Content for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
0…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.2…
4.8…
4.8.2a…
4.9…
5…
5.2…
5.4…
5.5
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
6…
6.2…
6.3
6.4…
6.4.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.10…
6.13…
6.15…
7…
7.2…
7.3
7.4…
7.5…
7.6…
7.8…
7.10…
8…
8.2.1.2
8.2.1.3…
8.2.2
8.2.3…
8.2.6…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
9…
9.3…
9.4…
10…
13…
16…
16.1.2…
16.1.6…
16.2…
16.2.1a…
16.3…
16.4…
16.7…
16.8…
16.10…
17…
A…
C…
E…
7.2 Initial Attach on S2b
7.2.1 Initial Attach with PMIPv6 on S2b
7.2.3 Initial Attach Procedure with PMIPv6 on S2b and Chained S2b and PMIP-based S8
7.2.4 Initial Attach with GTP on S2b
7.2.5 Initial Attach for emergency session (GTP on S2b)
...
...
7.2 Initial Attach on S2b p. 159
7.2.1 Initial Attach with PMIPv6 on S2b p. 159
This clause is related to the case when the UE powers-on in an untrusted non-3GPP IP access network via the PMIP based S2b interface.
PMIPv6 specification, RFC 5213, is used to setup a PMIPv6 tunnel between the ePDG and the PDN-GW. It is assumed that MAG is collocated with ePDG. The IPsec tunnel between the UE and the ePDG provides a virtual point-to-point link between the UE and the MAG functionality on the ePDG.
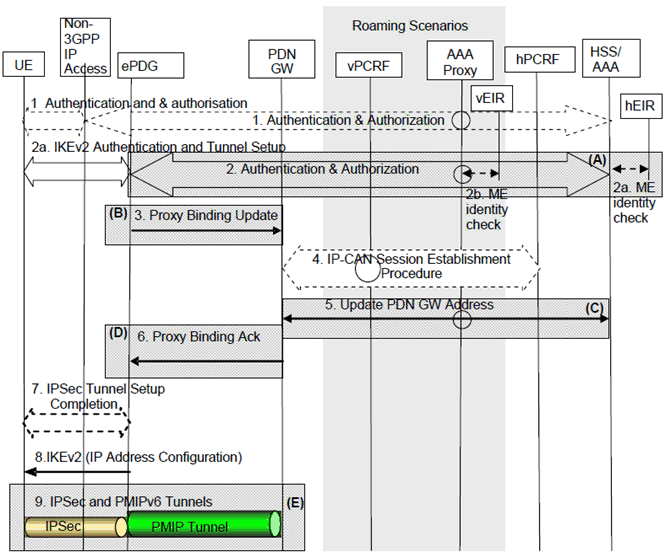
Figure 7.2.1-1: Initial attachment over PMIP based S2b for roaming, non-roaming and LBO
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The home routed roaming (Figure 4.2.3-1), LBO (Figure 4.2.3-4) and non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-1) scenarios are depicted in the Figure.
- In the LBO case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy acts as an intermediary, forwarding messages from the 3GPP AAA Server in the HPLMN to the PDN-GW in the VPLMN and visa versa. Messages between the PDN-GW in the VPLMN and the hPCRF in the HPLMN are forwarded by the vPCRF in the VPLMN.
- In the home routed roaming and non-roaming case, the vPCRF and the 3GPP AAA Proxy are not involved.
Step 1.
The Access authentication procedure between UE and the 3GPP EPC may be performed as defined by TS 33.402. In the roaming case signalling may be routed via a 3GPP AAA Proxy in the VPLMN. As part of the AAA exchange for network access authentication, the AAA/HSS and/or the 3GPP AAA Proxy may return to the Non-3GPP IP Access a set of home/visited operator's policies to be enforced on the usage of local IP address, or IPv6 prefix, allocated by the access system upon successful authentication. Subscription data is provided to the Non-3GPP IP Access by the HSS/AAA in this step.
Step 2.
The IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure is started by the UE. The UE may indicate in a notification part of the IKEv2 authentication request that it supports MOBIKE. The ePDG IP address to which the UE needs to form IPsec tunnel is discovered via DNS query as specified in clause 4.5.4. The UE may request connectivity to a specific PDN providing an APN, that is conveyed with IKEv2 as specified in TS 33.402. For networks supporting multiple mobility protocols, if there was any dynamic IPMS decision involved in this step, the decision is stored in the 3GPP AAA Server. The PDN-GW information is returned as part of the reply from the 3GPP AAA Server to the ePDG as described in clause 4.5.1. If the UE has provided an APN the ePDG verifies that it is allowed by subscription. If the UE has not provided an APN the ePDG uses the default APN. The PDN-GW selection takes place at this point as described in clause 4.5.1. This may entail an additional name resolution step, issuing a request to a DNS Server. If there is no requested IP address in the CFG_Request from the UE to the ePDG which indicates the attach is an initial attach, the ePDG may perform a new PDN-GW selection procedure as described in clause 4.5.1, e.g. to allocate a PDN-GW that allows for more efficient routeing. The UE shall indicate the type of address(es) (IPv4 address or IPv6 prefix /address or both) in the CFG_Request sent to the ePDG during IKEv2 message exchange. If the PDN requires an additional authentication and authorisation with an external AAA Server, the UE includes the authentication credentials in this step as specified in RFC 4739 and in TS 33.402. As part of the IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure, the ePDG may request the UE to provide its IMEI(SV). In that case the UE shall signal its IMEI(SV) to the ePDG. The ePDG forwards the IMEI(SV) received from the UE to the 3GPP AAA Server (over SWm).
Step 2a.
If IMEI check is required by operator policy and if the ePDG is in the HPLMN, the IMEI check shall be performed by the EIR in the home country. The 3GPP AAA server shall request the EIR to perform the IMEI check by sending the ME Identity Check Request (ME Identity, IMSI) to the EIR. Upon receiving the ME Identity Check Ack (Result) from the EIR, the 3GPP AAA server shall determine whether to continue or to stop the authentication and authorization procedure. If the 3GPP AAA server determines that the authentication and authorization procedure shall be stopped, it shall reply to the ePDG with a failure message with appropriate cause value.
Step 2b.
If IMEI check is required by operator policy and if the ePDG is in the visited PLMN, the IMEI check shall be performed by the EIR in the visited country. The 3GPP AAA proxy shall request the EIR to perform the IMEI check by sending the ME Identity Check Request (ME Identity, IMSI) to the EIR. Upon receiving the ME Identity Check Ack (Result) from the EIR, the 3GPP AAA proxy shall determine whether to continue or to stop the authentication and authorization procedure. If the 3GPP AAA proxy determines that the authentication and authorization procedure shall be stopped, the 3GPP AAA Proxy shall reply to the ePDG with a failure message with appropriate cause value.
Step 3.
The ePDG sends the Proxy Binding Update (MN-NAI, Lifetime, APN, Access Technology Type, Handover Indicator, GRE key for downlink traffic, UE Address Info, Charging Characteristics, Additional Parameters, IMEI(SV) if available) message to the PDN-GW. Access Technology Type option is set to a value matching the characteristics of the non-3GPP IP access. Handover Indicator is set to indicate attachment over a new interface. The proxy binding update message shall be secured. The MN NAI identifies the UE. The Lifetime field must be set to a nonzero value in the case of a registration and a zero value in the case of a de-registration. The APN is used by the PDN-GW to determine which PDN to establish connectivity for, in the case that the PDN-GW supports multiple PDN connectivity. The ePDG creates and includes a PDN connection identity if the ePDG supports multiple PDN connections to a single APN. The UE Address Info shall be set based on the CFG_Request in step 1 and subscription profile in the same way as the PDN type is selected during the E-UTRAN Initial Attach in TS 23.401. The Additional Parameters include the authentication credentials for an additional authentication and authorization with an external AAA server if it was provided by the UE in step 2. The PDN-GW performs the authentication and authorization with the external AAA server if it is required to get access for the given APN as specified in TS 33.402.
Step 4.
The PDN-GW initiates the IP-CAN Session Establishment Procedure with the PCRF, as specified in TS 23.203. If available, the PCRF provides the APN-AMBR and Default Bearer QoS to the PDN-GW in the response message.
Step 5.
The selected PDN-GW informs the 3GPP AAA Server of the PDN-GW identity. The 3GPP AAA Server then informs the HSS of the PDN-GW identity and APN associated with the UE's PDN Connection. The message includes information that identifies the PLMN in which the PDN-GW is located. This information is registered in the HSS as described in clause 12. The PDN-GW shall only use the APN-AMBR and Default Bearer QoS received from the 3GPP AAA server in this step if these parameters have not been received in step 4.
Step 6.
The PDN-GW processes the proxy binding update and creates a binding cache entry for the UE. The PDN-GW allocates an IP address for the UE. The PDN-GW then sends a Proxy Binding Ack (MN NAI, UE Address Info, GRE Key for uplink traffic, Charging ID) message to the ePDG, including the IP address(es) allocated for the UE (identified by the MN NAI). If the corresponding Proxy Binding Update contains the PDN connection identity, the PDN-GW shall acknowledge if multiple PDN connections to the given APN are supported. The Charging ID is assigned for the PDN connection for charging correlation purposes.
Step 7.
After the Proxy Binding Update is successful, the ePDG is authenticated by the UE and indicates to the UE that the authentication and authorization with the external AAA server is successful.
Step 8.
The ePDG sends the final IKEv2 message with the IP address in IKEv2 Configuration payloads. The ePDG also includes the identity of the associated PDN (APN) in the IDr payload of IKEv2. In case the UE provided APN to the ePDG in the earlier steps, the ePDG shall not change the provided APN.
Step 9.
IP connectivity from the UE to the PDN-GW is now setup. Any packet in the uplink direction is tunnelled to the ePDG by the UE using the IPSec tunnel. The ePDG then tunnels the packet to the PDN-GW. From the PDN-GW normal IP-based routing takes place. In the downlink direction, the packet for UE (HoA) arrives at the PDN-GW. The PDN-GW tunnels the packet based on the binding cache entry to the ePDG. The ePDG then tunnels the packet to the UE via proper IPsec tunnel.
7.2.2 Void
7.2.3 Initial Attach Procedure with PMIPv6 on S2b and Chained S2b and PMIP-based S8 p. 161
This procedure is described in clause 6.2.4.
7.2.4 Initial Attach with GTP on S2b |R10| p. 161
This clause is related to the case when the UE powers-on in an untrusted non-3GPP IP access network via the GTP based S2b interface.
GTPv2 (see TS 29.274) is used to setup GTP tunnel(s) between the ePDG and the PDN-GW. The IPsec tunnel between the UE and the ePDG provides a virtual point-to-point link between the UE and the ePDG.
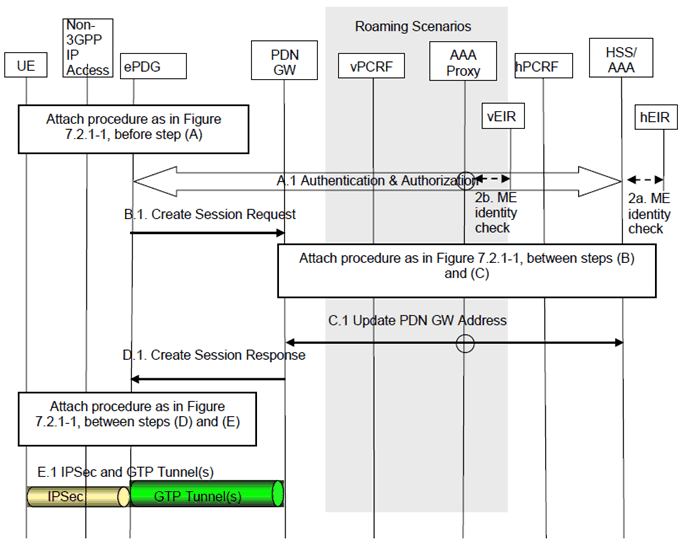
Figure 7.2.4-1: Initial attachment over GTP based S2b for roaming, non-roaming and LBO
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The home routed roaming (Figure 4.2.3-1), LBO (Figure 4.2.3-4) and non-roaming (Figure 4.2.2-1) scenarios are depicted in the Figure.
- In the LBO case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy acts as an intermediary, forwarding messages from the 3GPP AAA Server in the HPLMN to the PDN-GW in the VPLMN and visa versa. Messages between the PDN-GW in the VPLMN and the hPCRF in the HPLMN are forwarded by the vPCRF in the VPLMN.
- In the home routed roaming and non-roaming case, the vPCRF and the 3GPP AAA Proxy are not involved.
- In step 1, the subscription data that is provided to the Non-3GPP IP Access by the HSS/AAA shall also include the MPS subscription, if any.
- In step 2, when the IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure is started by the UE, a UE having a USIM with MPS subscription and supports MPS over untrusted WLAN feature shall indicate in a notification part of the IKEv2 authentication request that it has an MPS subscription.
Step A.1.
Step A.1 is the same as Step A of clause 7.2.1, with the following addition:
Step B.1.
- upon a successful authorization, the 3GPP AAA server returns the following additional information, regardless of which protocol variant the ePDG will select on S2b : APN-AMBR, static QoS Profile, MPS subscription indication and Trace Information (Trace Reference, Trace Type, Trigger Id, OMC Identity) if applicable. When the 3GPP AAA server has WLAN Location Information about the UE, it provides it over SWm to the ePDG together with the Age of this information. The WLAN Location information is provided to the ePDG only when the 3GPP AAA server considers that location information coming from the WLAN AN used by the UE is trustable. In addition to the above, the UE shall indicate at Initial Attach its capabilities, and whether it supports multiple IPsec SAs, so the ePDG can apply the necessary applicable procedures in this case.
- If it supports emergency services, the ePDG shall provide the UE with the corresponding indication as part of the IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure.
The ePDG sends a Create Session Request (IMSI, APN, RAT type, ePDG TEID for control plane, PDN Type, PDN Address, EPS Bearer Identity, Default EPS Bearer QoS, ePDG Address for the user plane, ePDG TEID of the user plane, APN-AMBR, Selection Mode, Dual Address Bearer Flag, Trace Information, Charging Characteristics, Additional Parameters, IMEI(SV), User Location Information) message to the PGW. The RAT type indicates the non-3GPP IP access technology type. The PDN Type shall be set based on the CFG_Request in step 1 and subscription profile in the same way as the PDN type is selected during the E-UTRAN Initial Attach in TS 23.401. The ePDG shall set the Dual Address Bearer Flag when the PDN type is set to IPv4v6 and all SGSNs which the UE may be handed over to are Release 8 or above supporting dual addressing, which is determined based on node pre-configuration by the operator. The ePDG shall include Trace Information if PDN-GW trace is activated. The Additional Parameters include the authentication credentials for an additional authentication and authorization with an external AAA server if it was provided by the UE before this step. The ePDG shall provide the IMEI(SV) if available; The PDN-GW performs the authentication and authorization with the external AAA server if it is required to get access for the given APN. The User Location Information shall include UE local IP address and optionally UDP or TCP source port number (if NAT is detected). It may also include WLAN Location Information (and its Age) the ePDG may have received from the 3GPP AAA server about the UE.
The PGW creates a new entry in its bearer context table and generates a Charging Id. The new entry allows the PGW to route user plane PDUs between the ePDG and the packet data network and to start charging.
Step C.1.
Step C.1 is the same as Step C of clause 7.2.1, with the following addition:
Step D.1.
- when informing the 3GPP AAA Server of the PDN-GW identity, the selected PDN-GW also indicates the selected S2b protocol variant (here GTP); this allows the option for the 3GPP AAA Server or 3GPP AAA Proxy not to return to the PDN-GW PMIP specific parameters (e.g. static QoS Profile, Trace Information, APN-AMBR) if GTP is used over S2b; the PDN-GW shall ignore those parameters if received from the 3GPP AAA Server or 3GPP AAA Proxy.
- The PDN-GW forwards to the PCRF in the IP-CAN Session Establishment procedure following information extracted from User Location Information it may have received from the ePDG:
- The UE local IP address and optionally UDP or TCP source port number (if NAT is detected).
- WLAN location information in conjunction with the Age of this information.
The PDN-GW returns a Create Session Response (PDN-GW Address for the user plane, PDN-GW TEID of the user plane, PDN-GW TEID of the control plane, PDN Type, PDN Address, EPS Bearer Identity, EPS Bearer QoS, APN-AMBR, Charging ID, Cause) message to the ePDG, including the IP address(es) allocated for the UE. The PDN-GW selects the PDN type to be used in the same way as done during the E-UTRAN Initial Attach in TS 23.401.
The PGW may initiate the creation of dedicated bearers on GTP based S2b (like it may do it on GTP based S5/S8 for an Attach on 3GPP access).
Step E.1.
Step E.1 is the same as Step E of clause 7.2.1, but with GTP tunnel(s).
7.2.5 Initial Attach for emergency session (GTP on S2b) |R13| p. 164
When the UE needs to establish an IMS emergency session over Untrusted WLAN access, the procedure described in this clause applies. The Initial Attach for emergency session follows the same steps that the Initial Attach for a non emergency session, so only the differences with regard to the procedures described in clauses 7.2.1 and 7.2.4 are documented.
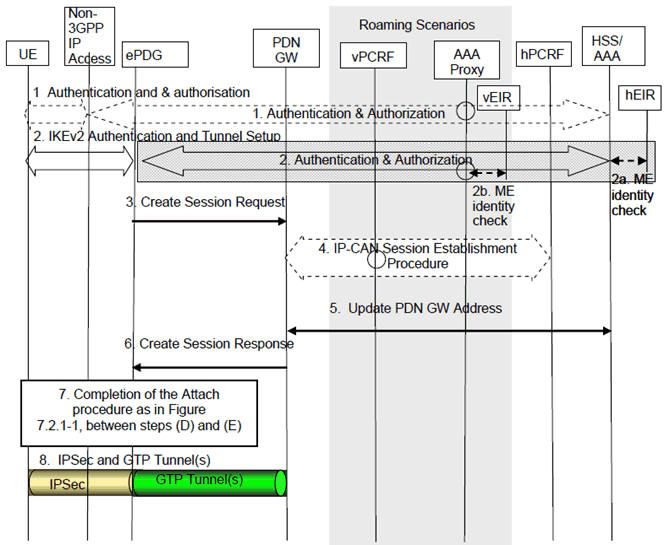
Figure 7.2.5-1: Initial attachment for emergency services over GTP based S2b
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
As in step 1 of Figure 7.2.1-1 with following modifications:
As part of procedures for Authentication and Authorization on an Access Point based NAI defined in clause 4.6.3, the 3GPP AAA server may store WLAN Location Information defined in clause 4.5.7.2.8.
Step 2.
The UE releases any connectivity it may have over Un-trusted access to EPC per the procedure defined in clause 7.4.3. The UE does not need to wait the procedure defined in clause 7.4.3 to be completed to proceed with following steps: the UE shall select an ePDG that supports emergency services as defined in clause 4.5.4a and initiate an IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure as in step 2 of clause 7.2.1 but with following specificities:
Step 3.
- The behaviour defined in clause 4.5.7.2.1 shall apply.
- The UE provides an indication that the EPC access is for emergency services.The indication is used by the 3GPP AAA server to give precedence to this session in case of signalling congestion (over SWx) and for authenticated UE without roaming permission to not carry out roaming and location checks for this UE. The indication is used by the ePDG to apply specific policies related with emergency PDN connection (e.g. stored in Emergency Configuration Data).
- For an Emergency Attach, the IMEI check to the EIR may be performed. Dependent upon the result, the 3GPP AAA server or 3GPP AAA proxy (roaming case with ePDG in VPLMN) decides whether to continue or to stop the authentication and authorization procedure is based on operator policies.
- Any APN received by the ePDG from the UE is ignored as the ePDG uses its Emergency Configuration Data to determine the APN to be associated with the emergency PDN connection and possibly to determine the PDN-GW to use.
- During the IKE tunnel establishment procedure, the identity provided by the UE in IKE_AUTH message to the ePDG is defined in clause 4.6.3. When local policies (related with local regulations) allow unauthenticated emergency sessions, the ePDG forwards the EAP payload received from the UE to the 3GPP AAA Server in the VPLMN serving the specific domain for unauthenticated emergency access.
- if the UE includes an identity based on IMEI and the ePDG is not configured to support Unauthenticated Emergency Attach (i.e for supporting cases c and d as defined in clause 4.3.12 of TS 23.401), the ePDG shall reject the Emergency Attach Request.
-
if the UE did not include the IMEI in the identity and the ePDG is configured for supporting Unauthenticated Emergency Attach (per cases c and d as defined in clause 4.3.12 of TS 23.401), the ePDG shall request the IMEI from the UE.
- Upon a successful authorization by the 3GPP AAA server, the ePDG stores subscription information if they are received from the 3GPP AAA, but does not use this information for the emergency PDN connection. It instead uses Emergency Configuration Data to get information on the APN and possibly PDN-GW and / or QoS (APN-AMBR, default QoS) to use for the emergency PDN connection.
The ePDG sends a Create Session Request message to the PGW as described in step B.1 of clause 7.2.4 but with following specificities:
Step 4.
- No parameter sent in the Create Session Request message is related with the user subscription. Parameters in the Emergency Configuration Data are used instead.
- No Additional Parameters are provided for additional authentication and authorisation with an external AAA Server.
- The PDN-GW deduces the emergency related policies to apply from the APN received in the Create Session Request message.
- For emergency attached UEs, if the IMSI cannot be authenticated or the UE has not provided it (according to cases c) and d) as defined in clause 4.3.12 of TS 23.401), then the IMEI shall be used as UE identifier.
As Step 4 of clause 7.2.1, with the following specificities:
Step 5.
- The PCRF deduces the emergency related policies to apply from the APN received in the IP-CAN Session Establishment message.
As in step C.1 of clause 7.2.4, with the following specificities:
Step 6.
- The PDN-GW sends an Emergency indication over S6b in order for the 3GPP AAA server to be able to apply specific policies for emergency services. For a UE without UICC or with an unauthenticated IMSI or a roaming authenticated UE, the 3GPP AAA server does not update the HSS with the identity of the PDN-GW. For a non-roaming authenticated UE, based on operator policy, this indication may be sent together with the "PDN-GW currently in use for emergency services", which comprises the PDN-GW address and the indication that the PDN connection is for emergency services to the HSS, which stores it as part of the UE context for emergency services.
As in step D.1 of clause 7.2.4.
Step 7.
As in step E.1 of clause 7.2.4, with the following specificities:
- No APN is provided by the ePDG in the IDr payload of the final IKEv2 message.