Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
4.2.8.4 Architecture Reference Model for Wireline Access network
4.2.8.5 Access to 5GC from devices that do not support 5GC NAS over WLAN access
4.2.8.5.1 General
4.2.8.5.2 Reference Architecture
4.2.8.5.3 Network Functions
4.2.8.5.4 Reference Points
...
...
4.2.8.4 Architecture Reference Model for Wireline Access network |R16| p. 68
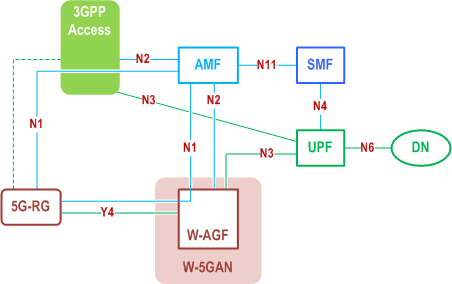
The 5G-RG can be connected to 5GC via W-5GAN, NG RAN or via both accesses.
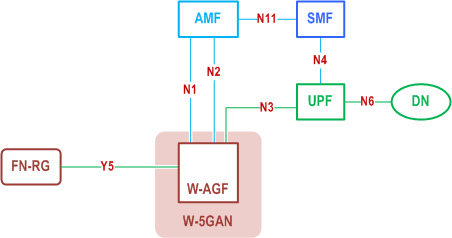
The N1 for the FN-RG, which is not 5G capable, is terminated on W-AGF which acts on behalf of the FN-RG.
The FN-RG can only be connected to 5GC via W-5GAN.
4.2.8.5 Access to 5GC from devices that do not support 5GC NAS over WLAN access |R16| p. 69
4.2.8.5.1 General p. 69
The devices that do not support 5GC NAS signalling over WLAN access are referred to as "Non-5G-Capable over WLAN" devices, or N5CW devices for short. A N5CW device is not capable to operate as a 5G UE that supports 5GC NAS signalling over a WLAN access network, however, it may be capable to operate as a 5G UE over NG-RAN.
Clause 4.2.8.5 specifies the 5GC architectural enhancements that enable N5CW devices to access 5GC via trusted WLAN access networks. A trusted WLAN access network is a particular type of a Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network (TNAN) that supports a WLAN access technology, e.g. IEEE 802.11. Not all trusted WLAN access networks support 5GC access from N5CW devices. To support 5GC access from N5CW devices, a trusted WLAN access network must support the special functionality specified below (e.g. it must support a TWIF function).
When a N5CW device performs an EAP-based access authentication procedure to connect to a trusted WLAN access network, the N5CW device may simultaneously be registered to a 5GC of a PLMN or SNPN. The 5GC registration is performed by the TWIF function (see next clause) in the trusted WLAN access network, on behalf of the N5CW device. The type of EAP authentication procedure, which is used during the 5GC registration to authenticate the N5CW device, is specified in TS 33.501. In this Release of the specification, Trusted WLAN Access for N5CW Device only supports IP PDU Session type.
4.2.8.5.2 Reference Architecture p. 70
The architecture diagram in Figure 4.2.8.5.2-1 is based on the general 5GS architecture diagrams in clause 4.2 and shows the main network functions required to support 5GC access from N5CW devices. Other network functions are not shown for simplicity.
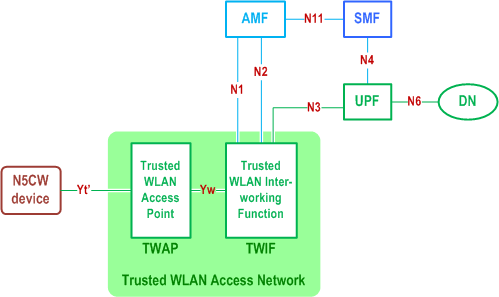
The reference architecture in Figure 4.2.8.5.2-1 also supports N5CW device access to the subscribed SNPN or access to the SNPN with credentials owned by Credentials Holder. Other parts of the architecture are the same as defined in clause 5.30.2.9.
4.2.8.5.3 Network Functions p. 70
Trusted WLAN Access Point (TWAP): It is a particular type of a Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point (TNAP) specified in clause 4.2.8.2, that supports a WLAN access technology, e.g. IEEE 802.11. This function is outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Trusted WLAN Interworking Function (TWIF): It provides interworking functionality that enables N5CW devices to access 5GC. The TWIF supports the following functions:
- Terminates the N1, N2 and N3 interfaces.
- Implements the AMF selection procedure.
- Implements the NAS protocol stack and exchanges NAS messages with the AMF on behalf of the N5CW device.
- On the user plane, it relays protocol data units (PDUs) between the Yw interface and the N3 interface.
- May implement a local mobility anchor within the trusted WLAN access network.
4.2.8.5.4 Reference Points p. 70
The Yt' and Yw reference points are both outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications. The Yt' reference point transports WLAN messages (e.g. IEEE 802.11 messages), while the Yw reference point:
- Shall be able to transport authentication messages between the TNAP and the TWIF for enabling authentication of a N5CW device;
- Shall allow the N5CW device to request and receive IP configuration from the TWIF, including an IP address, e.g. with DHCP.
- Shall support the transport of user-plane traffic for the N5CW device.