Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
8.2.1.3 General Procedure for GTP-based S5/S8 for UTRAN/GERAN p. 193
The steps involved in the handover from a trusted/untrusted non-3GPP IP access to UTRAN/GERAN connected to EPC are depicted below for both the non-roaming and roaming cases and when PMIPv6 is used on S2a or S2b. It is assumed that while the UE is served by the trusted/untrusted non-3GPP IP access, a PMIPv6 tunnel is established between the non-3GPP access network and the PDN-GW in the EPC.
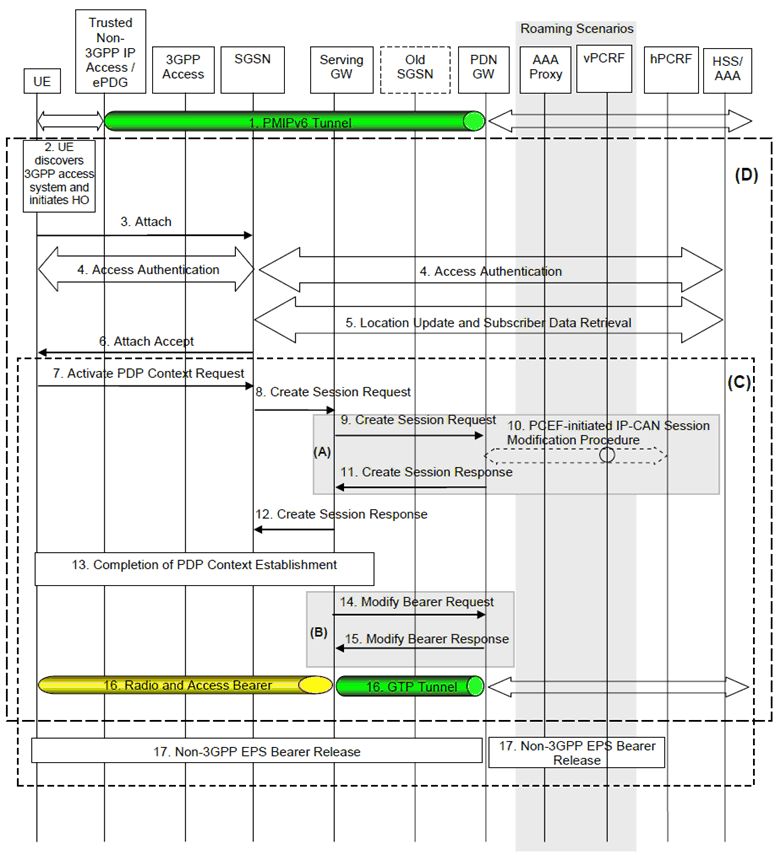
Figure 8.2.1.3-1: Handover from Trusted/untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access to UTRAN/GERAN with PMIP on S2a and GTP based S5/S8
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
In case of connectivity to multiple PDNs the following applies:
- If the UE is connected to both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, steps 2 to 6 shall be skipped.
- If the UE is connected only to non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, steps 2 to 6 shall be performed.
- The steps in (C) shall be repeated for each PDN connection that is being transferred from non-3GPP access.
Step 1.
The UE uses a trusted/untrusted non-3GPP access system and is being served by PDN-GW (as PMIPv6 LMA).
Step 2.
The UE discovers the 3GPP Access system (UTRAN or GERAN) and determines to transfer its current sessions (i.e. handover) from the currently used non-3GPP access system to the discovered 3GPP Access system. The mechanisms that aid the UE to discover the 3GPP Access system, are specified in clause 4.8 (Network Discovery and Selection).
Step 3.
The UE sends an Attach Request to the SGSN. The message from the UE is routed by 3GPP Access to the SGSN as specified in clause 6.5 of TS 23.060.
Step 4.
The SGSN may contact the HSS and authenticate the UE as described in TS 23.060.
Step 5.
The SGSN may perform location update procedure and subscriber data retrieval from the HSS as specified in TS 23.060. PDN-GW identity information is part of the subscriber data.
Step 6.
The SGSN sends the Attach Accept request to the UE to indicate the completion of the attach procedure as defined in TS 23.060.
Step 7.
The UE initiate at this stage this establishment of the primary PDP context as defined in clause 9.2.2 of TS 23.060.
Step 8.
The SGSN selects a Serving-GW as described in TS 23.060 and sends Create Session Request (Handover indication, and other parameters described in TS 23.060) message to the selected Serving-GW.
Step 9.
The Serving-GW sends a Create Session Request message to the PDN-GW as described in TS 23.060. The PDN-GW should not switch the tunnel from non-3GPP IP access to 3GPP access system at this point.
Step 10.
The PDN-GW may execute a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203 to report e.g. change in IP-CAN type.
Since the PDN-GW does not switch the tunnel in step 9, it defers any modification to the PCC Rules (due to changes received from the PCRF, if there is PCRF interaction) and still applies the existing PCC Rules for charging and policy until step 14.
Depending on the active PCC rules, the establishment of dedicated bearers for the UE may be required.
Step 11.
The PDN-GW responds with a Create Session Response message to the Serving-GW as described in TS 23.060.The Create Session Response contains the IP address or the prefix that was assigned to the UE while it was connected to the non-3GPP IP access. It also contains the Charging Id previously assigned to the PDN connection in the non-3GPP access although the Charging Id still applies to the non-3GPP access.
Step 12.
The Serving-GW returns a Create Session Response message to the SGSN as specified in TS 23.060. This message also includes the IP address of the UE. This message also serves as an indication to the SGSN that the S5 bearer setup and update has been successful.
Step 13.
The rest of the PDP context establishment as specified in TS 23.060 is completed here.
Step 14.
The Serving-GW sends a Modify Bearer Request message to the PDN-GW in the VPLMN or the HPLMN including the Handover Indication flag that prompts the PDN-GW to tunnel packets from non 3GPP IP access to 3GPP access system and immediately start routing packets to the Serving-GW for the default and any dedicated EPS bearers established. In case of non-roaming or roaming with home routed traffic this message is sent to the PDN-GW in the HPLMN. In case of local breakout traffic the message is sent to the PDN-GW in the VPLMN.
In this step, the PDN-GW applies any modification to the PCC Rules received from the PCRF, if there is PCRF interaction in step 10. The Charging Id previously in use for the PDN connection in the non-3GPP access now only applies to the default bearer in use in GERAN/UTRAN access. If dedicated bearers are created, a new Charging Id is assigned by the PGW for each of them according to TS 23.401.
Step 15.
The PDN-GW acknowledges by sending Modify Bearer Response to the Serving-GW.
Step 16.
The UE sends and receives data at this point via the 3GPP access system.
Step 17.
The PDN-GW shall initiate resource allocation deactivation procedure in the trusted/untrusted non-3GPP IP access as defined in clause 6.12 or clause 7.9.
8.2.1.4 Using PMIP-based S5/S8 p. 196
When a Trusted/untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access to UTRAN/GERAN handover occurs, the following steps are performed instead of and in addition to the steps performed in the GTP based S5/S8 case (see previous clause). In the case of PMIP based S5/S8, a Create Session Request and Modify Bearer Request is not sent from the Serving-GW to the PDN-GW. Rather, the serving GW interacts with the hPCRF and PMIP messages are exchanged between the Serving-GW and the PDN-GW.
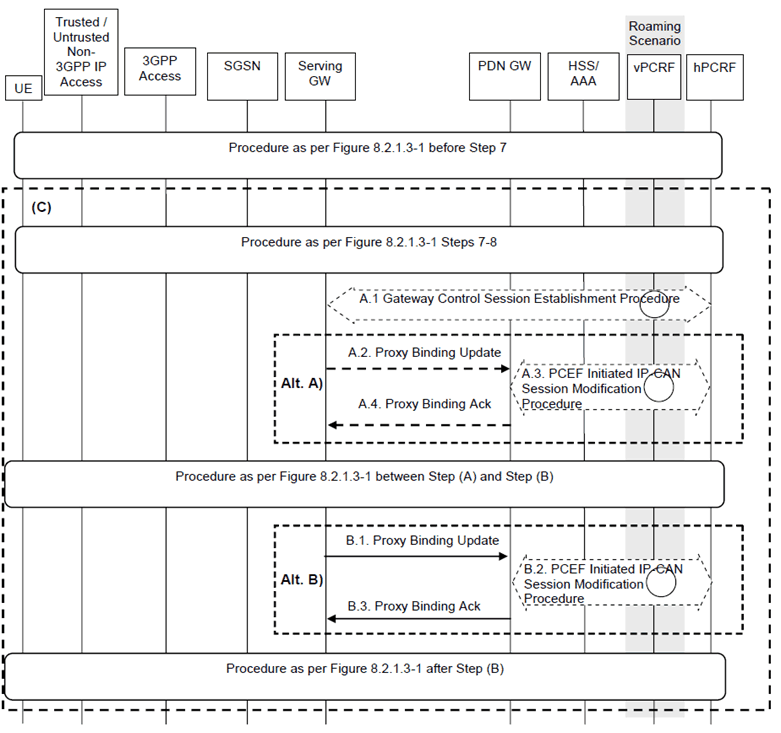
Figure 8.2.1.4-1: Trusted/untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access to GERAN/UTRAN over PMIP-based S2a and using PMIP-based S5/S8
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
In case of connectivity to multiple PDNs the following applies:
- If the UE is connected to both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, the procedure as per Figure 8.2.1.3-1 before step 7 shall be skipped.
- If the UE is connected only to non-3GPP access before the handover of PDN connections to 3GPP access is triggered, the procedure as per Figure 8.2.1.3-1 before step 7 shall be performed.
- The steps in (C) shall be repeated for each PDN connection that is being transferred from non-3GPP access.
Step A.1.
The description of steps A.1 to A.4 and B.1 to B.3 are the same as in clause 8.2.1.2.
The Serving-GW initiates a Gateway Control Session Establishment Procedure with the PCRF as specified in TS 23.203 to obtain the rules required for the Serving-GW to perform the bearer binding for all the active sessions the UE may establish as a result of the handover procedure.
If the updated PCC rules require establishment of dedicated bearer for the UE, the establishment of those bearers take place before step B.1.