Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.0.6…
4.1…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.4
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.4…
4.8
4.9…
4.10…
5…
5.2…
5.2.4
5.2.5…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.4…
5.7.8
5.8…
5.10…
5.10.5…
5.10.6…
5.11…
5.12…
5.12.4…
5.12.5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.5…
6.9.7
7…
8…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.8
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15…
A.15.3…
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
E…
4.1 General service architecture
4.1.1 Definition of 5G Media Streaming architecture
4.1.2 Generalized Media Delivery architecture
4.1.2.1 Generalized Media Delivery in the 5G System
4.1.2.2 Reference architecture for Media Delivery
4.1.2.3 Network Functions and UE entities
4.1.2.4 Reference points
4.1.2.5 Interfaces and APIs
4.1.2.5.1 Interfaces and APIs supporting media session handling
4.1.2.5.2 Interfaces and APIs supporting media transport
4.1.2.5.3 Interfaces and APIs supporting application functionality
...
...
4.1 General service architecture p. 23
4.1.1 Definition of 5G Media Streaming architecture |R18| p. 23
The overall 5G Media Streaming Architecture is shown in Figure 4.1.1-1 below.
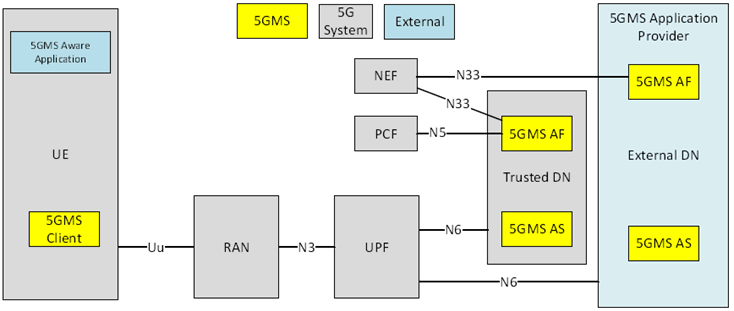
The 5GMS Application Provider uses 5GMS for streaming services. It provides a 5GMS Aware-Application on the UE to make use of 5GMS Client and network functions using interfaces and APIs defined in 5GMS.
The architecture in Figure 4.1.1-1 represents the specified 5GMS functions within the 5G System (5GS) as defined in TS 23.501. Three main functions are defined:
- 5GMS AF: An Application Function as defined in clause 6.2.10 of TS 23.501, dedicated to 5G Media Streaming.
- 5GMS AS: An Application Server dedicated to 5G Media Streaming.
- 5GMS Client: A UE internal function dedicated to 5G Media Streaming. The 5GMS Client is a logical function and its subfunctions may be distributed within the UE according to implementation choice.
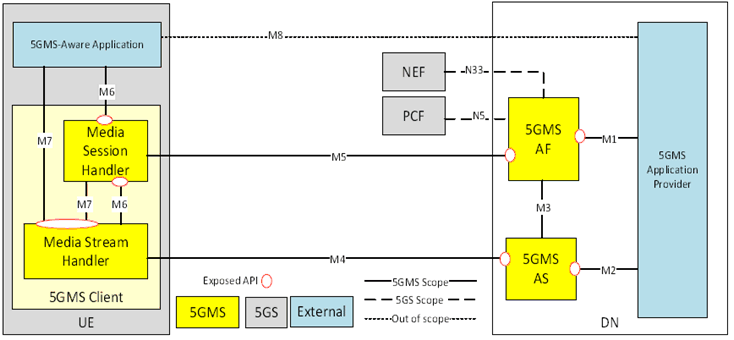
The remainder of the present document specifies stage 2 aspects of the media streaming functional entities shown in the general architecture of Figure 4.1.1-2.
This architecture specification addresses two main scenarios as concerns each individual media streaming operation:
- Downlink streaming: The network is the origin of the media and the UE acts as the consumption device.
- Uplink streaming: The UE is the origin of the media and the network acts as the consumption entity.
4.1.2 Generalized Media Delivery architecture |R18| p. 24
4.1.2.1 Generalized Media Delivery in the 5G System p. 24
This clause and subsequent subclauses of clause 4.1.2 define a generalized Media Delivery architecture of which the architecture for 5G Media Streaming (5GMS) defined elsewhere in the present document is one possible realisation. In case of any misalignment between the two, the 5GMS architecture has precedence over this generalised architecture.
Due to the similarity of the 5GMS architecture (as defined in the present document) to the architecture for Real-Time media Communication (RTC) defined in TS 26.506, the RTC functions and 5GMS functions may share or may make use of many common functionalities for both media session handling and media delivery. A generalized Media Delivery architecture that integrates 5GMS and RTC functionality in the 5G System is defined in Figure 4.1.2.1-1.
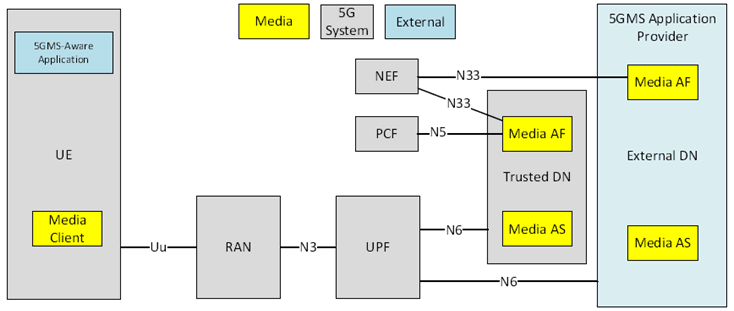
Figure 4.1.2.1-1: Generalized Media Delivery architecture within the 5G System
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
In this representation:
- The Media Application Provider plays the role of the 5GMS Application Provider.
- The Media-aware Application plays the role of the 5GMS-Aware Application.
- The 5GMS AF is one possible realisation of the general Media AF.
- The 5GMS AS is one possible realisation of the general Media AS.
- The 5GMS Client is part of the general Media Client.
4.1.2.2 Reference architecture for Media Delivery p. 26
A functional description with additional details as well as reference points is provided below, as illustrated in Figure 4.1.2.2-1.
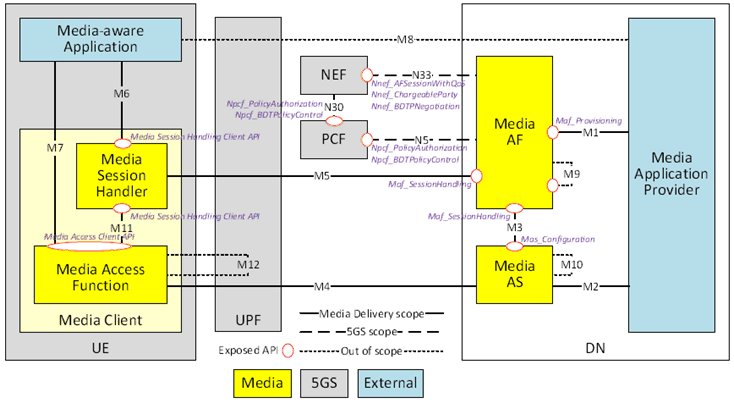
4.1.2.3 Network Functions and UE entities p. 26
Functional definitions may be generalized as follows:
- Media AF: An Application Function as defined in clause 6.2.10 of TS 23.501 dedicated to Media Delivery.
- Media AS: An Application Server dedicated to Media Delivery.
-
Media Client: A UE internal function dedicated to Media Delivery comprising:
- Media Session Handler: An entity on the UE that communicates with the Media AF in order to establish, control and support the delivery of a media session.
- Media Access Function: An entity on the UE that communicates with the Media AS in order to access and deliver media content. The media access function for example may be further sub-divided into content delivery protocols, codecs, media types and metadata representation.
- Media-aware Application: An application entity on the UE that makes use of 3GPP-defined APIs to invoke the Media Session Handler and/or the Media Access Function in order to support Media Delivery.
| Generalized media architecture function | 5GMSd function | 5GMSu function |
|---|---|---|
| Media AF | 5GMSd AF | 5GMSu AF |
| Media AS | 5GMSd AS | 5GMSu AS |
| Media Client | 5GMSd Client | 5GMSu Client |
|
Media Session Handler
| Media Session Handler | |
|
Media Access Function
| Media Stream Handler (Media Player) | Media Stream Handler (Media Streamer) |
| Media Application Provider | 5GMSd Application Provider | 5GMSu Application Provider |
| Media-aware Application | 5GMSd-Aware Application | 5GMSu-Aware Application |
4.1.2.4 Reference points p. 27
The following reference points are defined for Media Delivery:
M1:
Reference point between the Media Application Provider and the Media AF for the provisioning of Media Delivery.
M2:
Reference point between the Media Application Provider and the Media AS for the purposes of ingesting media into the Media AS or egesting media from the Media AS.
M3:
Reference point between the Media AF and the Media AS for the purposes of Media AS configuration and/or for media session handling in relation to Media Delivery.
M4:
Reference point between the Media AS and the Media Access Function in the UE for the purpose of downlink transport of media from the Media AS to the Media Access Function ("content distribution") or uplink transport of media from the Media Access Function to the Media AS ("content contribution").
M5:
Reference point between the Media AF and the Media Session Handler in the Media Client for the purpose of media session handling in relation to Media Delivery.
M6:
Reference point between the Media-aware Application and the Media Session Handler for the purpose of configuring the Media Session Handler.
M7:
Reference point between the Media-aware Application and the Media Access Function for the purpose of media access control.
M8:
Reference point between the Media-aware Application and the Media Application Provider.
M9:
Reference point between one instance of the Media AF and another for the purpose of Media AF instance chaining.
M10:
Reference point between one instance of the Media AS and another for the purpose of distributed service chaining of Media AS instances.
M11:
Reference point between the Media Session Handler and the Media Access Function (both in the Media Client) for the purpose of configuring the Media Session Handler and/or media access control.
M12:
Reference point between one Media Access Function and another for the purpose of peer-to-peer media transport between different Media Clients when this is permitted by the 5G System.
| Generalized Media Delivery architecture reference point | 5GMSd reference point | 5GMSu reference point |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | M1d | M1u |
| M2 | M2d | M2u |
| M3 | M3d | M3u |
| M4 | M4d | M4u |
| M5 | M5d | M5u |
| M6 | M6d | M6u |
| M7 | M7d | M7u |
| M8 | M8d | M8u |
| M9 | Not defined | Not defined |
| M10 | Not defined | Not defined |
| M11 | M6d, M7d | M6u, M7u |
| M12 | Not defined | Not defined |
4.1.2.5 Interfaces and APIs p. 28
4.1.2.5.1 Interfaces and APIs supporting media session handling p. 28
The Media AF exposes the following network service interfaces for media session handling:
- Provisioning API (Maf_Provisioning): External API, exposed to the Media Application Provider by the Media AF at reference point M1 to provision the usage of the Media Delivery and to obtain feedback.
- Media Session Handling API (Maf_SessionHandling) exposed by a Media AF to the Media Session Handler at reference point M5 and/or to the Media AS at reference point M3 for media session handling, control, reporting and assistance that also include appropriate security mechanisms, e.g. authorization and authentication.
- Media Session Handling Client API: exposed by the Media Session Handler to the Media-aware Application at reference point M6 and to the Media Access Function at reference point M11, for configuring media session handling, including service launch.
4.1.2.5.2 Interfaces and APIs supporting media transport p. 28
The Media AS exposes the following network service interfaces to support media transport:
- Media Application Server Configuration API (Mas_Configuration) used by the Media AF at reference point M3 to configure the Media AS.
- Application Provider media transport interface between the Media AS and the Media Application Provider, used to exchange media data using a media transport protocol at reference point M2.
- Client-facing media transport interface between the Media Access Function and the Media AS, used to exchange media data using a media transport protocol at reference point M4.
- Media Access Control API exposed by the Media Access Function to the Media-aware Application at reference point M7 and to the Media Session Handler at reference point M11, in order to configure and communicate with the Media Access Function.
4.1.2.5.3 Interfaces and APIs supporting application functionality p. 29
The Media Application Provider exposes the following network service interfaces to support application functionality:
- Application-private API used for information exchange between the Media-aware Application and the Media Application Provider at reference point M8.