Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
4.7.2 IP Address Allocation in Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access using PMIPv6 on S2a
4.7.3 IP Address Allocation in Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access using PMIPv6 or GTP on S2b
4.7.4 IP Address Allocation using S2c
4.7.5 IPv6 Prefix Delegation using S2c
4.7.6 IPv6 Prefix Delegation using PMIP-based S5/S8
...
...
4.7.2 IP Address Allocation in Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access using PMIPv6 on S2a p. 54
IP address is allocated to the UE when connectivity to new PDN is initiated. The IP address can be provided by either PDN-GW or external PDN. Access GW in trusted non-3GPP access system is responsible for delivering the IP address to the UE. Based on the signalling between the UE and the non-3GPP IP access system the UE should be able to know the connected PDN identity (APN). This enables the UE to uniquely associate each allocated IP address with the PDN from where it was allocated.
The trusted non-3GPP Access shall support at least one of the following functionalities in order to successfully allocate IP address to the UE in the EPC:
-
Support of DHCPv4 relay agent functionality for IPv4 parameter configuration and IP address allocation as specified in RFC 2131 and RFC 4039 and described in clause 4.7.1 for the Serving-GW. This functionality is used to support DHCPv4 based IPv4 address allocation mechanism in the UE. For this case the following applies:
- At initial attach or handover attach, if the PDN type is IPv4 only, the trusted non-3GPP IP Access shall request IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. The Protocol Configuration Options in the Proxy Binding Update includes the Address Allocation Preference to indicate that deferred IPv4 address allocation was requested by the UE. In the same way as it is defined in clause 4.7.1, the IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW during the initial attach procedure and the IPv4 address is returned in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication is included in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement to indicate that IPv4 address allocation using DHCPv4 is allowed. The MAG shall not deliver the assigned IPv4 address to the UE before the DHCPv4 address allocation. After the PMIPv6 tunnel is set up between the trusted non-3GPP Access and the PDN-GW, the trusted non-3GPP Access may relay the DHCPv4 messages between the UE and the PDN-GW for IPv4 parameter configuration and IPv4 address allocation as specified for the Serving-GW in Figure 4.7.1-1.
- At initial attach and handover attach, if the PDN type is IPv4v6 and deferred IPv4 address allocation is used, the trusted non-3GPP IP Access shall request both IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. The Protocol Configuration Options in the Proxy Binding Update includes the Address Allocation Preference to indicate that deferred IPv4 address allocation was requested by the UE. In the same way as it is defined in clause 4.7.1, if deferred IPv4 address allocation is allowed, no IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW during the initial attach procedure, only IPv6 network prefix is returned in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. The DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication is included in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement to indicate that IPv4 address allocation using DHCPv4 is allowed. After the PMIPv6 tunnel is set up between the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access and the PDN-GW, when the UE requests the IPv4 address via DHCPv4, the trusted non-3GPP Access and PDN-GW perform steps 2 and 3 in Figure 4.7.1-1, and then the non-3GPP Access may relay the DHCPv4 messages between the UE and the PDN-GW for IPv4 parameter configuration and IPv4 address allocation as specified in Figure 4.7.1-1.
- Any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or IPv4 address lease time expires, and if the PDN Type is IPv4, the PDN-GW initiates "PDN-GW-initiated PDN-disconnection" procedure for the given PDN connection. The same IPv4 address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
- Any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or IPv4 address lease time expires, and if the PDN Type is IPv4v6, the PDN-GW initiates the "PDN-GW initiated IPv4 address Delete Procedure" procedure to delete the IPv4 address from the PDN connection and from bearer contexts. The same IP address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
-
Support of DHCPv4 server functionality for IPv4 parameter configuration and IP address allocation as specified in RFC 2131 and RFC 4039. This functionality is used to support DHCPv4 based IPv4 address allocation mechanism in the UE. For this case the following applies:
- At initial attach and handover attach, if the PDN type is IPv4v6 and deferred IPv4 address allocation is used, the trusted non-3GPP IP Access shall request both IPv6 network prefix and IPv4 address in the Proxy Binding Update. The Protocol Configuration Options in the Proxy Binding Update includes the Address Allocation Preference to indicate that deferred IPv4 address allocation was requested by the UE. In the same way as it is defined in clause 4.7.1, if deferred IPv4 address allocation is allowed, no IPv4 address is assigned by the PDN-GW during the initial attach procedure, only IPv6 network prefix and the DHCPv4 Address Allocation Procedure Indication are returned in the Proxy Binding Acknowledgement. After the PMIPv6 tunnel is set up between the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access and the PDN-GW, when the UE requests the IPv4 address via DHCPv4, the MAG in Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access requests the IPv4 address for the UE from the PDN-GW via PMIPv6 signalling as it is described in Figure 4.7.2-1.
- Any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or IPv4 address lease time expires, and if the PDN Type is IPv4, the trusted non-3GPP access system will initiate "Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access requested PDN Disconnection Procedure with PMIPv6" procedure for the given PDN connection. The same IP address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
- Any time after the UE releases the IPv4 address using DHCPv4 or IPv4 address lease time expires, and if the PDN Type is IPv4v6, the non-3GPP access may initiate "Non-3GPP access initiated IPv4 address Delete Procedure" procedure to delete the IPv4 address from the PDN connection and bearer contexts. The same IP address shall not be allocated to another UE immediately.
- Support of DHCPv6 (relay agent or server) functionality for IPv6 parameter configuration as specified in RFC 3736. This functionality is required to support DHCPv6 based parameter configuration mechanism in the UE.
- Support of prefix advertisement for IPv6 prefix received from PDN-GW in PMIPv6 Proxy Binding Acknowledgement.
- Support for IPv4 Address allocation that is received from PDN-GW from PMIPv6 Proxy Binding Acknowledgement using access specific mechanisms.
- Support of static IP address allocation. The non-3GPP access may receive a static IP address (i.e. a static IPv4 address and/or a static IPv6 prefix) from HSS/AAA during access authentication and authorization procedure. Then the non-3GPP access should forward the static IP address to the PDN-GW.
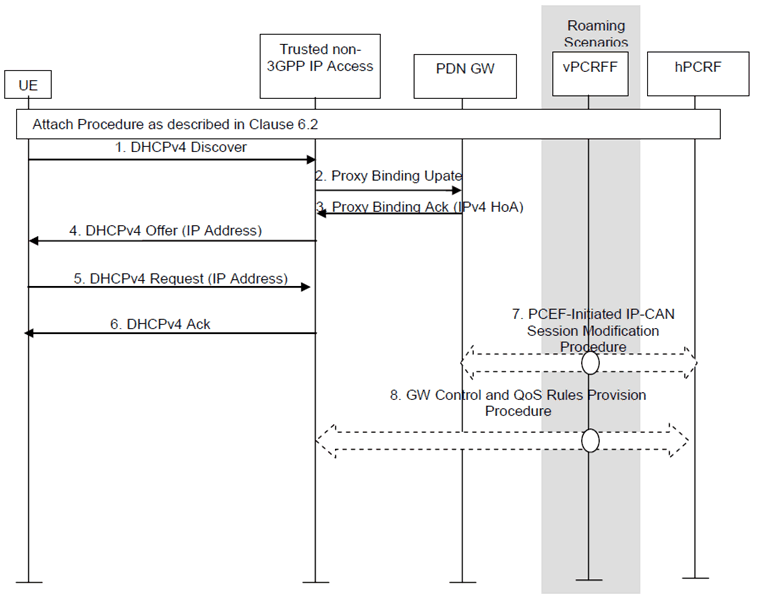
Figure 4.7.2-1: IPv4 Address Allocation using DHCP with DHCP Server Collocated with the MAG when PDN type is IPv4v6
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
If the PDN type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4v6, after the PDN connection establishment, the UE sends a DHCPv4 Discovery message in broadcast to the network to find available servers.
Step 2.
The MAG in the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access sends a Proxy Binding Update (MN NAI, APN, UE Address Info) to the PDN-GW in order to request the new IPv4 address and update the current registration. The MN NAI identifies the UE for whom the message is being sent. To request for IPv4 address for the UE, the UE Address Information should contain IPv4 address option set to 0.0.0.0, and the HNP shall be set to the HNP of the PDN connection.
Step 3.
Upon receiving the PBU message from the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access the PDN-GW allocates an IPv4 address for the UE in accordance with the operator's policies. The PDN-GW responds with a PMIPv6 Binding Acknowledgement (MN NAI, UE Address Info) message to the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access. The MN NAI is identical to the MN NAI sent in the Proxy Binding Update. The UE address info returns the assigned IPv4 Address and IPv6 prefix previously assigned to the UE during attach.
Step 4.
The Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access acting as a DHCPv4 server sends the DHCPv4 Offer with the assigned UE IPv4 address received in the PBA message in step 3.
Step 5.
When the UE receives the lease offer, it sends a DHCPREQUEST message containing the received IPv4 address.
Step 6.
The MAG in the Trusted Non-3GPP IP Access acting as DHCPv4 server sends a DHCPACK packet to the UE. This message includes the lease duration and any other configuration information that the client might have requested.
When receiving the DHCPACK message, the UE completes TCP/IP configuration process.
Step 7.
In case a new IPv4 address is allocated, the PDN-GW initiates the PCEF initiated IP-CAN session modification procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the PCRF of the IPv4 address allocated to the UE. If PCC rules have changed the PCRF provides the updated PCC rules to the PDN-GW as part of this procedure. This step can happen any time after step 3.
Step 8.
In case QoS rules have to be modified, e.g. change of SDF filters, the PCRF initiates a GW Control and QoS rules provision procedure as described in TS 23.203 to inform the S-GW of the updated QoS rules.
4.7.3 IP Address Allocation in Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access using PMIPv6 or GTP on S2b p. 57
When an Untrusted Non-3GPP IP access is used two types of IP address are allocated to the UE:
- An IP address, which is used by the UE within the Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access Network to get IP connectivity towards the ePDG.
- One or more IP address(es), which is used by the UE towards the external PDNs via the allocated PDN-GW(s).
4.7.4 IP Address Allocation using S2c p. 57
Prior the use of S2c an IP address which will be used as a care-of address shall be allocated to the UE.
When a Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network is used one or more IP addresses are allocated to the UE by the Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network. One of these IP addresses is used by the UE as care-of address within DSMIPv6. The allocation of these IP addresses is out of the scope this specification.
When an Untrusted Non-3GPP Access Network is used one or more IP addresses are allocated to the UE by the Untrusted Non-3GPP Access Network. The allocation of these IP addresses is out of the scope of 3GPP. One of these IP addresses is used by the UE as the IP address towards the ePDG when IPSec SAs are established. During the IPSec SA establishment the ePDG allocates and delivers an IP address to the UE, which IP address is used by the UE as care-of address within DSMIPv6. This IP address is allocated by the ePDG either by using an internal address pool or using an external server, such as DHCP. The allocation of this IP address is implementation specific.
When a UE is connecting to a PDN via S2c, address allocation for that PDN takes place as follows.
During IKEv2 exchange for bootstrapping the DSMIPv6 security association (see clause 6.3) the following parameters can be negotiated between the UE and the PDN-GW/HA:
- The IPv6 prefix to which the IPv6 Home Address belongs, also called the "Home Network Prefix" and the PDN associated with the IPv6 prefix (PDN is indicated with APN);
- The UE's IPv6 Home Address;
- The DNS server address for that PDN.
4.7.5 IPv6 Prefix Delegation using S2c |R10| p. 58
Optionally a single network prefix shorter than a /64 prefix may be assigned to a PDN connection (TS 23.401). When S2c is used to access a PDN, the UE acting as a Mobile Router may request delegation of one or more IPv6 prefix(es) via DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation signalling as described in RFC 6276. The UE does not need to explicitly register these additional prefixes using S2c signaling as implicit mode registration is used.
4.7.6 IPv6 Prefix Delegation using PMIP-based S5/S8 |R13| p. 58
Optionally a single network prefix shorter than the default /64 prefix may be assigned to a PDN connection as specified in TS 23.401. When PMIP-based S5/S8 is used, the UE may request delegation of one or more IPv6 prefix(es) via DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation signalling as described in RFC 7148. In this case, the Serving-GW shall support DHCPv6 relay agent functionality for intercept the related DHCPv6 message. The UE uses DHCPv6 to request additional IPv6 prefixes (i.e. prefixes in addition to the default prefix) from the PDN-GW after completing stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration procedures as specified in Figure 4.7.6-1.
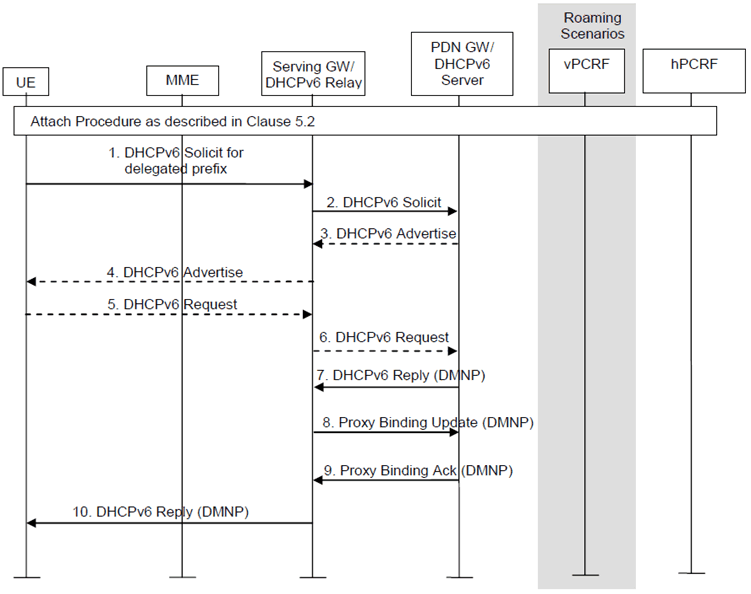
Figure 4.7.6-1: Prefix Delegation with DHCP Server Collocated with the PDN-GW and DHCP Relay in the Serving-GW when using PMIP-based S5/S8
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
If the PDN type associated with the PDN connection is IPv4v6 or IPv6, after the PMIPv6 tunnel is setup, the UE sends a DHCPv6 Solicit message including the IA_PD option to the Serving-GW to acquire a network prefix shorter than a /64 prefix.
Step 2.
The DHCPv6 relay agent in the Serving-GW shall relay the DHCPv6 solicit message within the PMIPv6 tunnel to PDN-GW acting as a DHCPv6 server.
Step 3-7.
The DHCPv6 procedures is then completed as described in RFC 3633 ending with the delegating router sending a Reply message conveying the delegated prefixes.
Step 8.
Once the Serving-GW receives the set of delegated prefixes from the delegating router function running on thePDN-GW, the Serving-GW shall send the delegated prefixes in a Proxy Binding Update.
Step 9.
On reception of the PBU the PDN-GW returns the assigned prefix in the DMNP option carried by a PBA to the Serving-GW. The PDN-GW shall add the assigned prefix to the binding cache which is extended as specified in RFC 7148.
Step 10.
The Serving-GW acting as DHCPv6 relay agent relays the DHCPv6 Reply message with deleageted prefix to the UE.