Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
AA.3 SBI Capable HSS Discovery and Selection
AA.3.1 General
AA.3.2 HSS Registration in NRF
AA.3.3 HSS Discovery and Selection via NRF
AA.3.3.1 General
AA.3.3.2 HSS Discovery
AA.3.3.3 Handling of HSS Group ID in IMS Procedures
AA.4 NRF based Discovery and Selection for other IMS nodes
...
...
AA.3 SBI Capable HSS Discovery and Selection p. 367
AA.3.1 General p. 367
An SBI capable IMS entity (e.g. I-CSCF, S-CSCF, IMS AS or DCSF) performs HSS discovery to discover an HSS that manages the user subscriptions.
The SBI capable IMS entity shall utilize the NRF to discover the SBI capable HSS instance(s) unless the information about SBI capable HSS instances is available by other means, e.g. locally configured on the SBI capable IMS entity. The HSS selection function in SBI capable IMS entities selects an SBI capable HSS instance based on the available SBI capable HSS instances (obtained from the NRF or locally configured).
An SBI capable IMS entity always selects an HSS within its own PLMN. The HSS selection should consider one of the following factors when available to the SBI capable IMS entity:
- HSS Group ID of the IMS identity (IMPI or IMPU, or PSI).
- IMS private identity (IMPI); e.g. the SBI capable IMS entity selects an SBI capable HSS instance based on the IMPI set the UE's IMPI belongs to, configured locally or based on the results of a discovery procedure with NRF using the UE's IMPI as input for HSS discovery.
- IMS public identity (IMPU); e.g. the SBI capable IMS entity selects an SBI capable HSS instance based on the IMPU set the UE's IMPU belongs to, configured locally or based on the results of a discovery procedure with NRF using the UE's IMPU as input for HSS discovery.
- Public Service Identity (PSI); e.g. the SBI capable IMS entity selects an SBI capable HSS instance based on the PSI set the received PSI belongs to, configured locally or based on the results of a discovery procedure with NRF using the received PSI as input for HSS discovery.
- MSISDN; e.g. the SBI capable IMS entity selects an SBI capable HSS instance based on the MSISDN set the UE's MSISDN belongs to, configured locally or based on the results of a discovery procedure with NRF using the MSISDN as input for HSS discovery.
AA.3.2 HSS Registration in NRF p. 367
An SBI capable HSS registers in the NRF using the Nnrf_NFManagement_NFRegister Request message as defined in TS 23.502. The NF profile of the HSS registered in NRF includes necessary information for an SBI capable IMS entity to send SBI service requests to the selected SBI capable HSS service instance.
Different SBI capable HSS instances managing different sets of IMPIs/IMPUs may be deployed in a given PLMN. In this case, the SBI capable HSS instances register in NRF using either different ranges of IMPIs/IMPUs and/or HSS Group IDs.
AA.3.3 HSS Discovery and Selection via NRF p. 368
AA.3.3.1 General p. 368
During the IMS procedure, an SBI capable IMS entity sends a Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request to NRF as defined in TS 23.502 to discover SBI capable HSS instances within a given PLMN. The SBI capable IMS entity may store all returned SBI capable HSS instances and their NF profiles for subsequent use, including, if applicable, supported IMPIs/IMPUs ranges, and/or HSS Group IDs. If no SBI capable HSS instance is available in the PLMN, then the NRF replies to the SBI capable IMS entity with no information. In this case, the SBI capable IMS may then attempt to communicate with the HSS using non-SBA protocols.
When an SBI capable IMS entity receives an NRF response that HSS supports SBI and stores the information received from the HSS, it shall make use of Nnrf_NFStatusSubscribe /Unsubscribe service operations with NRF as defined in TS 23.502 to receive Nnrf_NFStatusNotify service operation for updates to the NF profiles of SBI capable HSS instances registered in NRF.
AA.3.3.2 HSS Discovery p. 368
The call flow in Figure AA.3.3.2-1 illustrates the steps to locate the HSS instance for an IMS public identity.
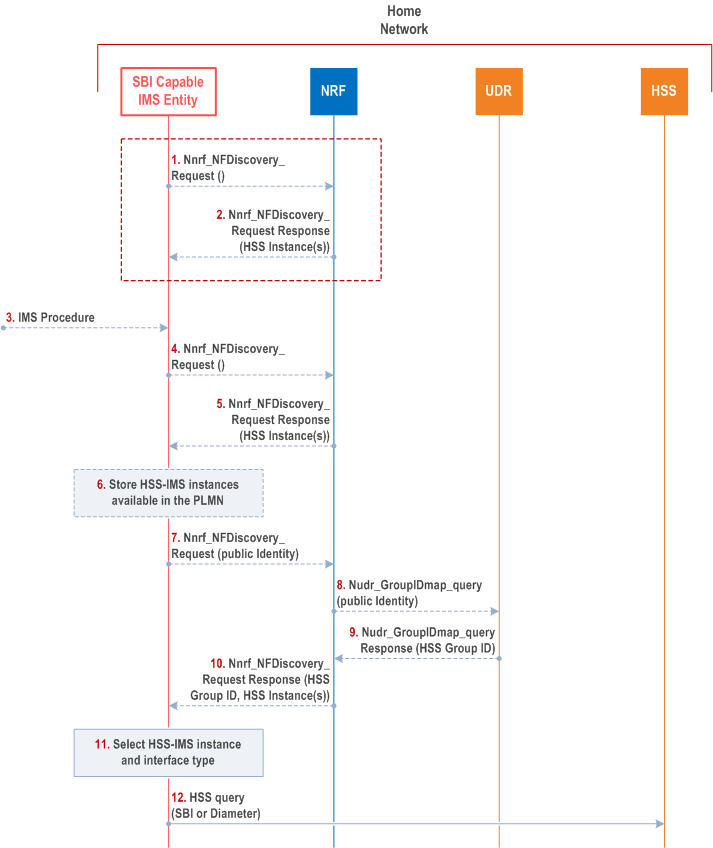
Steps 1 - 2 may be performed, any time after power up, e.g. in the scenario where only a single HSS instance or HSS group is deployed, and in the scenario where an operator has IMPI/IMPU ranges that are registered in NRF as described in clause AA.3.2. In this case there is no need for any IMPU to perform the 2 steps.
Step 1.
Steps 4 - 6 may be performed, e.g. if the SBI capable IMS entity did not retrieve and store information about HSS instances and/or HSS Group IDs registered in the PLMN at an earlier stage (performed steps 1-2).
An SBI capable IMS entity may discover the SBI capable HSS instances available in the PLMN via Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request .
Step 2.
The NRF provides the SBI capable IMS entity with the HSS instances and/or any HSS Group IDs registered in the PLMN. If no SBI capable HSS instance and/or any HSS Group ID is available in the PLMN, then the NRF will reply to the SBI capable IMS entity with no information about available SBI capable HSS instances.
Step 3.
The SBI capable IMS entity receives an IMS procedure related to a given IMS user (IMPI or IMPU depending on the procedure).
Step 4.
Steps 7 - 10 are performed only if the SBI capable IMS entity cannot locate an HSS instance corresponding to the IMS public identity based on stored information.
An SBI capable IMS entity may discover the SBI capable HSS instances available in the PLMN via Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request .
Step 5.
The NRF provides the SBI capable IMS entity with the HSS instances and/or any HSS Group IDs registered in the PLMN. If no SBI capable HSS instance and/or any HSS Group ID is available in the PLMN, then the NRF will reply to the SBI capable IMS entity with no information about available SBI capable HSS instances.
Step 6.
The SBI capable IMS entity stores the result of the NRF discovery, if any is received. The IMS capable entity may store the received response for future use, otherwise the IMS entity must perform the query in response to each IMS request it receives.
If the SBI capable IMS entity received no results at all, the procedure is exited, and the SBI capable IMS entity may use Diameter interfaces to interact with an HSS.
Step 7.
The SBI capable IMS entity sends to NRF an Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request with the IMS public identity received in step 3.
Step 8.
NRF may query the UDR, via the Nudr_GroupIDmap service, for the HSS Group ID corresponding to the IMS public identity.
Step 9.
If requested the UDR returns the HSS-IMS Group ID to NRF.
Step 10.
NRF locates HSS instance(s) corresponding to the HSS Group ID. NRF returns and provides and them to the SBI capable IMS entity the HSS instance(s) profile which includes the HSS Group ID.
Step 11.
The SBI capable IMS entity selects the HSS instance.
Step 12.
The SBI capable IMS entity can then start interaction with the selected HSS instance.
AA.3.3.3 Handling of HSS Group ID in IMS Procedures |R17| p. 369
The HSS group ID may be transported in SIP signalling related to the following procedures:
- Initial IMS Registration procedure.
- IMS Terminating session establishment procedure.
- IMS Originating session establishment procedure.
AA.4 NRF based Discovery and Selection for other IMS nodes |R18| p. 370
AA.4.1 Service Based MRF Discovery and Selection p. 370
AA.4.1.1 General p. 370
While no SBI procedures are defined for MRF (and hence MRFC and MRFP), it is possible to utilize NRF to discover and select the MRF. In networks where MRFC and MRFP are co-located it is only necessary to indicate that the service function is MRF, in networks where separated MRFC and MRFP are deployed the network function discovering the MRF (or MRFC) may not know the network topology, and thus the service function descriptor is always set to MRF (even when registering/discovering an MRFC).
The MRFP service descriptor is only used by the MRFC when separate MRFC and MRFP are deployed, and the MRFC is configured to use the NRF to discover a suitable of MRFP.
When an SBI capable IMS entity selects a MRF it shall use the IMS media service list to ensure that the selected MRF supports the required media capabilities for the application. The SBI capable IMS entity may utilize other available information to assist in selecting the MRF based on implementation criteria (e.g. proximity of the UE to MRF to minimize transmission delays).
A SBI capable IMS entity always selects an MRF (or MRFC within its own PLMN.
AA.4.1.2 MRF Registration p. 370
If an MRF has been configured to support NRF based discovery or selection it shall register with the NRF using the Nnrf_NFManagement_NFRegister Request message as defined in TS 23.502.
The NF profile for the MRF includes all common information for SBI capable IMS entities plus a text-based list of IMS media services offered by the MRF (e.g. "video transcoding", "data channel services", "voice conferencing", "in-call announcements").
The MRF registration may include other optional information pertaining to the implementation (e.g.NF location to support routing media to the nearest MRF).
In the case when the MRFC and MRFP are separate entities, the MRFC identifies itself using the MRF service descriptor during SBA interactions.
In cases where the MRFP is a separate entity to the MRFC, it may be necessary for the MRFP to perform registration with the NRF (unless local configuration is used). In such cases the MRFP registers with the NRF using a NF profile that also includes a similar list of media services and uses the NF identifier "MRFP".
AA.4.1.3 MRF Discovery and Selection p. 371
During the IMS procedure, an SBI capable IMS entity sends a Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request to NRF as defined in TS 23.502 to discover applicable MRF instances within a given PLMN. The SBI capable entity may include a list of the service or services it is requesting to use, in which case the NRF will respond with the MRF (s) that support all the services listed.
When separate MRFC and MRFP (or a mix of MRF, MRFC, MRFP) are deployed in a network - the entity performing discovery of the MRFC may not know the network topology, and thus the discovery request sent by the SBI entity uses the MRF service descriptor, even if the resulting node is an MRFC.
If necessary when there is no direct linkage between an MRFC and MRFP, then discovery and selection of the MRFP may be needed after the MRFC discovery; in such a case the MRFC may perform SBI discovery of the MRFP using the NRF, in such a case the requested service descriptor is MRFP. Only an MRFC may discover the MRFP in this manner.