Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.4.2
0…
6…
8…
9…
9.3…
9.3.3…
9.3.8…
9.3.13…
9.3.20…
9.3.23…
9.4…
10…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.4…
11…
12…
13…
14…
14.3…
14.3.3
14.3.4
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.5…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.5…
14.3.9…
14.4…
15…
17…
18…
A…
10.3.7 Location-based group creation
10.3.8 Group announcement and join
10.3.9 Group member leave
10.3.10 Temporary groups
10.3.11 Group List Fetch
10.3.12 Location-based group update
10.3.13 Group deletion
...
...
10.3.7 Location-based group creation p. 159
Figure 10.3.7-1 below illustrates the location-based group creation.
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client, group management server, VAL server, location management server and the VAL group members belong to the same VAL system.
- The authorized VAL user/UE/administrator or VAL server is not aware of the users' or UE identities which will be combined to form the VAL group.
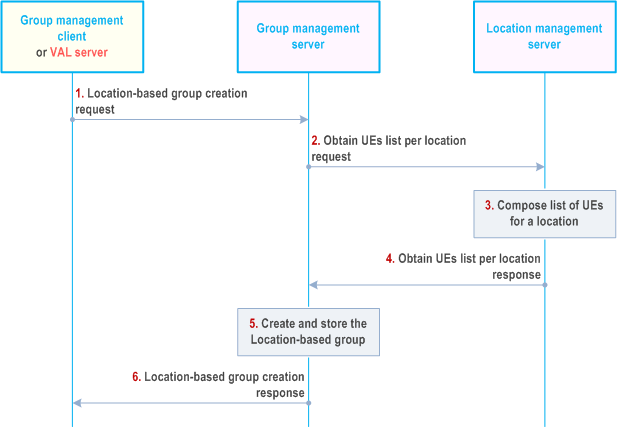
Step 1.
The group management client or the VAL server requests location-based group create operation to the group management server. The location criteria for determining the identities of the users or UEs to be combined shall be included in this message and the location criteria may be the VAL service area identified by the VAL service area ID.
Step 2.
The group management server requests the location management server for obtaining the users or UEs corresponding to the location information or the VAL service area identified by the VAL service area ID as defined in clause 9.3.2.9.
Step 3.
The location management server composes the list of users or UEs within the requested location as defined in clause 9.3.10.
Step 4.
The group management server receives the composed list of users or UEs from the location management server as described in clause 9.3.2.10. The location management server may include VAL service IDs associated with the list of users or UEs.
Step 5.
During the group creation, the group management server creates and stores the information of the location-based group. The group management server performs the check on the policies e.g. maximum limit of the total number of VAL group members for the VAL group(s). If an external group identifier, identifying the member UEs of the VAL group at the 3GPP core network is available, then the external group ID is stored in the newly created VAL group's configuration information. If VAL service ID list was received in step 1 as part of group formation criteria and not in step 4 for the composed list of users or UEs, the group management server shall retrieve the VAL service data from the configuration management server as described in clause 11.3.2.13 and form the group with relevant users or UEs.
Step 6.
The group management server provides a location-based group creation response to the group management client or the VAL server.
10.3.8 Group announcement and join p. 160
10.3.8.1 General p. 160
This subclause describes the procedures for establishing group communication from the group management server to the group management clients.
10.3.8.2 Procedure p. 160
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client, group management server, VAL server and the VAL clients belong to the same VAL system.
- The VAL server is aware of the users' identities and is authorized to form a VAL group.
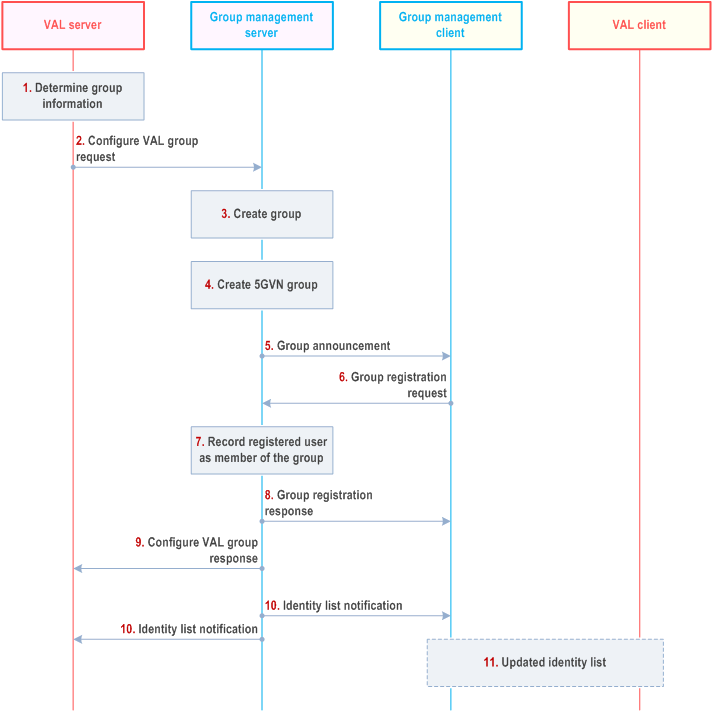
Step 1.
The VAL server determines group information and the identity list to which the group announcement shall be sent. The decision can be based on the list of authorized UEs and other criteria (e.g. user consent, service, or vehicle driving profile).
Step 2.
The VAL server configures VAL group for Uu communication defined by VAL Group ID for one or more VAL services with list of VAL Service ID with the group management server.
Step 3.
The group management server creates an empty group based on the information provided in the Configure VAL group request. The group management server stores the mapping between the VAL group ID and the external Group Id in the VAL group document, along with a list of GPSIs corresponding to the identity list provided by the VAL server. The group management server also determines whether the group is for 5G LAN-Type communication and whether Ethernet or IP (IPv4 and/or IPv6) transport shall be used for the 5G LAN-Type communication.
Step 4.
If 5G LAN-Type communication is to be used, the group management server creates a 5GVN group in the 5GS via N33 using the create group procedure specified in clause 5.29.2 of TS 23.501 and clause 4.15.6 of TS 23.502. The group management server creates the 5GVN group data and the 5GVN group membership data defined in clause 4.15.6.3b of TS 23.502 to be configured in the 5GS. To create the 5GVN group data the group management server uses the 5G LAN-Type communication type information provided by the VAL server to set the PDU session type (Ethernet or IP) and maps the VAL service IDs to Application descriptors. To create the 5GVN group membership data the group management server maps the VAL group ID to the External Group ID and makes a list of GPSIs corresponding to the identity list provided by the VAL server.
Step 5.
The group management server announces the VAL group to the group management clients. For a 5GVN group the announcement includes the communication type (IP or Ethernet), DNN, and S-NSSAI corresponding to the 5GVN group.
Step 6.
The group management client registers to VAL group communication using the VAL Group ID.
Step 7.
The group management server records the users who have registered to be the members of the group.
Step 8.
The group management server sends a VAL group registration response to the group management client.
Step 9.
The group management server sends a configure VAL group response to the VAL server.
Step 10.
The group management server sends identity list notification about the newly registered users to the other members of the group and VAL server, whose subscription to receive notifications of newly registered VAL UE IDs is successful in step 8 and step 9 respectively.
Step 11.
The group management client may inform VAL client about the updated identity list.
10.3.9 Group member leave p. 161
10.3.9.1 General p. 161
This subclause describes the procedures for group member to leave the group by de-registering.
10.3.9.2 Procedure p. 161
Pre-conditions:
- Group is previously defined on the group management server including the list of registered users and each member of the group and VAL server is aware of it.
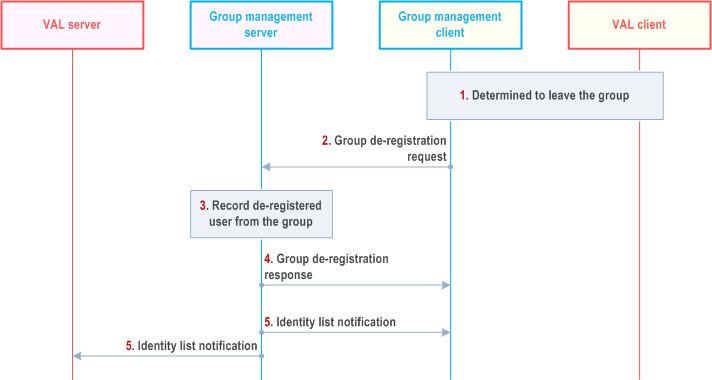
Step 1.
The VAL client determines to de-register member from the group and group management client is aware of it.
Step 2.
The group management client initiates the group de-registration request towards the group management server.
Step 3.
The group management server checks the authorization of group de-registration request and updates the group member list.
Step 4.
The group management server sends a group de-registration response to the group management client.
Step 5.
The group management server sends identity list notification about the leaving registered user to the other members of the group and the VAL server, whose subscription to receive notifications of de-registered VAL UE IDs is successful in step 7 and step 8 of the procedure in clause 10.3.8.2 respectively.
10.3.10 Temporary groups |R17| p. 162
10.3.10.1 Temporary group formation within a VAL system p. 162
Figure 10.3.10.1-1 below illustrates the temporary group formation within a VAL system.
Temporary groups are formed by combining two or more groups. The temporary group formation is applicable only for groups configured with at least one common VAL service. The temporary group formation shall be rejected if any of the requested VAL services are not common to all the constituent VAL service groups.
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client, group management server, VAL server and the VAL group members belong to the same VAL system.
- The group management client has retrieved the group configurations of the groups.
- The VAL server has subscribed to receive group management event notifications.
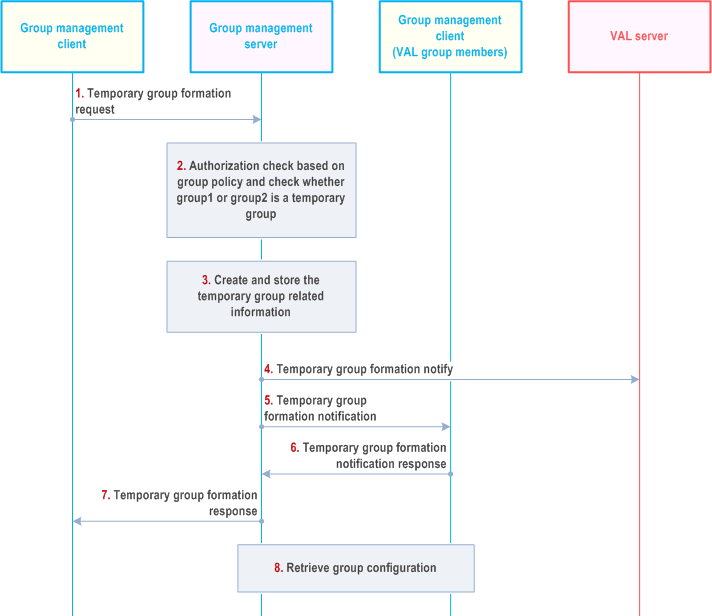
Step 1.
The group management client of the VAL user requests temporary group formation operation to the group management server, which is the group management server of one of the groups to be regrouped. The identities of the groups being combined shall be included in this message. The group management client may indicate the security level required for the temporary group. The group management client may indicate the priority level required for the temporary group.
Step 2.
The group management server checks whether temporary group formation operation is performed by an authorized VAL user, based on group policy. The group management server checks whether group1 or group2 is a temporary group. If group 1 or group2 is a temporary group, then the group regrouping will be rejected, otherwise the group regrouping can proceed.
Step 3.
The group management server creates and stores the information of the temporary group, including the temporary VAL group ID, the VAL group ID of the groups being combined, the priority level of the temporary group and the security level of the temporary group. If the authorized VAL user does not specify the security level and the priority level, the group management server shall set the lowest security level and the highest priority of the constituent groups. If VAL service types of the groups being combined are not identical, group management server determines the overlapping part and stores the VAL service list for the temporary group.
Step 4.
The group management server notifies the VAL server regarding the temporary group creation with the information of the constituent groups, i.e. temporary VAL group ID, group1's VAL group ID and group2's VAL group ID. If VAL service list is included, VAL server stores it and provides VAL service types accordingly.
Step 5.
The group management server notifies the VAL group members of the constituent VAL groups by sending temporary group formation notification messages.
Step 6.
The VAL group members of the constituent VAL groups send individual temporary group formation notification response messages.
Step 7.
The group management server provides a temporary group formation response to the group management client of the authorized VAL user. If VAL service list is included, group management client stores it and initiates VAL service types accordingly.
Step 8.
The VAL group members of the constituent VAL groups individually request group configuration data from the group management server for the temporary group. The group configuration data includes security, priority, and other parameters.
10.3.11 Group List Fetch |R17| p. 164
Figure 10.3.11-1 illustrates the group list fetch operations to fetch list of groups by the group management client.
Pre-conditions:
- List of groups to which a VAL UE/ VAL User belongs to is known to the Group management server for each of the VAL UE/ VAL User.
- VAL user has not received group announcement message as it was offline previously.
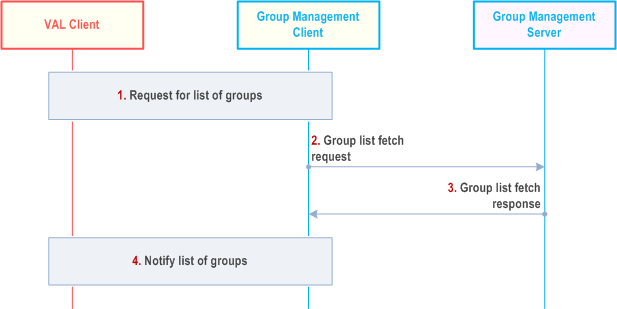
Step 1.
The VAL client requests group management client to provide the list of groups in which the VAL UE or VAL User is a member.
Step 2.
The group management client initiates the group list fetch request towards the Group management server. The information elements described in clause 10.3.2.36 are included in the group list fetch request.
Step 3.
The group management server checks the authorization of group list fetch request and if authorized, sends the group list fetch response containing list of groups in which the VAL user is member. The information elements described in clause 10.3.2.37 are included in the group list fetch response.
Step 4.
The group management client notifies the list of groups to the VAL client.
10.3.12 Location-based group update |R17| p. 164
Figure 10.3.12-1 below illustrates the location-based group update.
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client, group management server, VAL server, location management server and the VAL group members belong to the same VAL system.
- The location based group has been created as specified in clause 10.3.7.
- The group management server has subscribed to monitor UEs moving in or out of the fixed location area as specified in clause 9.3.12.
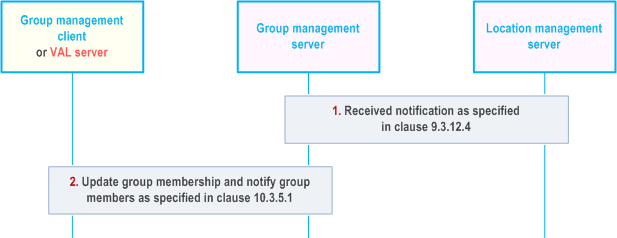
Step 1.
The group management server receives location area monitoring notification from location management server as specified in clause 9.3.12.4.
Step 2.
The group management server updates the group members and sends notification as specified in clause 10.3.5.1.
10.3.13 Group deletion |R17| p. 165
Figure 10.3.13-1 below illustrates the group deletion operation by authorized VAL user/UE/administrator to delete a group. It applies to group deletion by a VAL administrator or by authorized user/UE.
Pre-conditions:
- The group management client, group management server, VAL server and the VAL group members belong to the same VAL system.
- The authorized VAL user/UE/administrator is aware of the group identity which needs to be deleted.
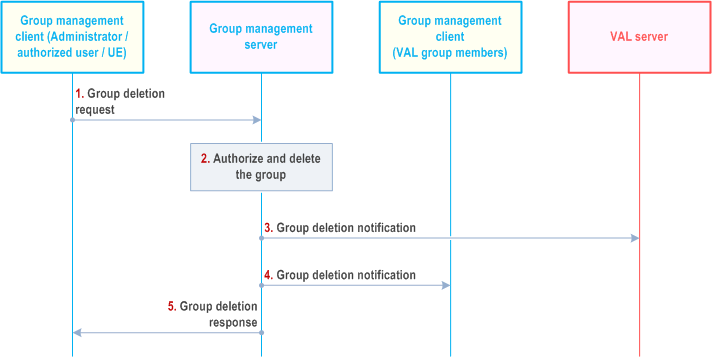
Step 1.
The group management client of the authorized VAL user/UE/administrator requests group deletion operation to the group management server. The identity of the group to be deleted shall be included in this message.
Step 2.
The group management server authorizes the request and if authorized, deletes the group.
Step 3.
The group management server notifies the VAL server regarding the group deletion.
Step 4.
The group members of the VAL group are notified about the deleted VAL group.
Step 5.
The group management server provides a group deletion response to the group management client of the administrator/authorized VAL user/UE.