Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
4.2.8 Support of non-3GPP access
4.2.8.0 General
4.2.8.1 General Concepts to Support Trusted and Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
4.2.8.1A General Concepts to support Wireline Access
4.2.8.2 Architecture Reference Model for Trusted and Untrusted Non-3GPP Accesses
4.2.8.2.1 Non-roaming Architecture
...
...
4.2.8 Support of non-3GPP access p. 59
4.2.8.0 General |R16| p. 59
In this Release of the specification, the following types of non-3GPP access networks are defined:
- Untrusted non-3GPP access networks;
- Trusted non-3GPP access networks; and
- Wireline access networks.
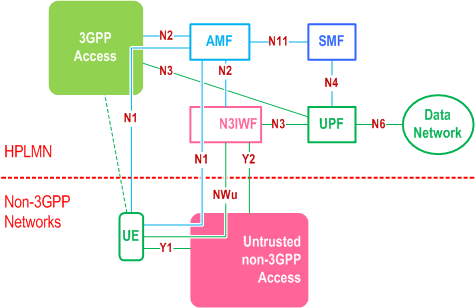
4.2.8.1 General Concepts to Support Trusted and Untrusted Non-3GPP Access p. 59
The 5G Core Network supports connectivity of UEs via non-3GPP access networks, e.g. WLAN access networks.
Only the support of non-3GPP access networks deployed outside the NG-RAN is described in this clause.
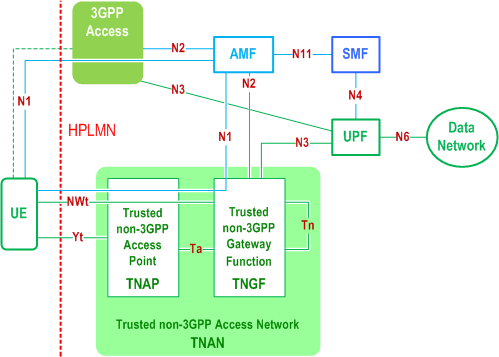
The 5G Core Network supports both untrusted non-3GPP access networks and trusted non-3GPP access networks (TNANs).
An untrusted non-3GPP access network shall be connected to the 5G Core Network via a Non-3GPP InterWorking Function (N3IWF), whereas a trusted non-3GPP access network shall be connected to the 5G Core Network via a Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function (TNGF). Both the N3IWF and the TNGF interface with the 5G Core Network CP and UP functions via the N2 and N3 interfaces, respectively.
A non-3GPP access network may advertise the PLMNs or SNPNs for which it supports trusted connectivity and the type of supported trusted connectivity (e.g. "5G connectivity"). Therefore, the UEs can discover the non-3GPP access networks that can provide trusted connectivity to one or more PLMNs or SNPNs. This is further specified in clause 6.3.12 (Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network selection).
The UE decides to use trusted or untrusted non-3GPP access for connecting to a 5G PLMN or SNPNs by using procedures not specified in this document. Examples of such procedures are defined in clause 6.3.12.1.
When the UE decides to use untrusted non-3GPP access to connect to a 5G Core Network in a PLMN:
- the UE first selects and connects with a non-3GPP access network; and then
- the UE selects a PLMN/SNPN and an N3IWF in this PLMN/SNPN. The PLMN/SNPN/N3IWF selection and the non-3GPP access network selection are independent. The N3IWF selection is defined in clause 6.3.6.
- the UE first selects a PLMN/SNPN; and then
- the UE selects a non-3GPP access network (a TNAN) that supports trusted connectivity to the selected PLMN/SNPN. In this case, the non-3GPP access network selection is affected by the PLMN/SNPN selection.
4.2.8.1A General Concepts to support Wireline Access |R16| p. 60
Wireline 5G Access Network (W-5GAN) shall be connected to the 5G Core Network via a Wireline Access Gateway Function (W-AGF). The W-AGF interfaces the 5G Core Network CP and UP functions via N2 and N3 interfaces, respectively.
For the scenario of 5G-RG connected via NG RAN the specification for UE defined in this TS, TS 23.502 and TS 23.503 are applicable as defined for UE connected to 5GC via NG RAN unless differently specified in this TS and in TS 23.316.
When a 5G-RG is connected via a NG-RAN and via a W-5GAN, multiple N1 instances shall exist for the 5G-RG i.e. there shall be one N1 instance over NG-RAN and one N1 instance over W-5GAN.
A 5G-RG simultaneously connected to the same 5G Core Network of a PLMN over a 3GPP access and a W-5GAN access shall be served by a single AMF in this 5G Core Network.
5G-RG shall maintain the NAS signalling connection with the AMF over the W-5GAN after all the PDU Sessions for the 5G-RG over that access have been released or handed over to 3GPP access.
The 5G-RG connected to 5GC via NG-RAN is specified in TS 23.316.
For the scenario of FN-RG, which is not 5G capable, connected via W-5GAN to 5GC, the W-AGF provides the N1 interface to AMF on behalf of the FN-RG.
An UE connected to a 5G-RG or FN-RG can access to the 5GC via the N3IWF or via the TNGF where the combination of 5G-RG/FN-RG, W-AGF and UPF serving the 5G-RG or FN-RG is acting respectively as Untrusted Non-3GPP access network or as a Trusted Non-3GPP access network defined in clause 4.2.8.2; for example a UE is connecting to 5G-RG by means of WLAN radio access and connected to 5GC via N3IWF. The detailed description is specified in TS 23.316.
The roaming architecture for 5G-BRG, FN-BRG, 5G-CRG and FN-CRG with the W-5GAN is not specified in this Release. The Home Routed roaming scenario is supported for 5G-RG connected via NG RAN, while Local Breakout scenario is not supported.
5G Multi-Operator Core Network (5G MOCN) is supported for 5G-RG connected via NG RAN as defined in clause 5.18