSMIPv6 home link for the given PDN, as described for DSMIPv6 Home Link Detection Function in clause 4.5.6.
In some cases this procedure may result in a PDN-GW that is different than the one the UE is connected to in step 0. In this case the PDN-GW reallocation procedure defined in clause 6.10 is applied.