Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.4.2
0…
6…
8…
9…
9.3…
9.3.3…
9.3.8…
9.3.13…
9.3.20…
9.3.23…
9.4…
10…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.4…
11…
12…
13…
14…
14.3…
14.3.3
14.3.4
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.5…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.5…
14.3.9…
14.4…
15…
17…
18…
A…
9.3.3 Event-triggered location reporting procedure
9.3.3.1 General
9.3.3.2 Fetching location reporting configuration
9.3.3.3 Location reporting
9.3.3.4 Update Location reporting configuration
9.3.4 On-demand location reporting procedure
9.3.5 Client-triggered or VAL server-triggered location reporting procedure
9.3.6 Location reporting triggers configuration cancel
9.3.7 Location information subscription procedure
9.3.7a Location information subscription update procedure
...
...
9.3.3 Event-triggered location reporting procedure p. 81
9.3.3.1 General p. 81
The location management server provides location reporting configuration to the location management clients, indicating what information the location management server expects and what events will trigger the sending of this information to the location management server. The decision to report location information can be triggered at the location management client by different conditions, e.g., the reception of the location reporting configuration, initial registration, distance travelled, elapsed time, cell change, MBMS SAI change, MBMS session change, leaving a specific MBMS bearer service area, tracking area change, PLMN change, call initiation, or other types of events such as emergency. The location report can include information described as ECGI, MBMS SAIs, geographic coordinates and other location information.
9.3.3.2 Fetching location reporting configuration p. 81
Figure 9.3.3.2-1 illustrates the procedure for fetching location reporting configuration.
Pre-condition:
- If multicast delivery mode is used, the MBMS bearer being used is activated by the location management server.
- The location management client is aware that the location reporting configuration is available at the location management server.
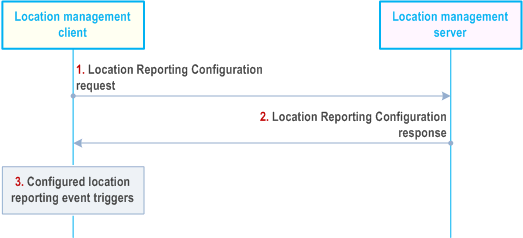
Step 1.
The location management client sends location reporting configuration request message to the location management server.
Step 2.
The location management server sends location reporting configuration message to the location management client(s) containing the initial location reporting event triggers configuration (or a subsequent update) , e.g. minimum time between consecutive reports, SAI changes, access RAT changes, or ECGI changes for reporting the location of the VAL UE. This message can be sent over a unicast bearer to a specific location management client or as a group message over an MBMS bearer to update the location reporting configuration for multiple location management clients at the same time.
Step 3.
The location management client stores or updates the location reporting event triggers configuration. A location reporting event occurs, triggering step 3.
9.3.3.3 Location reporting p. 82
Figure 9.3.3.3-1 illustrates the procedure for location reporting.

Step 1.
The location management client sends a location information report to the location management server, containing location information identified by the location management server and available to the location management client.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the report, the location management server updates location of the reporting location management client. If the location management server does not have location information of the reporting location management client before, then just stores the reporting location information for that location management client.
9.3.3.4 Update Location reporting configuration |R18| p. 82
The location management server may update the location reporting configuration information and inform the location management client of the update ones at any time by triggering the location reporting configuration update procedure.
Figure 9.3.3.4-1 illustrates the procedure for location reporting configuration update.
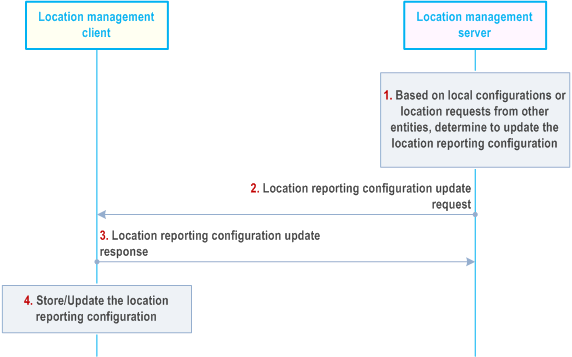
Step 1.
Based on the local configurations or the location information request from other entities (e.g., another location management client, VAL server) or if the VAL server updates the geographical location information of the existing VAL service area ID and there is triggering criteria corresponding to the updated VAL service area ID, the location management server decides to update the location reporting configuration and informs the updated information to the location management client.
Step 2.
The location management server sends location reporting configuration update request message to the location management client(s) which may contain the updated location reporting configuration, e.g. the event triggers, the minimum time between consecutive reports, the requested location access type and positioning methods when VAL UE fetches the UE location report. This message can be sent over a unicast bearer to a specific location management client or as a group message over an MBMS bearer to update the location reporting configuration for multiple location management clients at the same time. If the location reporting trigger from VAL server contains the triggering criteria based on the VAL service area ID, then the location management server converts those triggers into geographical area based triggers while sending it to the location management client.
Step 3.
The location management client(s) reply with location reporting configuration update response to the location management server with the update result.
Step 4.
The location management client stores or updates the new location reporting configuration received in step 2.
9.3.4 On-demand location reporting procedure p. 83
The location management server can request UE location information at any time by sending a location information request to the location management client, which may trigger location management client to immediately send the location report.
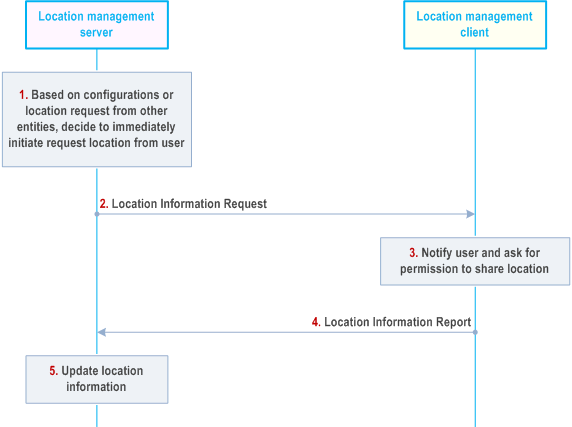
Step 1.
Based on configurations such as periodical location information timer, or location information request from other entities (e.g., another location management client, VAL server), location management server initiates the immediately request location information from the location management client.
Step 2.
The location management server sends a location information request to the location management client.
Step 3.
If the target VAL UE ID or user ID is not equal to its own VAL UE or VAL User identity, the LM client triggers off-network location management procedures as described in clause 9.5 to obtain target VAL UE location. If the received UE positioning method is PC5 SEAL LM, target VAL UE location information (including velocity) is obtained via off-network procedure as defined in clause 9.5; if the received UE positioning method is non-3GPP (e.g. WiFi, BT), target VAL UE location information (including velocity) is obtained via the corresponding non-3GPP method. If SEAL LM client is unable to find the target VAL UE's location (either the target VAL UE has moved away, or required positioning method is not supported by target VAL UE) then SEAL LM client may send the failure message to the SEAL LM server. If the target VAL UE ID or user ID is equal to its own VAL UE or VAL user identity, VAL user or VAL UE is notified and asked about the permission to share its location. VAL user can accept or deny the request.
Step 4.
The location management client immediately responds to the location management server with a report containing location information identified by the location management server and available to the location management client or the failure reason when the requested UE's location information cannot be obtained.
Step 5.
Upon receiving the report, the location management server updates location of the reporting location management client. If the location management server does not have location information of the reporting location management client before, then just stores the reporting location information for that location management client.
9.3.5 Client-triggered or VAL server-triggered location reporting procedure p. 84
Figure 9.3.5-1 illustrates the high level procedure of client-triggered or VAL server-triggered location reporting.
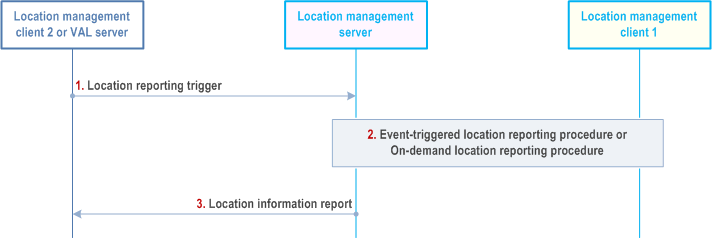
Step 1.
Further, if adaptive reporting is enabled by the VAL server with "SUGGESTIVE UPDATE", the location management server dynamically adjusts the reporting configuration as specified above (in step 2.a.ii).
Once location configuration is adjusted and if it is required to update the triggers to the SEAL client, the SEAL LMS may suggest the adaptive location configuration to the VAL server (or authorized SEAL location management client) as specified in clause 9.3.19. If VAL server accepts the suggested adaptive location configuration, then the location management server initiates an on-demand location reporting procedure or an event-triggered location reporting procedure for the location of location management client 1. If VAL server rejects the suggested adaptive location configuration, then the location management server will discard the updated configuration.
Location management client 2 (authorized VAL user or VAL UE) or VAL server sends a location reporting trigger to the location management server to activate a location reporting procedure for obtaining the location information of location management client 1. The location reporting event triggers as specified in Table 9.3.2.4-1, e.g. minimum time between consecutive reports, SAI changes, access RAT changes, or ECGI changes for reporting the location of the VAL UE, are included.
Step 2.
Location management server checks whether location management client 2 or VAL server is authorized to send a location reporting trigger. If the immediate report indicator is included or the triggering criteria is periodical reporting in step 1 and there is valid location report of the target UE (i.e. the timer for the stored location report is not expired), the location management server reuses the stored UE location report and sends the report to the location management client 2 or VAL server.
Step 3.
-
If the adaptive reporting is requested in step 1, the location management server interacts with NWDAF (e.g., UE mobility analytics as defined in clause 6.7.2 of TS 23.288) to obtain the location management client 1 moving statistic and prediction
- If "DIRECT UPDATE" is requested, the location management server determines the reporting configuration based on VAL service ID, VAL server ID, and the retrieved location management client 1 moving statistic and prediction. In order to adapt the configuration, the location management server may determine, for example, whether to increase or decrease the frequency of the report based on the UE's mobility pattern, or update location change condition (e.g., to change the location accuracy).
- If "SUGGESTIVE UPDATE" is requested, the location management server initially uses the configuration provided by VAL server and later dynamically adjusts the reporting configuration to determine adaptive location configuration based on VAL service ID, VAL server ID, and by analysing the retrieved location management client 1 moving statistic and prediction and received location information. In order to adapt the configuration, the location management server may determine, for example, whether to increase or decrease the frequency of the report based on the UE's mobility pattern, or update the location change condition (e.g., to change the location accuracy).
- If the valid location report is not available, depending on the information specified by the location reporting trigger or determined reporting configuration (if "DIRECT UPDATE" is requested), location management server initiates an on-demand location reporting procedure or an event-triggered location reporting procedure for the location of location management client 1.
Once the location information of the location management client 1 is available in the location management server by the on-demand location reporting procedure, a location information report is sent to the location management client 2 or VAL server.
9.3.6 Location reporting triggers configuration cancel p. 86
Figure 9.3.6-1 illustrates the procedure used for cancelling the location reporting triggers configuration at the target location management client.
Pre-conditions:
- The location management server has subscribed the location management client 2 location with the location reporting event triggers.
- If multicast delivery mode is used, the MBMS bearer being used is activated by the location management server.
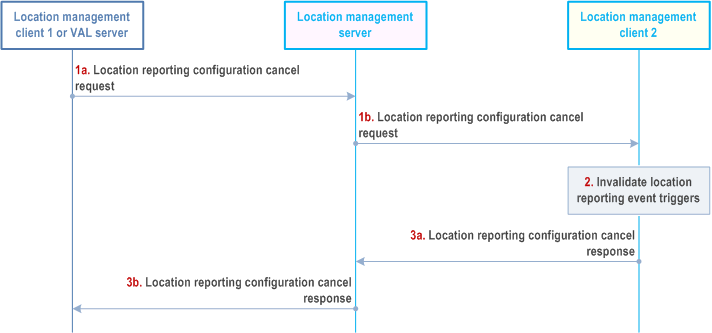
Step 1.
The location management client 1 (authorized VAL user or VAL UE) or VAL server sends a location reporting configuration cancel request to the location management server (1a). The location management server sends the location reporting configuration cancel request to the location management client 2 to stop receiving the UE location information (1b). This message can be sent via unicast or multicast.
Step 2.
The location management client invalidates the location reporting triggers configuration and no longer reports its location to the location management server.
Step 3.
The location management client 2 sends the location reporting configuration cancel response to the location management server (3a) as an acknowledgement. The location management server sends the location reporting configuration cancel response to the location management client 1 (3b) as an acknowledgement.
9.3.7 Location information subscription procedure p. 86
Figure 9.3.7-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location information subscription request. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other entities that would like to subscribe to VAL user or VAL UE location information. This procedure is also used for initiating tracking a UE's location. The procedure considers target UE location information provided by its surrounding UEs, the procedure can improve location accuracy and can be used also for target UE temporarily out of 3GPP radio coverage. Location management client 1 is used as example in the figure as target UE that the VAL server is interested to know its location information.
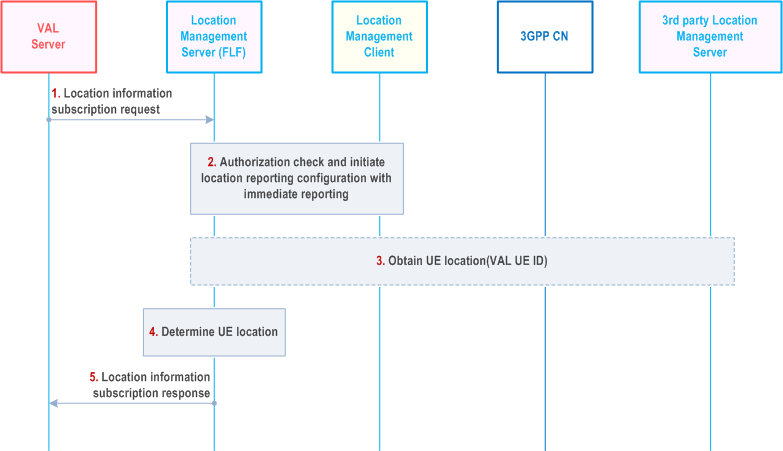
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a location information subscription request to the location management server to subscribe location information of one or more VAL users or VAL UEs. The request may include an indication for supplementary location information, the location QoS which contains the location accuracy, response Time and QoS class as defined in clause 4.1b of TS 23.273, the velocity information of target UEs, and an indication whether the statistic of target UE location is needed per e.g., temporal/spatial granularity. If the indication whether the statistic of target UE location is needed, the corresponding time/location information should also be included. In addition, the VAL server may request velocity information of the VAL UEs/Users in step 1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate the location information subscription request and may retrieve the available and proper location access type and positioning methods (e.g. as described in TS 23.273 and TS 29.572) for the target VAL UE based on the received location QoS. Further, the location management server may initiate location reporting configuration optionally including the retrieved location access type and positioning methods with the location management client of the UE for immediate reporting.
Step 3.
The location management server may optionally subscribe for UE location information from 3GPP core network for the UE. If the indication for supplementary location information is included in step 1, then UE location information is obtained from the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server.
If the velocity information of target UE is requested in step 1, the location management server asks the location management client or 3GPP core network to report the target UE location data with the requested velocity information.
Step 4.
The location management server determines the UE location information of the UE as received in steps 2 and 3 and checks if it meets the location QoS requirements (if any) or not.
If the indication whether the statistic of target UE location is included in step 1, the location management server performs the following actions based on different granularity.
If the indication whether the statistic of target UE location is needed per temporal granularity is included in step 1, the location management server calculates the UE location data received in step 3 per the temporal granularity with the requested time condition.
If the indication whether the statistic of target UE location is needed per spatial granularity is included in step 1, the location management server calculates the UE location data received in step 3 per the spatial granularity with the requested location information.
Step 5.
The location management server may optionally request the UE location from its surrounding UEs (as described in step 5 to 9). The location management server decides how to retrieve surrounding UEs which may be based on location management client 1 registered positioning method in location service registration. If the location management server decides to use UE-assisted surrounding UE retrieval, step 6 is executed; otherwise, NW-assisted surrounding UE retrieval is used as described in step 7.
Step 6.
The location management server requests the location management client 1 with an optional surrounding UE retrieval method (e.g. ProSe, BT, WiFi) to provide its surrounding UEs and the location management client 1 responds the location management server with VAL UE/User ID of discovered UEs as described in clause 9.3.22.
Step 7a.
The location management server derives an appropriate location area (where UE to UE communication is possible) internally using the location information of UE 1 (determined in step 4) as reference location. If the UE 1 location is last known UE location, the location management server uses UE mobility analytics service from 3GPP CN to derive UE location estimation for UE 1.
Step 7b.
The location management server uses 3GPP CN service (NEF service of Number of UEs present in a geographical area) to obtain all UEs within the derived location area in step 6.
Step 8.
The location management server selects a set of UEs (location management client 2..n) from UEs obtained in step 5 or step 7 based on registered location service information (e.g. positioning method) from location management client 2..n. Then location management server sends location request to location management client 2..n using On-demand location reporting procedure (as defined in clause 9.3.4) to obtain UE 1 location including an optional UE positioning method (e.g. PC5 SEAL LM, BT, WiFi) to be used to retrieve location.
Step 9.
The location management server akes the location information of UE 1 reported by location management client 2..n into consideration to calibrate UE 1 location determined in step 4.
Step 10.
The location management server replies with a location information subscription response indicating the subscription status and if immediate reporting was requested, the location information of the VAL UE(s).
9.3.7a Location information subscription update procedure |R19| p. 88
Figure 9.3.7a-1 illustrates the high level procedure for allowing a VAL server update an existing subscription about location information at the location management server.
Pre-conditions:
- the VAL server has an active location information subscription at the location management server.
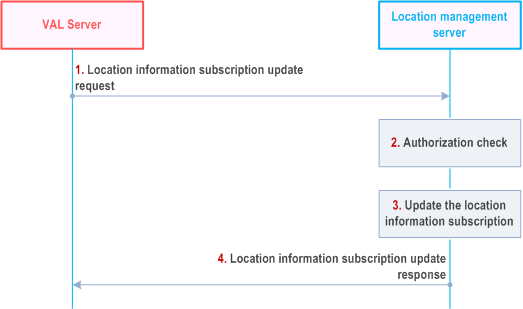
Step 1.
When the VAL server decides to update an active location information subscription, it sends a location information subscription update request to the location management server including the information specified in Table 9.3.2.5-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to update the subscription.
Step 3.
If the VAL server is authorized to update the subscription, the location management server updates the location information subscription.
Step 4.
The location management server sends a location information subscription update response to the VAL server including the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.6-1.