Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.0.6…
4.1…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.4
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.4…
4.8
4.9…
4.10…
5…
5.2…
5.2.4
5.2.5…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.4…
5.7.8
5.8…
5.10…
5.10.5…
5.10.6…
5.11…
5.12…
5.12.4…
5.12.5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.5…
6.9.7
7…
8…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.8
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15…
A.15.3…
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
E…
5.12.5 Procedures for dynamic provisioning of 5GMS content delivery via MBS
5.12.5.1 General
5.12.5.2 Operation modes
...
...
5.12.5 Procedures for dynamic provisioning of 5GMS content delivery via MBS p. 149
5.12.5.1 General p. 149
In this scenario the same content is distributed via MBS and via a 5GMS System. The resources of the MBS System are statically configured. MBS-based distribution may, for example, be used only for services in high demand, and the resources and quality of the service distributed through broadcast may be adjusted according to demand. Demand may be identified through 5GMS Consumption Reporting.
The call flow in Figure 5.12.5.1-1 and Figure 5.12.5.1-2 extends that defined in clause 5.12.1 to address generic use cases for MBS-on-demand. Specific additional use cases are presented in the remainder of clause 5.12.5.
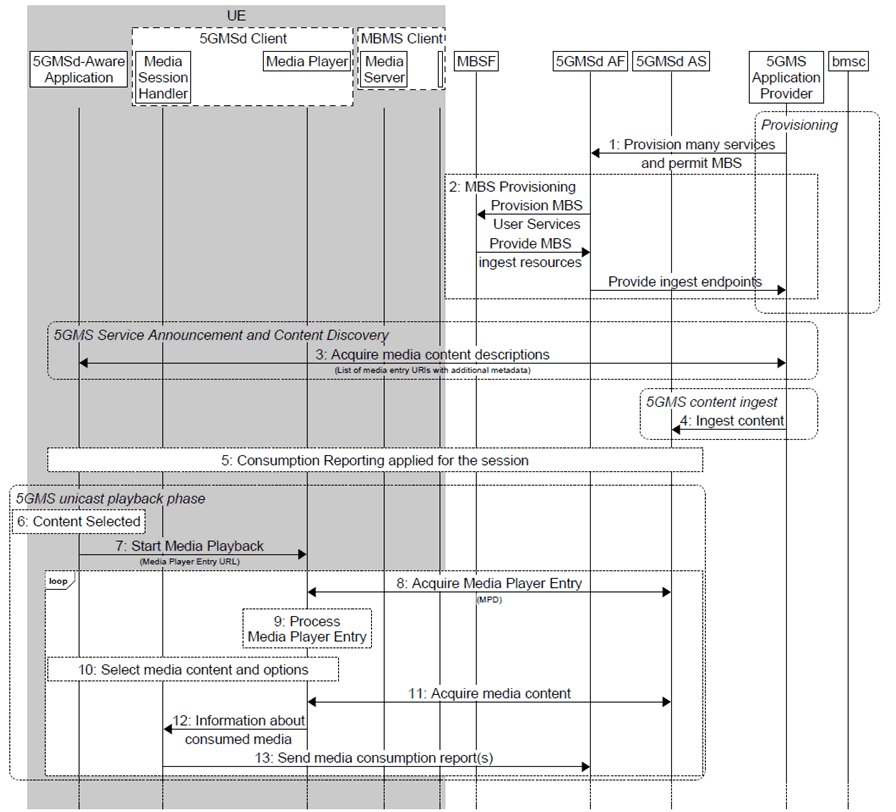
Figure 5.12.5.1-1: High-level procedure for DASH content delivered via MBS-on-demand
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Steps:
Step 1.
Media playback initially uses unicast 5G Media Streaming:
The 5GMS Application Provider provisions one or more 5GMSd services and permits broadcast distribution of the media content.
Step 2.
As a consequence, the 5GMSd AF provisions MBS delivery and the MBSF informs the 5GMSd AF about the resources it will use to ingest media content.
Step 3.
The media content is announced to the 5GMSd-Aware Application and the application request the entry points for the service.
Step 4.
The 5GMSd AS starts to ingest content from the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 5.
Consumption Reporting is applied for the downlink media streaming session.
Step 6.
Subsequently, media playback switches to MBS:
The media content is selected by the 5GMSd-Aware Application.
Step 7.
The 5GMSd-Aware Application triggers the start of media playback by the Media Player.
Step 8.
The Media Entry Point docuent (e.g. DASH MPD) is requested by the Media Player from the 5GMSd AS.
Step 9.
The Media Player processes the media presentation manifest and identifies that the media content is available on the 5GMSd AS
Step 10.
The Media Player, under the control of the application, selects the media content and different content options.
Step 11.
Media content is received from the 5GMSd AS via reference point M4d.
Step 12.
The Media Player informs the Media Session Handler about the consumed media content.
Step 13.
The Media Session Handler sends consumption reports to the 5GMSd AF.
Step 14.
By analysing the consumption reports submitted to it in the previous step, the 5GMSd AF identifies a high level of demand for the service.
Step 15.
Additional MBS Distribution Sessions are provisioned to add delivery of the service via MBS.
Step 16.
The MBSTF starts ingesting media content from the 5GMSd AS.
Step 17.
MBS media distribution starts.
Step 18.
The 5GMSd AF informs the Media Session Handler that MBS media distribution is initiated by providing updated Service Access Information.
Step 19.
MBS content reception is initiated by the Media Session Handler.
Step 20.
Once the service is ready, the content delivered on MBS is used by the Media Player. Consumption reporting continues. Specific cases may use different policies, similar to the hybrid case in clause 5.12.5.
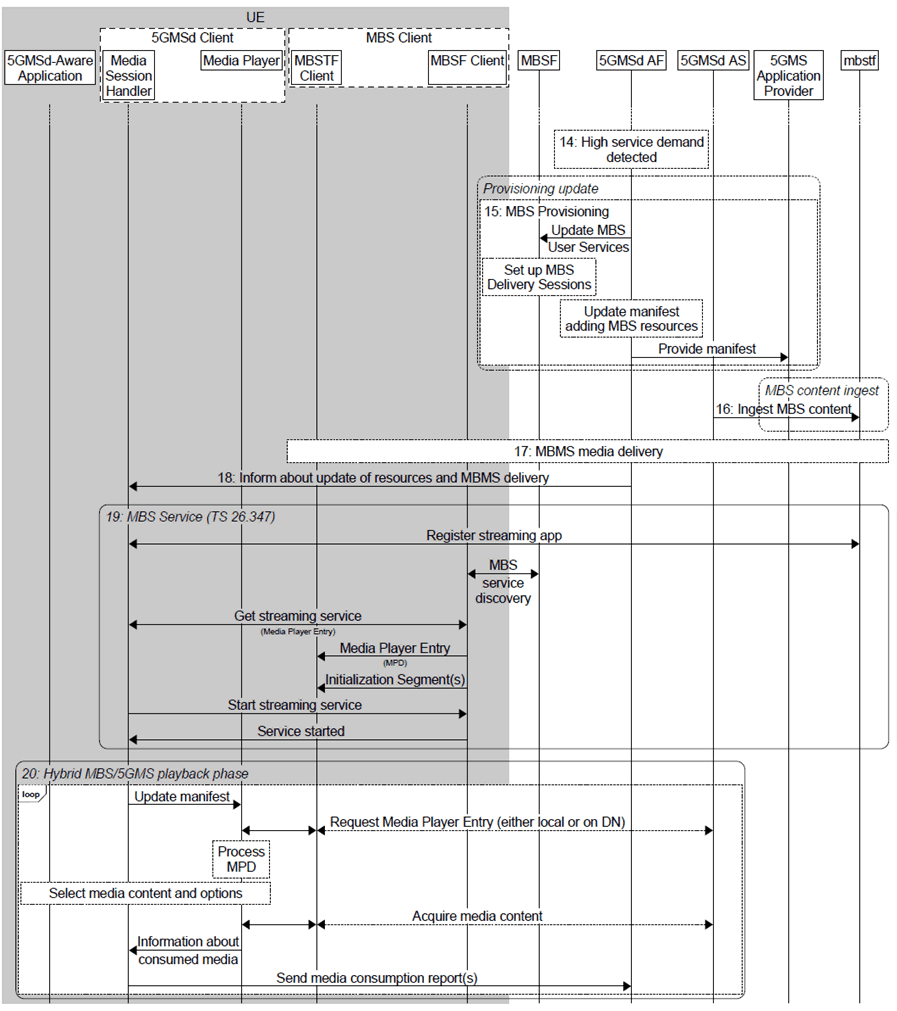
Figure 5.12.5.1-2: High-level procedure for DASH content delivered via MBS-on-demand (continued)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
5.12.5.2 Operation modes p. 152
At least the following operation modes are supported based on the general procedures in clause 5.12.5.1:
- Every 5GMS media service is mapped to exactly one MBS User Service. Whether the MBS User Service is announced and delivered or not depends on service demand. The MBS Distribution Session is adjusted dynamically - for example the MBS Distribution Session is disabled, or the bit rate is changed - depending on service demand and/or content requirements.
- A set of MBS User Services and MBS Distribution Sessions is defined in the initial provisioning. Downlink media streaming components are dynamically mapped to statically configured MBS Distribution Services based on demand and content requirements.
- Components of the downlink media streaming session, for example audio service components for different languages, are assigned dynamically to MBS Distribution Sessions depending on demand.