Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.0.6…
4.1…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.4
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.4…
4.8
4.9…
4.10…
5…
5.2…
5.2.4
5.2.5…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.4…
5.7.8
5.8…
5.10…
5.10.5…
5.10.6…
5.11…
5.12…
5.12.4…
5.12.5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.5…
6.9.7
7…
8…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.8
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15…
A.15.3…
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
E…
5.2 Baseline procedure for unicast downlink Media Streaming session establishment
5.2.1 General
5.2.2 Progressive download of on-demand content
5.2.3 DASH streaming
...
...
5.2 Baseline procedure for unicast downlink Media Streaming session establishment p. 78
5.2.1 General p. 78
This clause describes the baseline procedure for establishing a unicast downlink media streaming session. This baseline procedure assumes that the 5GMSd AF and the 5GMSd AS both reside in the external DN and that there are no interactions between the 5GMSd AF and the 5G System.
5.2.2 Progressive download of on-demand content p. 78
This baseline procedure describes the establishment of a unicast downlink streaming session. A streaming session may use 3GP File Format (Progressive Download), 3GP Timed Text or other (potentially non-3GPP defined) formats.

Figure 5.2-1: High Level Procedure for progressive download for on-demand media
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Prerequisites:
- The 5GMSd Application Provider has provisioned the 5G Media Streaming System and has set up content ingest.
- The 5GMSd-Aware Application has received the service announcement from the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 1.
The 5GMSd-Aware Application triggers the Service Announcement and Service and Content Discovery procedure. The Service Announcement includes either the whole Service Access Information (i.e. details for Media Session Handling (M5d) and for Media Streaming access (M4d)) or a reference to the Service Access Information.
Step 2.
A Media Player Entry is selected.
Step 3.
The 5GMSd-Aware Application triggers the Media Session Handler to start the playback. The Media Player Entry is provided to the Media Session Handler.
Step 4.
When the 5GMS-Aware Application has received only a reference to the Service Access Information (see step 1), the Media Session Handler interacts with the 5GMSd AF to acquire the whole Service Access Information.
Step 5.
The Media Session Handler triggers the Media Player to start the session.
Step 6.
The Media Player establishes the transport session.
Step 7.
The Media Player sends the request for the progressive download content.
Step 8.
The Media Player receives the initialization information of the progressive download content. The initialization information contains configuration parameters for reception of the media and, optionally, also DRM information.
Step 9.
The Media Player configures the rendering pipeline for media playback.
Step 10.
The Media Player notifies the Media Session Handler, providing the transport session information and some media content related information.
Step 11.
Optional: The Media Player acquires a DRM License from the 5GMSd Application Provider.
Step 12.
The Media Player receives media content and puts it into the rendering pipeline.
Step 13.
The Media Player continuously receives and plays back the media content.
5.2.3 DASH streaming p. 80
It is assumed here that the key information to initialize the media decoding and rendering pipeline is present in the Media Player Entry (or referenced by the Media Player Entry). The intention is to provide the 5GMSd Client with information to set up the media decoding and rendering pipeline in such a way that no pipeline reset is needed during the session. Implementations need to consider that parts of the information are provided with the initialization segments.
It is assumed that the client is enabled to use the same media decoding and rendering pipeline during the session.
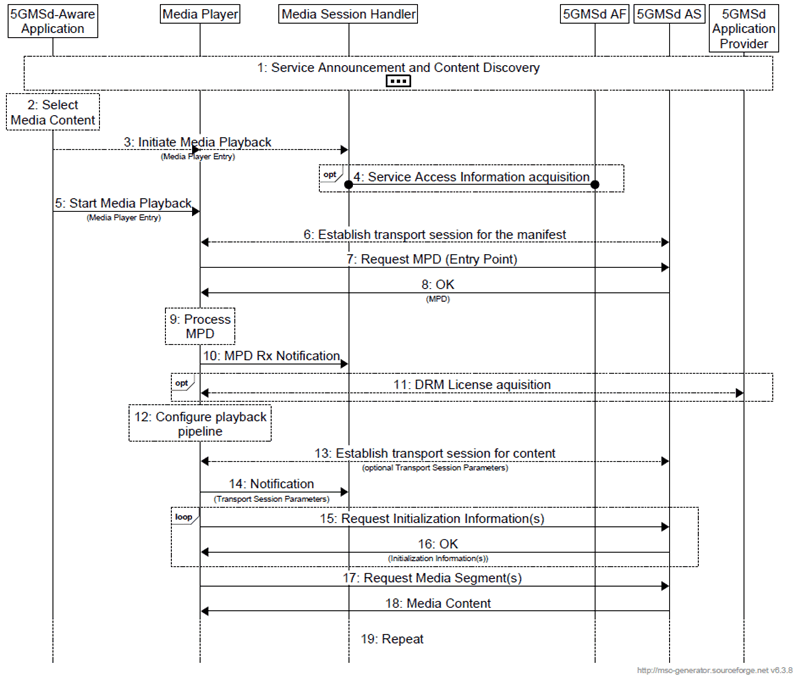
Prerequisites:
- The 5GMSd Application Provider has provisioned the 5G Media Streaming System and has setup content ingest.
- The 5GMSd Aware Application has received the service announcement from the 5GMS Application Provider.
Step 1.
The 5GMSd Aware Application triggers the Service Announcement and Service and Content Discovery procedure. The Service and Content Discovery procedure only involves the App and the external Application Server. The Service Announcement includes either the whole Service Access Information (i.e. details for Media Session Handling (M5d) and for Media Streaming access (M4d)) or a reference to the service access information.
Step 2.
A media content item is selected.
Step 3.
The 5GMSd-Aware Application triggers the 5GMSd Client to start media playback. The Media Player Entry is provided to the 5GMSd Client.
Step 4.
When the 5GMS-Aware Application has received only a reference to the Service Access Information (see step 1), the Media Session Handler interacts with the 5GMSd AF to acquire the whole Service Access Information.
Step 5.
In parallel, the Media Player is invoked to start media access and playback.
Step 6.
The Media Player establishes the transport session for acquiring the MPD referenced by the Media Player Entry.
Step 7.
The Media Player requests the MPD.
Step 8.
The Media Player receives the MPD.
Step 9.
The Media Player processes the MPD. It determines for example the number of needed transport sessions for media acquisition. The Media Player should be able to use the MPD information to initialize the media pipelines for each media stream. The MPD should also contain information to initialize the DRM client, when DRM is used.
Step 10.
The Media Player notifies the Media Session Handler about the MPD. The notification may contain parameters from the MPD.
Step 11.
Optional: the Media Player acquires the necessary DRM information, for example a DRM License.
Step 12.
The Media Player configures the media playback pipeline.
Step 13.
The Media Player establishes the necessary transport sessions for the content. For example, the Media Player may establish one transport session for each media component (audio, video, etc) and possibly additional transport sessions for other media representations.
Step 14.
The Media Player notifies the Media Session Handler that it is ready to commence playback and optionally provides transport session parameters.
Step 15.
The Media Player requests initialization information. The Media Player repeats this step for each required initialization segment.
Step 16.
The Media Player receives the initialization information.
Step 17.
The Media Player requests media segments according to the MPD.
Step 18.
the Media Player receives media segments and puts the information into the appropriate media rendering pipeline.
Step 19.
Previous steps are repeated according to the MPD information.