Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.7.9…
AC.7.9.3…
AC.7.10…
AC.7.10.4.2…
AC.9…
AC.10…
AC.11…
AD…
AE…
AF…
AG…
U.2 Procedures
U.2.0 WWSF discovery
U.2.1 Registration
U.2.1.1 Introduction
U.2.1.2 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity using IMS authentication
U.2.1.3 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity based on web authentication
U.2.1.4 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity from a pool of Public User Identities
U.2.2 Session management related procedures
U.2.3 De-Registration procedures
U.2.4 Media plane Optimization
...
...
U.2 Procedures p. 318
U.2.0 WWSF discovery |R15| p. 318
The URI to a WWSF for WebRTC access to IMS may be configured in the UICC.
Prior to performing registration, a UE may use the following mechanism to determine the URI of the WWSF:
- If the UICC contains a URI to a WWSF for WebRTC access to IMS, then the UE uses this URI for registration.
- Otherwise, the UE derives the URI to WWSF from the home domain name as specified in TS 23.003.
U.2.1 Registration p. 318
U.2.1.1 Introduction p. 318
The WebRTC IMS architecture supports the following different IMS registration scenarios that may differ in the authentication method, and ownership of the WWSF (i.e. operator network or third party):
- "WIC registration of individual Public User Identity using IMS authentication": The user has a subscription with an individual Public User Identity and an IMS authentication mechanism as specified in TS 33.203 is used to authenticate with IMS. Clause U.2.1.2 provides detailed procedures for this scenario.
- "WIC registration of individual Public User Identity based on web authentication": The user has an IMS subscription. The WWSF or WAF authenticates the user using a web identity and authentication scheme. The WWSF determines IMS identities for the user (e.g. based on the user's web identity via database lookup or other translation means). An individual registration is handled by the S-CSCF per WIC registration. Clause U.2.1.3 provides detailed procedures for this scenario.
- "WIC registration of individual Public User Identity from a pool of Public User Identities": The WWSF is typically located in a third party network and has a business arrangement with the IMS operator. The WWSF or WAF authenticates the user using a web identity and authentication scheme, or authorizes the WIC without authenticating the user. The WWSF assigns IMS identities to the user from within a pool allocated by the operator. An individual registration is handled by the S-CSCF per WIC registration. Clause U.2.1.4 provides detailed procedures for this scenario.
U.2.1.2 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity using IMS authentication p. 319
The WIC obtains information needed for IMS registration (e.g. Private User Identity and Public User Identity) via unspecified means. For example, some of this information might be stored in cookies or local browser storage after visiting a secure web site provided by the IMS operator.
Figure U.2.1.2-1 shows a registration call flow where IMS authentication is used to register the WIC.
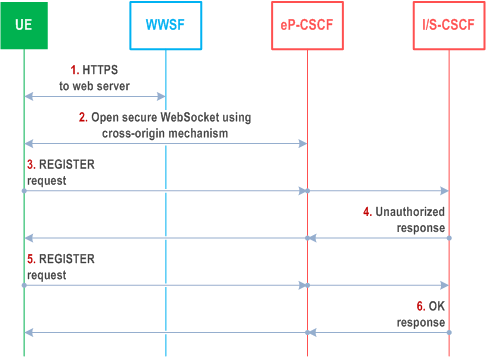
Step 1.
The WIC initiates an HTTPS connection to the WWSF. The TLS connection provides one-way authentication of the server based on the server certificate. The browser downloads and initializes the WIC from the WWSF.
Step 2.
The WIC opens a WSS (secure WebSocket) connection using cross-origin mechanism to the eP-CSCF. Standard cross-origin resource sharing procedures are used to ensure that the WIC originated from a WWSF authorized to access this eP-CSCF.
Step 3-6.
The WIC initiates a registration transaction with IMS via the eP-CSCF by sending a REGISTER request to the eP-CSCF via the WSS (secure Web Socket) connection. The REGISTER request includes IMS Authentication parameters, Private User Identity, Public User Identity and other information as needed for proper IMS registration. This request is translated into an IMS registration process by the eP-CSCF. This process leverages user credentials in HSS.
U.2.1.3 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity based on web authentication p. 319
Figure U.2.1.3-1 shows a registration call flow where the WIC registers with IMS based on web authentication with the WWSF.
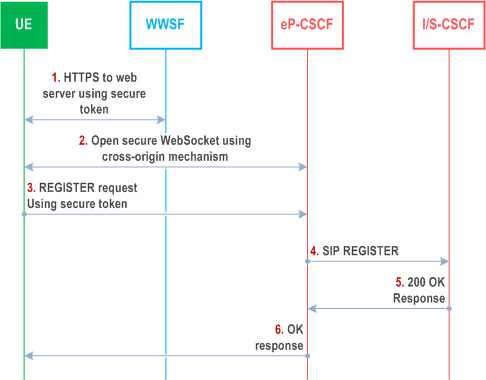
Step 1.
As the security token may be associated with a lifetime, the WIC may need to periodically refresh its registration. This registration refresh process entails all steps above with following exceptions:
The WIC initiates an HTTPS connection to the WWSF. The TLS connection provides one-way authentication of the server based on the server certificate. The browser downloads and initializes the WIC from the WWSF. The WWSF or WAF authenticates the user using a common web authentication procedure. The WWSF determines the Private User Identity and Public User Identity for the WIC and returns the security token which is issued by the WAF to the WIC. The IMS identities may be provided to the WIC in addition to the security token.
Step 2.
The WIC opens a WSS (secure WebSocket) connection using cross-origin mechanism to the eP-CSCF. Standard cross-origin resource sharing procedures are used to ensure that the WIC originated from a WWSF authorized to access this eP-CSCF.
Step 3.
The WIC sends a REGISTER request to the eP-CSCF via the WSS (secure Web Socket) connection. The request includes the security token received from the WWSF. If the WIC received the IMS identities in step 1, the request shall include the IMS identities.
Step 4.
The eP-CSCF validates the contents of the security token and obtains the IMS identities being registered. The eP-CSCF then forwards the authorized REGISTER request to IMS to initiate authentication-less IMS registration using TNA (see TS 33.203, Annex U) procedures, with an indication that the authentication has already been carried out.
Step 5.
The S-CSCF responds with a 200 OK message are accepted.
Step 6.
The eP-CSCF sends the OK response back to the WIC.
- For Step 1, the opening of the TLS connection, the downloading of the WIC and the web authentication of the user using the WIC may not be needed.
- Step 2 may not be needed.
U.2.1.4 WIC registration of individual Public User Identity from a pool of Public User Identities p. 320
The WWSF is provided with a pool of IMS subscriptions, each associated to a single Private User Identity and one or more Public User Identities as specified in clause 4.3.3.4. The WWSF can assign individual Public and Private User Identities from this pool. The WWSF may be located in a third party network and have a business arrangement with the IMS operator.
For pool management, the IMS operator may also provide the WWSF with an unbounded number of Private User Identities/Public User Identities associations to be allocated to WIC users, where each user may use multiple WICs sharing the same Public User Identity and each WIC being assigned a different Private User Identity.
The registration call flow for a WIC being assigned an individual Public User Identity from a pool of Public User Identities assigned to the WWSF is the same registration call flow defined in Figure U.2.1.3-1 with following differences:
- In step 1, the WWSF or WAF may decide not to authenticate the user. Unauthenticated users are anonymous to the third party but may still be authorized for IMS service.
- The lifetime of the security should be coordinated between the IMS provider and the WWSF provider; otherwise, the WWSF cannot know when a Public User Identity Private User Identity association from its pool can be re-assigned to another user.
- Alternatively, as an implementation specific option, eP-CSCF may indicate to the WWSF when a certain Public User Identity can be re-assigned.
U.2.2 Session management related procedures p. 320
Origination and termination and Session release procedures for WebRTC IMS clients follow standard IMS procedures in the core network (see clause 5.6 and clause 5.7 and clause 5.10) with the exception that routing of all messages between the WIC and S-CSCF traverse the eP-CSCF (rather than P-CSCF) and that parameters of Iq procedures take into account the WebRTC-specific extensions used by the WIC to send and receive media.
U.2.3 De-Registration procedures p. 321
De-registration procedure for WebRTC IMS clients follows standard IMS procedures in the core network (see clause 5.3) with the exception that routing of all messages between the WIC and S-CSCF traverse the eP-CSCF (rather than P-CSCF).
U.2.4 Media plane Optimization |R13| p. 321
The IMS operator is able to convey the audio and chat session without bearer level protocol conversion when session is between WebRTC clients.
When both ends are WebRTC client, the eIMS-AGWs remain allocated but media plane interworking is disabled, except when LI is needed. When media plane optimization is enabled, the eIMS-AGW forwards all protocol layers either including DTLS, or on top of DTLS transparently (see clause U.1.5).
When LI is performed, media plane interworking is performed according to TS 33.328.
Figure U.2.4-1 shows a call flow diagram establishing the e2ae communication between WebRTC clients through the IMS network. I/S-CSCFs are not shown for brevity.
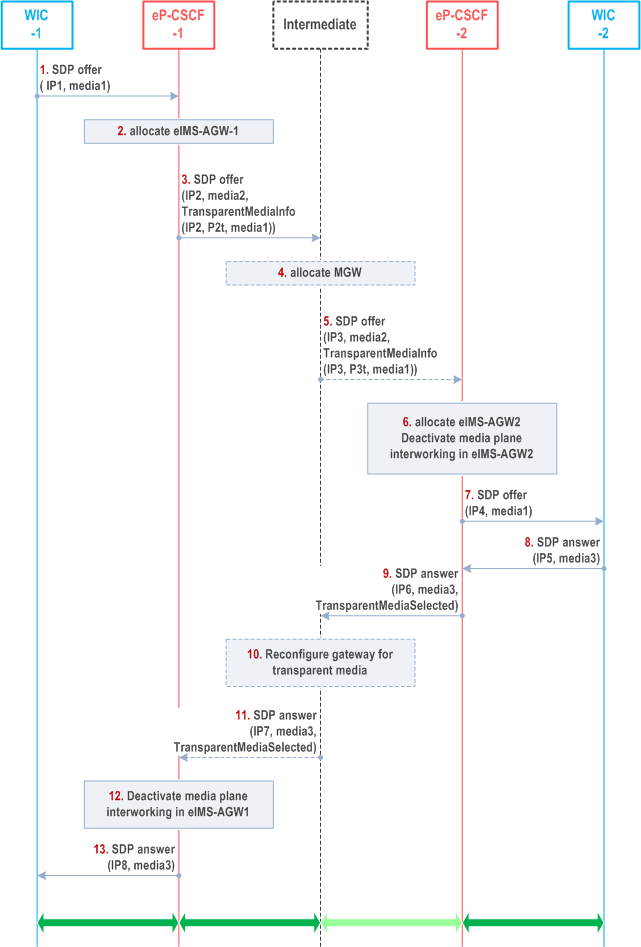
Step 1.
WebRTC client (WIC-1) initiates a call, creating a Session Description Protocol (SDP) offer and sends it to the originating side eP-CSCF. The SDP offer may contain SRTP, ICE and Data Channel information. The WIC-1 IP address is IP1.
Step 2.
The eP-CSCF-1 receives the SDP offer from WIC-1. The eP-CSCF-1 allocates eIMS-AGW1 and configures it to terminate ICE procedures and provide interworking (e.g. transcoding, or transport interworking between a Data Channel and transport outside a Data Channel). eIMS-AGW1 allocates address IP2. It also requests the media gateway to provide a transport port suitable for a transparent forwarding of the media. IMS-AGW1 allocates port P2t for that purpose. Depending on configuration, it either configures the IMS-AGW1to terminate or to transparently forward the DTLS layer for transparent media. The eP-CSCF-1 shall not apply OMR procedures according to Annex Q.
Step 3.
The eP-CSCF-1 describes the new media2 that result from the interworking and inserts the address IP2 at the eIMS-AGW1 in the SDP offer connection line it sends. Within the SDP offer, the eP-CSCF-1 also indicates that the media1 targeted for transparent forwarding (those media are called "transparent media" in what follows) can be selected instead and also encapsulates in SDP attribute(s) information about those transparent media (SDP attributes, SDP media line including transport protocol and port P2t, Data Channel related information, but no ICE related information. A DTLS fingerprint is included, and depending on configuration, it either contains the fingerprint received from the WIC-1 or a fingerprint allocated by eIMS-AGW1). To enable the check in step 6 wether intermediates which do not support switching to the encapsulated media are inserted into the media path, the eP-CSCF-1 also encapsulates the address IP2.
Step 4.
A possible intermediate (e.g. IBCF with attached TrGW or MTFC with attached MRFP) may also insert a media gateway into the user plane. Such an intermediate may optionally also support switching to the transparent media; this is required to allow the transparent media to be selected when its media gateway is present in the media path. Intermediates which do not support switching to the transparent media will be detected and will cause media 2 to be selected in step 6.
The possible intermediate can also apply OMR procedures according to Annex Q to offer that its media gateway is bypassed by an optimised media path.
Step 5.
The intermediate replaces the transport address within the connection line in the SDP offer with the address IP3 allocated at its media gateway. If the intermediate supports switching to the transparent media, it also modifies the transparent media information encapsulated in SDP attribute(s) by replacing the encapsulated transport address with IP3 and the port information with P3t.
Step 6.
eP-CSCF-2 allocates eIMS-AGW2. It compares the transport address in the SDP connection line with the transport address in the transparent media information encapsulated in SDP attribute(s). Because both addresses match, the eP-CSCF-2 takes the transparent media information into consideration. Otherwise it shall ignore the transparent media information. The eP-CSCF-2 shall not apply OMR procedures according to Annex Q and shall discard any received OMR related information. Because eP-CSCF2 knows that the served WIC-2 is a WIC, it decides that the transparent media information is appropriate and configures the eIMS-AGW2 to transparently forward those media; depending on configuration, eP-CSCF2 either configures the eIMS-AGW2 either transparently forward the DTLS layer or to terminate it, and it either forwards the fingerprint received as part of the transparent media information or a fingerprint allocated by eIMS-AGW2.
Step 7.
The eP-CSCF-2 forwards SDP offer with the transparent media1 and the transport address IP4 allocated at eIMS-AGW2 to WIC-2.
Step 8.
WIC2 selects media3 from the offered media1 and sends the selected media3 in the SDP answer to the eP-CSCF-2.
Step 9.
The eP-CSCF-2 forwards the SDP answer including connection information for eIMS-AGW2 and the unmodified media3, and includes an indication that the transparent media have been selected. Depending on configuration, it either forwards the fingerprint received from WIC2 or a fingerprint allocated by eIMS-AGW2.
Step 10.
The possible intermediate reconfigures its MGW to transparently pass media3.
Step 11.
The intermediate forwards the SDP answer with unmodified media3 and indication that the transparent media have been selected and includes address information IP7 of the controlled MGW.
Step 12.
According to received SDP answer, the eP-CSCF-1 knows that there is no bearer level protocol conversion. So eP-CSCF-1 deactivates media plane interworking in eIMS-AGW1.
Step 13.
The eP-CSCF-1 forwards the SDP answer to WIC-1. Depending on configuration, it either forwards the fingerprint received in step 12 or a fingerprint allocated by eIMS-AGW1.