Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4…
5
6…
6.4…
6.5…
6.5.3…
7…
8…
8.2.2…
9…
9.3…
9.3.2.21…
9.3.3…
9.3.6…
9.3.11…
9.3.13…
9.3.14…
9.4…
9.4.6…
9.5…
10…
10.3…
10.3.2.22…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.3.10…
10.4…
11…
11.3…
11.3.3…
11.4…
12…
12.3…
13…
14…
14.2.2.2…
14.3…
14.3.2.20…
14.3.2.40…
14.3.3…
14.3.3.3…
14.3.4…
14.3.4.6
14.3.4.7…
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.3…
14.3.4A.4…
14.3.4A.6…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.4A.9…
14.3.4A.10…
14.3.5…
14.3.6…
14.3.9…
14.3.12…
14.4…
15…
16…
17…
18…
A
B…
14.3.4.7 MBMS suspension notification
14.3.4.8 MBMS bearer event notification
14.3.4.9 Switching between MBMS bearer and unicast bearer
...
...
14.3.4.7 MBMS suspension notification p. 226
14.3.4.7.1 General p. 226
In this procedure the NRM client is requested by the NRM server to send a MBMS suspension report. This request for MBMS suspension report can be included in the MBMS bearer announcement and the NRM server may choose to only send this request for MBMS suspension report to a subset of all NRM clients.
14.3.4.7.2 Procedure p. 226
Figure 14.3.4.7.2-1 illustrates a procedure in which the NRM client notifies the NRM server about an MBMS suspension decision in RAN.
The NRM server can decide on a subset of all VAL UEs in the MBMS broadcast area that shall report on MBMS bearer suspension. When the NRM server makes the decision of the VAL UE subset, consideration shall be taken to the location of the VAL UEs, since VAL UEs' location is dynamically changed. This means that the MBMS suspension reporting instruction may need to be updated regularly based on the VAL UEs mobility.
Pre-condition:
- It is assumed that there is at least one active MBMS bearer
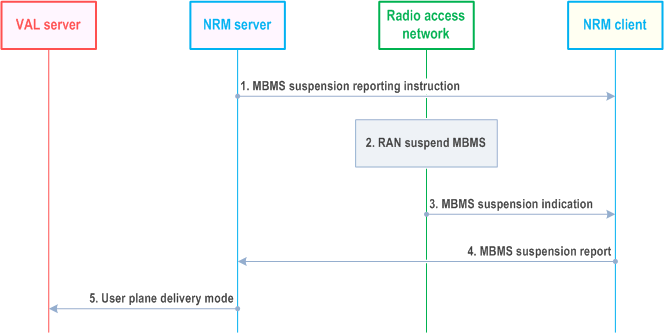
Step 1.
The NRM client that is not instructed to send an MBMS suspension report shall still detect the MBMS suspension indication from RAN (step 3). A NRM client shall in this case not send other types of report (e.g. MBMS listening reports).
The same procedure can be applied at MBMS resumption or other MBMS events that may be detected by the NRM client.
The NRM server sends an MBMS suspension reporting instruction to the NRM client.
Step 2.
RAN decides to suspend the MBMS bearer, according to existing procedures in TS 36.300.
Step 3.
An MBMS suspension indication is sent in the MSI (MCH Scheduling Information), according to existing procedures in TS 36.300.
Step 4.
The NRM client detect the MBMS suspension and sends an MBMS suspension report.
Step 5.
Based on the MBMS suspsension report received, the NRM server determines whether to switch to a new bearer (unicast or MBMS). If NRM server determines to switch to unicast bearer, then the NRM server sends the user plane delivery mode message to VAL server , and the VAL server sends the downlink data over the new bearer.
14.3.4.8 MBMS bearer event notification p. 227
14.3.4.8.1 General p. 227
The NRM server is an instantiation of a GCS AS. For the NRM server to know the status of the MBMS bearer, and thus know the network's ability to deliver the VAL service, it is required that the network provides MBMS bearer event notifications to the NRM server. The different events notified to the NRM server include the MBMS bearer start result (e.g. when the first cell successfully allocated MBMS resources), including information if any cells fail to allocate MBMS resources to a specific MBMS bearer, the current status of the MBMS bearer, MBMS bearer suspension/resume or overload scenarios.
14.3.4.8.2 Procedure p. 227
The procedure in Figure 14.3.4.8.2-1 shows notification information flows from NRM server to BM-SC.
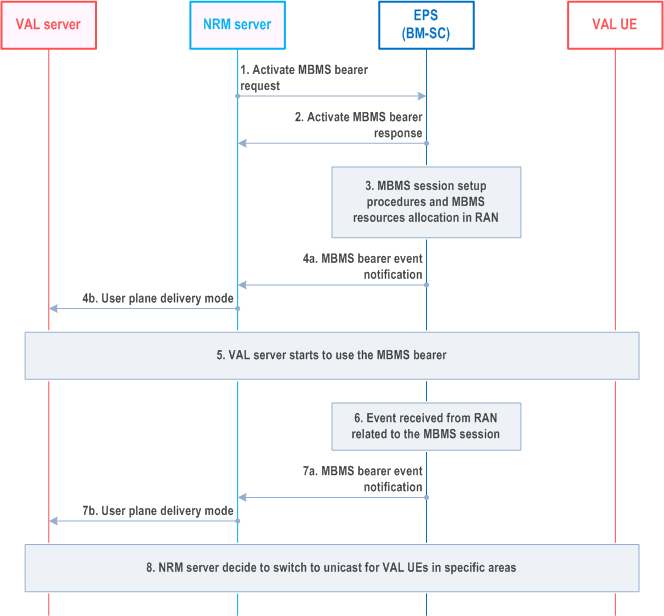
Step 1.
The NRM server activates an MBMS bearer. The activation of the MBMS bearer is done on the MB2-C reference point and according to TS 23.468.
Step 2.
The BMSC will respond to the activation with an Activate MBMS bearer response message, according to TS 23.468.
Step 3.
The EPC and RAN will initiate the MBMS session start procedure according to TS 23.246. This procedure is outside the scope of this specification.
Step 4a.
At the first indication of a successful MBMS session start procedure, the BM-SC sends a MBMS bearer event notification, indicating that the MBMS bearer is ready to use.
Step 4b.
The NRM server notifies user plane delivery mode to the VAL server.
Step 5.
The VAL server starts to use the MBMS bearer according to the MBMS procedures in this specification.
Step 6.
An event from RAN related to the MBMS session is received by the BM-SC.
Step 7a.
The BM-SC notifies the NRM server of certain MBMS related events including references to affected MBMS services areas or list of cells. Example of such events may be radio resources not available, overload, MBMS suspension.
Step 7b.
The NRM server notifies user plane delivery mode to the VAL server.
Step 8.
The NRM server may decide, based on the received events, to switch to unicast transmission for relevant VAL UEs.
14.3.4.9 Switching between MBMS bearer and unicast bearer p. 229
14.3.4.9.1 General p. 229
The NRM server monitors the bearers used for VAL service communications and decides to switch between MBMS and unicast bearers.
14.3.4.9.2 Procedure p. 229
Figure 14.3.4.9.2-1 shows the procedure for service continuity when a UE is about to move out of MBMS coverage or getting into good MBMS coverage by switching between MBMS bearer and unicast bearer.
Pre-condition:
- It is assumed that a bearer (unicast or MBMS) has been activated by the VAL server for downlink delivery.
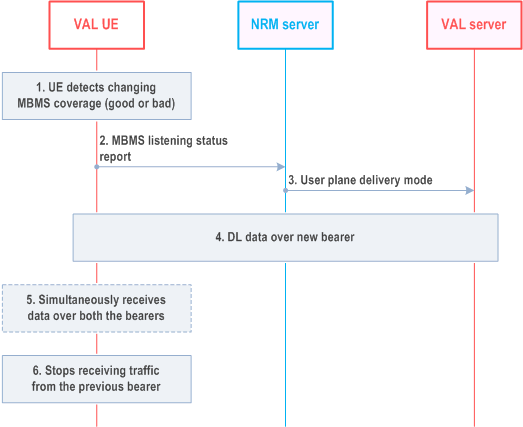
Step 1.
The VAL UE detects changing MBMS bearer condition (good or bad MBMS coverage) for the corresponding MBMS service. The method to detect is implementation specific.
Step 2.
The NRM client notifies the NRM server about the MBMS bearer condition for the corresponding MBMS service by sending the MBMS listening status report.
Step 3.
The NRM server makes the decision to switch between MBMS delivery and unicast delivery based on available information at the NRM server including the MBMS listening status report as described in clause 14.3.4.5. The NRM server notifies a user plane delivery mode to the VAL server.
Step 4.
The VAL server sends the downlink data over the new bearer (unicast or MBMS) to the VAL client as per step 3.
Step 5.
During the switching, the VAL client simultaneously receives downlink data through both bearers (unicast bearer and MBMS bearer). If there is no downlink data to the VAL client, this step can be skipped.
Step 6.
The VAL client ceases to receive the downlink data through previous bearer but continues receiving data through new bearer.