Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
5.32 Support for ATSSS
5.32.1 General
5.32.2 Multi Access PDU Sessions
5.32.3 Policy for ATSSS Control
5.32.4 QoS Support
5.32.5 Access Network Performance Measurements
5.32.5.1 General principles
5.32.5.1a Address of PMF messages
5.32.5.2 Round Trip Time Measurements
5.32.5.2a Packet Loss Rate Measurements
5.32.5.3 Access Availability/Unavailability Report
5.32.5.4 Protocol stack for user plane measurements and measurement reports
5.32.5.5 UE Assistance Operation
5.32.5.6 Suspend and Resume Traffic Duplication
...
...
5.32 Support for ATSSS |R16| p. 462
5.32.1 General p. 462
The ATSSS feature is an optional feature that may be supported by the UE and the 5GC network.
The ATSSS feature enables a multi-access PDU Connectivity Service, which can exchange PDUs between the UE and a data network by simultaneously using one 3GPP access network and one non-3GPP access network and two independent N3/N9 tunnels between the PSA and RAN/AN. The multi-access PDU Connectivity Service is realized by establishing a Multi-Access PDU (MA PDU) Session, i.e. a PDU Session that may have user-plane resources on two access networks. This assumes both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access are allowed for the S-NSSAI of the PDU Session.
The UE may request a MA PDU Session when the UE is registered via both 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses, or when the UE is registered via one access only.
After the establishment of a MA PDU Session and when there are user-plane resources on both access networks, the UE applies network-provided policy (i.e. ATSSS rules) and considers local conditions (such as network interface availability, signal loss conditions, user preferences, etc.) for deciding how to distribute the uplink traffic across the two access networks. Similarly, the UPF anchor of the MA PDU Session applies network-provided policy (i.e. N4 rules) and feedback information received from the UE via the user-plane (such as access network Unavailability or Availability) for deciding how to distribute the downlink traffic across the two N3/N9 tunnels and the two access networks. When there are user-plane resources on only one access network, the UE applies the ATSSS rules and considers local conditions for triggering the establishment or activation of the user plane resources over another access.
The type of a MA PDU Session may be one of the following types defined in clause 5.6.1: IPv4, IPv6, IPv4v6 and Ethernet. In this release of the specification, the Unstructured type is not supported. The clause 5.32.6.2.1, the clause 5.32.6.2.2 and the clause 5.32.6.3.1 below define what Steering Functionalities can be used for each supported type of a MA PDU Session.
The handling of 3GPP PS Data Off feature for MA PDU Session is specified in clause 5.24.
The ATSSS feature can be supported over any type of access network, including untrusted and trusted non-3GPP access networks (see clauses 4.2.8 and 5.5), wireline 5G access networks (see clause 4.2.8), etc. as long as a MA PDU Session can be established over this type of access network.
In this Release of the specification, a MA PDU Session using IPv6 multi-homing (see clause 5.6.4.3) or UL Classifier (see clause 5.6.4.2) is not specified.
In this Release of the specification, support for ATSSS assumes SMF Service Areas covering the whole PLMN or that a MA PDU Session is released over both accesses when the UE moves out of the SMF Service Area.
A MA PDU Session does not support LADN. If the AMF receives a request to establish a MA PDU Session for a LADN DNN, the AMF shall reject the request. If the AMF receives a request to establish a PDU Session for a LADN DNN with "MA PDU Network-Upgrade Allowed" indication, the AMF shall not forward "MA PDU Network-Upgrade Allowed" indication to the SMF.
If the UE, due to mobility, moves from being served by a source AMF supporting ATSSS to a target AMF not supporting ATSSS, the MA PDU Session is released as described in TS 23.502.
A Multi-Access PDU Session may, for the 3GPP access and/or non-3GPP access, use user-plane resources of an associated PDN Connection in EPC (e.g. one 3GPP access path via EPC and one non-3GPP access path via 5GC or one 3GPP access path via 5GC and one non-3GPP access path via ePDG/EPC). Such use of ATSSS with EPS interworking may apply to Ethernet and IP-based PDU Session and PDN Connection types.
For a MA PDU Session established for the Ethernet PDU Session type, if the UE has not indicated support for Ethernet PDN connection type or if the network does not support Ethernet PDN connection type, when the 3GPP access use user-plane resources of an associated PDN Connection, the following takes place:
- The SMF+PGW-C considers that the Multi-Access PDU Session is still using the Ethernet PDU Session / PDN Connection type but in a restricted mode where EPS signalling can only refer to non-IP PDN Connection type.
- MAR rules in the UPF are still used for distributing DL traffic between 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- For traffic on 3GPP access, the SMF may update N4 rules and QoS rules/EPS bearer contexts on the UE to take into account that no QoS differentiation is possible over 3GPP access.
5.32.2 Multi Access PDU Sessions p. 463
A Multi-Access PDU (MA PDU) Session is managed by using the session management functionality specified in clause 5.6, with the following additions and modifications:
-
When the UE wants to request a new MA PDU Session:
- If the UE is registered to the same PLMN over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses, then the UE shall send a PDU Session Establishment Request over any of the two accesses. The UE also provides Request Type as "MA PDU Request" in the UL NAS Transport message. The AMF informs the SMF that the UE is registered over both accesses and this triggers the establishment of user-plane resources on both accesses and two N3/N9 tunnels between PSA and the RAN/AN.
- If the UE is registered to different PLMNs over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses, then the UE shall send a PDU Session Establishment Request over one access. The UE also provides Request Type as "MA PDU Request" in the UL NAS Transport message. After this PDU Session is established with one N3/N9 tunnel between the PSA and (R)AN established, the UE shall send another PDU Session Establishment Request over the other access. The UE also provides the same PDU Session ID and Request Type as "MA PDU Request" in the UL NAS Transport message. Two N3/N9 tunnels and User-plane resources on both accesses are established.
- If the UE is registered over one access only, then the UE shall send a PDU Session Establishment Request over this access. The UE also provides Request Type as "MA PDU Request" in the UL NAS Transport message. One N3/N9 tunnel between the PSA and (R)AN and User-plane resources on this access only are established. After the UE is registered over the second access, the UE shall establish user-plane resources on the second access.
- In the PDU Session Establishment Request that is sent to request a new MA PDU Session, the UE shall provide also its ATSSS capabilities, which indicate the steering functionalities and the steering modes supported in the UE. These functionalities are defined in clause 5.32.6.
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting:
- the "ATSSS-LL functionality with any steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting:
- the MPTCP functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting
- the "MPQUIC-UDP functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting:
- the "MPQUIC-IP functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting:
- the "MPQUIC-E functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
-
If the UE indicates it is capable of supporting:
- the "MPQUIC IP functionality with any steering mode without any ATSSS-LL functionality" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
- If the UE requests an S-NSSAI, this S-NSSAI should be allowed on both accesses. Otherwise, the MA PDU Session shall not be established.
-
The SMF determines the ATSSS capabilities supported for the MA PDU Session taking into consideration one or more of the following aspects based on the ATSSS capabilities provided by the UE and per DNN configuration on SMF:
-
If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPTCP functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1), then:
- If the DNN configuration allows MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL), including RTT measurement without using PMF protocol, the MA PDU Session is capable of (1) MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL) in the downlink and (2) MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink.
- If the DNN configuration allows MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL), but not RTT measurement without using PMF protocol, the MA PDU Session is capable of (1) MPTCP in the downlink (2) ATSSS-LL with any steering mode except Smallest Delay steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL except Smallest Delay steering mode) in the downlink and (3) MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink.
- If the DNN configuration allows MPTCP with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode, the MA PDU Session is capable of MPTCP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the DNN configuration does not allow MPTCP steering functionality and the DNN configuration allows ATSSS-LL functionality with at least the Active-Standby steering mode, then the MA PDU Session is capable of ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
-
If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPQUIC-UDP functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1), then:
- If the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL), including RTT measurement without using PMF protocol, the MA PDU Session is capable of (1) MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL) in the downlink and (2) MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink.
- If the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with any steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL), but not RTT measurement without using PMF protocol, the MA PDU Session is capable of (1) MPQUIC-UDP in the downlink (2) ATSSS-LL with any steering mode except Smallest Delay steering mode (i.e. any Steering Mode allowed for ATSSS-LL except Smallest Delay steering mode) in the downlink and (3) MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink.
- If the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC-UDP with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode, the MA PDU Session is capable of MPQUIC-UDP and ATSSS-LL with Active-Standby mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the DNN configuration does not allow MPQUIC-UDP steering functionality and the DNN configuration allows ATSSS-LL functionality with at least the Active-Standby steering mode, then the MA PDU Session is capable of ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "ATSSS-LL functionality with any steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1) and the DNN configuration allows ATSSS-LL with any steering mode allowed for ATSSS-LL, the MA PDU Session is capable of ATSSS-LL with any steering mode allowed for ATSSS-LL in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPQUIC IP functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1) and the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC IP functionality with any steering mode, the MA PDU Session is capable of MPQUIC IP with any steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink. If the DNN configuration does not allow MPQUIC-IP steering functionality and the DNN configuration allows ATSSS-LL functionality with at least the Active-Standby steering mode, then the MA PDU Session is capable of ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPQUIC E functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1) and the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC E functionality with any steering mode, the MA PDU Session is capable of MPQUIC E with any steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink. If the DNN configuration does not allow MPQUIC-E steering functionality and the DNN configuration allows ATSSS-LL functionality with at least the Active-Standby steering mode, then the MA PDU Session is capable of ATSSS-LL with only Active-Standby steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink.
- If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPQUIC IP functionality with any steering mode without any ATSSS-LL functionality" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1) and the DNN configuration allows MPQUIC IP functionality with any steering mode, the MA PDU Session is capable of MPQUIC IP with any steering mode in the uplink and in the downlink. If the DNN configuration does not allow MPQUIC-IP steering functionality, then the SMF rejects the MA PDU Session request.
-
If the UE includes in its ATSSS capabilities "MPTCP functionality with any steering mode and ATSSS-LL functionality with only Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1), then:
- The PCC rules provided by PCF include MA PDU Session Control information (see TS 23.503). They are used by SMF to derive ATSSS rules for the UE and N4 rules for the UPF. When dynamic PCC is not used for the MA PDU Session, the SMF shall provide ATSSS rules and N4 rules based on local configuration (e.g. based on DNN or S-NSSAI).
- The UE receives ATSSS rules from SMF, which indicate how the uplink traffic should be routed across 3GPP access and non-3GPP access. Similarly, the UPF receives N4 rules from SMF, which indicate how the downlink traffic should be routed across 3GPP access and non-3GPP access.
- When the SMF receives a PDU Session Establishment Request and a "MA PDU Request" indication and determines that UP security protection (see clause 5.10.3) is required for the PDU Session, the SMF shall only confirm the establishment of the MA PDU session if the 3GPP access network can enforce the required UP security protection. The SMF needs not confirm whether the non-3GPP access can enforce the required UP security protection.
- The UE indicates during MA PDU Session Establishment to the AMF whether it supports non-3GPP access path switching, i.e. whether the UE can transfer the non-3GPP access path of the MA PDU Session from a source non-3GPP access (N3IWF/TNGF) to a target non-3GPP access (a different N3IWF/TNGF). If the UE has indicated support for non-3GPP access path switching and the AMF supports non-3GPP access path switching, the AMF selects an SMF that supports non-3GPP access path switching, if such an SMF is available. If the AMF supports to maintain two N2 connections for non-3GPP access during the Registration procedure and the selected SMF supports non-3GPP path switching, the AMF indicates whether the UE supports non-3GPP path switching to the SMF. The SMF indicates support for non-3GPP path switching to the UE in the PDU Session Establishment Accept message.
-
After the MA PDU Session establishment:
- At any given time, the MA PDU session may have user-plane resources on both 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses, or on one access only, or may have no user-plane resources on any access.
- The AMF, SMF, PCF and UPF maintain their MA PDU Session contexts, even when the UE deregisters from one access (but remains registered on the other access).
- When the UE deregisters from one access (but remains registered on the other access), the AMF informs the SMF to release the resource of this access type in the UPF for the MA PDU Session. Subsequently, the SMF notifies the UPF that the access type has become unavailable and the N3/N9 tunnel for the access type are released.
- If the UE wants to add user-plane resources on one access of the MA PDU Session, e.g. based on access network performance measurement and/or ATSSS rules, then the UE shall send a PDU Session Establishment Request over this access containing PDU Session ID of the MA PDU Session. The UE also provides Request Type as "MA PDU Request" and the same PDU Session ID in the UL NAS Transport message. If there is no N3/N9 tunnel for this access, the N3/N9 tunnel for this access is established.
- If the UE wants to re-activate user-plane resources on one access of the MA PDU Session, e.g. based on access network performance measurement and/or ATSSS rules, then the UE shall initiate the UE Triggered Service Request procedure over this access.
- If the network wants to re-activate the user-plane resources over 3GPP access or non-3GPP access of the MA PDU Session, the network shall initiate the Network Triggered Service Request procedure, as specified in clause 4.22.7 of TS 23.502.
- If the UE wants to move the non-3GPP user-plane resources of the MA PDU Session from a source non-3GPP access (e.g. source N3IWF or TNGF) to a target non-3GPP access (e.g. target N3IWF or TNGF), the UE initiates a Mobility Registration Update via the target non-3GPP access as described in clause 4.22.9.5 of TS 23.502. This procedure may also be used to move the non-3GPP user-plane resources of single access PDU Session(s).
- The SMF may add, remove or update one or more individual ATSSS rules of the UE by sending new or updated ATSSS rules with the corresponding Rule IDs to the UE.
- when it is explicitly requested by an ATSSS-capable UE; or
- when an ATSSS-capable UE requests a single-access PDU Session but the network decides to establish a MA PDU Session instead. This is an optional scenario specified in clause 4.22.3 of TS 23.502, which may occur when the UE requests a single-access PDU Session but no policy (e.g. no URSP rule) and no local restrictions in the UE mandate a single access for the PDU Session.
- request establishment of a MA PDU Session (as described in clause 4.22.2 of TS 23.502); or
- request addition of User Plane resources for an existing MA PDU Session (as described in clause 4.22.7 of TS 23.502); or
- request establishment of a PDU Session with "MA PDU Network-Upgrade Allowed" indication (as described in clause 4.22.3 of TS 23.502); or
- request PDU Session Modification with Request Type of "MA PDU request" or with "MA PDU Network-Upgrade Allowed" indication after moving from EPC to 5GC (as described in clause 4.22.6.3 of TS 23.502).
5.32.3 Policy for ATSSS Control p. 469
If dynamic PCC is to be used for the MA PDU Session, the PCF may take ATSSS policy decisions and create PCC rules that contain MA PDU Session Control information, (as specified in TS 23.503), which determines how the uplink and the downlink traffic of the MA PDU Session should be distributed across the 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses. If dynamic PCC is not deployed, local policy in SMF is used.
The SMF receives the PCC rules with MA PDU Session Control information and maps these rules into (a) ATSSS rules, which are sent to the UE and (b) N4 rules, which are sent to the UPF. The ATSSS rules are provided as a prioritized list of rules (see clause 5.32.8), which are applied by the UE to enforce the ATSSS policy in the uplink direction and the N4 Rules are applied by the UPF to enforce the ATSSS policy in the downlink direction.
The ATSSS rules are sent to UE with a NAS message when the MA PDU Session is created or updated by the SMF, e.g. after receiving updated/new PCC rules from the PCF. Similarly, the N4 rules are sent to UPF when the MA PDU Session is created or updated by the SMF.
The details of the policy control related to ATSSS are specified in TS 23.503.
5.32.4 QoS Support p. 469
The 5G QoS model for the Single-Access PDU Session is also applied to the MA PDU Session, i.e. the QoS Flow is the finest granularity of QoS differentiation in the MA PDU Session. One difference compared to the Single-Access PDU Session is that in a MA PDU Session there can be separate user-plane tunnels between the AN and the PSA, each one associated with a different access. However, the QoS Flow is not associated with specific access, i.e. it is access agnostic, so the same QoS is supported when the traffic is distributed over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses. The SMF shall provide the same QFI in 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses so that the same QoS is supported in both accesses.
A QoS Flow of the MA PDU Session may be either Non-GBR or GBR depending on its QoS profile.
For a Non-GBR QoS Flow, the SMF provides a QoS profile to both 5G-ANs during MA PDU Session Establishment or MA PDU Session Modification procedure:
- During MA PDU Session Establishment procedure, the QoS profile to both ANs if the UE is registered over both accesses.
- During MA PDU Session Modification procedure, the QoS profile is provided to the 5G-AN(s) over which the user plane resources are activated.
- If the PCC rule allows a GBR QoS Flow in a single access, the SMF provides the QoS profile for the GBR QoS Flow to the access network allowed by the PCC rule.
- If the PCC rule allows a GBR QoS Flow in both accesses and the Steering Mode is different from Redundant, the SMF decides to which access network to provide the QoS profile for the GBR QoS Flow based on its local policy (e.g. the access where the traffic is ongoing according to the Multi Access Routing rule).
- If the PCC rule allows a GBR QoS Flow in both accesses and the Steering Mode is Redundant, the SMF provides the QoS profile for the GBR QoS Flow to both access networks. Whenever the SMF recognizes that resources are not allocated in one access network, the SMF shall notify the PCF about the resource allocation failure and indicate the respective Access Type. Whenever the SMF recognizes that resources are not allocated in both access networks, the SMF shall release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
- if the PCC rule allows the GBR QoS Flows only on this access, the SMF shall release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
- if the corresponding PCC rule allows the GBR QoS Flow on both accesses and the other access is not available, the SMF shall release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
-
if the PCC rule allows the GBR QoS Flow on both accesses and the other access is available, the SMF shall try to move the GBR QoS Flow to the other access. The SMF may trigger a PDU session modification procedure to provide the QoS profile to the other access and release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow in the current access.
- if Notification Control parameter is not included in the PCC rule for the GBR QoS Flow and the other access does not accept the QoS profile, the SMF shall release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
- if the Notification Control parameter is included in the PCC rule, the SMF shall notify the PCF that GFBR can no longer be guaranteed. After the other access accepts the QoS profile, the SMF shall notify the PCF that GFBR can again be guaranteed. If the other access does not accept the QoS profile, the SMF shall delete the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
- if both accesses are not available, the SMF shall release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow and report to the PCF about the removal of the PCC rule.
- when one of the accesses becomes unavailable while the other access is still available, the SMF shall neither release the resources for the GBR QoS Flow nor notify the PCF that GFBR can no longer be guaranteed (if the Notification Control parameter is included in the PCC rule).
- any QoS rules or PDRs that apply to the MA PDU Session IP address/prefix and port also apply (a) to the MPTCP "link-specific multipath" IP addresses/prefixes and ports used by the UE to establish MPTCP subflows over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses and (b) to the "MPQUIC link-specific multipath" IP addresses/prefixes and ports used by the UE to transmit IP/UDP flows over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses; and
- any QoS rules or PDRs that apply to the IP address/prefix and port of the final destination server in DN also apply (a) to the IP address and port of the MPTCP proxy for corresponding MPTCP subflows that are terminated at the proxy and (b) to the IP address and port of the MPQUIC proxy for corresponding IP/UDP flows that are terminated at the proxy.
- any QoS rules or PDRs that apply to the source MAC address for the MA PDU Session of Ethernet type also apply to the "MPQUIC link-specific multipath" IP addresses/prefixes and ports used by the UE to transmit Ethernet flows over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses.
- any QoS rules or PDRs that apply to the destination MAC address of the server in DN for the MA PDU Session of Ethernet type also apply to the IP address and port of the MPQUIC proxy for corresponding Ethernet flows that are terminated at the proxy.
5.32.5 Access Network Performance Measurements p. 471
5.32.5.1 General principles p. 471
When an MA PDU Session is established, the network may provide the UE with Measurement Assistance Information. This information assists the UE in determining which measurements shall be performed over both accesses, as well as whether measurement reports need to be sent to the network.
Measurement Assistance Information shall include the addressing information of a Performance Measurement Function (PMF) in the UPF, the UE can send PMF protocol messages to:
- For a PDU Session of IP type, Measurement Assistance Information contains one IP address for the PMF, one UDP port associated with 3GPP access and another UDP port associated with non-3GPP access. PMF messages sent by UE to one of these UDP ports, shall be transmitted to UPF via the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule.
- For a PDU Session of Ethernet type, Measurement Assistance Information contains one MAC address associated with 3GPP access and another MAC address associated with non-3GPP access. PMF messages sent by UE to one of these MAC addresses, shall be transmitted to UPF via the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule.
- The QFI of the associated QoS Flow.
- For a PDU Session of IP type, one UDP port associated with 3GPP access and another UDP port associated with non-3GPP access. PMF messages sent by UE to one of these UDP ports, shall be transmitted to UPF via the associated QoS Flow.
- For a PDU Session of Ethernet type, one MAC address associated with 3GPP access and another MAC address associated with non-3GPP access. PMF messages sent by UE to one of these MAC addresses, shall be transmitted to UPF via the associated QoS Flow.
- using the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule; or
- using the target QoS Flow, which is the QoS Flow that the SDF traffic is transmitted on.
- The SMF determines a list of QoS Flows over which access performance measurements may be performed and provides this list to the UE (within the Measurement Assistance Information) and to the UPF.
- The UE and the UPF may initiate access performance measurements on one or more of the QoS Flows included in this list. The UE and the UPF shall be able to receive and respond to PMF messages sent on any QoS Flow included in this list.
- The SMF may update the list of QoS Flows over which access performance measurements may be performed during the lifetime of a MA PDU Session, e.g. when a new PCC rule that could benefit from PMF access performance measurements is bound to a QoS Flow.
- Messages to allow for Round Trip Time (RTT) measurements, i.e. when the "Smallest Delay" steering mode is used or when either "Priority-based", "Load-Balancing" or "Redundant" steering mode is used with RTT threshold value being applied;
- Messages to allow for Packet Loss Rate (PLR) measurements, i.e. when steering mode is used either "Priority-based", "Load-Balancing" or "Redundant" steering mode is used with PLR threshold value being applied;
- Messages for reporting Access availability/unavailability by the UE to the UPF.
- Messages for sending UE-assistance data to UPF. Such messages may be sent from the UE to UPF only when the UE receives the UE-assistance indicator in an ATSSS rule, as specified in clause 5.32.8. Further details are provided in clause 5.32.5.5.
- Messages for sending Suspend Traffic Duplication and Resume Traffic Duplication from UPF to UE to suspend or resume traffic duplication as defined in clause 5.32.5.6.
- the "MPTCP functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
- the "MPQUIC-UDP functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode" (as specified in clause 5.32.6.1);
- the "MPQUIC-IP functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode";
- the "MPQUIC-E functionality with any steering mode and the ATSSS-LL functionality with only the Active-Standby steering mode";
5.32.5.1a Address of PMF messages |R17| p. 473
As described in clause 5.32.5.2, 5.32.5.2a and 5.32.5.3, a UE and UPF may exchange PMF messages to measure access performance and report access availability/unavailability. When the UE and UPF exchanges PMF message, source and destination address of the PMF messages shall be assigned as follows:
-
In the case of a MA PDU Session of IP type:
- If access performance measurements are performed only over the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule, the PMF in the UE sends PMF messages to the PMF in the UPF over UDP/IP. The destination IP address is the IP address contained in the Measurement Assistance Information and the destination UDP port is one of the two UDP ports contained in the Measurement Assistance Information. One UDP port is used for sending PMF messages to UPF over 3GPP access and the other UDP port is used for sending PMF messages to UPF over non-3GPP access. The source IP address is the IP address assigned to UE for the MA PDU Session and the source UDP port is a UDP port that is dynamically allocated by the UE for PMF communication. This source UDP port in the UE remains the same for the entire lifetime of the MA PDU Session. If access performance measurements per QoS Flow is performed, the Measurement Assistance Information contains UDP ports, one for each QoS Flow and access combination. When the UE sends PMF message over a QoS Flow of an access, the UE shall set the destination UDP port as the UDP port for the QoS Flow and the access in Measurement Assistance information.
- If access performance measurements are performed only over the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule, the PMF in the UPF sends PMF messages to the PMF in the UE over UDP/IP. The source IP address is the same IP address as the one provided in the Measurement Assistance Information and the source UDP port is one of the two UDP ports as provided in the Measurement Assistance Information. One UDP port is used for sending PMF messages to UE over 3GPP access and the other UDP port is used for sending PMF messages to UE over the non-3GPP access. The destination IPv4 address is the IPv4 address assigned to UE for the MA PDU Session (if any) and the destination IPv6 address is an IPv6 address selected by the UE from the IPv6 prefix assigned for the MA PDU Session (if any). The destination UDP port is the dynamically allocated UDP port in the UE, which is contained in all PMF messages received from the UE. If access performance measurements per QoS Flow is performed, when the UPF sends PMF message over a QoS Flow of an access, the UPF shall set the source UDP port with the UDP port for the QoS Flow and the access as the one for the QoS Flow and the access provided in Measurement Assistance information.
- If the UE receives Measurement Assistance Information, the UE shall inform the network via the user plane about the UE's dynamically allocated UDP port and the IPv6 address if IPv6 is used for PMF messages, so that it is possible for the UPF to know the UE's IPv6 address (if applicable) and dynamically allocated UDP port as soon as the MA PDU Session has been established.
-
In the case of a MA PDU Session of Ethernet type:
- The PMF in the UE sends PMF messages to the PMF in the UPF over Ethernet. The Ethertype is the Ethertype contained in the Measurement Assistance Information. If access performance measurements are performed only over the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule, the destination MAC address is one of the two MAC addresses contained in the Measurement Assistance Information. One MAC address is used for sending PMF messages to UPF over 3GPP access and the other MAC address is used for sending PMF messages to UPF over non-3GPP access. The source MAC address is a MAC address of the UE, which remains the same for the entire lifetime of the MA PDU Session. If access performance measurements per QoS Flow is performed, Measurement Assistance Information contains MAC addresses for each QoS Flow and each access. When the UE sends PMF message over a QoS Flow of an access, the UE shall set the destination MAC address as the MAC address for the QoS Flow and the access in Measurement Assistance information.
- The PMF in the UPF sends PMF messages to the PMF in the UE over Ethernet. The Ethertype is the same Ethertype as the one provided in the Measurement Assistance Information. If access performance measurements are performed only over the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule, the source MAC address is one of the two MAC addresses as provided in the Measurement Assistance Information. One MAC address is used for sending PMF messages to UE over 3GPP access and the other MAC address is used for sending PMF messages to UE over non-3GPP access. The destination MAC address is the MAC address of the UE, which is contained in all PMF messages received from the UE. If access performance measurements per QoS Flow is performed, when the UPF sends PMF message over a QoS Flow of an access, the UPF shall set the source MAC address with the MAC address for the QoS Flow and the access as the one for the QoS Flow and the access provided in Measurement Assistance information.
- If the UE receives Measurement Assistance Information, the UE shall inform the network via the user plane about the UE's MAC address so that it is possible for the UPF to know the UE's MAC address as soon as the MA PDU Session has been established.
5.32.5.2 Round Trip Time Measurements p. 474
RTT measurements can be conducted by the UE and UPF independently. There is no measurement reporting from one side to the other. RTT measurements are defined to support the "Smallest Delay", "Priority-based", "Load Balancing" or "Redundant" steering mode (i.e. when RTT threshold value is applied).
The estimation of the RTT by the UE and by the UPF is based on the following mechanism:
- The PMF in the UE sends over the user plane PMF-Echo Request messages to the PMF in the UPF and the PMF in the UPF responds to each one with a PMF-Echo Response message. Similarly, the PMF in the UPF sends over the user plane PMF-Echo Request messages to the PMF in the UE and the PMF in the UE responds to each one with a PMF-Echo Response message.
- When the UP connection of the MA PDU session is deactivated on an access, no PMF-Echo Request messages are sent on this access. The PMF in the UPF shall not send PMF-Echo Request on this access if the UP connection is not available or after it receives notification from the (H-)SMF to stop sending the PMF-Echo Request on this access.
- The UE and the UPF derive an estimation of the average RTT over an access type and QoS Flow by averaging the RTT measurements obtained over this access type and QoS Flow.
5.32.5.2a Packet Loss Rate Measurements |R17| p. 475
The UE and the UPF may decide to estimate the Packet Loss Rate (PLR) for an SDF over both accesses. For example, the UE may take this decision when an ATSSS rule in the UE requires the traffic of an SDF to be steered in accordance with a PLR-based threshold condition (e.g. PLR < 2%).
The UE and the UPF calculate the PLR for an SDF by exchanging PMF-PLR Report messages, as specified below. A PMF-PLR Report message is sent over 3GPP access or over non-3GPP access, using either the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule or a "target" QoS Flow, as specified in clause 5.32.5.1.
The calculation of the PLR by the UE and by the UPF is based on the following mechanism. It is assumed that the PLR should be calculated for a target QoS Flow, however, the same mechanism applies when the PLR should be calculated for the QoS Flow associated with the default QoS rule.
- The UE requests from UPF to start counting the number of received UL packets by sending a PMF-PLR Count Request message over the target QoS Flow. The UPF starts counting of the received UL packets over the target QoS Flow and over the access network which the PMF-PLR Count Request message was received from. The UE starts counting the transmitted UL packets over the target QoS Flow and access network when it sends a PMF-PLR Count Request message to UPF.
- The UE stops the counting and requests from UPF to report the number of counted UL packets by sending a PMF-PLR Report Request message over the target QoS Flow. The UPF stops the counting and sends a PMF-PLR Report Response message over the QoS Flow including the number of UL packets counted since it received the last PMF-PLR Count Request message.
- The UE calculates the UL packet loss ratio based on the local counting result of the number of transmitted UL packets and reported number of received UL packets in the UPF.
- The UPF applies the same procedure for calculating the DL PLR, i.e. it sends to UE a PMF-PLR Count Request message on a target QoS Flow to request from UE to start counting the number of DL packets received on this target QoS Flow. As defined in clause 5.32.5.1, the UE determines which DL packets are received on the target QoS Flow by checking the QFI included in the header of DL packets (e.g. in the SDAP header). If no QFI is included in the header of a DL packet, the UE determines the QFI for this DL packet by applying the Packet Filters for downlink in the QoS Rules received from SMF.
- When the UP connection of the MA PDU session is deactivated on an access, no PMF-PLR messages are sent on this access. The PMF in the UPF shall not send PMF-PLR message on this access if the UP connection is not available or after it receives notification from the (H-)SMF to stop sending the PMF-PLR message on this access.
- The UE and the UPF derive an estimation of the average PLR per QoS Flow over an access type by averaging the PLR measurements obtained over this access.
5.32.5.3 Access Availability/Unavailability Report p. 476
If required by the network in the Measurement Assistance Information, the UE shall provide access availability/unavailability reports to the network. How the UE detects the unavailability and the availability of an access is based on implementation. The CM state of a UE is not a factor when determining whether the 3GPP access is available. When the UE detects the unavailability/availability of an access, it shall:
- build a PMF-Access Report containing the access type and an indication of availability/unavailability of this access;
- send the PMF-Access Report to the UPF via the user plane.
5.32.5.4 Protocol stack for user plane measurements and measurement reports p. 476
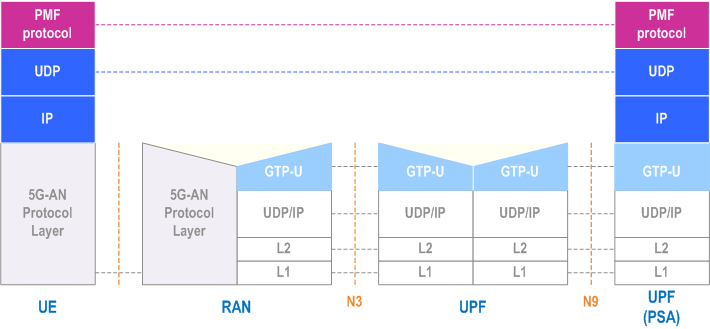
In the case of an MA PDU Session with type Ethernet, the protocol stack over 3GPP access is that same as the one in the above Figure, but the PMF protocol operates on top of Ethernet, instead of UDP/IP.
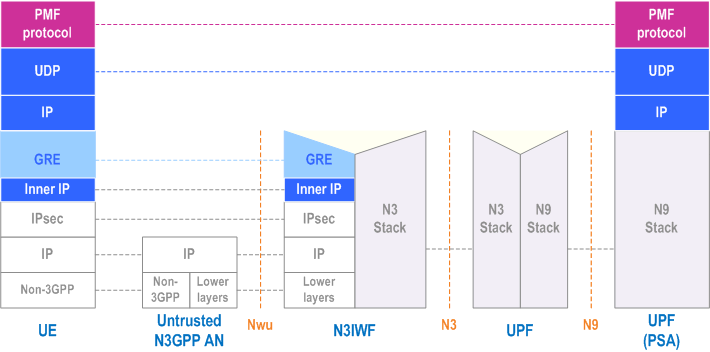
In the case of an MA PDU Session with type Ethernet, the protocol stack over Untrusted non-3GPP access is the same as the one in the above Figure, but the PMF protocol operates on top of Ethernet, instead of UDP/IP.
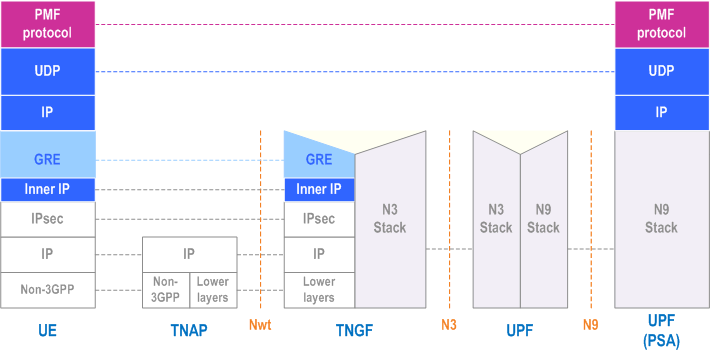
In the case of an MA PDU Session with type Ethernet, the protocol stack over Trusted non-3GPP access is the same as the one in the above Figure, but the PMF protocol operates on top of Ethernet, instead of UDP/IP.
5.32.5.5 UE Assistance Operation |R17| p. 477
When UE-assistance operation is authorized by the PCF in the PCC Rule, the SMF provides an indication for UE-assistance in the ATSSS Rule to the UE, as described in clause 5.32.8 and in the MAR to the UPF, as described in clause 5.8.5.8.
If the UE receives the UE-assistance indicator in an ATSSS rule (as specified in clause 5.32.8) and the UE decides to apply a different UL traffic distribution for an SDF than the default UL traffic distribution indicated in the Steering Mode component of the ATSSS rule (e.g. because the UE is running out of battery), then the following applies:
- The UE may apply any split percentages for the UL traffic distribution of an SDF, based on implementation specific criteria.
- The UE may send a PMF-UAD (UE Assistance Data) message to UPF that contains the split percentages that may be used by UPF for all DL traffic that the UE-assistance operation applies. The UPF acknowledges the reception of the PMF-UAD message by sending a PMF-UAD complete message to the UE.
- The UPF may apply the information in a received PMF-UAD message to align the DL traffic distribution for traffic that is allowed to use UE-assistance operation, i.e. traffic where the MAR contains a Steering Mode Indicator set to UE-assistance operation.
- If the UE decides to terminate the UE assistance operation, the UE may send a PMF-UAT (UE Assistance Termination) message to the UPF indicating that the UE assistance operation is terminated and the UE performs the UL traffic distribution according to the split percentages in the ATSSS rule received from the network. If the UPF receives the PMF-UAT message, the UPF acknowledges the reception by sending a PMF-UAT complete message and performs DL traffic distribution by applying the split percentages included in the MAR.
5.32.5.6 Suspend and Resume Traffic Duplication |R18| p. 477
As part of the Redundant Steering Mode, a UPF can decide to suspend traffic duplication for a UE by sending PMF- Suspend Duplication Request message to the UE. How the UPF determines to suspend traffic duplication is implementation specific.
The UPF may indicate in the PMF-Suspend Duplication Request message the type of traffic (i.e. GBR or non-GBR) for which traffic duplication is being suspended. The PMF-Suspend Duplication Request message is sent over the user plane of any available access network of the MA PDU Session. Once the UE receives the PMF-Suspend Duplication Request message from the UPF, the UE shall stop duplicating the type of traffic for which traffic duplication is suspended.
If the UPF does not provide the type of traffic (GBR or non-GBR) in the PMF-Suspend Duplication Request message, traffic duplication is suspended for all traffic for which traffic duplication is being performed. Once UPF suspended traffic duplication and if no Primary Access is configured, both the UE and the UPF decide, based on their own implementation, which access network to use for sending UL and DL traffic. If the Primary Access is configured, both the UE and the UPF use the Primary Access for sending UL and DL traffic.
The UPF may decide to resume traffic duplication for a UE by sending the PMF-Resume Duplication Request message. How the UPF determines to resume traffic duplication is implementation specific.
Once the UE receives the PMF-Resume Duplication Request message from the UPF, the UE may restart to duplicate the type of traffic for which traffic duplication is resumed based on the provided Redundant steering mode policies and UE implementation.