Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.4.2
0…
6…
8…
9…
9.3…
9.3.3…
9.3.8…
9.3.13…
9.3.20…
9.3.23…
9.4…
10…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.4…
11…
12…
13…
14…
14.3…
14.3.3
14.3.4
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.5…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.5…
14.3.9…
14.4…
15…
17…
18…
A…
18 Data Delivery
19 Application Data Analytics Enablement
20 AIML Enablement
21 SEAL services over Satellite Access
21.1 General
21.2 Satellite coverage availability information configuration
21.2.1 General
21.2.2 Procedures
21.2.3 Information flows
21.3 Satellite S&F events information
21.3.1 General
21.3.2 Procedures
21.3.3 Information flows
21.3.4 APIs for Satellite S&F events information
22 Spatial anchors (SAn) service
23 Spatial map (SM) service
24 Digital Asset
18 Data Delivery |R18| p. 330
18.1 General p. 330
With increasing demand of applications consumption over mobile networks, more and more application content is transmitted over the mobile networks. Vertical applications have diverse requirements for the application content distribution and delivery. To ease the various data delivery demands for vertical applications, a data delivery enabler offers the data delivery and storage capabilities to one or more vertical applications. The detailed specification of SEAL Data Delivery is provided in TS 23.433.
19 Application Data Analytics Enablement |R18| p. 330
19.1 General p. 330
With increasing demand of applications consumption over mobile networks, more and more application content is transmitted over the mobile networks. Vertical applications have diverse requirements for the application content distribution and delivery. To ease the various data delivery demands for vertical applications, a data delivery enabler offers the data delivery and storage capabilities to one or more vertical applications. The detailed specification of SEAL Data Delivery is provided in TS 23.436.
20 AIML Enablement |R19| p. 330
20.1 General p. 330
AIML enablement (AIMLE) SEAL service exposes the capabilities assisting the VAL layer for providing AIML services. The detailed specification of AIMLE is provided in TS 23.482.
21 SEAL services over Satellite Access |R19| p. 330
21.1 General p. 330
This clause provides clarifications on the procedures and information flows for enabling SEAL services using satellite access.
21.2 Satellite coverage availability information configuration p. 330
21.2.1 General p. 330
The following clauses describe the satellite coverage availability information provisioning procedure.
21.2.2 Procedures p. 330
21.2.2.1 Procedures of the satellite coverage availability information provisioning p. 330
The procedure for VAL UE obtaining the satellite coverage availability information configuration for a particular location of UE is illustrated in Figure 21.2.2.1-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL UE has registered to the 3GPP network via satellite access as defined in clause 5.3.2.1 of TS 23.401 or clause 4.2.2.2.2 of TS 23.502.
- The configuration management server may interact with the SEAL location management server to obtain the VAL UE's information (e.g., location).
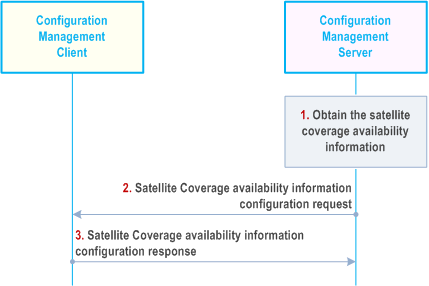
Step 1.
The configuration management server obtains the satellite coverage availability information locally or from the satellite service provider, and in order to provide accurate information to the UE, the VAL UE's information (e.g. location data) may also be considered. If the configuration management server receives the different kinds of satellite information from different satellite information providers for the same satellite, it may consolidate them in a unified format. The example of satellite coverage availability information can refer to the Annex Q of TS 23.501.
Step 2.
The configuration management server sends the satellite coverage availability information configuration request to the configuration management client to indicate whether the coverage is available for a particular location and time when the VAL UE uses the satellite access.
Step 3.
The configuration management client acknowledges the configuration management server if it supports the satellite access.
21.2.2.2 Procedures of UE requesting the satellite coverage availability information(SCAI) p. 331
The procedure for VAL UE/VAL server requesting and obtaining the satellite coverage availability information from the application enabler is illustrated in Figure 21.2.2.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL UE has registered to the 3GPP network via satellite access as defined in clause 5.3.2.1 of TS 23.401 or clause 4.2.2.2.2 of TS 23.502 and has not received the satellite coverage availability information from the network yet.
- The configuration management server has obtained the satellite coverage availability information as described in clause 21.2.2.1.

Step 1.
The consumer (Configuration management client, VAL server) sends Get satellite coverage availability information (SCAI) request to the configuration management server to require satellite coverage availability information when it is using the satellite access. The request may contain the dedicated satellite ID for the requested UE, the current UE location data, etc.
Step 2.
The configuration management server authorizes the request. If the request is granted, it checks the requested SCAI is available or not. If it's not available, the configuration management server obtains the SCAI as described in step 1 of clause 21.2.2.1.
Step 3.
The configuration management server replies the satellite coverage availability information to the consumer (VAL UE/configuration management client, VAL server) to guide them how to minimize the service impact (e.g. indicate when to trigger the UL/DL service flow if the VAL UE is accessing the satellite). And the VAL UE may retrieve the UE unavailability period (e.g., unavailability period duration or the start time for the unavailability period) as defined in clause 5.4.1.4 of TS 23.501 based on the received satellite coverage availability information.
21.2.3 Information flows p. 332
21.2.3.1 Satellite coverage availability information configuration request p. 332
Table 21.2.3.1-1 describes the information flow from the configuration management server to the configuration management client to configure the satellite coverage availability information.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL user or VAL UE. |
| VAL service ID | O | Identity of the VAL service that is requested. |
| Satellite coverage availability information (NOTE) | M | Indicates when the satellite coverage is available for a particular location and time. |
| NOTE: | ||
21.2.3.2 Satellite coverage availability information configuration response p. 332
Table 21.2.3.2-1 describes the information flow from the configuration management client to the configuration management server for the response of the satellite coverage availability information configuration request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL user or VAL UE. |
| Result | M | Indicates the request result. |
21.2.3.3 Get satellite coverage availability information request p. 333
Table 21.2.3.3-1 describes the information flow from the configuration management client or VAL server to the configuration management server to obtain the satellite coverage availability information.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identities of the requesting VAL user or VAL UE or VAL server. |
| VAL service ID | O | Identity of the VAL service that is requested. |
| Satellite ID | O | Indicates the dedicated satellite ID for the requested VAL UE. |
| Location | O | Indicates the current location data for the VAL UE. |
21.2.3.4 Get satellite coverage availability information response p. 333
Table 21.2.3.4-1 describes the information flow from the configuration management server to the configuration management client or VAL server to notify the satellite coverage availability information.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL user or VAL UE. |
| VAL service ID | O | Identity of the VAL service that is requested. |
| Satellite coverage availability information (NOTE) | M | Indicates when the satellite coverage is available for a particular location and time. |
| NOTE: | ||
21.3 Satellite S&F events information p. 333
21.3.1 General p. 333
This following sub-clauses shows how the application enablers provisioning the satellite S&F configuration to the VAL UE and expose the satellite S&F events information to the VAL server to help minimize the service interruption (e.g., adjust the DL frequency, etc.) when the VAL UE starts to perform the satellite S&F operation.
21.3.2 Procedures p. 333
21.3.2.1 NRM Server exposing the S&F events to the VAL server procedure p. 333
Pre-condition:
- The NRM client, the NRM server and the VAL server all are deployed on the ground.
- The PGW-U in 3GPP CN is deployed on the satellite.
- The VAL UE has registered to the 3GPP network via satellite access as defined in clause 5.3.2.1 of TS 23.401 and supports the S&F mode.
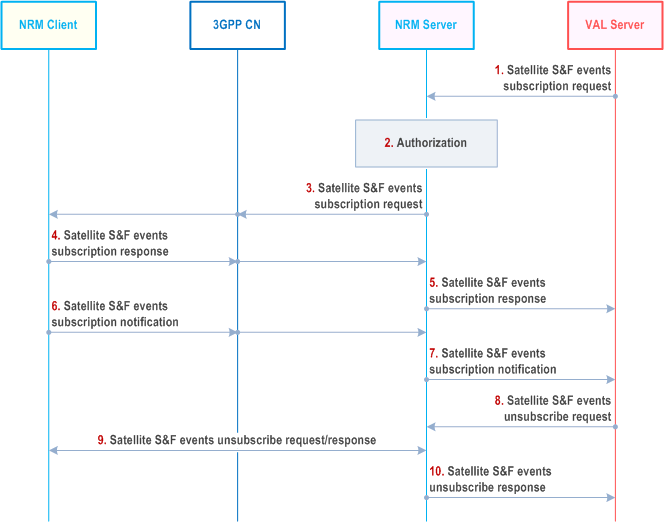
Step 1.
The VAL server sends the satellite S&F events subscription request to the NRM server in which the subscribed events may include the UE status in S&F mode, the DL estimated delivery time, the trigger conditions, etc.
Step 2.
The NRM server authorizes the subscription request from the VAL server.
Step 3.
If the subscription request is authorized, the NRM server sends the satellite S&F events subscription request to the NRM client and/or the 3GPP CN respectively.
Step 4.
The NRM client and/or 3GPP CN acknowledge the NRM server with the satellite S&F events subscription response respectively.
Step 5.
The NRM server responds to the VAL server with the satellite S&F events subscription response.
Step 6.
If the trigger condition in the subscription request is met, the NRM client and/or 3GPP CN may report the requested satellite S&F events as specified in Table 21.3.3.3-1 to the NRM server via the satellite S&F events subscription notification.
Step 7.
The NRM server notifies the VAL server for the received satellite S&F events in step 6. The VAL server may take them into consideration and adjust the application behaviour (e.g. pending the DL data transition when the UE is in S&F Mode, re-transmit the pending DL data when the feeder link is available, adjust the DL traffic volume according to the DL estimated delivery time, etc.) to minimize the service interruption.
Step 8.
The VAL server sends the satellite S&F events unsubscribe request to the NRM server to unsubscribe the subscription to monitor the satellite S&F events.
Step 9.
The NRM server relays the satellite S&F events unsubscribe request to the NRM client and/or 3GPP CN. And receives the response from the NRM client and/or 3GPP CN respectively.
Step 10.
The NRM server replies to the VAL server with the satellite S&F events unsubscribe response.
21.3.2.2 VAL UE reports the UE satellite information procedure p. 334
The Figure 21.3.2.2-1 illustrates the procedure of the VAL UE/NRM client reports the UE satellite information to the NRM server.
This procedure also applies when the VAL UE/NRM client updating its UE satellite information to the NRM server.
Pre-condition:
- The VAL UE has registered to the 3GPP network via satellite access as defined in clause 5.3.2.1 of TS 23.401 and supports the S&F mode.
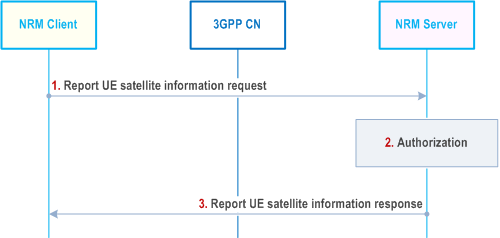
Step 1.
The NRM client reports the UE satellite information to the NRM server which may contain the UE identity, the UE type (e.g. IoT) and the UE satellite related information, such as the serving satellite ID, the accessing satellite types (LEO, MEO and GEO), the S&F mode indicator, the maximum data storage quota which indicates the maximum data storage quota per application layer on the UE for all of services, etc.
Step 2.
The NRM server checks the authorization for the request from the NRM client.
Step 3.
After successful authorization, the NRM server sends a Report UE satellite capability response to the NRM client and stores the UE identity and the satellite information.
21.3.2.3 NRM server provisioning the S&F configuration procedure p. 335
Figure 21.3.2.3-1 shows how the NRM Server provides the S&F configuration to the NRM Client based on the service request from VAL server and the VAL UE reported satellite information.
This procedure also applies when the NRM server provides the updated S&F configuration to the NRM client.
Pre-condition:
- The NRM client and the NRM server are deployed on the ground.
- The PGW-U in 3GPP CN is deployed on the satellite.
- The NRM Client has reported the UE satellite information to the NRM server as described in clause 21.3.2.2.
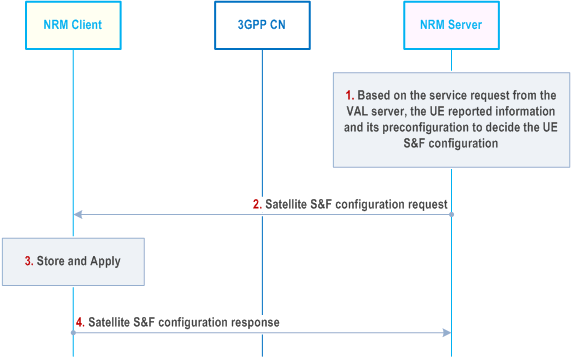
Step 1.
The NRM server takes advantage of the service request initiated by the VAL server, the reported UE satellite information (e.g. serving satellite ID, the maximum data storage quota per UE) as described in clause 21.3.2.2 and its pre-configuration, etc. to determine the on-board S&F parameters for the application layer (e.g., maximum S&F data storage quota per UE/service, maximum S&F data retention per UE/service, etc.).
Step 2.
After determined the satellite S&F parameters, the NRM server provides such information to the NRM client via sending a satellite S&F configuration request.
Step 3.
The NRM client/VAL UE stores the received satellite S&F parameters and may take them into account when the VAL UE starts to operate the S&F operations based on its satellite S&F configuration per service.
Step 4.
The NRM client sends the satellite S&F configuration response to the NRM server.
21.3.3 Information flows p. 336
21.3.3.1 Satellite S&F events subscription request p. 336
Table 21.3.3.1-1 describes the information flow from VAL server to NRM server or from the NRM server to NRM client for satellite S&F events subscription request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL server/VAL users or VAL UEs or NRM server. |
| Satellite S&F events | O | Lists of the satellite S&F events that to be monitored for one or more UEs (e.g. UE status in S&F mode, the DL S&F estimated delivery time). |
| Triggering conditions | M | Identifies the conditions that triggered NRM client sending the notification report. |
21.3.3.2 Satellite S&F events subscription response p. 337
Table 21.3.3.2-1 describes the information flow from NRM server to the VAL server or from NRM client to NRM server for response of satellite S&F events subscription request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL server/VAL users or VAL UEs or NRM server. |
| Subscription status | M | It indicates the subscription result. |
21.3.3.3 Satellite S&F events notification p. 337
Table 21.3.3.3-1 describes the information flow from NRM server to VAL server or from the NRM client to NRM server to notify the subscribed satellite S&F events.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL server/VAL users or VAL UEs or NRM server. |
| Satellite S&F events | O | List the notification for satellite S&F events that to be monitored for one or more UE(s). |
| > UE status in S&F mode | O
(NOTE) | Indicates the UE is registered in S&F mode or moving from S&F mode to not registered in S&F mode. |
| > The DL S&F estimated delivery time | O
(NOTE) | Indicates the estimated/expected time required to deliver the data to the UE from the time data has been received in the network. |
| Triggering events | M | Identifies the events that triggered NRM client sending the report. |
| Timestamp | O | Timestamp of the notification report. |
|
NOTE:
The definition refers to the clause 5.6.3 of TS 23.682.
|
||
21.3.3.4 Satellite S&F events unsubscribe request p. 337
Table 21.3.3.4-1 describes the information flow from VAL server to NRM server or from the NRM server to NRM client for satellite S&F events unsubscribe request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | Identity of the requesting ID for VAL server or NRM server. |
21.3.3.5 Satellite S&F events unsubscribe response p. 337
Table 21.3.3.5-1 describes the information flow from NRM server to the VAL server or from NRM client to NRM server for response of satellite S&F events unsubscribe request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Request status | M | It indicates the unsubscribe request result. |
21.3.3.6 Report UE satellite information request p. 338
Table 21.3.3.6-1 describes the information flow from the NRM client to the NRM server for reporting the UE satellite related capabilities.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the VAL user or identity of the VAL UE. |
| UE type | O | Indicate the type of VAL UEs (e.g. IoT). |
| Satellite information | O | The satellite information of VAL UE when the VAL UE supports the satellite access. |
| > Satellite ID | O | Indicates the serving satellite ID for the VAL UE. |
| > Satellite type | O | Indicates the accessing satellite RAT types (LEO, MEO and GEO) for the VAL UE. |
| > S&F mode indicator | O | Indicates the UE support the S&F mode or not. |
| > Maximum data storage quota | O | Indicates the maximum data storage quota for the VAL UE for all of services on the application layer. |
| > Maximum data retention | O | Indicates the maximum data retention for the VAL UE per service on the application layer. |
21.3.3.7 Report UE satellite information response p. 338
Table 21.3.3.7-1 describes the information flow the NRM server to the NRM client for the response of reporting the UE satellite related information request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Result | M | It indicated the request result. |
21.3.3.8 Satellite S&F configuration request p. 338
Table 21.3.3.8-1 describes the information flow from the NRM server to the NRM client for satellite S&F configuration request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL user or VAL UE. |
| VAL service ID | O | Identity of the VAL service that is requested. |
| Satellite S&F configuration information | O | Indicates the S&F configuration per UE per service when it is using the satellite S&F operation. |
| > Maximum S&F data storage quota | O | Indicates the maximum data storage quota per UE per service on the application layer when the UE is using the satellite S&F operation. |
| > Maximum S&F data retention | O | Indicates the maximum data retention per UE per service on the application layer when the UE is using the satellite S&F operation. |
21.3.3.9 Satellite S&F configuration response p. 338
Table 21.3.3.9-1 describes the information flow from the NRM client to the NRM server for the response of satellite S&F configuration request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | M | Identity of the requesting VAL users or VAL UEs or NRM server. |
| Result | M | It indicates the request result. |
21.3.4 APIs for Satellite S&F events information p. 339
21.3.4.1 General p. 339
Table 21.3.4.1-1 illustrates the APIs for Satellite S&F events information.
| API Name | API Operations | Known Consumer(s) | Communication Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SS_ | Subscribe_S&F_Info | VAL server | Subscribe/Notify |
| Unsubscribe_ S&F _Info | VAL server | ||
| Update_ S&F _Info_Subscription | VAL server | ||
| Notify_ S&F _Info | VAL server |
21.3.4.2 SS_SatelliteS&FInfoEvent API p. 339
21.3.4.2.1 General p. 339
API description: This API enables the VAL server to trigger reporting of satellite S&F information from the NRM server over LM-S.
21.3.4.2.2 Subscribe_S&F_Info operation p. 339
API operation name:
Subscribe_S&F_Info
Description:
Subscription to the satellite S&F events.
Known Consumers:
VAL server.
Inputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.1
Outputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.2
See subclause 21.3.2.2 for the details of usage of this API operation.
21.3.4.2.3 Unsubscribe_S&F_Info operation p. 339
API operation name:
Unsubscribe_S&F_Info
Description:
Unsubscribe to the satellite S&F events.
Known Consumers:
VAL server.
Inputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.4
Outputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.5
See subclause 21.3.2.2 for the details of usage of this API operation.
21.3.4.2.4 Update_ S&F _Info_Subscription operation p. 339
API operation name:
Update_ S&F _Info_Subscription
Description:
Update the subscription to the satellite S&F events.
Known Consumers:
VAL server.
Inputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.1
Outputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.2
See subclause 21.3.2.2 for the details of usage of this API operation.
21.3.4.2.5 Notify_ S&F _Info operation p. 340
API operation name:
Notify_ S&F _Info
Description:
Notification to the existing subscription.
Known Consumers:
VAL server.
Inputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.3
Outputs:
Refer subclause 21.3.3.3
See subclause 21.3.2.2 for the details of usage of this API operation.
22 Spatial anchors (SAn) service |R19| p. 340
22.1 General p. 340
Spatial anchors (SAn) SEAL service exposes the capabilities assisting the VAL layer for managing spatial anchors for their applications. The detailed specification of SAn service is provided in TS 23.437. The spatial anchor service is used for metaverse applications enablement.
23 Spatial map (SM) service |R19| p. 340
23.1 General p. 340
Spatial map (SM) SEAL service exposes the capabilities assisting the VAL layer for managing spatial map for their applications. The detailed specification of SM service is provided in TS 23.437. The spatial map service is used for metaverse application enablement.
24 Digital Asset |R19| p. 340
24.1 General p. 340
Digital Asset SEAL service exposes the capabilities for Digital Asset management towards the VAL application layer. The detailed specification of Digital Asset service is provided in 3GPP TS 23.438 [59].