Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.0.6…
4.1…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.4
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.4…
4.8
4.9…
4.10…
5…
5.2…
5.2.4
5.2.5…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.4…
5.7.8
5.8…
5.10…
5.10.5…
5.10.6…
5.11…
5.12…
5.12.4…
5.12.5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.5…
6.9.7
7…
8…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.8
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15…
A.15.3…
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
E…
5.3.2 Baseline provisioning procedure
5.3.3 Baseline provisioning procedure with authorisation of 5GMSd Application Provider
...
...
5.3.2 Baseline provisioning procedure p. 89
The present clause describes the baseline procedure to provision the features using the 5GMS System.

Figure 5.3.2-1: High-level procedure for provisioning the 5GMS System for downlink media streaming sessions
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Steps:
Optional:
Depending on the parameters of the Provisioning Session:
According to schedule, or upon request:
The 5GMSd AF may request the creation or reuse of one or more network slices for distributing the content of the provisioned session. If more than one network slice is provisioned for the distribution of the content of a session, the list of allowed S-NSSAIs shall be conveyed to the target UEs (e.g. through URSP or through M5d or M8d).
Step 1.
The 5GMSd Application Provider discovers the address (URL) of the 5GMSd AF (M1d) for Session Provisioning.
Step 2.
Void.
Step 3.
The 5GMSd Application Provider creates a Provisioning Session, providing its 5GMSd Application Provider identifier as input. 5GMSd Application Provider queries the capabilities and authorized features.
Step 4.
The 5GMSd Application Provider specifies one or more 5GMSd features in the Provisioning Session. A set of authorized features is activated, such as content consumption measurement, logging, collection and reporting; QoE metrics measurement, logging, collection and reporting; dynamic policy; network assistance; and content hosting (including ingest).
One or more External service identifiers are supplied by the 5GMSd Application Provider to support the later retrieval of Service Access Information from the 5GMSd AF by the Media Session Handler.
When the content hosting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMS Application Provider configures the content hosting behaviour of the 5GMSd AS. This Content Hosting Configuration is specified in clause 5.4 and includes selecting the ingest protocol and format, caching and proxying of media objects, content preparation, access protection (e.g. URL signing) and indicating a target distribution area (e.g. through geofencing).
When the dynamic policy feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider specifies a set of policies which can be invoked for the unicast downlink streaming session. The UE becomes aware of the selected policies in the form of a list of valid Policy Template Ids.
When the content consumption measurement, logging, collection and reporting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider indicates the desired reporting interval. When the 5GMSd Application Provider has delegated Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then location reporting is also selected or de-selected.
When the QoE metrics measurement, logging, collection and reporting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides configuration input on the QoE post processing. When the 5GMSd Application Provider has delegated Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then more detailed metrics reporting is configured.
When the edge computing feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides one or more Edge Resources Configurations that can be used to support either client-driven management or Application Provider-driven management of edge resources associated with the Provisioning Session.
When the event data processing feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides one or more Event Data Processing Configurations that determine how, in the scope of the Provisioning Session, content consumption and QoE metrics collected from the UE and application logs collected from the 5GMSd AS are processed into events and exposed to subscribers.
Step 5.
When content hosting is desired, the 5GMSd AF interacts with the 5GMSd AS at reference point M3d to allocate M2d resources and to configure the ingest format by means of a Content Hosting Configuration (defined in clause 5.4) which may reference Server Certificates and Content Preparation Templates, as required. The 5GMSd AS responds with the M2d content ingest address.
Step 6.
The 5GMSd AF compiles the Service Access Information. The Service Access Information contains access details and options such as the Provisioning Session identifier, M5d (Media Session Handling) addresses for content consumption reporting, QoE metrics reporting, dynamic policy, network assistance, etc. When content hosting is offered and has been selected in step 4, then also M4d (Media Streaming) information such as the DASH MPD is included.
Step 7.
The 5GMSd AF provides the results to the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 8.
- When the 5GMSd Application Provider has selected full Service Access Information, then the results are provided in the form of addresses and configurations for M2d (Ingest), M5d (Media Session Handling) and M4d (Media Streaming).
- When the 5GMSd Application Provider delegated the Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then a reference to the Service Access Information (e.g., a URL) is provided. The Media Session Handler fetches the full Service Access Information later from the 5GMSd AF.
When content hosting is offered and has been selected in step 4, the 5GMSd Application Provider can start supplying content at the M2d ingest interface. In the case of progressive download or on-demand DASH sessions, the 5GMSd Application Provider makes the content assets available. In the case of Live DASH streaming sessions, the 5GMSd Application Provider starts supplying the live content.
Step 9.
The 5GMSd Application Provider executes Service Announcement and updates the UEs (during the lifetime of the Provisioning Session).
Step 10.
The 5GMSd Application Provider may update the Provisioning Session.
Step 11.
The 5GMSd AF may send event-related or periodic notifications to the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 12.
The 5GMSd Application Provider may manually terminate the Provisioning Session (at any time). All associated resources are released. Content may be removed from the 5GMSd AS. The 5GMSd Application Provider may configure a schedule for Provisioning Session termination.
Step 13.
The 5GMSd AF sends a notification upon Provisioning Session termination.
5.3.3 Baseline provisioning procedure with authorisation of 5GMSd Application Provider |R18| p. 91
This clause describes the baseline procedure to provision the features using the 5GMS System with authorisation of the 5GMSd Application Provider to support subsequent authorisation of media session handling for downlink media streaming per clause 5.2.5. When CAPIF is used, the authorization server is realised by the CAPIF core function, as shown in Figure 5.2.5.3-1 (a). Otherwise, it is realised by the 5GMSd AF, as shown in Figure 5.2.5.3-1 (b).

The steps in the call flow sequence are as follows with differences from the baseline call flow in clause 5.3.2 highlighted in bold.
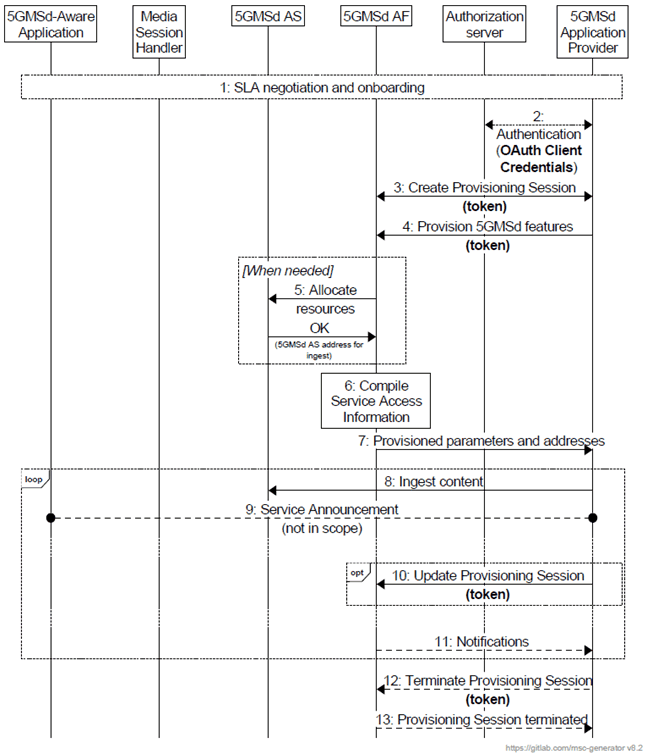
Figure 5.3.3-2: High-level procedure for provisioning the 5GMS System for downlink media streaming sessions
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Steps:
Optional:
Depending on the parameters of the Provisioning Session:
According to schedule, or upon request:
The 5GMSd AF may request the creation or reuse of one or more network slices for distributing the content of the provisioned session. If more than one network slice is provisioned for the distribution of the content of a session, the list of allowed S-NSSAIs shall be conveyed to the target UEs (e.g. through URSP or through M5d or M8d).
Step 1.
The 5GMSd Application Provider discovers the address (URL) of the 5GMSd AF (M1d) for Session Provisioning. During the self-onboarding procedure, the 5GMSd Application Provider obtains the API access credentials.
Step 2.
The 5GMSd Application Provider authenticates itself with the system. This procedure reuses existing authentication/authorisation procedures, e.g. leveraging CAPIF 1/1e TS 23.222. The AuthZ subfunction of the5GMSd AF acts here as OAuth authorization server. The 5GMSd AF acts as OAuth resource server. The 5GMSd Application Provider obtains an access token which is used for any subsequent operation invocations at reference point M1.
Step 3.
The 5GMSd Application Provider creates a Provisioning Session, providing its 5GMSd Application Provider identifier as input. 5GMSd Application Provider queries the capabilities and authorised features.
Step 4.
The 5GMSd Application Provider specifies one or more 5GMSd features in the Provisioning Session. A set of authorised features is activated, such as content consumption measurement, logging, collection and reporting; QoE metrics measurement, logging, collection and reporting; dynamic policy; network assistance; and content hosting (including ingest).
One or more External service identifiers are supplied by the 5GMSd Application Provider to support the later retrieval of Service Access Information from the 5GMSd AF by the Media Session Handler.
When the content hosting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMS Application Provider configures the content hosting behaviour of the 5GMSd AS. This Content Hosting Configuration is specified in clause 5.4 and includes selecting the ingest protocol and format, caching and proxying of media objects, content preparation, access protection (e.g. URL signing) and indicating a target distribution area (e.g. through geofencing).
When the dynamic policy feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider specifies a set of policies which can be invoked for the unicast downlink streaming session. The UE becomes aware of the selected policies in the form of a list of valid Policy Template Ids.
When the content consumption measurement, logging, collection and reporting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider indicates the desired reporting interval. When the 5GMSd Application Provider has delegated Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then location reporting is also selected or de-selected.
When the QoE metrics measurement, logging, collection and reporting feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides configuration input on the QoE post processing. When the 5GMSd Application Provider has delegated Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then more detailed metrics reporting is configured.
When the edge computing feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides one or more Edge Resources Configurations that can be used to support either client-driven management or Application Provider-driven management of edge resources associated with the Provisioning Session.
When the event data processing feature is offered and selected, the 5GMSd Application Provider provides one or more Event Data Processing Configurations that determine how, in the scope of the Provisioning Session, content consumption and QoE metrics collected from the UE and application logs collected from the 5GMSd AS are processed into events and exposed to subscribers.
Step 5.
When content hosting is desired, the 5GMSd AF interacts with the 5GMSd AS at reference point M3d to allocate M2d resources and to configure the ingest format by means of a Content Hosting Configuration (defined in clause 5.4) which may reference Server Certificates and Content Preparation Templates, as required. The 5GMSd AS responds with the M2d content ingest address.
Step 6.
The 5GMSd AF compiles the Service Access Information. The Service Access Information contains access details and options such as the Provisioning Session identifier, M5d (Media Session Handling) addresses for content consumption reporting, QoE metrics reporting, dynamic policy, network assistance, etc. When content hosting is offered and has been selected in step 4, then also M4d (Media Streaming) information such as the DASH MPD is included.
Step 7.
The 5GMSd AF provides the results to the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 8.
- When the 5GMSd Application Provider has selected full Service Access Information, then the results are provided in the form of addresses and configurations for M2d (Ingest), M5d (Media Session Handling) and M4d (Media Streaming).
- When the 5GMSd Application Provider delegated the Service Access Information handling to the 5GMS System, then a reference to the Service Access Information (e.g., a URL) is provided. The Media Session Handler fetches the full Service Access Information later from the 5GMSd AF.
When content hosting is offered and has been selected in step 4, the 5GMSd Application Provider can start supplying content at the M2d ingest interface. In the case of progressive download or on-demand DASH sessions, the 5GMSd Application Provider makes the content assets available. In the case of Live DASH streaming sessions, the 5GMSd Application Provider starts supplying the live content.
Step 9.
The 5GMSd Application Provider executes Service Announcement and updates the UEs (during the lifetime of the Provisioning Session).
Step 10.
The 5GMSd Application Provider may update the Provisioning Session.
Step 11.
The 5GMSd AF may send event-related or periodic notifications to the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 12.
The 5GMSd Application Provider may manually terminate the Provisioning Session (at any time). All associated resources are released. Content may be removed from the 5GMSd AS. The 5GMSd Application Provider may configure a schedule for Provisioning Session termination.
Step 13.
The 5GMSd AF sends a notification upon Provisioning Session termination.