Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
4.2.9 Network Analytics architecture
4.2.10 Architecture Reference Model for ATSSS Support
4.2.11 Architecture for 5G multicast-broadcast services
4.2.12 Architecture for Proximity based Services (ProSe) in 5GS
4.2.13 Architecture enhancements for Edge Computing
4.2.14 Architecture for Support of Uncrewed Aerial Systems connectivity, identification and tracking
...
...
4.2.9 Network Analytics architecture p. 71
The Network Analytics architecture is defined in TS 23.288.
4.2.10 Architecture Reference Model for ATSSS Support |R16| p. 71
In order to support the ATSSS feature, the 5G System Architecture is extended as shown in Figure 4.2.10-1, Figure 4.2.10-2 and Figure 4.2.10-3. The additional functionality that is supported by the UE and the network functions shown in these Figures is specified in clause 5.32 below. In summary:
- The UE supports one or more of the steering functionalities specified in clause 5.32.6. Each steering functionality in the UE enables traffic steering, switching and splitting across 3GPP access and non-3GPP access, in accordance with the ATSSS rules provided by the network.
- The UPF may support the MPTCP Proxy functionality, which communicates with the MPTCP functionality in the UE by using the MPTCP protocol (RFC 8684), as defined in clause 5.32.6.2.1.
- The UPF may support one or more of the MPQUIC Proxy functionalities (i.e. the MPQUIC-UDP, MPQUIC-IP, MPQUIC-E Proxy functionalities), which communicates with the respective MPQUIC-UDP functionality, the MPQUIC-IP functionality, or the MPQUIC-E functionality in the UE by using the QUIC protocol (RFC 9000, RFC 9001, RFC 9002) and its multipath extensions (draft-ietf-quic-multipath [174]), as defined in clause 5.32.6.2.2.
- The UPF shall support at least ATSSS-LL functionality with Active Standby steering mode and may support ATSSS-LL functionality with other steering modes. There is no user plane protocol defined between the ATSSS-LL functionality in the UE and the ATSSS-LL functionality in the UPF.
- In addition, the UPF supports Performance Measurement Functionality (PMF), which may be used by the UE to obtain access performance measurements (see clause 5.32.5) over the user-plane of 3GPP access and/or over the user-plane of non-3GPP access.
- The AMF, SMF and PCF are extended with new functionality that is further discussed in clause 5.32.
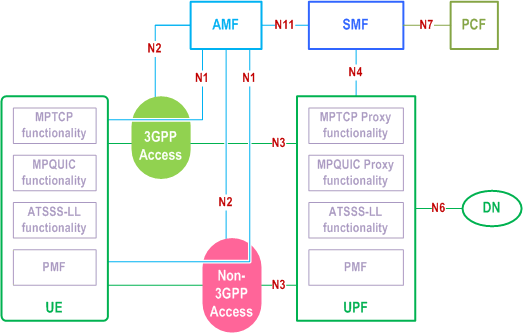
Figure 4.2.10-2 shows the 5G System Architecture for ATSSS support in a roaming case with home-routed traffic and when the UE is registered to the same VPLMN over 3GPP and non-3GPP accesses. In this case, the MPTCP Proxy functionality, the MPQUIC based Proxy functionality(ies), the ATSSS-LL functionality and the PMF are located in the H-UPF.
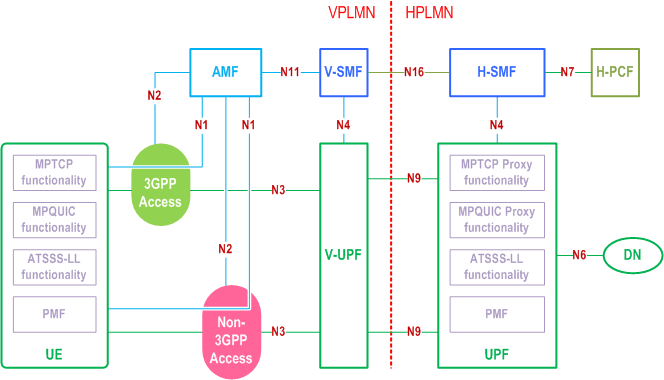
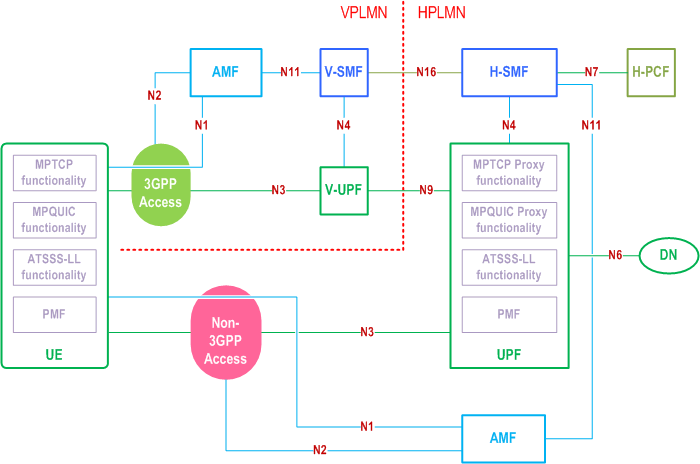
Figure 4.2.10-3 shows the 5G System Architecture for ATSSS support in a roaming case with home-routed traffic and when the UE is registered to a VPLMN over 3GPP access and to HPLMN over non-3GPP access (i.e. the UE is registered to different PLMNs). In this case, the MPTCP Proxy functionality, the MPQUIC based Proxy functionality(ies), the ATSSS-LL functionality and the PMF are located in the H-UPF.
4.2.11 Architecture for 5G multicast-broadcast services |R17| p. 73
The architecture for 5G multicast-broadcast services is defined in TS 23.247.
4.2.12 Architecture for Proximity based Services (ProSe) in 5GS |R17| p. 73
The architecture for Proximity based Services (ProSe) in the 5G System is defined in TS 23.304.
4.2.13 Architecture enhancements for Edge Computing |R17| p. 73
The architecture enhancements for edge computing are outlined in clause 5.13 and further described in TS 23.548.
4.2.14 Architecture for Support of Uncrewed Aerial Systems connectivity, identification and tracking |R17| p. 73
The architecture for Support of Uncrewed Aerial Systems (UAS) connectivity, identification and tracking is defined in TS 23.256.