Content for TS 23.434 Word version: 19.4.2
0…
6…
8…
9…
9.3…
9.3.3…
9.3.8…
9.3.13…
9.3.20…
9.3.23…
9.4…
10…
10.3…
10.3.3…
10.3.7…
10.4…
11…
12…
13…
14…
14.3…
14.3.3
14.3.4
14.3.4A…
14.3.4A.5…
14.3.4A.8…
14.3.5…
14.3.9…
14.4…
15…
17…
18…
A…
9.3.8 Event-trigger location information notification procedure
9.3.9 On-demand usage of location information procedure
9.3.10 Obtaining UE(s) information at a location
9.3.11 Monitoring Location Deviation
9.3.12 Location area monitoring information procedure
9.3.12.1 Location area monitoring subscription procedure
9.3.12.2 Location area monitoring subscription modify procedure
9.3.12.3 Location area monitoring unsubscribe procedure
9.3.12.4 Location area monitoring notification procedure
...
...
9.3.8 Event-trigger location information notification procedure p. 89
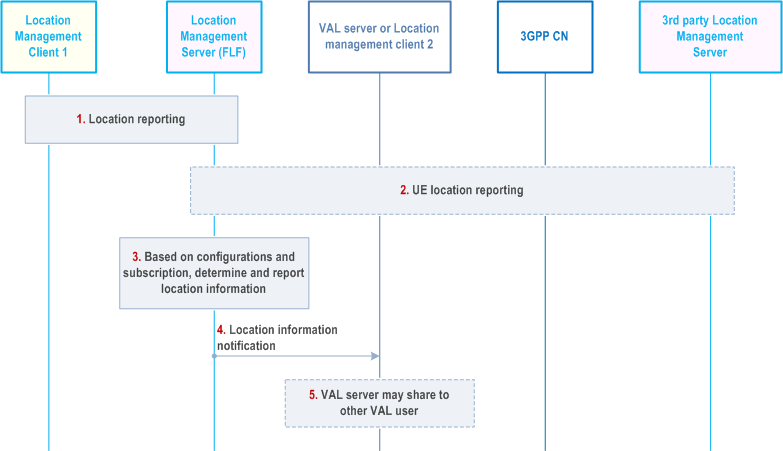
Figure 9.3.8-1 illustrates the high level procedure of event-trigger usage of location information. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other entities that would like to subscribe to location information of VAL user or VAL UE. This procedure is also used for obtaining latest UE's location for tracking purpose.
Step 1.
The location management server receives the latest location information of the UE as per the location report procedure described in clause 9.3.3.3.
Step 2.
The location management server may optionally receive the location information of the UE from 3GPP core and/or the 3rd party location management server network. If the indication for supplementary location information is included in the subscription, then UE location information is obtained from the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server. If the velocity information of target UE is requested, the location management server asks the location management client or 3GPP core network to report the target UE location data with the requested velocity information.
Step 3.
Based on the configurations, e.g., subscription, periodical location information timer, location management server is triggered to report the latest user location information to VAL server. The location management server determines the location information of UE as received in steps 1 and 2, including the supplementary location information (if indicated). The location management server may report the location to the VAL server considering the location information received via non-3GPP positioning technologies (e.g. GNSS, Bluetooth), for instance, to improve the location accuracy. The location management server may reuse the stored and valid UE location information (if any) to report to the VAL server/location management client to reduce the response time when the trigger condition is time-based (the triggering criteria is periodical reporting). And the LM server may interact with NWDAF to obtain the target UE's prediction location as defined in clause 6.7.2 of TS 23.288 to report to the VAL server during the periodic time interval.
If the indication whether the statistic of target UE location is included in the request from the VAL server/location management client, the location management server calculates the received UE location data per temporal/spatial granularity as requested and then expose them to the VAL server/location management client for the valued-added location information.
Step 4.
Same as step 5-9 of Figure 9.3.7-1.
Step 5.
The location management server sends the location information report including the latest location information of one or more VAL users or VAL UEs to the VAL server or to the location management client that has previously configured. In addition, velocity of the requested VAL UEs may be included as part of the location information report.
Step 6.
VAL server may further share this location information to a group or to another VAL user or VAL UE.
9.3.9 On-demand usage of location information procedure p. 91
The VAL server can request UE location information at any time by sending a location information request to the location management server, which may trigger location management server to immediately send the location report.
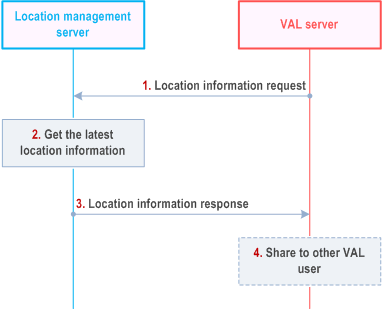
Figure 9.3.9-1 illustrates the high level procedure of on demand usage of location information. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other entities that would like to subscribe to location information of VAL user or VAL UE.
Pre-condition:
- The LM Server has confirmed the target UE is associated with other UEs and they are sharing the same location.
- The LM Server has obtained the UE's location who is associated with the target UE.
Step 1.
VAL server sends a location information request to the location management server to request locations for one or more VAL UEs or VAL user(s) which may include the location QoS that contains the location accuracy, response Time and QoS class as defined in clause 4.1b of TS 23.273.
Step 2.
The location management server checks if there is stored and valid UE location report (e.g. the timer for the stored UE location report is not expired) for the target UE. If available, it reuses the stored UE location information and reports it to the VAL server. If there isn't, it acquires the latest location of the UEs being requested, by triggering an on-demand location report procedure as described in subclause 9.3.4, or from PLMN operator, and checks if the obtained location of the VAL UE could meet the location QoS requirements (if any).
If the LM Server identified that target UE is associated with other UE(s) and they are sharing the same location as specified in clause of 9.3.23.2 or 9.3.23.3, it determines to reuse the associated UE's location data instead of obtaining the target UE's location data directly. The LM Server may select the associated UE(s) based on the requested LCS QoS, and the operator's policies, etc. But if the LM Server doesn't store the associated UE's location data or the stored location data is invalid (e.g. the valid timer for the confirmation of sharing location information is expired, or the verify location sharing response is negative), the LM Server will ask the target UE to report the UE location data as described in clause 9.3.4.
Step 3.
Then, location management server immediately sends the location information report including the latest location information of associated UE(s) or acquired of target one or more VAL users or VAL UEs. The location management server may report the location to the VAL server considering the location information received via non-3GPP positioning technologies (e.g. GNSS, Bluetooth), for instance, to improve the location accuracy.
Step 4.
VAL server may further share this location information to a group or to another VAL user or VAL UE.
9.3.10 Obtaining UE(s) information at a location |R17| p. 92
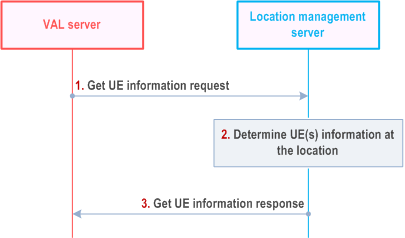
Figure 9.3.10-1 describes the procedure for obtaining UE(s) information at a location. This procedure also applies for the Geofencing service that the VAL server may request the UE(s) information when the UE entering the Geofencing location area.
Pre-condition:
- The VAL server has a jurisdiction over a geographical area for which the location management server is configured to operate.
- The UE(s) in the geographical area have provided its location information to the location management server.
- The location management server has obtained the requested UE location information either from 3GPP CN or the target location management client/VAL UE.
Step 1.
The consumer (VAL server or group management server) sends get UE information request to the location management server. The request contains the location information (e.g. geographic area, VAL service area identified by the VAL service area ID, Geofencing location area represented by different types of shape, etc) and application defined proximity range as defined in Table 9.3.2.9-1.
Step 2.
The location management server authorizes the request and determines the VAL UE(s) or VAL User(s) whose location are within the application defined proximity range of the location information or VAL service area identified by the VAL service area ID or Geofencing location area provided in step 1.
Step 3.
The location management server sends get UE information response to the VAL server with a list of VAL UE(s) or VAL user(s) and its corresponding location information as determined in step 1.
9.3.11 Monitoring Location Deviation |R17| p. 92
9.3.11.1 General p. 92
The VAL server requests the location management server to monitor the location of the VAL UE in relation to an area of interest. The LMS fetches the VAL UE's location information periodically from 3GPP core network as specified in TS 23.502 and also, using the Location Information procedures specified in clause 9.3.7 and clause 9.3.10. With the periodic location information of the UE from 3GPP core network and SEAL procedures, the location management server evaluates the current location of the VAL UE in relation to the area of interest configured by the VAL server. If subscribed, the VAL server is notified by the location management server when the VAL UE relationship (e.g. inside or outside) to the area of interest changes along with current location information of the VAL UE. The area of interest can be predefined or mobile where the latter one is used to support dynamic geofencing function.
9.3.11.2 Monitoring Location Deviation procedure p. 92
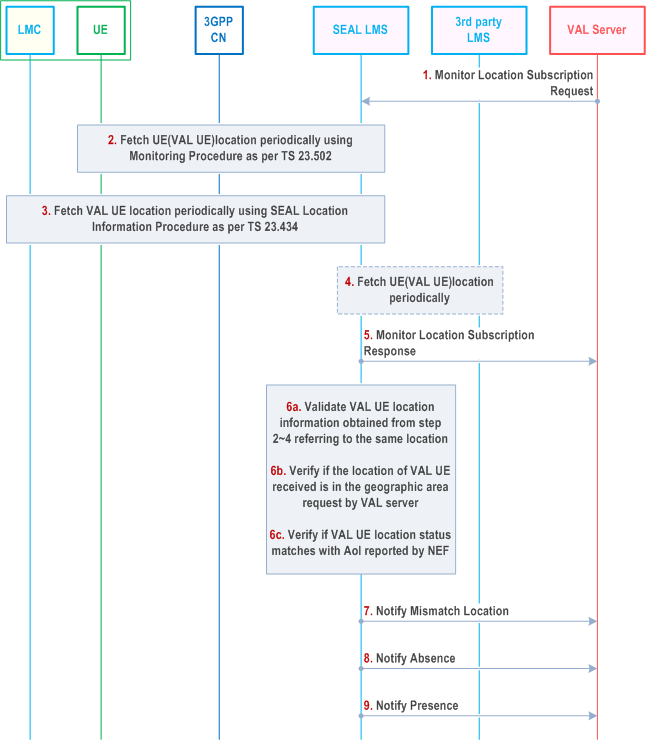
Figure 9.3.11.2-1 describes the procedure for monitoring the VAL UE's location in a given area of interest.
Pre-condition:
- The location management server authorized to consume the 3GPP core network service (Monitoring events provided by NEF as specified in TS 23.502).
Step 1.
The VAL server sends Monitor Location Subscription Request to location management server including target VAL UE Identifier(s), predetermined or dynamic area of interest information, notification interval and notification URI where the VAL server intends to receive the notifications from location management server regarding target VAL UE's presence in a given area, interested notification information, dynamic geofencing conditions.
Step 2.
- "Area of interest" is the location information, which the VAL server wishes to monitor the target VAL UE's location adherence. This parameter can include an area of interest information and other relevant parameters. In the case of dynamic area of interest, it includes a reference VAL UE Identifier and its proximity range.
- "Notify_Interval" represents the periodic interval in which the location management server needs to notify target VAL UE's location information to the VAL server. When the target VAL UE moves away from the "Area of interest", then the location management server ignores the "Notify_Interval" and sends the location notification to the VAL server immediately.
- "dynamic geofencing conditions" includes a temporal condition(s) (e.g. time of day and day of week), connectivity condition(s) (e.g. operator information, roaming status, access type) and/or a spatial condition(s) (e.g. location area(s)) for the reference VAL UE. For instance, the monitoring is valid when a reference VAL UE is served by operator A without using satellite in location area X from 7:00am to 9:00am on working days.
If dynamic area of interest information and dynamic geofencing conditions are received, the location management server requests 3GPP CN (e.g. NEF service for location, access type and roaming status monitoring as specified in TS 23.502) to monitor the reference VAL UE location change, access type change and roaming status change, in order to determine spatial dynamicity in area of interest related to the target UE(s). If spatial condition is received, the location management server also requests 3GPP CN (i.e. NEF service for area of interest monitoring as specified in TS 23.502) to know whether the reference VAL UE is in the VAL server's predetermined area (e.g. PLMN x). The location management server will process the monitoring considering the received dynamic geofencing conditions for the reference UE.
Step 3.
If dynamic area of interest information is received, the location management server requests 3GPP CN (i.e. NEF service for loss of connectivity as specified in TS 23.502) for both target UE(s) and reference UE.
Step 4a.
Location management server processes the Area of interest information in the request, and then subscribes to target UE location monitoring as specified in TS 23.502 with appropriate parameters mapping. Based on the subscription, the location management server receives the target VAL UE location information periodically from the 3GPP core network. The location management server also invokes NEF service for Area of Interest monitoring as specified in clause 5.3.3 of TS 23.256 to know whether the target VAL UE is in the VAL server's predetermined or dynamic area of interest.
Step 4b.
Location management server shall use the Location information procedures as specified in clause 9.3.7 and clause 9.3.10, to periodically obtain the target VAL UE location information. Based on the geographic information from the VAL server, the location management server may determine to additionally include the positioning methods in SEAL LMS procedures to obtain location information.
Step 4c.
LMS may periodically obtain the target VAL UE location information from the 3rd party location management server based on the geographic information from the VAL server.
Step 4d.
Location management server may configure the off-network position and report policy to the target VAL UE and/or reference VAL UE as described in clause 9.3.21.4.1 when they still have connectivity. This is to initiate the UE-only Operation SL/Ranging as described in TS 23.586, cache the location, report the location result when the connectivity is back. Time duration is included if the Dynamic geofencing conditions is specified in step 1.
Step 5.
Location management server, after successful subscription according to steps 2~4, sends Monitor Location Subscription response, indicating that the location management server accepts VAL server's request and will monitor the location of the target VAL UE(s) to verify if the target VAL UE(s) is in the area of interest.
Either step 6 or step 7 is performed if it is notified about loss of connectivity for the reference VAL UE and target VAL UE(s).
Step 6.
The location management server requests the target VAL UE to obtain the reference UE's location information (i.e., the absolute location or the relative location).
Step 6a.
The location management server determines the reference VAL UE lost connectivity and the target VAL UE still has the connectivity, the location management server sends location subscription request to the target VAL UE. The reference VAL UE identity and the Ranging/SL positioning method, location type (i.e., the absolute location or the relative location) are included. The location management client in the target VAL UE returns a location subscription response.
Step 6b.
The target VAL UE initiates the Ranging/SL based MO-LR procedure as described in clause 6.20 of TS 23.273 to obtain the reference VAL UE location information. The target VAL UE obtains the reference UE's location information.
Step 6c.
The target VAL UE sends the location notification with the reference UE's location information.
Step 7.
Alternatively, the location management server requests the target UE's location information from the core network. The core network initiates the Ranging/SL based MT-LR procedure as described in clause 6.20 of TS 23.273 and obtains the target VAL UE location information.
Step 8.
Location management server processes the location information received from SEAL Location Information procedures, the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server, and validates the information. If the location information is matching, then the Location management server shall check if the VAL UE's current location is within the predetermined or dynamic area of interest received in step 1
Location management server verifies its determined target VAL UE location status (i.e. presence or absence with regard to the predetermined area of interest) with the retrieved 3GPP core network result from the NEF monitoring service for Area of Interest. The location management server will continue with step 7, step 8 and step 9 as applicable.
Step 9a.
If the location information received from location management client, the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server do not match or the NEF reported Area of Interest monitoring result does not match with the determined target VAL UE location status (present/absence) in location management server, then the location management server shall consider the target VAL UE as outside from its specified area of interest and shall notify ("Notify Mismatch Location" message) the VAL server of the same, including target VAL UE ID and the location information from location management server, the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server in the notification message.
Step 9b.
If the target VAL UE's current location is from location management client, the 3GPP core network and/or the 3rd party location management server matches, and either not in the predetermined area of interest received from VAL server in Monitor Location Subscription Request message or not within the proximity range of the reference UE, and such out of area of interest result is also aligned with the NEF reported area of interest monitoring result, then the location management server considers the target VAL UE as outside from its specified area of interest and shall notify the VAL server that the target VAL UE's current location is outside of area of interest and target VAL UE ID in "Notify Absence" message.
If either the target VAL UE or the reference VAL UE lost connectivity, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is outside the predetermined area of interest or dynamic area of interest as follows.
Step 9c.
- If the target VAL UE lost connectivity, and the target VAL UE's current absolute location is obtained in step 6 or step 7, the LMS server determines the target VAL UE is outside the predetermined area of interest according to the target VAL UE's absolute location. The location management server determines the target VAL UE is not within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target VAL UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
- If the target VAL UE lost connectivity, and target VAL UE's current relative location is obtained in step 6, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is not in the predetermined area of interest or not within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference VAL UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target VAL UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
- If the reference VAL UE lost connectivity, and the reference VAL UE's absolute location or relative location is obtained instep 6 or step 7, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is not within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference VAL UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target VAL UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
When the target VAL UE's current location is either in the predetermined area of interest or in the proximity range of the reference UE, and such in area of interest result is also aligned with the NEF reported area of interest monitoring result, then the location management server shall notify ("Notify Presence" message) the VAL server periodically, according to the "Notify_Interval" value in "Monitor Location Subscription Request" message, indicating the VAL server that the target VAL UE is within the area of interest, along with target VAL UE's current location information.
If either the target VAL UE or the reference VAL UE lost connectivity, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is within the predetermined area of interest or dynamic area of interest as follows.
Step 9d.
- If the target VAL UE lost connectivity, and the target VAL UE's current absolute location is obtained in step 6 or step 7, the LMS server determines the target VAL UE is within the predetermined area of interest according to the target VALUE's absolute location. The location management server determines the target VAL UE is within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference VAL UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target VAL UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
- If the target VAL UE lost connectivity, and target VAL UE's current relative location is obtained in step 6 or step 7, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is within the predetermined area of interest or within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference VAL UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
- If the reference VAL UE lost connectivity, and the reference VAL UE's absolute location or relative location is obtained in step 6 or step 7, the location management server determines the target VAL UE is within the proximity range of the reference VAL UE based on the reference VAL UEs' location obtained in step 4 and the target VAL UE's absolute location in step 6 or step 7.
If the location management server is notified by the 3GPP CN about loss of connectivity for the reference VAL UE and target VAL UE(s), or fails to obtains the target VAL UE's location or the reference UE' location in step 6 or step 7 (e.g., due to the target VAL UE and reference VAL UE are beyond the Ranging/SL range), then the location management server notifies ("Notify Unknown" message with detailed reason) the VAL server indicating that the location management server does not know whether the target VAL UE is "Presence" or "Absence", therefore the dynamic geofencing monitoring for the impacted target UE(s) is suspended.
Step 10.
If both the target VAL UE and/or reference VAL UE lost the connectivity, the off-network target VAL UE and/or reference VAL UE initiate the UE-only Operation SL/Ranging as described in TS 23.586 or the procedure as defined in clause 9.5.3 and clause 9.5.4, and cache the location result as configured in step 4e.
Step 11.
If the connectivity is back, the target VAL UE and/or reference VAL UE check whether it is still within the valid duration if configured. If yes, the the target UE and/or reference VAL UE report the cached history location to the location management server as described in clause 9.3.21.4.1.
Step 12.
The location management server may use the cached history location e.g., to notify the VAL server about the history target VAL UE location status during the loss of connectivity.
9.3.12 Location area monitoring information procedure |R17| p. 96
9.3.12.1 Location area monitoring subscription procedure p. 96
Figure 9.3.12.1-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location area monitoring subscription request. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other SEAL servers that would like to subscribe to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area. The subscription request can be for a reference UE for which the subscriber is authorized to monitor location information.
The procedure is also applied for Geofencing service which initiated via VAL server to subscribe to the location management server to report the Geofencing monitoring events.
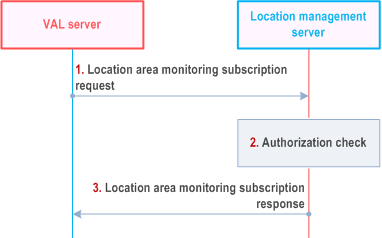
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a location area monitoring subscription request to the location management server to subscribe to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.14-1. The location information criteria may include the geographic location information or the VAL service area identified by the VAL service area ID where the UEs moving in or moving out to be monitored, or it may include reference UE information where in the UEs moving in or moving out of given application defined proximity range from the reference UE (target UE) to be monitored. The reference UE information may include VAL UE ID.
If the VAL server initiates the subscription for the Geofencing service, the Geofencing monitoring events (i.e. the UEs moving in/out of the pre-defined location area, the number of UEs moving in/out of the pre-defined location area, the time period of UEs enter/leave the pre-defined location area) may be included in the request message as specified in Table 9.3.2.14-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate the location area monitoring subscription request.
Step 3.
The location management server replies with a location area monitoring subscription response indicating the subscription status. In the response message, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.15-1.
9.3.12.2 Location area monitoring subscription modify procedure p. 97
Figure 9.3.12.2-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location area monitoring subscription modify request. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other SEAL servers that would like to modify the subscription to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area. The subscribe modify request can be for a reference UE for which the subscriber is authorized to monitor location information.
The procedure is also applied for Geofencing service that the VAL server modifies the subscription to the location management server to report the Geofencing monitoring events.
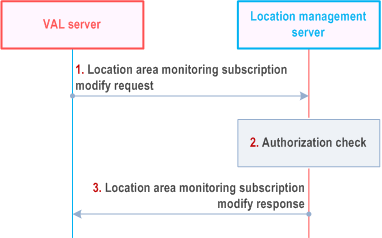
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a location area monitoring subscription modify request to the location management server to modify the subscription to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area or the Geofencing monitoring events. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.17-1.
Step 2.
The location management server shall check if the VAL server is authorized to initiate the location area monitoring subscription modify request.
Step 3.
The location management server replies with a location area monitoring subscription modify response indicating the subscription status. In the response message, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.18-1.
9.3.12.3 Location area monitoring unsubscribe procedure p. 98
Figure 9.3.12.3-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location area monitoring unsubscribe request. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other SEAL servers that would like to unsubscribe to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area. The unsubscribe request can be for a reference UE for which the subscriber is authorized to monitor location information.
The procedure is also applied for Geofencing service that the VAL server unsubscribes to the location management server to report the Geofencing monitoring events.
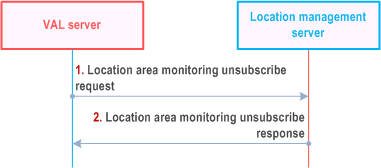
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a location area monitoring unsubscribe request to the location management server to unsubscribe to the subscription to the list of UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area or the Geofencing monitoring events. In the request message, the VAL server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.19-1.
Step 2.
The location management server replies with a location area monitoring unsubscribe response indicating the subscription status. In the response message, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.20-1.
9.3.12.4 Location area monitoring notification procedure p. 98
Figure 9.3.12.4-1 illustrates the high level procedure of location area monitoring notification. The same procedure can be applied for location management client and other SEAL servers who have subscribe to the list of the UEs moving in or moving out of the specific location area.
The procedure is also applied for Geofencing service which requests the location management server to report the Geofencing monitoring events.
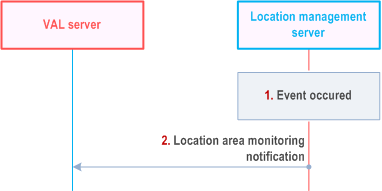
Step 1.
One of the events occurs at the location management server as specified in the subscribe request. The location management server identifies the UEs which are moved into the area or moved out of the area based on the received UEs location data and time stamp of the location. The LMS may report the list of all UEs in the given location or UEs moved in and moved out.
When the Geofencing service is triggered, the location management server also checks whether the UE is inside/outside the area based on the location information criteria as defined in Table 9.3.2.14-1 and the received UE location data. Further, the LM Server statistics and reports the Geofencing monitoring events (e.g. the list of UEs moving in/out of the location area, the number of UEs moving in/out of the location area, the time period of UEs enter/leave the location area, etc.) to the VAL server.
Step 2.
The location management server sends a location area monitoring notification to the VAL server. In the notification message, the location management server includes the information as specified in Table 9.3.2.16-1.
If the location management server didn't obtain any UE location information due to UE issues or network issues in step 1, it informs the VAL server with the proper reason (e.g., "UE cannot be connected") in the notification report.
Step 3.
After received the Geofencing information report from the location management server, the VAL server may take some actions to inform the VAL UE (e.g. send the alarms or warnings to the UE).