Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
P Transcoding Support involving the MRFC/MRFP
P.1 General
P.1.1 Scope
P.1.2 Description
P.1.3 Session flows
P.1.3.1 General
P.1.3.2 Proactive transcoding invocation
P.1.3.3 Reactive transcoding invocation
...
...
P Transcoding Support involving the MRFC/MRFP |R8| p. 279
P.1 General p. 279
P.1.1 Scope p. 279
This clause describes media transcoding services involving the MRFC/MRCP applicable in the following cases:
- between two IMSs;
- between an IMS and other SIP based multimedia network; and
- internal to an IMS servicing media endpoints with different media encoding requirements. This can arise due to support of different access technologies (e.g. wireline-wireless interworking, or support of non-3GPP wireless technologies), or from divergence in supported or allowed media encoding formats (e.g. configuration of devices to only allow certain codecs).
P.1.2 Description p. 279
Application Servers can invoke the MRFC for the purpose of media transcoding between UEs that have no supported codec in common. The MRFC controls functionality in the MRFP to perform media plane transcoding.
The decision to perform media transcoding requires knowledge of the codecs supported by the calling and called UEs. Media transcoding services can be triggered proactively (before the session request is sent to the called UE) or reactively (after the session request has been sent to, and rejected by, the called UE). Proactive transcoding invocation requires prior knowledge of the codecs supported by the UE at which the called party is registered. In the case of reactive transcoding the list of codecs supported by the called UE is carried in the SIP response message.
P.1.3 Session flows p. 279
P.1.3.1 General p. 279
The following use cases illustrate session procedures involving the MRFC required to support transcoding between UEs due to error cases or incompatible terminal equipment. In addition, transcoding procedures are applicable to both the originating and the terminating side of the session or even (in inter-network scenarios) in a transit network, and are subject to bilateral agreements and operator configuration. A media transcoding session refers to a SIP session between an entity in the IMS control plane (hereafter referred to as the "invoking function") and the MRFC/MRFP as actual transcoding device, setup for the purpose to mediate between calling and called UEs. The SIP session between the invoking function and the MRFC is used to reserve resources at the transcoding unit, in this case the MRFP, and to exchange transport address and port information. The session flows described here have been simplified by abbreviating the message exchange, e.g. by eliminating 100 trying messages. Similar session flows are available in Annex B of TS 23.218.
P.1.3.2 Proactive transcoding invocation p. 279
As noted above, proactive transcoding invocation requires prior knowledge of the codecs supported by the UE at which the called party is registered. At session initiation the calling UE capabilities are contained in the SDP offer, while called UE capabilities can be either preconfigured or known by other means in the network (e.g. if the control plane entity responsible for detecting the need of transcoding previously learned the codecs supported by the UE that is now called by monitoring session requests initiated by it).
The following session flow illustrates proactive media transcoding:
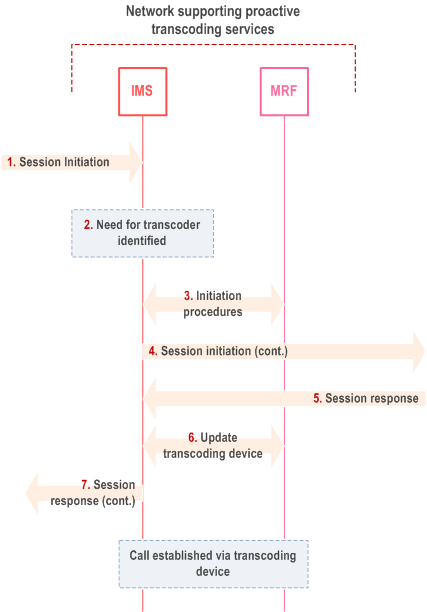
Step 1.
Calling UE sends a SIP request targeted at an address registered at the called UE, including an SDP offer containing codec(s) and the IP address and TCP or UDP port number at which the calling UE wishes to receive media.
Step 2.
The SIP request is received by an IMS control plane entity responsible for detecting the need of proactive transcoding invocation. If the SDP offer does not include any codec supported by the called UE, then the invoking function is triggered to set up a SIP session with the MRFC, providing codecs and transport parameters to initiate a transcoding session.
Step 3.
The invoking function instructs the MRFC to:
Step 4.
- allocate media processing resources from an MRFP entity under the MRFC's control, configured with the address and port at which the calling UE wishes to receive media, using a codec (say, codec-A) previously included by the calling UE in the SDP offer and hence known to be supported;
- allocate media processing resources from the same MRFP entity to the called UE, using a codec (say, codec-B) known to be supported by the called UE; and
- cause the MRFP entity to bridge those two media flows, such that media received on one will be converted to the format of and transmitted on the other.
The invoking function updates the SIP request received in step 1 by appending codec-B to the list of codecs in the SDP offer (after all codecs that were previously in the offer), and altering the transport address and port information to indicate the addresses associated by the MRFP with its resources of type codec-B.
Step 5.
Called UE acknowledges the SDP offer and makes a codec selection (codec-B), providing also its actual IP address/port number information in the SDP answer.
Step 6.
Upon receipt of the answer from the called UE, the invoking function updates the session with the MRFC (providing the codec selected and the address /port information from the SDP answer). The MRFC processes the received information to configure the transcoding unit with the codec, the destination address and port towards the called UE.
Step 7.
The invoking function modifies the SDP answer to reference codec-A, and the transport address and port information to indicate the addresses associated by the MRFP with its resources of type codec-A. The invoking function forwards the SIP message containing the SDP answer to the calling UE.
P.1.3.3 Reactive transcoding invocation p. 281
Reactive invocation of media transcoding is useful in the case that the calling and called UE support no common codec, and for whatever reason transcoding is not proactively invoked. In this case the SDP offer received by the called UE contains no codecs that the called UE supports. The called UE will answer with an appropriate SIP error response, which can include information about actually supported codecs. Transcoding invoked in response to receipt of such an error response is termed Reactive.
The following example session flow describes reactive invocation of media transcoding:
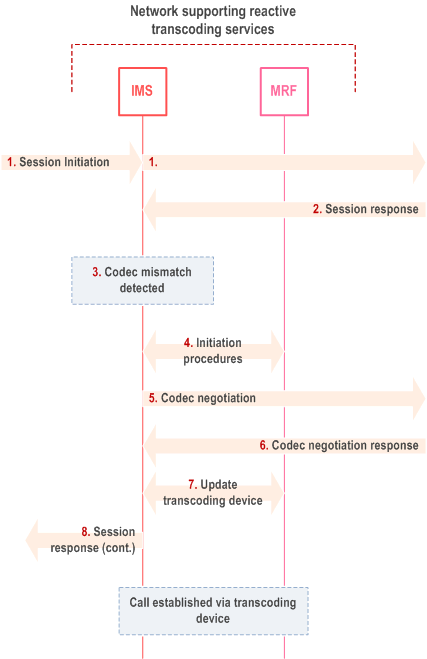
Step 1.
Calling UE sends a SIP request, including an SDP offer containing codec(s) and the IP address and TCP or UDP port number at which calling UE wishes to receive media. For some reason, e.g. because proactive invocation of media transcoding is not supported in the terminating network, transcoding is not proactively invoked.
Step 2.
The called UE or a terminating network entity (such as MGCF) determines that it does not support any codec in the SDP offer and answers with an appropriate error response. This response can include a list of codecs that the called UE can support.
Step 3.
Based on the response from called UE indicating that it does not support the offered codecs, an IMS control plane entity responsible for detecting the need of reactive transcoding invocation triggers the invoking function to set up a SIP session with the MRFC, providing codecs and transport parameters to initiate a transcoding session.
Step 4.
The invoking function instructs the MRFC to:
Step 5.
- allocate media processing resources from an MRFP entity under the MRFC's control, configured with the address and port at which the calling UE wishes to receive media, using a codec (say, codec-A) previously included by calling UE in the SDP offer hence known to be supported by calling UE;
- allocate media processing resources from the same MRFP entity to called UE, using a codec (say, codec-B) known to be supported by called UE; and
- cause the MRFP entity to bridge those two media flows, such that media received on one will be converted to the format of and transmitted on the other.
Based on the information received from the MRFC, the invoking function creates a new SDP offer that contains the information provided by the MRFC (codec and transport addresses). If no information about supported codecs was available from the error response, the invoking function offers all codecs supported by the transcoding device. It sends this offer to the called UE.
Step 6.
Called UE acknowledges the SDP offer and makes a codec selection, providing in the SDP answer the IP address and TCP or UDP port at which it wants to receive media.
Step 7.
Upon receipt of the answer from the called UE, the invoking function updates the session with the MRFC (providing the codec selected and the address /port information from the SDP answer). The MRFC processes the received information to configure the transcoding unit with the codec, the destination address and port towards the called UE.
Step 8.
The invoking function modifies the SDP answer received from the called UE such that it refers to codec-A and the MRFP address and port number associated with it in step 4, and sends this message to the calling UE. The session between the end points is now established with the media flow traversing the transcoding device.