Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.4.2
0…
6…
8…
9…
9.3…
9.3.3…
9.3.8…
9.3.13…
9.3.20…
9.3.23…
9.4…
10…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.4…
11…
12…
13…
14…
14.3…
14.3.3
14.3.4
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.5…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.5…
14.3.9…
14.4…
15…
17…
18…
A…
9.3.13 VAL Service Area configuration
9.3.13.1 General
9.3.13.2 Configure VAL service area identifier procedure
9.3.13.3 Obtain VAL service area identifier procedure
9.3.13.4 Update VAL service area identifier procedure
9.3.13.5 Delete VAL service area identifier procedure
9.3.13.6 VAL service area identifier subscribe procedure
9.3.13.7 VAL service area identifier notify procedure
9.3.13.8 VAL service area identifier unsubscribe procedure
9.3.13.9 VAL service area identifier subscription update procedure
9.3.14 Location profiling for supporting location service enablement
9.3.14.1 Location profiling
9.3.14.2 Procedure of Location profiling for location service
9.3.15 Location service registration procedure
9.3.16 Location information unsubscribe procedure
9.3.17 Monitor location unsubscribe procedure
9.3.18 Location service registration update procedure
9.3.19 Location service deregistration procedure
...
...
9.3.13 VAL Service Area configuration |R18| p. 99
9.3.13.1 General p. 99
The VAL service area refers to the geographical area(s) (e.g., coordinates, civic addresses, network areas) served by a VAL server. The VAL service area is identified by the VAL service area identifier (ID). The VAL server may have more than one VAL service area defined. These VAL service areas are configured by the VAL server to the location management server and are assigned with a unique VAL service area identifier. When the VAL service area configurations are in place the VAL server may use the VAL service area ID as part of the location information in the SEAL APIs requiring location information. These configurations can be updated by the VAL server in-order to modify the geographical area(s) associated with the VAL service area and when is updated, the SEAL internally manage the updates without requiring the VAL server to re-invoke the APIs where the updated VAL service area are being used.
9.3.13.2 Configure VAL service area identifier procedure p. 99
Figure 9.3.13.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the VAL service area identifier configuration.
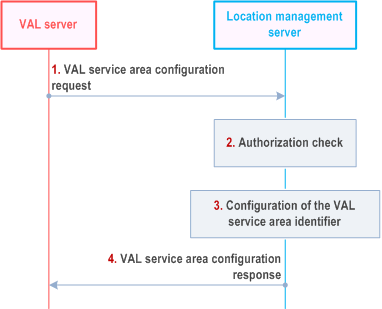
Step 1.
The VAL server sends the VAL service area configuration request to the location management server to configure a new VAL service area identifier. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.21-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate VAL service area identifier configuration request.
Step 3.
If the VAL server is authorized to configure the VAL service area identifiers, the VAL server checks the consistency of the provided identifiers (e.g., all VAL service area identifiers shall be unique) and configures the provided VAL service area identifiers.
Step 4.
the location management server sends the VAL service area configuration response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.22-1.
9.3.13.3 Obtain VAL service area identifier procedure p. 100
Figure 9.3.13.3-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the VAL service area retrieval.
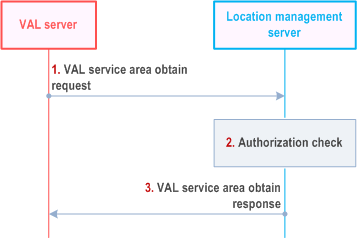
Step 1.
The VAL server sends the VAL service area obtain request to the location management server to retrieve the VAL service area identifiers. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.26-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate VAL service area obtain request.
Step 3.
If the VAL server is authorized to obtain the VAL service area identifiers, the location management server sends the VAL service area obtain response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.27-1.
9.3.13.4 Update VAL service area identifier procedure p. 100
Figure 9.3.13.4-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the VAL service area update.
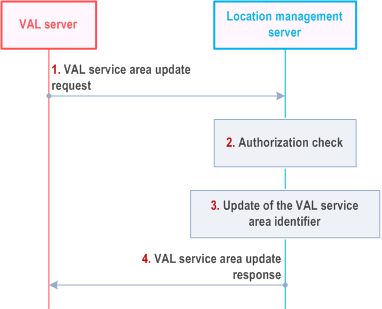
Step 1.
The VAL server sends the VAL service area update request to the location management server to update the VAL service area identifier(s) configured by the VAL server. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.28-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate VAL service area update request.
Step 3.
The location management server checks whether the VAL service area IDs exist and then updates the VAL service area identifier(s).
Step 4.
The location management server sends the VAL service area update response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.29-1.
9.3.13.5 Delete VAL service area identifier procedure p. 101
Figure 9.3.13.5-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the VAL service area delete.
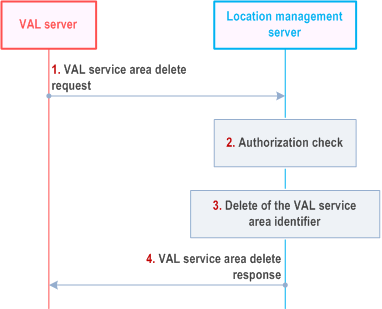
Step 1.
The VAL server sends the VAL service area delete request to the location management server to delete the VAL service area identifier(s) configured by the VAL server. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.30-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate VAL service area delete request.
Step 3.
The location management server checks whether the VAL service area IDs exist and then deletes the VAL service area identifier(s).
Step 4.
The location management server sends the VAL service area delete response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.31-1.
9.3.13.6 VAL service area identifier subscribe procedure p. 101
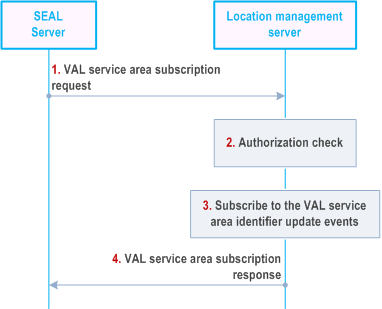
Figure 9.3.13.6-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the subscribe VAL service area update events.
Step 1.
The SEAL server sends the VAL service area subscription request to the location management server to subscribe for the VAL service area identifier(s) update events. In the request message, the SEAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.42-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the SEAL server is authorized to susbcribe for the VAL service area identifier(s) update event(s).
Step 3.
if the SEAL server is authorized to subscribe for the VAL service area identifier(s) update events, the location management server creates the subscription based on the provided parameters in the request.
Step 4.
The location management server sends the VAL service area subscription response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.43-1.
9.3.13.7 VAL service area identifier notify procedure p. 102
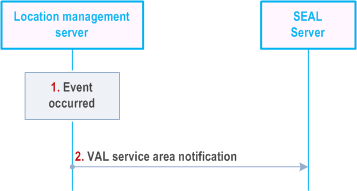
Figure 9.3.13.7-1 illustrates the high level procedure for notification of a SEAL server about the VAL service area identifier update events at the location management server.
Pre-conditions:
- the SEAL server has an active VAL service area subscription at the location management server; and
- the subscribed event has occurred.
Step 1.
The location management server identifies the list of the occurred events for which the SEAL server subscribed.
Step 2.
The location management server sends a VAL service area notification to the SEAL server. In the notification message, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.44-1.
9.3.13.8 VAL service area identifier unsubscribe procedure p. 102
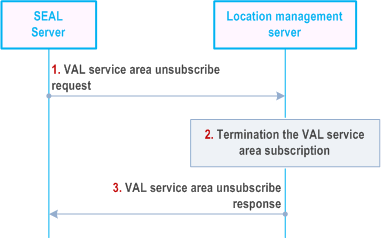
Figure 9.3.13.8-1 illustrates the high level procedure for a SEAL server to unsubscribe the notifications about the VAL service area identifier update events at the location management server.
Pre-conditions:
- the SEAL server has an active VAL service area subscription at the location management server.
Step 1.
When the SEAL server decides to terminate a VAL service area subscription, it sends a VAL service area unsubscribe request to the location management server. In the request message, the SEAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.45-1.
Step 2.
If the SEAL server is authorized to terminate the subscription, the location management server terminates the VAL service area subscription.
Step 3.
The location management server sends a VAL service area unsubscribe response to the SEAL server, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.46-1.
9.3.13.9 VAL service area identifier subscription update procedure p. 103
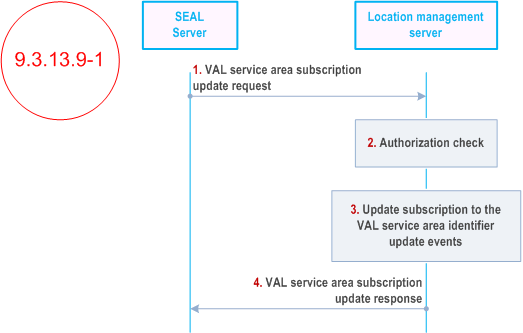
Figure 9.3.13.9-1 illustrates the high level procedure of the update subscription for the VAL service area update events.
Step 1.
The SEAL server sends the VAL service area subscription update request to the location management server to update the existing subscription for the VAL service area identifier(s) update events. In the request message, the SEAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.42-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the SEAL server is authorized to update the subscription for the VAL service area identifier(s) update event(s).
Step 3.
if the SEAL server is authorized, the location management server checks whether the target susbcription exists and then updates the subscription for the VAL service area identifier(s) update events.
Step 4.
The location management server sends the VAL service area subscription update response with the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.43-1.
9.3.14 Location profiling for supporting location service enablement |R18| p. 103
9.3.14.1 Location profiling p. 103
The location management server enhanced with the Fuse Location Function(FLF) supports the creation of location profiles for location service at the application enablement layer and the mapping of location profiles to one or more vertical applications. Location profiling is based on the vertical driven hybrid positioning requirements and policies.
The example of attributes that can be used for the location profiles is specified in Annex D.
9.3.14.2 Procedure of Location profiling for location service p. 103
The procedure includes the translation of the vertical request to a location profile and the derivation of the requested location information report.
Pre-condition:
The location management server has configured a set of location service profiles.
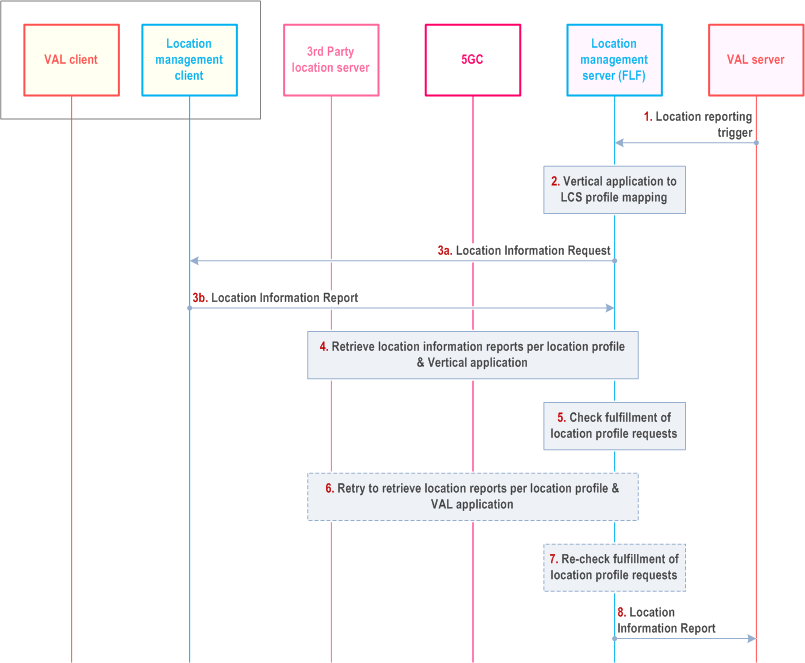
Step 1.
The location management server receives a location reporting trigger from VAL server and activates a location reporting procedure as defined in clause 9.3.5.
Step 2.
The fused location function determines a mapping of the vertical location services to a location service profile based on the location request information, the location profiles and the location capability of VAL UE which registered to the location management server before.
Step 3a.
The location management server requests from the LMC the location information of the target VAL UE optionally with the requested location information (the access type, positioning method) based on the determined location profiles in location management server obtained in step 2.
Step 3b.
The location management client responds to the location management server the location report based on the request.
Step 4.
The location management server performs a location information request to one or more of the following (based on the location profile):
Step 5.
- to GMLC directly or via NEF (as defined in TS 23.273), acting as AF.
- to 3rd party location servers.
The fused location function calculates the location information based on combined location reports from step 3~4 and checks whether the location reports fulfil the location profile requirements.
Step 6-7.
If the requirements are not fulfilled, the location management server will repeat the step 3~5 iteratively to request location information and re-check whether the requirements are met or not.
Step 8.
If the requirements are fulfilled, the location management server sends the location information report to the VAL server.
9.3.15 Location service registration procedure |R18| p. 105
Before the location management server requesting the location information for the target UE, the location management client may register the available location services to the location management server to report the UE's location capabilities.
Figure 9.3.15-1 illustrates the procedure of client-triggered location service registration.
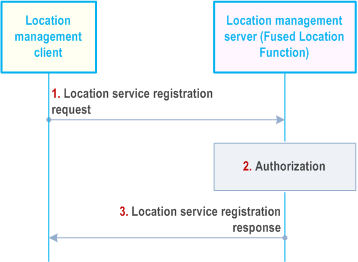
Step 1.
The location management client of a VAL UE sends location service registration request to the location management server, with the identifier of the UE (e.g. GPSI) and UE-based location capabilities, the associated ID with other UEs, etc.
Step 2.
The location management server checks authorization for the VAL UE's registration request.
Step 3.
After successful authorization, location management server sends location service registration response to the location management client and stores the UE's information received in step 1.
9.3.16 Location information unsubscribe procedure |R18| p. 105
Figure 9.3.16-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location information unsubscribe request. The same procedure can be applied for the location management client and other entities that would like to unsubscribe to the VAL UE's location information.
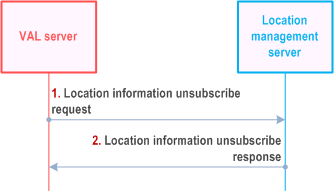
Step 1.
The VAL server sends location information unsubscribe request to the location management server to unsubscribe the subscription to the VAL UE's location information.
Step 2.
The location management server replies with location information unsubscribe response indicating the unsubscribe status.
9.3.17 Monitor location unsubscribe procedure |R18| p. 106
Figure 9.3.17-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location monitoring unsubscribe request. The same procedure can be applied for other entities that would like to unsubscribe the subscription to monitor the VAL UE's location in a given area of interest.
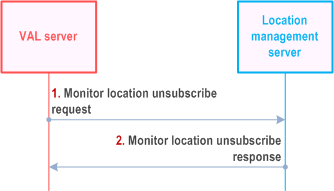
Step 1.
The VAL server sends Monitor location unsubscribe request to the location management server to unsubscribe the subscription to monitor the VAL UE's location in a given area of interest.
Step 2.
The location management server replies with Monitor location unsubscribe response indicating the unsubscribe status.
9.3.18 Location service registration update procedure |R18| p. 106
Figure 9.3.18-1 illustrates the procedure of client-triggered location service registration update. The location management client may update its supported location capabilities (e.g. location access type, position methods) which has registered to the location management server before.
Pre-condition:
The location management client has registered to the location management server.
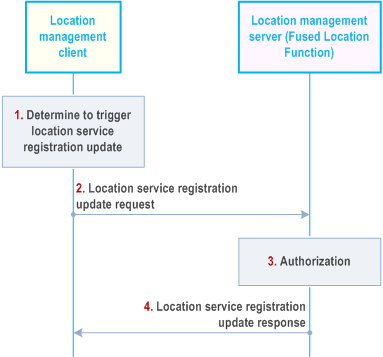
Step 1.
The location management client decides to trigger the registration update request to location management server to update the location capabilities which have registered to the location management server before.
Step 2.
The location management client sends location service registration update request to the location management server with the identifier of the VAL UE, the VAL service ID and updated location capabilities.
Step 3.
The location management server checks the authorization for the VAL UE's registration update request. If the authorization is successful, the location management server will update the UE's location capabilities received in step 2.
Step 4.
The location management server sends location service registration update response to the location management client.
9.3.19 Location service deregistration procedure |R18| p. 107
Figure 9.3.19-1 illustrates the procedure of client-triggered location service deregistration. By deregistration, the location management client may deregister the available location services which have registered to the location management server before.
Pre-condition:
The location management client has registered to the location management server.
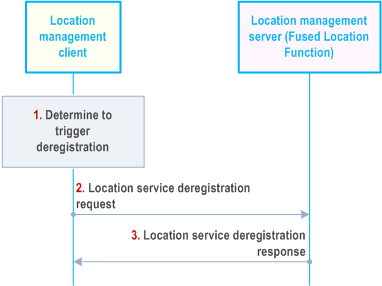
Step 1.
The location management client decides to trigger the deresgistration request to location management server to deregister the location services which have registered to the location management server before.
Step 2.
The location management client sends location service deregistration request to the location management server with the identifier of the UE.
Step 3.
The location management server sends location service deregistration response to the location management client and removes all registration information of the UE.