Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
AC.7.10 Multiplexing multiple DC streams over single SCTP connection
AC.7.10.1 General
AC.7.10.2 Capability negotiation
AC.7.10.2.1 Capability negotiation between UE and IMS network
AC.7.10.2.2 Capability negotiation between originating and terminating network
AC.7.10.3 Determination and handling of multiplexing and de-multiplexing
AC.7.10.3.1 Determination of multiplexing and de-multiplexing
AC.7.10.3.2 Handling multiplexing and de-multiplexing at the originating network
AC.7.10.3.3 Handling at the terminating network
AC.7.10.4 Procedures
AC.7.10.4.1 Bootstrap data channel establishment
...
...
AC.7.10 Multiplexing multiple DC streams over single SCTP connection |R19| p. 398
AC.7.10.1 General p. 398
When multiple data channels are used in an IMS session, the UE and IMS network may support SDP negotiation to multiplex multiple data channel streams into a single data channel SDP media description m line and transport streams of multiple applications in the same SCTP connection, to save the number of m lines used by the UE and to improve the efficient usage of media resources.
The UE and IMS network also need to support data channel de-multiplexing when supporting data channel multiplexing. If the UE receives streams targeting to different applications over a single SCTP connection, it identifies the applications and delivers the data of the streams to corresponding applications. If the IMS network receives multiplexed streams which have different remote endpoints, e.g. a local bootstrap data channel and a remote bootstrap data channel of a UE, the MF terminates the multiplexing and sends different streams to corresponding endpoints based on instructions of DCSF.
The following multiplexing scenarios are supported in this Release:
- Multiplexing local bootstrap data channel and remote bootstrap data channel between the UE and its home IMS network using a single SDP m line media description if both support data channel multiplexing capability;
- Multiplexing different application data channels for applications with compatible QoS requirements between the UE and its IMS network using a single SDP m line media description if both support multiplexing capability;
- Multiplexing different application data channels for applications with compatible QoS requirements between the originating IMS network and terminating IMS network using a single SDP m line media description if both support DC multiplexing capability.
- The supporting IMS network de-multiplexes local bootstrap data channel and remote bootstrap data channel from a SDP media description towards a UE that does not support multiplexing;
- The supporting IMS network de-multiplexes application data channels from a SDP media description, if the data channels have different endpoints e.g. a P2P application and a P2A application or towards a UE that does not support multiplexing;
- The supporting originating IMS network de-multiplex data channels towards remote network if the remote network or remote UE does not support DC multiplexing.
AC.7.10.2 Capability negotiation p. 399
AC.7.10.2.1 Capability negotiation between UE and IMS network p. 399
The UE and IMS network may support DC multiplexing capability negotiation as follows:
- The UE and the IMS network mutually negotiate their capabilities of data channel multiplexing during registration procedure.
- If the UE supports data channel multiplexing, when the UE registers on the IMS network, the UE shall include a media feature tag in the Contact header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing in the initial and any subsequent REGISTER request.
- If the UE supports data channel multiplexing, when the UE initiates a IMS session using data channel multiplexing, the UE shall include the media feature tag in the Contact header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing in the INVITE request.
- If the P-CSCF supports data channel multiplexing, when the P-CSCF receives the REGISTER request from the UE, the P-CSCF shall include a Feature-Caps header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing in the initial and any subsequent REGISTER request.
- If the home IMS network supports this feature, the S-CSCF includes a Feature-Caps header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing in the 200 OK response to the initial and any subsequent REGISTER request.
- If the IMS network supports this feature, the S-CSCF includes a Feature-Caps header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing in the SIP request messages to the remote network.
AC.7.10.2.2 Capability negotiation between originating and terminating network p. 400
The DCSF in originating IMS network shall determine whether the terminating IMS network supports data channel multiplexing by local configuration or based on the SDP answer received from remote network setting port of multiplexed DC media to zero.
AC.7.10.3 Determination and handling of multiplexing and de-multiplexing p. 400
AC.7.10.3.1 Determination of multiplexing and de-multiplexing p. 400
When the IMS AS receives the INVITE request with data channel multiplexing, if data channel multiplexing is supported, it reports the event to the DCSF for data channel management. The DCSF determines whether the data channel multiplexing is allowed and whether serving network needs to de-multiplex the data channel traffic based on subscription data, binding information, the endpoints of data channels and capability of terminating network.
AC.7.10.3.2 Handling multiplexing and de-multiplexing at the originating network p. 400
The IMS AS and DCSF in the originating network follows the following principles to handle data channel multiplexing and de-multiplexing:
- If the data channels are kept multiplexed, the DCSF instructs originating IMS AS accordingly. The originating IMS AS further instructs the MF to reserve the same media termination for multiplexed data channels. This attempt may succeed and IMS session establishment may be successful.
- If the data channels are kept multiplexed, the DCSF instructs originating IMS AS accordingly. The originating IMS AS further instructs the MF to reserve the same media termination for multiplexed data channels. If the terminating network rejects the SDP offer because the terminating network does not support multiplexing, then originating IMS AS and originating DCSF needs to revert to a new demultiplexed SDP offer towards the target network as described in next bullet.
- If the originating network determines to demultiplex the data channels is determined, the DCSF in the originating network instructs originating IMS AS accordingly. The originating IMS AS further instructs the MF to reserve separate media terminations for the de-multiplexed streams. When the originating IMS AS sends the SDP offer to terminating IMS network, the data channels are not multiplexed in the SDP offer. IMS session establishment continues.
AC.7.10.3.3 Handling at the terminating network p. 401
The IMS AS and DCSF in the terminating network follows the following principles to handle data channel multiplexing and de-multiplexing:
- If the data channels are kept multiplexed, the terminating DCSF instructs terminating IMS AS accordingly. The terminating IMS AS further instructs the MF to reserve the same media termination for multiplexed data channels;
- If the data channels is determined to be de-multiplexed, the terminating DCSF instructs terminating IMS AS accordingly. The terminating IMS AS further instructs the MF to reserve separate media terminations for the de-multiplexed streams. When the terminating IMS AS sends the SDP offer to terminating UE, the data channels are not multiplexed in the SDP offer.
AC.7.10.4 Procedures p. 401
AC.7.10.4.1 Bootstrap data channel establishment p. 401
AC.7.10.4.1.1 Bootstrap data channels multiplexing in originating network p. 401
Figure AC.7.10.4.1.1-1 shows the procedure when the local bootstrap data channel and remote bootstrap data channel is multiplexed by the originating UE. The originating UE initiates an IMS session with multiplexed SDP for the two bootstrap data channels. The originating IMS network de-multiplexes the bootstrap data channel due to the two data channels have different endpoints.
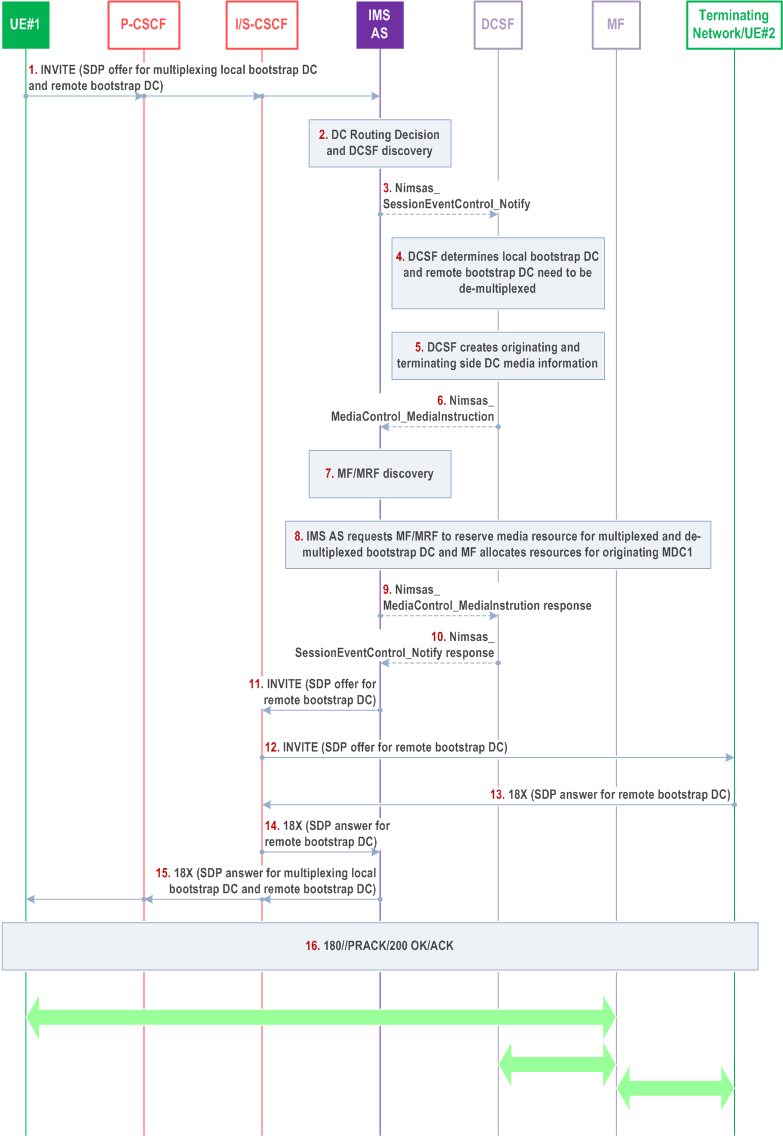
Step 1.
The streams of local data channel and remote data channel are transported in the same SCTP connection between UE#1 and MF and are routed to DCSF and remote network correspondingly.
When the UE wants to multiplex its bootstrap data channels, i.e. local bootstrap data channel and remote bootstrap data channel, the UE includes multiplexed SDP media description in initial INVITE request. The media feature tag in the Contact header field indicating its capability of supporting data channel multiplexing is included in reINVITE request.
Step 2-3.
The IMS AS selects and report event to DCSF.
Step 4.
The DCSF determines based on stream id in the SDP that local bootstrap and remote bootstrap data channels need to be de-multiplexed.
Step 5.
The DCSF generates data channel media information for originating side and terminating side.
Step 6.
The DCSF instructs the IMS AS to reserve resources on MF.
Step 7.
The IMS AS selects MF supporting data channel multiplexing.
Step 8.
The IMS AS instructs MF to reserve media resources for multiplexed data channel streams and other media resources based on instructions from DCSF.
Step 9-12.
The session continues after the media resource is reserved successfully. The SDP offer in the INVITE request may also be multiplexed if needed.
Step 13-16.
The terminating network responds and the session is established successfully.
AC.7.10.4.1.2 Bootstrap data channel multiplexing in terminating network p. 403
Figure AC.7.10.4.1.2-1 shows the procedure when the terminating IMS network multiplexes the received remote data channel and the local bootstrap data channel towards the terminating UE.
In this procedure, when the terminating IMS network receives the SDP offer of remote bootstrap DC for terminating UE, it multiplexes this bootstrap data channel with the local bootstrap data channel for terminating UE. When the terminating UE receives the multiplexed SDP offer, it replies with the multiplexed SDP answer to allow multiplexing of the two bootstrap data channels between terminating UE and terminating IMS network.
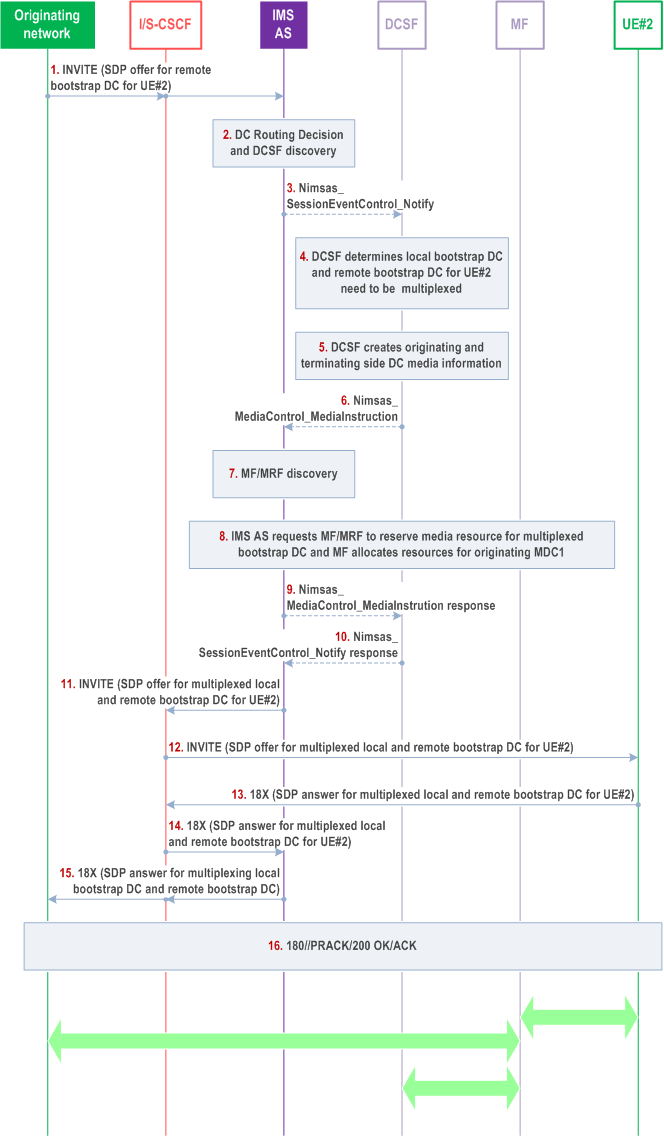
Step 1.
The streams of local data channel and remote data channel are transported in the same SCTP connection to UE#2.
The originating network sends initial INVITE request with SDP offer for remote bootstrap data channel to UE#2.
Step 2-3.
The IMS AS selects and reports event to DCSF.
Step 4.
The DCSF determines that local bootstrap and remote bootstrap data channels to UE#2 need to be multiplexed.
Step 5.
The DCSF generates data channel media information for originating side and terminating side.
Step 6.
The DCSF instructs the IMS AS to reserve resources on MF.
Step 7.
The IMS AS selects MF supporting data channel multiplexing.
Step 8.
The IMS AS instructs MF to reserve media resources for multiplexed data channel streams and other media resources based on instructions from DCSF.
Step 9-12.
The session continues after the media resource is reserved successfully.
Step 13-16.
The UE#2 responds and the session is established successfully.