Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
5.5.3 (S-S#3) Session origination with PSTN termination in the same network as the S-CSCF
5.5.4 (S-S#4) Session origination with PSTN termination in a different network from the S-CSCF
...
...
5.5.3 (S-S#3) Session origination with PSTN termination in the same network as the S-CSCF p. 117
The Serving-CSCF handling session origination performs an analysis of the destination address, and determines, with support of applications or other databases, that the session is destined to the PSTN. The request is therefore forwarded to a local BGCF. The BGCF determines that the MGCF should be in the same network, and selects a MGCF in that network. The request is then forwarded to the MGCF.
Refer to Table 5.2 in sub clause 5.4a to see which origination sequences share this common S-S procedure. In addition the text below clarifies the role of the" Originating Network".
MO#1
Refer to Table 5.2 in clause 5.4a to see which termination sequences share this common S-S procedure. In addition the text below clarifies the role of the "Terminating Network".
Mobile origination, roaming. The "Originating Network" of S-S#3 is therefore a visited network.
MO#2
Mobile origination, located in home service area. The "Originating Network" of S-S#3 is therefore the home network.
AS-O
Application Server origination. The" Originating Network" of S-S#1 is the home network. The element labelled S-CSCF corresponds to the S-CSCF in Figure 5.16b.
PSTN-T
PSTN termination. This occurs when the MGCF is selected to be in the same network as the S-CSCF.
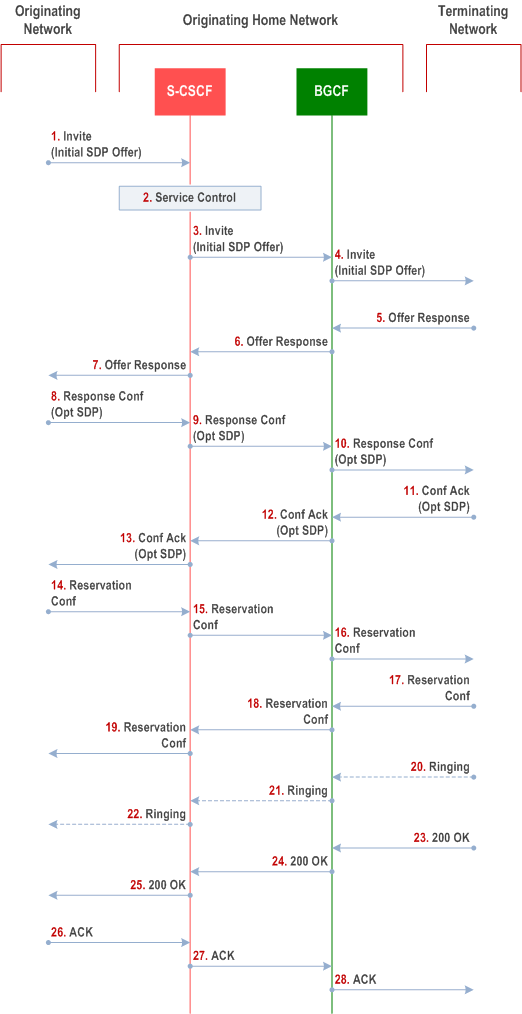
Procedure S-S#3 is as follows:
Step 1.
The SIP INVITE request is sent from the UE to S-CSCF#1 by the procedures of the originating flow. This message should contain the initial media description offer in the SDP.
Step 2.
S-CSCF#1 invokes whatever service logic is appropriate for this session setup attempt
Step 3.
S-CSCF#1 performs an analysis of the destination address. From the analysis of the destination address, S-CSCF#1 determines that this is for the PSTN, and passes the request to the BGCF.
Step 4.
The BGCF determines that the MGCF shall be in the same network, and hence proceeds to select an appropriate MGCF. The SIP INVITE request is forwarded to the MGCF. The PSTN terminating information flows are then followed.
Step 5-7.
The media stream capabilities of the destination are returned along the signalling path, as per the PSTN termination procedure.
Step 8.
The originator decides the offered set of media streams, confirms receipt of the Offer Response with a Response Confirmation, and forwards this information to S-CSCF#1 by the origination procedures. The Response Confirmation may also contain SDP. This may be the same SDP as in the Offer Response received in Step 7 or a subset.
Step 9-10.
S-CSCF#1 forwards the offered SDP to the terminating endpoint as per the PSTN terminating procedures via the established session path.
Step 11-13.
The terminating end point answers to the offered SDP and the message is passed through the established session path to the originating end point.
Step 14-16.
When the originating endpoint has completed the resource reservation procedures, it sends the successful resource reservation message to S-CSCF#1 by the origination procedures and it is passed to the terminating end point through the session path.
Step 17-19.
The terminating endpoint acknowledges the result and the message is passed onto the originating end point via the session path.
Step 20-22.
Terminating end point generates ringing message and forwards it to BGCF which in tern forwards the message to SCSCF#1. S-CSCF#1 forwards the ringing message to the originator, per the origination procedure
Step 23.
When the destination party answers, the termination procedure results in a SIP 200-OK final response to the BGCF
Step 24-25.
The BGCF forwards this information to the S-CSCF#1 and then it is forwarded to the originating end point.
Step 26.
The 200-OK is returned to the originating endpoint, by the origination procedure from terminating end point.
Step 27.
The originating endpoint sends the final acknowledgement to S-CSCF#1 by the origination procedures.
Step 28.
S-CSCF#1 forwards this message to the terminating endpoint as per the PSTN terminating procedures.
5.5.4 (S-S#4) Session origination with PSTN termination in a different network from the S-CSCF p. 119
The Serving-CSCF handling session origination performs an analysis of the destination address, and determines, with support of applications or other databases, that the session is destined to the PSTN. The request is therefore forwarded to a local BGCF. The BGCF determines that the PSTN interworking should occur in another network, and forwards this to a BGCF in the interworking network. The BGCF then selects a MGCF in that network. The request is then forwarded to the MGCF.
Refer to Table 5.2 in clause 5.4a to see which origination sequences share this common S-S procedure. In addition the text below clarifies the role of the" Terminating Network".
MO#1
Refer to Table 5.2 in clause 5.4a to see which termination sequences share this common S-S procedure. In addition the text below clarifies the role of the" Terminating Network".
Mobile origination, roaming. The "Originating Network" of S-S#4 is therefore a visited network.
MO#2
Mobile origination, located in home service area. The "Originating Network" of S-S#4 is therefore the home network.
AS-O
Application Server origination. The" Originating Network" of S-S#1 is the home network. The element labelled S-CSCF#1 corresponds to the S-CSCF in Figure 5.16b.
PSTN-T
PSTN termination. This occurs when the MGCF is selected to be in a different network than the S-CSCF.
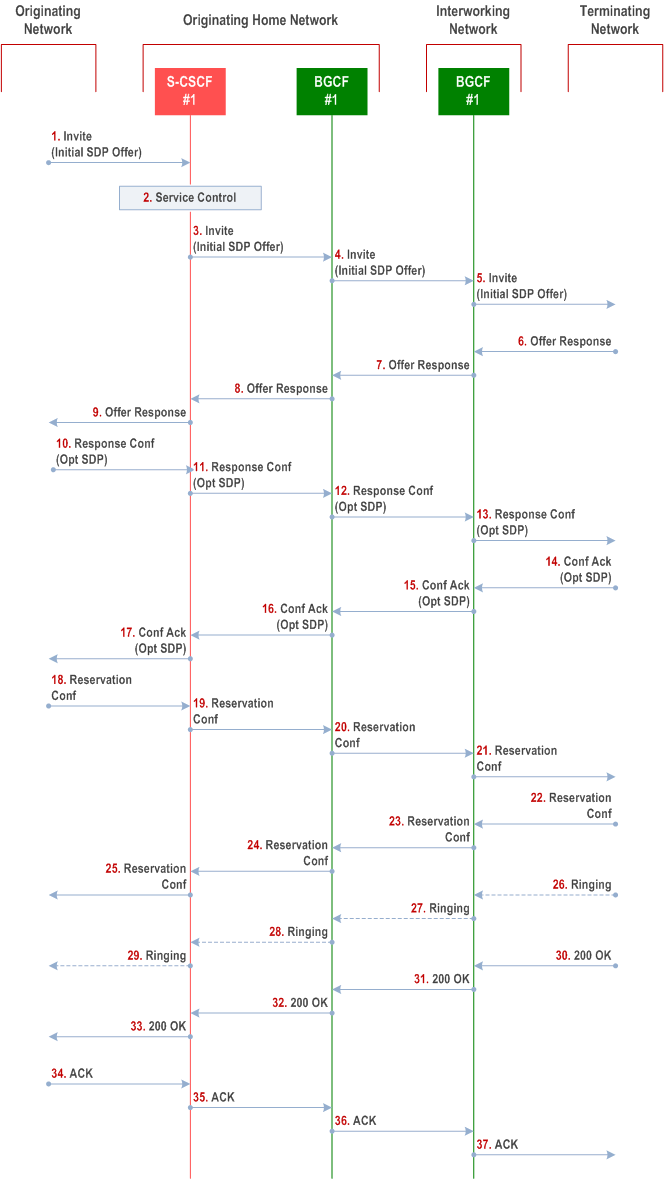
Procedure S-S#4 is as follows:
Step 1.
The SIP INVITE request is sent from the UE to S-CSCF#1 by the procedures of the originating flow. This message should contain the initial media description offer in the SDP.
Step 2.
S-CSCF#1 invokes whatever service logic is appropriate for this session setup attempt
Step 3.
S-CSCF#1 performs an analysis of the destination address. From the analysis of the destination address, S-CSCF#1 determines that this is for the PSTN, and passes the request to the BGCF#1.
Step 4.
The BGCF#1 determines that the PSTN interworking should occur in interworking network, and forwards the request on to BGCF#2.
Step 5.
BGCF#2 determines that the MGCF shall be in the same network, and hence proceeds to select an appropriate MGCF. The SIP INVITE request is forwarded to the MGCF. The PSTN terminating information flows are then followed.
Step 6-8.
The media stream capabilities of the destination are returned along the signalling path, as per the PSTN termination procedure.
Step 9.
S-CSCF#1 forwards the SDP to the originator, as per the originating procedure.
Step 10.
The originator decides the offered set of media streams, confirms receipt of the Offer Response with a Response Confirmation, and forwards this information to S-CSCF#1 by the origination procedures. The Response Confirmation may also contain SDP. This may be the same SDP as in the Offer Response received in Step 12 or a subset.
Step 11-13.
S-CSCF#1 forwards the offered SDP to the terminating endpoint, as per the PSTN terminating procedure.
Step 14-17.
Terminating end point responds to the offer via the established session path towards the originating end point.
Step 18-21.
When the originating endpoint has completed the resource reservation procedures, it sends the successful resource reservation message to S-CSCF#1 by the origination procedures and it is forwarded to the terminating end point via established session path.
Step 22-25.
The terminating end point responds to the message towards the originating end point.
Step 26-29.
Terminating end point generates ringing message towards the originating end point.
Step 30-33.
Terminating end point sends 200 OK when the destination party answers the session.
Step 34-37.
Originating end point acknowledges the establishment of the session.