Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
AE Support of UE-Satellite-UE communication in IMS
AE.1 General
AE.2 Architecture and functional entities
AE.2.1 Architecture
AE.2.2 Functional entities
AE.3 Optimized media routing activation
AE.4 Interaction with IMS AGW
AE.5 Procedures for optimized media routing
...
...
AE (Normative) Support of UE-Satellite-UE communication in IMS |R19| p. 434
AE.1 General p. 434
This Annex describes IMS architecture enhancements to support UE-Satellite-UE communication in IMS, i.e., optimized media routing via IMS user plane on-board satellite.
In this Release of the specification, this feature is supported only for IMS voice/video service and for UEs belonging to the same PLMN and in the non-roaming scenario.
The term and the 5GS architecture for UE-Satellite-UE communication is defined in TS 23.501. The optimized media routing described in this Annex refers to a routing of media between UEs under the coverage of the same or of different serving satellites, using this IP-CAN and with the media not transiting through any network elements on the ground. The ground fallback routing refers to the case with the media transiting through the ground segment.
The P-CSCF is responsible for determining whether to activate UE-satellite-UE communication, that is, whether it is possible to apply media routing that only relies on IMS user plane on-board satellite. P-CSCFs serving the MO UE and the MT UE negotiate with each other to determine whether to activate UE-satellite-UE communication.
AE.2 Architecture and functional entities p. 434
AE.2.1 Architecture p. 434
AE.2.1.1 Support of IMS satellite media plane optimization with IMS-AGW deployed on satellite(s) p. 434
To support IMS satellite media plane optimization, as depicted in Figure AE.2.1.1-1, the IMS-AGW may be deployed on the satellite(s) that host the gNB and UPF (UL CL/BP and L-PSA) of the 5GC.
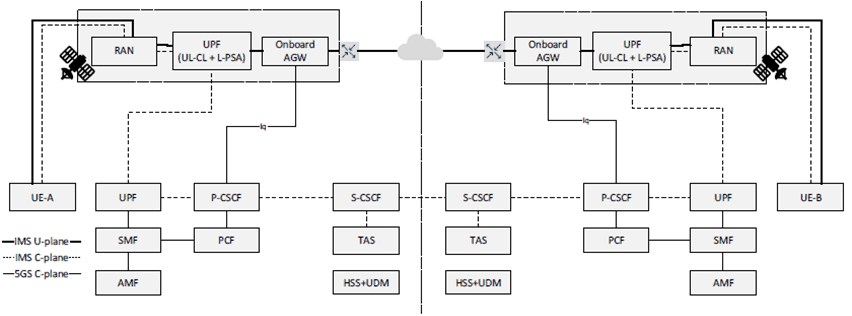
The above Figure depicts a reference architecture for IMS satellite media plane optimization with following assumption:
- For the IMS related PDU Session, the IP address allocated to the UE corresponds to a PSA UPF located on the ground. Thus, the IP address of the UE is not changed when serving satellite is changed.
- UE(s) register onto IMS with this IP address and don't need to reregister when there is change of serving satellite.
- The architecture deployment assumes, ISL(s) can be set-up within the same satellite constellation or across different constellations depending on satellite operator's deployments (SLA). The set of ISL(s) builds up an IP network which is out of 3GPP scope.
- The routing between Onboard AGWs across satellite via ISL is assumed to be based on IP routing and the Onboard AGWs in satellite need to have non-conflicting IP address during resource allocation. It is up to the deployment to manage IP routing across ISL links and is out of 3GPP scope.
AE.2.2 Functional entities p. 435
AE.2.2.1 P-CSCF p. 435
The P-CSCF used for this feature is enhanced to support the following functionalities:
- the P-CSCF determines the activation of optimized media routing and interacts with 5GS, as described in clause AE.3.
- the P-CSCF interacts with IMS AGW, as described in clause AE.4.
AE.3 Optimized media routing activation p. 435
AE.3.1 General p. 435
If UE-Satellite-UE communication in IMS is supported, and if enabled subject to operator policy, the following behaviour described in clause AE.3 applies.
AE.3.2 At call setup p. 435
The P-CSCF receives from the PCF the identifier of the satellite serving the UE and receives from the P-CSCF serving the remote UE the identifier of the satellite serving the remote UE. The P-CSCF uses this information to determine whether or not activate optimized media routing.
If P-CSCF determines the activation of optimized media routing, the P-CSCF instructs PCF to authorize the necessary resources according to clause 5.6.2 and clause 5.7.2, so that the PCF proceeds to establish a path for optimized media routing.
AE.4 Interaction with IMS AGW p. 436
AE.4.1 General p. 436
If UE-Satellite-UE communication in IMS is supported, and if enabled subject to operator policy, the following behaviour described in clause AE.4 applies.
AE.4.2 At call setup p. 436
P-CSCF selects an IMS AGW on ground at call setup according to TS 23.334 and proceeds with the determination of whether UE-Satellite-UE communication is possible. If the P-CSCF determines the activation of optimized media routing is possible, the P-CSCF releases the IMS AGW on ground when needed and select instead an IMS AGW on satellite according to TS 23.334.
AE.5 Procedures for optimized media routing p. 436
AE.5.1 At call setup p. 436
When the originating P-CSCF receives the initial INVITE request from the originating UE using regenerative NR satellite access, it selects the IMS-AGW on ground and triggers media negotiation by sending SDP offer to the terminating side indicating that satellite access is used on the originating side. If the terminating P-CSCF activates UE-satellite-UE communication, the originating P-CSCF re-selects an IMS-AGW on satellite. See Figure AE.5.1-1 that describes the procedure.
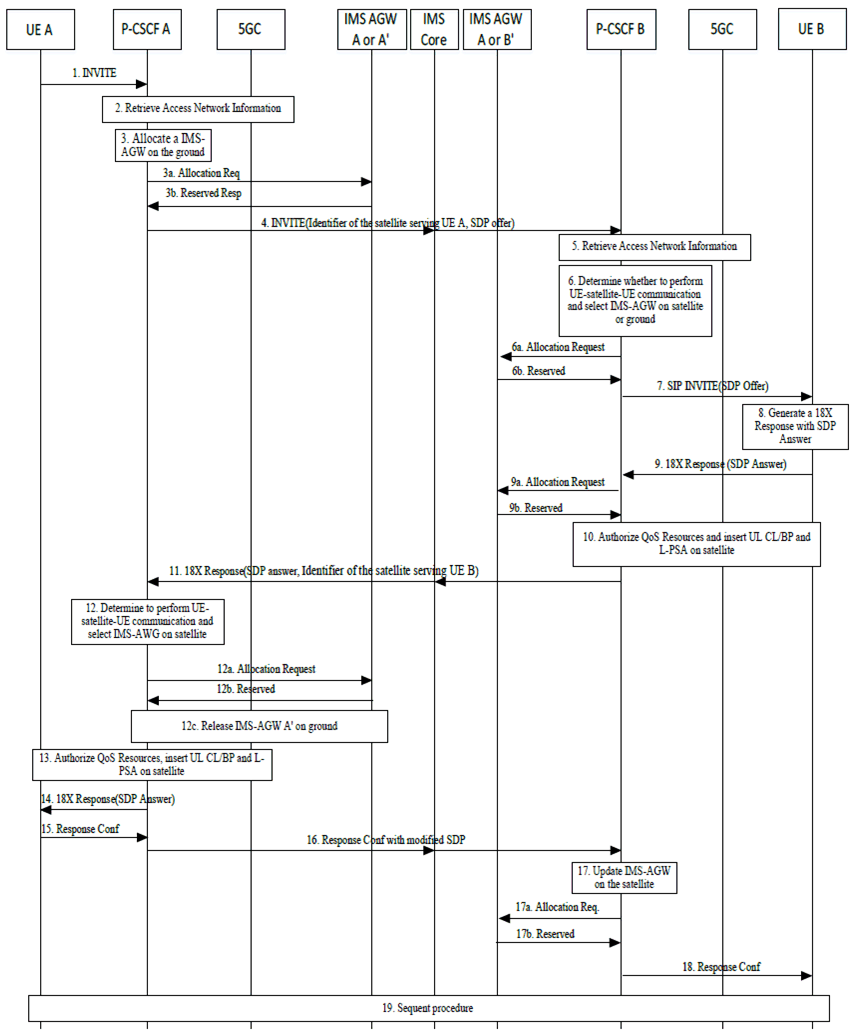
Step 1.
Steps 4-20 are performed if the UE-Satellite-UE communication is possible based on the decision in step 2 (i.e. UE A is using NR generate satellite access and in non-roaming scenario). Otherwise, SIP message routing procedures with IMS-AGW on ground should be performed after P-CSCF A selecting a ground IMS-AGW for usage (details have been omitted from the diagram).
UE A sends a SIP INVITE request, containing an initial SDP offer, to P-CSCF A. The access information in the SIP INVITE request indicates that the UE is accessing from NR satellites access as defined in TS 24.229.
Step 2.
After receiving the SIP INVITE request indicating NR satellite access, if UE A is in the non-roaming scenario and the P-CSCF A supports UE-Satellite-UE communication, it may perform following actions to determine whether UE-satellite-UE communication is possible:
Step 3.
- P-CSCF A retrieves Access Network Information from PCF based on the mechanism defined in TS 23.503 and determines whether the UE A is using regenerative satellite access or not based on whether a serving satellite identification is obtained as part of the Access Network Information or not.
The P-CSCF A allocates an IMS-AGW A' on the ground as default. P-CSCF A interacts with IMS-AGW A' to allocate transport resources based on the mechanism defined in TS 23.334.
Step 4.
Steps 7-20 are performed if the UE-Satellite-UE communication is activated. Otherwise, SIP message routing procedures with IMS-AGW on the ground should be performed after P-CSCF B selecting a ground IMS-AGW B' for usage (details have been omitted from the diagram).
P-CSCF A updates the SIP INVITE request inserting the identification of the satellite serving UE A and updates SDP offer with the IMS-AGW transport addresses allocated in step 3. Then, P-CSCF A forwards the updated SIP INVITE request to the terminating side via IMS core (details have been omitted from the diagram).
Step 5.
After receiving the SIP INVITE request which contains a satellite identification indicating that UE A is using regenerative satellite access, if UE B is not in roaming, P-CSCF B retrieves Access Network Information of UE B from PCF network based on the mechanism defined in TS 23.503. If the UE B is also using the regenerative satellite access, the serving satellite identification is contained in the Access Network Information.
Step 6.
When UE B is not in roaming, and the two satellites identified by the two satellite identifications received in step 4 and 5 are same or connected with ISL(s), P-CSCF B determines to activate the UE-Satellite-communication.
If UE-Satellite-UE communications is not activated, P-CSCF B selects an IMS-AGW B' on ground for UE B; otherwise, P-CSCF B selects an IMS-AGW B on satellite for UE B.
Step 6a-6b.
Based on the decision in step 6, P-CSCF B interacts with IMS-AGW B on satellite or IMS-AGW B' on ground to allocate transport resources based on the mechanism defined in TS 23.334.
Step 7-9.
P-CSCF B forwards the updated SIP INVITE request to UE B. UE B returns a 18X response with SDP Answer.
Step 9a-9b.
After receiving the SDP Answer, P-CSCF B interacts with the IMS-AGW B to allocate transport resources based on the mechanism defined in TS 23.334.
Step 10.
P-CSCF B instructs the PCF to authorize the resources necessary to establish a QoS flow for media via Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update service operation.
To indicate SMF to insert UL CL/BP and L-PSA UPF for IMS PDU session to enable UE-Satellite-UE communication, P-CSCF B should send following parameters via the request based on Application Function influence on traffic routing mechanism described in clause 5.6.7 of TS 23.501 and clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.502:
Step 11.
- A flow description information which contains the IP address of the IMS-AGW B;
- A DNAI associated with the IMS-AGW B on satellite and corresponding N6 traffic routing information.
P-CSCF B updates the 18X response to carry the identifier of the satellite serving UE B to indicate that UE-Satellite-UE communication is activated. Then, P-CSCF B returns the updated 18X response to originating side via IMS core (details have been omitted from the diagram).
Step 12.
Based on the identification of the satellite serving UE B in step 11, P-CSCF A determines to perform UE-satellite-UE communication and select an IMS-AGW A on satellite.
Step 12a-12c.
P-CSCF A interacts with IMS-AGW A on satellite to allocate transport resources for both IMS access and core network sides. P-CSCF A also releases the IMS-AGW A' on ground.
Step 13.
P-CSCF A instructs the PCF to authorize the resources necessary to establish a QoS flow for media via Npcf_PolicyAuthorization_Update service operation.
To indicate SMF to insert UL CL/BP and L-PSA UPF for IMS PDU session to enable UE-Satellite-UE communication, P-CSCF B should send following parameters via the request based on Application Function influence on traffic routing mechanism described in clause 5.6.7 of TS 23.501 and clause 4.3.6 of TS 23.502:
Step 14.
- A flow description information which contains the IP address of the IMS-AGW A;
- A DNAI associated with the IMS-AGW A on satellite and corresponding N6 traffic routing information.
P-CSCF A updates the SDP answer in the 18X response with the IMS-AGW transport addresses allocated in step 12, and forwards the updated 18X response to UE A.
Step 15.
UE A acknowledges the Response and sends the Response Confirmation to P-CSCF A.
Step 16-17.
P-CSCF A forwards the Response Confirmation to P-CSCF B. The Response Confirmation includes SDP offer modified/generated by P-CSCF A which contains the IMS-AGW transport address obtained in step 12. Upon receiving the SDP offer, P-CSCF B updates the allocated IMS-AGW on the satellite for UE B with the transport address in the SDP offer.
Step 18.
P-CSCF B sends the Response Confirmation to UE B.
Step 19.
Procedure continues to setup the call as defined in clauses 5.6 and 5.7.