Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
4.7 IP Address Allocation p. 49
4.7.1 IP Address Allocation with PMIP-based S5/S8 p. 49
The IP address allocation mechanisms described in clause 5.3.1.1 of TS 23.401 are also valid for the PMIP based S5/S8. This clause is complementary to clause 5.3.1 of TS 23.401 and describes the differences in the IP Address allocation when PMIP-based S5/S8 is used.
For IP address allocation with PMIP-based S5/S8, the following clarifications apply:
-
If the PDN Type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4:
- If initial and handover attach and deferred IPv4 address allocation is not used, the IPv4 address is allocated via default bearer activation. This case does not present any architecture differences from the GTP based S5/S8 described in clause 5.3.1.2.1 of TS 23.401. In this case, the Serving-GW shall request IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. Then the IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW and returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement.
- If initial and handover attach and deferred IPv4 address allocation is used, the IPv4 address allocation and IPv4 parameter configuration via DHCPv4 according to RFC 2131 and RFC 4039 procedure does not present any architecture differences from the GTP based S5/S8 described in clause 5.3.1.2.4 of TS 23.401, except that the Serving-GW shall have DHCPv4 relay agent functionality. The Serving-GW shall request IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. Then the IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW and returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The PDN-GW shall also send the DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication in the same Proxy Binding Acknowledgement message. In this case, the UE IPv4 address assigned by the PDN-GW is not provided as part of the default bearer activation procedures to the UE. The Serving-GW replaces the IPv4 address assigned by the PDN-GW to 0.0.0.0 in the response message to the MME. The MME then forwards the 0.0.0.0 address to the UE. After the default bearer establishment procedure is completed, the UE uses the connectivity with the EPS and initiates the IPv4 address allocation on its own using DHCPv4 as specified in Figure 4.7.1-1. The IPv4 address provided to the UE by DHCPv4 procedure shall correspond to the value provided in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement message.
- If the IPv4 address is allocated by using DHCPv4 procedure, then at any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or the IPv4 address lease time expires, the PDN-GW initiates the "PDN-GW initiated PDN-disconnection" procedure for the given PDN connection. The same IPv4 address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
-
If the PDN Type associated with the PDN connection is IPv6:
- IPv6 network prefix allocation via IPv6 Stateless Address auto-configuration: The IPv6 network prefix is assigned by the PDN-GW and returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The Serving-GW shall advertise the same information as the PDN-GW would advertise with GTP based S5/S8. To ensure that link-local address generated by the UE does not collide with the link-local address of the Serving-GW, the PDN-GW shall provide an interface identifier to the UE and the UE shall use this interface identifier to configure its link-local address. For stateless address auto-configuration however, the UE can choose any interface identifier to generate IPv6 address, other than link-local, without involving the network. The PDN-GW shall also provide a link-local address to the Serving-GW and the Serving-GW shall use the link-local address on the access link shared with the UE. In the case of PMIP-S5/S8 because any prefix that the Serving-GW will advertise to the UE is unique, there is no need for the UE to perform Duplicate Address Detection for global uniqueness for any IPv6 address configured from the allocated IPv6 network prefix. However, the Serving-GW shall respond with Neighbor Advertisement upon receiving Neighbor Solicitation messages from a given UE. For example, the UE may perform Neighbor Unreachability Detection towards the Serving-GW, the Serving-GW supports the DAD related functionality similar to that supported by PDN-GW in the case of GTP based S5/S8 described in clause 5.3.1.2.2 of TS 23.401. Otherwise the PDN-GW has the same functions as it is defined in clause 5.3.1.2.2 of TS 23.401.
- IPv6 parameter configuration via Stateless DHCPv6 procedure does not present any architecture differences from the GTP based S5/S8 described in clause 5.3.1.2.3 of TS 23.401, except that the Serving-GW shall have DHCPv6 relay agent functionality. The P-GW notifies the UE with the same DNSv6 information as was provided via PCO during the PDN connection establishment procedure, e.g. Attach, if DHCPv6 procedure is performed by the UE.
- If sent, the router solicitation from the UE comes subsequent to the Attach procedure, as shown in Figure 4.7.1-2. The IPv6 network prefix assigned in the PMIP Binding Acknowledgement is sent in the Router Advertisement.
-
If the PDN type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4v6:
- The IPv6 network prefix allocation via IPv6 Stateless Address auto-configuration procedure and IPv6 parameter configuration via Stateless DHCPv6 procedure are the same as for PDN type IPv6 defined in pervious bullets.
- If initial attach and deferred IPv4 address allocation is used, the Serving-GW shall request both IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. In this case no IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW during the attach procedure. Only IPv6 network prefix is returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The PDN-GW shall also send the DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication in the same PBA message. Then the Serving-GW shall respond to the UE by setting the IPv4 PDN Address to 0.0.0.0. The UE may obtain an IPv4 address subsequently, by initiating DHCPv4 procedure as specified in Figure 4.7.1-1.
- If initial attach and deferred IPv4 address allocation is not used, the Serving-GW shall request both IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. In this case IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW during the attach procedure. IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address is returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The Serving-GW shall deliver IPv4 address to the UE.
- For handover attach (i.e. Request Type set to "handover"), the Serving-GW shall request both IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update, irrespective of whether the UE requested deferred IPv4 address or not. The previously assigned IPv6 network prefix and/or IPv4 address are returned to the Serving Gateway in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement during the handover attach procedure. If deferred IPv4 address allocation is used for this PDN connection, the PDN-GW shall also send the DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication in the same PBA message. In this case, the UE IPv4 address is not provided as part of the default bearer activation procedures to the UE. The Serving-GW shall respond to the MME by setting the PDN Address to 0.0.0.0. The MME then forwards the 0.0.0.0 address to the UE. After the default bearer establishment procedure is completed, the UE uses the connectivity with the EPS and may renew the IPv4 address allocation using DHCPv4. The IPv4 Address provided to the UE by subsequent DHCPv4, when initiated by the UE, must correspond to the value provided in the PBA.
- If the IPv4 address is provided to the UE by using DHCPv4 procedure, then at any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or IPv4 address lease time expires, the PDN-GW initiates the "PDN Gateway initiated IPv4 address Delete" procedure to delete the IPv4 address from the PDN connection and bearer contexts. The same IPv4 address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
- If an external PDN Address Allocation is needed, the PDN-GW follows the same procedures defined in TS 23.401 to obtain the external IP address after the PBU is received and before the PBA is sent.
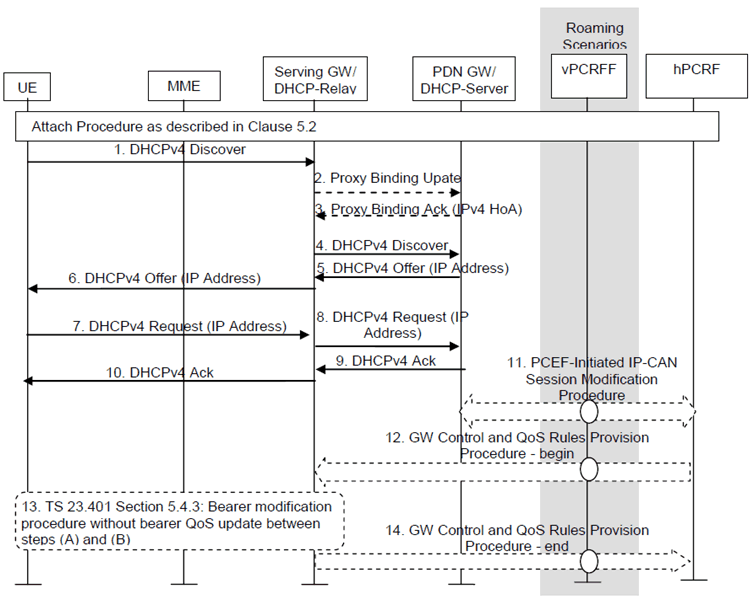
Figure 4.7.1-1: IPv4 Address Allocation using DHCP with DHCP Server Collocated with the PDN-GW and DHCP Relay in the Serving-GW
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
If the PDN type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4v6 or IPv4, after the default bearer is setup, the UE sends a DHCPv4 Discovery message in broadcast to the network to find available servers.
Steps 2-3 and 11-14 are only executed if the PDN type is IPv4v6 and IPv4 address was not allocated by the PDN-GW in the initial attach procedure. The interaction of PBU messages (2-3) with DHCPv4 related messages (1, 4-10) is based on RFC 5844.
Step 2.
The Serving-GW sends a Proxy Binding Update (MN NAI, APN, UE Address Info) to the PDN-GW in order to request the new IPv4 address and update the current registration. The MN NAI identifies the UE for whom the message is being sent. To request for IPv4 address for the UE, the UE Address Information should contain IPv4 address option set to 0.0.0.0, and the HNP shall be set to the HNP of the IP-CAN Session.
Step 3.
The PDN-GW responds with a PMIPv6 Binding Acknowledgement (MN NAI, UE Address Info) message to the Serving-GW. The MN NAI is identical to the MN NAI sent in the Proxy Binding Update. The PDN-GW takes into account the request from Serving-GW and the policies of operator when the PDN-GW allocates the UE Address Info. The UE address info returns the assigned IPv4 Address and/or IPv6 prefix previously assigned to the UE during attach, if one was requested in the PMIPv6 Proxy Binding Update message. Otherwise, the PDN-GW validates the addresses and returns in the UE Address Info IE the IPv4 address and/or IPv6 prefix received in the Proxy Binding Update message.
Step 4.
Upon receiving the DHCPv4 Discovery message, the Serving-GW acting as a relay agent shall add its address in the GIADDR option and add the assigned UE IPv4 address (received from PDN-GW at the PBA message), if available in the "Address Request" option, and relay the message in unicast within the PMIPv6 tunnel to PDN-GW acting as a DHCPv4 server.
Step 5.
When receiving the DHCPv4 Discovery message, the PDN-GW should verify the GIADDR option. Then the PDN-GW uses "Address Request" option and/or the PMIPv6 tunnel on which the DHCPv4 message is received to identify the UE binding and update it with the 'client identifier' and 'chaddr' combination for subsequent DHCPv4 procedure. After that the PDN-GW extends an IPv4 lease offer and sending the DHCPv4 Offer with the assigned UE IPv4 address.
Step 6.
The Serving-GW acting as DHCPv4 relay agent relays the DHCPv4 message to the UE.
Step 7.
When the UE receives the lease offer, it sends a DHCPREQUEST message containing the received IPv4 address.
Step 8.
The Serving-GW acting as DHCPv4 relay agent relays the DHCPv4 message to the PDN-GW.
Step 9.
When the PDN-GW receives the DHCPREQUEST message from the UE, it sends a DHCPACK packet to the UE. This message includes the lease duration and any other configuration information that the client might have requested.
Step 10.
The Serving-GW acting as DHCPv4 relay agent relays the DHCPv4 message to the UE.
When receiving the DHCPACK message, the UE completes TCP/IP configuration process.
Step 11.
In case a new IPv4 address is allocated, the PDN-GW initiates the PCEF initiated IP-CAN session modification procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the PCRF of the IPv4 address allocated to the UE. If PCC rules have changed the PCRF provides the updated PCC rules to the PDN-GW as part of this procedure.
Step 12.
In case QoS rules have to be modified, e.g. change of SDF filters, the PCRF initiates a GW Control and QoS rules provision procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the S-GW of the updated QoS rules.
Step 13.
The S-GW initiates the "Bearer Modification Procedure without bearer QoS update" as described in clause 5.4.3 of TS 23.401, between steps (A) and (B).
Step 14.
The S-GW informs the PCRF of the success of the QoS rules enforcement, thus ending the GW Control and QoS rules provision procedure described in TS 23.203.
The PDN-GW shall discard the unicast DHCPv4 Discovery or Request message with an empty or unknown GIADDR option, if the assigned UE IPv4 address is not delivered to the UE yet.
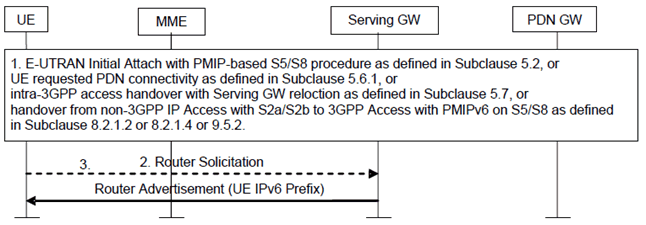
Figure 4.7.1-2: IPv6 Prefix allocation after the PDN connection setup procedure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
A PDN connection is setup over 3GPP access, after the E-UTRAN initial Attach with PMIP-based S5/S8 procedure as defined in clause 5.2, UE requested PDN connectivity as defined in clause 5.6.1, or intra-3GPP access handover with Serving-GW relocation as defined in clause 5.7, or handover from non-3GPP IP Access with S2a/S2b to 3GPP Access with PMIPv6 on S5/S8 as defined in clause 8.2.1.2 or 8.2.1.4.
Step 2.
If the PDN type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4v6 or IPv6, the UE may send a Router Solicitation message to the network to solicit a Router Advertisement message.
Step 3.
Upon receiving the Route Solicitation message or after the PDN connection setup procedure, the Serving-GW shall send an IPv6 Router Advertisement message as specified in RFC 4862 to the UE for PDN connection type IPv4v6 or IPv6 (i.e. the Serving-GW acts as an advertising interface as specified in RFC 4861 for the PDN connection type IPv4v6 or IPv6). The Router Advertisement messages shall contain the assigned IPv6 prefix received in the PMIPv6 Binding Acknowledgement message. After the UE has received the Router Advertisement message, it constructs a full IPv6 address via IPv6 Stateless Address autoconfiguration in accordance with RFC 4862. However, the UE shall not use any identifiers defined in TS 23.003 as the basis for generating the interface identifier. For privacy, the UE may change the interface identifier used to generate full IPv6 address, as defined in TS 23.221 without involving the network.
When sending the IPv6 Router Advertisement message, the Serving-GW may trigger the paging (e.g. by sending a Downlink Data Notification message to the MME) if the UE is in idle state.