Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4…
5
6…
6.4…
6.5…
6.5.3…
7…
8…
8.2.2…
9…
9.3…
9.3.2.21…
9.3.3…
9.3.6…
9.3.11…
9.3.13…
9.3.14…
9.4…
9.4.6…
9.5…
10…
10.3…
10.3.2.22…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.3.10…
10.4…
11…
11.3…
11.3.3…
11.4…
12…
12.3…
13…
14…
14.2.2.2…
14.3…
14.3.2.20…
14.3.2.40…
14.3.3…
14.3.3.3…
14.3.4…
14.3.4.6
14.3.4.7…
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.3…
14.3.4A.4…
14.3.4A.6…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.4A.9…
14.3.4A.10…
14.3.5…
14.3.6…
14.3.9…
14.3.12…
14.4…
15…
16…
17…
18…
A
B…
14.3.3.3 Unicast resource management without SIP core
14.3.3.3.1 Network resource adaptation
14.3.3.3.2 Request for unicast resources at VAL service communication establishment
14.3.3.3.3 Request for modification of unicast resources
14.3.3.4 Unicast QoS monitoring
14.3.3.4.1 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription procedure
14.3.3.4.2 Unicast QoS monitoring notification procedure
14.3.3.4.3 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription termination procedure
14.3.3.4.4 Unicast QoS monitoring data retrieval procedure
14.3.3.4.5 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription update procedure
...
...
14.3.3.3 Unicast resource management without SIP core p. 209
14.3.3.3.1 Network resource adaptation p. 209
14.3.3.3.1.1 General p. 209
This subclause describes the procedure for network resource adaptation using PCC procedures. This procedure satisfies the requirements for requesting unicast resources and modification to already allocated unicast resources to VAL communications.
14.3.3.3.1.2 Procedure p. 209
Figure 14.3.3.3.1.2-1 illustrates the procedure for the network resource adaptation.
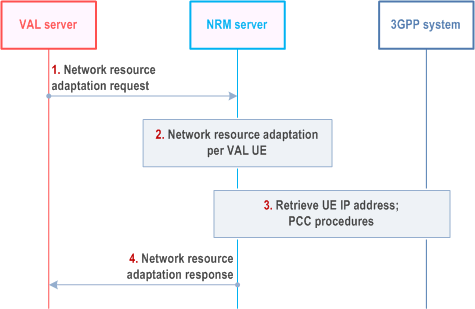
Step 1.
The VAL server (or SEALDD server) sends a network resource adaptation request to the NRM server for one or more users belonging to one or more VAL services, and may comprise one or more VAL UEs that will have updated resource requirement. This requirement may be in the form of exact resources /resource pools to be used or indication of bandwidth increase/decrease for the corresponding VAL UEs or set of VAL UEs. The BDT Reference ID may also be included for setting BDT policies.
Step 2.
The NRM server processes the request and applies / enforces the resource adaptation per VAL UE.
Step 3.
The NRM server retrieves UE IP address by using event monitoring capability for PDU session status (or PDN connectivity status) and initiates the PCC procedures for each VAL UE.
Step 4.
The NRM server provides a network resource adaptation response to the VAL server, providing information on the fulfilment of the network resource adaptation request. This will include information either per VAL UE or per set of VAL UEs, as indicated by the request of the VAL server in step 1.
14.3.3.3.2 Request for unicast resources at VAL service communication establishment p. 210
14.3.3.3.2.1 General p. 210
The procedure defined in this subclause specifies how network resources are requested at VAL service communication establishment. If concurrent sessions are used the NRM server may utilize the capability of resource sharing specified for underlying network policy and charging functions. The request for resources includes application type, bandwidth, priority, application identifier and resource sharing information.
14.3.3.3.2.2 Procedure p. 210
The procedure is generic to any type of session establishment that requires requests for network resources.
Procedures in Figure 14.3.3.3.2.2-1 are the signalling procedures for the requesting resource at session establishment.
Pre-condition:
- The VAL client has requested VAL service communication with the VAL server.
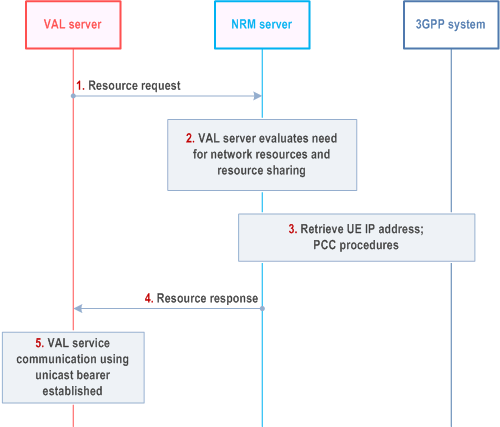
Step 1.
The VAL server sends request for resources to the NRM server.
Step 2.
The NRM server evaluates the need for network resources and use of resource sharing.
Step 3.
PThe NRM server retrieves UE IP address by using event monitoring capability for PDU session status (or PDN connectivity status), and then PCC procedures are initiated from NRM server.
Step 4.
The NRM server sends a resource response to the VAL server.
Step 5.
The VAL service communication is established, and resources have been allocated.
14.3.3.3.3 Request for modification of unicast resources p. 211
14.3.3.3.3.1 General p. 211
To modify unicast resources, the NRM server shall send a resource modification request containing the parameters to be modified for the UE.
Possible scenarios when this procedure may be used are:
- Modify the allocation and retention priority for unicast resources;
- Release and resume resources in-between VAL service communications; or
- Release and resume resources when a UE is able to receive the VAL service communications over multicast transmission
14.3.3.3.3.2 Procedure p. 211
Procedures in Figure 14.3.3.3.3.2-1 are the signalling procedures for the modification of a unicast:
Pre-condition:
- A VAL service communication is already in progress;
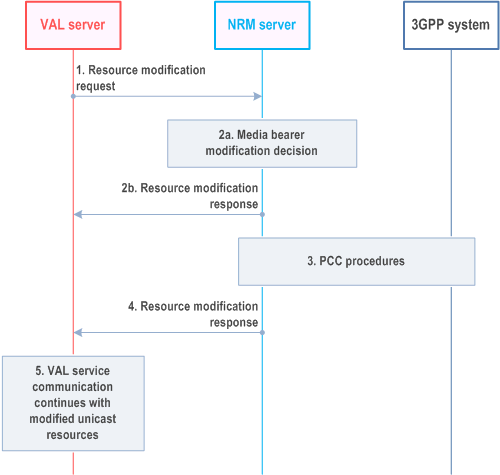
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a resource modification request to the NRM server.
Step 2a.
The NRM server decides to modify the parameters of a unicast bearer.
Step 2b.
If the media bearer modification is not required, the NRM server sends a resource modification response to the VAL server.
Step 3.
PCC procedures are initiated from NRM server.
Step 4.
The NRM server sends a resource modification response to the VAL server.
Step 5.
The VAL service communication continues with the modified unicast resources.
14.3.3.4 Unicast QoS monitoring |R17| p. 212
14.3.3.4.1 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription procedure p. 212
14.3.3.4.1.1 General p. 212
This subclause describes the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring subscription. This procedure satisfies the requirements for monitoring of unicast QoS for already allocated unicast resources to VAL communications.
14.3.3.4.1.2 Procedure p. 212
Figure 14.3.3.4.1.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring subscription.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL UE has an established connection in the 5GS
- The VAL server may have Monitoring profile ID pre-configured in the NRM server local configuration.
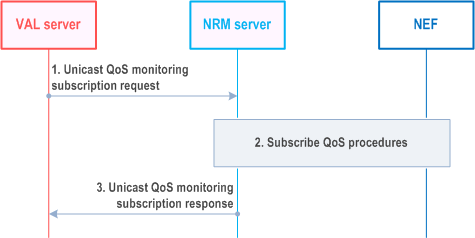
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a unicast QoS monitoring subscription request to the NRM server either in conjunction with a request for unicast network resources requiring QoS or when the unicast QoS connection is already established. The NRM server checks if the VAL server is authorized to initiate the unicast QoS monitoring request for the requested target VAL UEs, VAL group ID, or VAL stream IDs. The request may include monitoring profile (represents the monitoring and reporting requirements) or list of monitoring profile identifiers.
Step 2.
If the the monitoring profile ID and monitoring profile information elements are not provided, the NRM server shall determine the monitoring profile including the QoS measurement requirements and reporting requirements with subscription termination criteria based on the VAL service identifier and/or requester identity received in step 1. If monitoring profile ID is provided in step 1, the NRM server shall obtain the corresponding monitoring profile internally and apply for the subscription. The NRM server interacts with the NEF to establish relevant QoS monitoring subscriptions. The NRM server uses the NEF procedures for the AFsessionWithQoS described in clause 5.2.6.9 of TS 23.502 and the NEF procedures for the AnalyticsExposure described in clause 5.2.6.16 of TS 23.502 and in particular the UE Communication Analytics described in clause 6.7.3 of TS 23.288 and DN Performance Analytics described in clause 6.14 of TS 23.288. Based on the input received from the VAL server in step 1, the NRM server determines the relevant NEF subscription procedures and the parameters for these subscriptions, such as the QoS parameters to be measured (e.g. packet delay, data rate, traffic volume), the frequency of reporting etc. For the frequency of reporting which can be event triggered, periodic, or when the PDU Session is released, the NRM server determines the following:
Step 3.
-
if the reporting frequency is event triggered:
- the corresponding reporting threshold to each QoS parameter;
- minimum waiting time between subsequent reports;
- if the reporting frequency is periodic, the reporting period.
The NRM server responds with a unicast QoS monitoring subscription response indicating the subscription status. If the monitoring profile is not provided in step 1, the NRM server shall provide the proposed termination of reporting condition.
14.3.3.4.2 Unicast QoS monitoring notification procedure p. 213
14.3.3.4.2.1 General p. 213
This subclause describes the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring notification.
14.3.3.4.2.2 Procedure p. 213
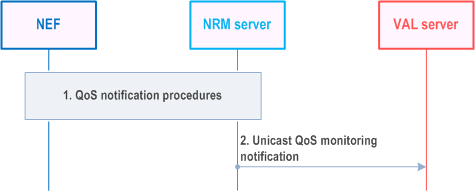
Figure 14.3.3.4.2.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure of unicast QoS monitoring notification event.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL server has an active unicast QoS monitoring subscription with the NRM server
Step 1.
The NRM server receives QoS monitoring data by means of notifications provided by the NEF. The NRM server coordinates and combines the information from the NEF notifications and determines whether to send a notification to the VAL server based on the VAL server subscription's frequency of reporting. For a VAL group or a list of VAL UEs, the NRM server aggregates QoS monitoring data for each UE belonging to the group or the list; for a VAL stream, the NRM server aggregates the QoS monitoring data for the stream. The NRM server stores the QoS monitoring data as needed for later retrieval.
Step 2.
The NRM server sends a unicast QoS monitoring notification including the measured QoS data and monitoring profile identifier whose reporting requirements triggered notification to the VAL server. If the reporting termination criteria is met (e.g. number of reports reached, threshold reached), NRM server shall also terminate the subscription and notify the VAL server about the subscription termination.
14.3.3.4.3 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription termination procedure p. 214
14.3.3.4.3.1 General p. 214
This subclause describes the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring subscription termination.
14.3.3.4.3.2 Procedure p. 214
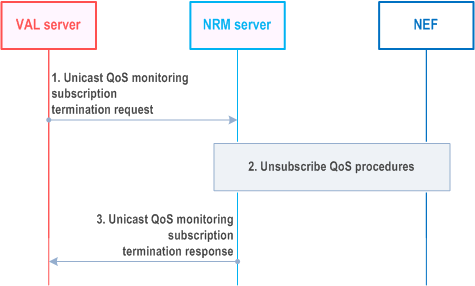
Figure 14.3.3.4.3.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure of unicast QoS monitoring subscription termination.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL server has an active unicast QoS monitoring subscription with the NRM server
Step 1.
When the VAL server decides to terminate a unicast QoS monitoring subscription, it sends a QoS monitoring unsubscribe request to the NRM server.
Step 2.
The NRM server interacts with the NEF to terminate the related QoS monitoring subscriptions.
Step 3.
The NRM server sends a QoS monitoring unsubscribe response to the VAL server.
14.3.3.4.4 Unicast QoS monitoring data retrieval procedure p. 214
14.3.3.4.4.1 General p. 214
This subclause describes the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring data retrieval.
14.3.3.4.4.2 Procedure p. 214
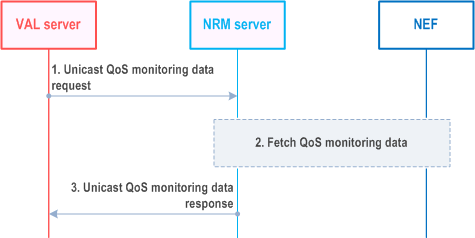
Figure 14.3.3.4.4.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure of unicast QoS monitoring data retrieval.
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a unicast QoS monitoring data request to the NRM server specifying the details of the requested data and the time period of interest. The NRM server checks if the VAL server is authorized to initiate the unicast QoS monitoring data request for the requested target VAL UEs, VAL group ID, or VAL stream IDs.
Step 2.
The NRM server determines if it has the requested data stored internally or whether it needs to interact with the NEF to fetch the data using the AnalyticsExposure described in clause 5.2.6.16 of TS 23.502 and in particular the UE Communication Analytics described in clause 6.7.3 of TS 23.288 and DN Performance Analytics described in clause 6.14 of TS 23.288. The NRM server collects and processes the collected data to match the measurement data requirement provided in the VAL server request.
Step 3.
The NRM server responds with a unicast QoS monitoring data response with the requested data or with a failure indication, and optionally the cause of the failure, in case the requested data is not available.
14.3.3.4.5 Unicast QoS monitoring subscription update procedure |R18| p. 215
14.3.3.4.5.1 General p. 215
This subclause describes the high-level procedure to update unicast QoS monitoring subscription. This procedure updates the parameters to be monitored of an already existing unicast QoS monitoring subscription.
14.3.3.4.5.2 Procedure p. 215
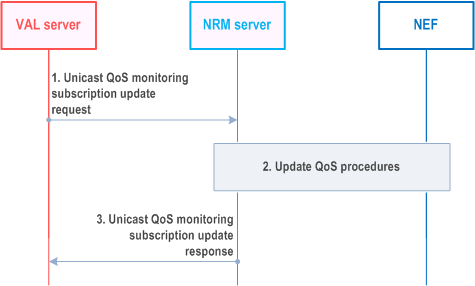
Figure 14.3.3.4.5.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure for unicast QoS monitoring subscription update.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL UE has an established connection in the 5GS
- Unicast QoS monitoring subscription has successfully been invoked established for the VAL UE
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a unicast QoS monitoring subscription update request to the NRM server. It shall refer to an existing subscription, identified by the list of VAL UEs, VAL UE group or VAL stream IDs included into the message.
Step 2.
The NRM server interacts with the NEF to update the relevant QoS monitoring subscription parameters and reporting frequency as specified in step 2 of clause 14.3.3.4.1.2 of this document.
Step 3.
The NRM server responds with a unicast QoS monitoring subscription update response indicating the subscription status.