Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 19.2.1
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
5.49…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
S…
T…
4.2.5 Data Storage architectures
4.2.5a Radio Capabilities Signalling optimisation
4.2.6 Service-based interfaces
4.2.7 Reference points
...
...
4.2.5 Data Storage architectures p. 53
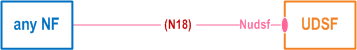
As depicted in Figure 4.2.5-1, the 5G System architecture allows any NF to create/read/update/delete its unstructured data in a UDSF (e.g. UE contexts). If such an NF is using UDSF is part of an NF set, then any of the NF instance within this NF set may read/update/delete the unstructured data that was created by this NF. The UDSF belongs to the same PLMN where the network function is located. CP NFs/NF Sets may share a UDSF for storing their respective unstructured data or may each have their own UDSF (e.g. a UDSF may be located close to the respective NF).
As depicted in Figure 4.2.5-2, the 5G System architecture allows the UDM, PCF and NEF to store data in the UDR, including subscription data and policy data by UDM and PCF, structured data for exposure and application data (including Packet Flow Descriptions (PFDs) for application detection, AF request information for multiple UEs) by the NEF. UDR can be deployed in each PLMN and it can serve different functions as follows:
- UDR accessed by the NEF belongs to the same PLMN where the NEF is located.
- UDR accessed by the UDM belongs to the same PLMN where the UDM is located if UDM supports a split architecture.
- UDR accessed by the PCF belongs to the same PLMN where the PCF is located.
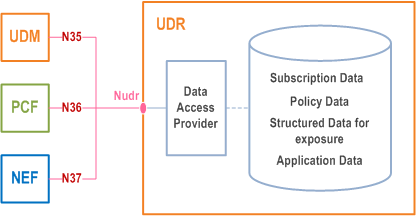
The Nudr interface is defined for the network functions (i.e. NF Service Consumers), such as UDM, PCF and NEF, to access a particular set of the data stored and to read, update (including add, modify), delete and subscribe to notification of relevant data changes in the UDR.
Each NF Service Consumer accessing the UDR, via Nudr, shall be able to add, modify, update or delete only the data it is authorised to change. This authorisation shall be performed by the UDR on a per data set and NF service consumer basis and potentially on a per UE, subscription granularity.
The following data in the UDR sets exposed via Nudr to the respective NF service consumer and stored shall be standardized:
- Subscription Data,
- Policy Data,
- Structured Data for exposure,
- Application data: Packet Flow Descriptions (PFDs) for application detection and AF request information for multiple UEs, as defined in clause 5.6.7.
4.2.5a Radio Capabilities Signalling optimisation |R16| p. 55
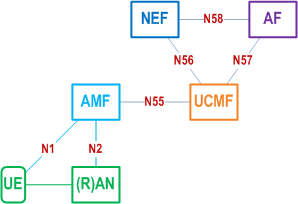
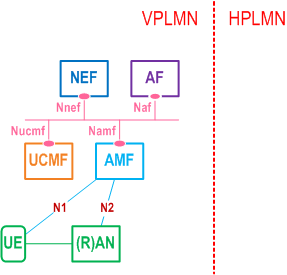
Figure 4.2.5a-1 depicts the AMF to UCMF reference point and interface. Figure 4.2.5a-2 depicts the related interfaces in AMF and UCMF for the Radio Capabilities Signalling optimisation in the roaming architecture.
4.2.6 Service-based interfaces p. 55
The 5G System Architecture contains the following service-based interfaces:
Namf:
Service-based interface exhibited by AMF.
Nsmf:
Service-based interface exhibited by SMF.
Nnef:
Service-based interface exhibited by NEF.
Npcf:
Service-based interface exhibited by PCF.
Nudm:
Service-based interface exhibited by UDM.
Naf:
Service-based interface exhibited by AF.
Nnrf:
Service-based interface exhibited by NRF.
Nnsacf:
Service-based interface exhibited by NSACF.
Nnssaaf:
Service-based interface exhibited by NSSAAF.
Nnssf:
Service-based interface exhibited by NSSF.
Nausf:
Service-based interface exhibited by AUSF.
Nudr:
Service-based interface exhibited by UDR.
Nudsf:
Service-based interface exhibited by UDSF.
N5g-eir:
Service-based interface exhibited by 5G-EIR.
Nnwdaf:
Service-based interface exhibited by NWDAF.
Nchf:
Service-based interface exhibited by CHF.
Nucmf:
Service-based interface exhibited by UCMF.
Ndccf:
Service based interface exhibited by DCCF.
Nmfaf:
Service based interface exhibited by MFAF.
Nadrf:
Service based interface exhibited by ADRF.
Naanf:
Service-based interface exhibited by AANF.
N5g-ddnmf:
Service-based interface exhibited by 5G DDNMF.
Nmbsmf:
Service-based interface exhibited by MB-SMF.
Nmbsf:
Service-based interface exhibited by MBSF.
Ntsctsf:
Service-based interface exhibited by TSCTSF.
Nbsp:
Service-based interface exhibited by an SBI capable Boostrapping Server Function in GBA.
Neasdf:
Service-based interface exhibited by EASDF.
Nupf:
Service-based interface exhibited by UPF.
Neif:
Service-based interface exhibited by EIF.
4.2.7 Reference points p. 56
The 5G System Architecture contains the following reference points:
N1:
Reference point between the UE and the AMF.
N2:
Reference point between the (R)AN and the AMF.
N3:
Reference point between the (R)AN and the UPF.
N4:
Reference point between the SMF and the UPF.
N6:
Reference point between the UPF and a Data Network.
N9:
Reference point between two UPFs.
The following reference points show the interactions that exist between the NF services in the NFs. These reference points are realized by corresponding NF service-based interfaces and by specifying the identified consumer and producer NF service as well as their interaction in order to realize a particular system procedure.
N5:
Reference point between the PCF and an AF or TSN AF.
N7:
Reference point between the SMF and the PCF.
N8:
Reference point between the UDM and the AMF.
N10:
Reference point between the UDM and the SMF.
N11:
Reference point between the AMF and the SMF.
N12:
Reference point between AMF and AUSF.
N13:
Reference point between the UDM and Authentication Server function the AUSF.
N14:
Reference point between two AMFs.
N15:
Reference point between the PCF and the AMF in the case of non-roaming scenario, PCF in the visited network and AMF in the case of roaming scenario.
N16:
Reference point between two SMFs, (in roaming case between SMF in the visited network and the SMF in the home network).
N16a:
Reference point between SMF and I-SMF.
N17:
Reference point between AMF and 5G-EIR.
N18:
Reference point between any NF and UDSF.
N19:
Reference point between two PSA UPFs for 5G LAN-type service.
N22:
Reference point between AMF and NSSF.
N23:
Reference point between PCF and NWDAF.
N24:
Reference point between the PCF in the visited network and the PCF in the home network.
N27:
Reference point between NRF in the visited network and the NRF in the home network.
N28:
Reference point between PCF and CHF.
N29:
Reference point between NEF and SMF.
N30:
Reference point between PCF and NEF.
N31:
Reference point between the NSSF in the visited network and the NSSF in the home network.
N32:
Reference point between a SEPP in one PLMN or SNPN and a SEPP in another PLMN or SNPN; or between a SEPP in a SNPN and a SEPP in a CH/DCS, where the CH/DCS contains a UDM/AUSF.
N33:
Reference point between NEF and AF.
N34:
Reference point between NSSF and NWDAF.
N35:
Reference point between UDM and UDR.
N36:
Reference point between PCF and UDR.
N37:
Reference point between NEF and UDR.
N38:
Reference point between I-SMFs and between V-SMFs.
N40:
Reference point between SMF and the CHF.
N41:
Reference point between AMF and the CHF in HPLMN.
N42:
Reference point between AMF and the CHF in VPLMN.
N43:
Reference point between PCFs.
N50:
Reference point between AMF and the CBCF.
N51:
Reference point between AMF and NEF.
N52:
Reference point between NEF and UDM.
N55:
Reference point between AMF and the UCMF.
N56:
Reference point between NEF and the UCMF.
N57:
Reference point between AF and the UCMF.
N58:
Reference point between AMF and the NSSAAF.
N59:
Reference point between UDM and the NSSAAF.
N60:
Reference point between AUSF and NSWOF.
N80:
Reference point between AMF and NSACF.
N81:
Reference point between SMF and NSACF.
N82:
Reference point between NSACF and NEF.
N83:
Reference point between AUSF and NSSAAF.
N84:
Reference point between TSCTSF and PCF.
N85:
Reference point between TSCTSF and NEF.
N86:
Reference point between TSCTSF and AF.
N87:
Reference point between TSCTSF and UDM.
N88:
Reference point between SMF and EASDF.
N88a:
Reference point between I-SMF and EASDF.
N89:
Reference point between TSCTSF and AMF.
N96:
Reference point between TSCTSF and NRF.
N97:
Reference point between two NSACFs in different PLMNs.
N99:
Reference point between two NSACFs within the same PLMN.
Nx1:
Reference point between EIF and AF.
Nx2:
Reference point between EIF and NEF.
Nx3:
Reference point between EIF and UDM.
Nx4:
Reference point between EIF and PCF.
Nx5:
Reference point between EIF and SMF.
The reference points to support SMS over NAS are listed in clause 4.4.2.2.
The reference points to support Location Services are listed in TS 23.273.
The reference points to support SBA in IMS (N5, N70 and N71) are described in TS 23.228.
The reference points to support AKMA (N61, N62 and N63) are described in TS 33.535.
The reference points to support 5G ProSe are described in TS 23.304.
The reference points to support 5G multicast-broadcast services are described in TS 23.247.
The reference points to Support Uncrewed Aerial Systems (UAS) connectivity, identification and tracking are described in TS 23.256.
The reference points to support SBA in GBA and GBA push (N65, N66, N67 and N68) are described in TS 33.220 and TS 33.223.
The reference points to support SMS delivery using SBA are described in TS 23.540.
The reference points to support Ranging based services and Sidelink Positioning are described in TS 23.586.