Content for TS 23.433 Word version: 19.4.0
0…
4…
7…
8…
9.2…
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.4…
9.3…
9.3.2.2…
9.3.3…
9.3.4…
9.4…
9.5…
9.5.3…
9.5.4…
9.6…
9.7…
9.7.3…
9.7.4…
9.8…
9.9…
9.9.3…
9.10…
9.10.3…
9.11…
9.11.3…
9.12…
9.12.3…
9.13
10…
A…
C
D…
9.9 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee
9.9.1 General
9.9.2 Procedures
9.9.2.1 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee by switching SEALDD server
9.9.2.2 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee with redundant transport
9.9.2.3 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee with BAT and periodicity adaptation
9.9.2.4 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee using Non-3GPP access
9.9.2.5 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee to support the user group level QoS
...
...
9.9 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee p. 94
9.9.1 General p. 94
The following clauses specify procedures, information flows and APIs for SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee.
9.9.2 Procedures p. 94
9.9.2.1 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee by switching SEALDD server p. 94
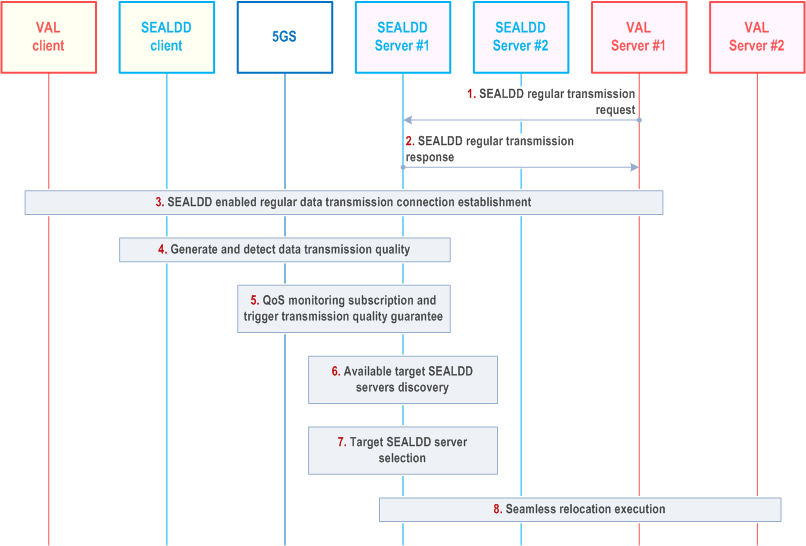
Figure 9.9.2.1-1 illustrate the procedure for data transmission quality guarantee based on transmission quality report from SEALDD server and QoS monitoring from 5GS. The procedure is applicable to the scenario where there is a single path between UE and SEALDD server.
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL server discovers and selects the SEALDD server by CAPIF functions.
-
The VAL server has requested the transmission quality measurement to the SEALDD server by invoking the Sdd_
TransmissionQualityMeasurement_ API in clause 9.7.4.2.subscription - A SEALDD service policy (i.e., the necessary SEALDD layer actions for meeting the service policy requirements) has been configured in SEALDD server and shared with the SEALDD client.
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a Sdd_RegularTransmission request to the SEALDD server, as specified in clause 9.2.2.2. The request includes the identifiers of the application traffic (e.g. VAL service ID, VAL server ID), and optionally, the QoS information for the application traffic, e.g. QoS requirements.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SEALDD server performs an authorization check. If authorization is successful, the SEALDD server sends a response to the VAL server. The QoS information may be allocated by SEALDD server according to VAL service ID for different service type of application traffic if the QoS information is not provided by VAL server.
Step 3.
The regular data transmission connection is established according to clause 9.2.2.2.
Step 4.
The S-SEALDD server (i.e., SEALDD server#1) can generate the transmission quality measurement report according to the SEALDD enabled transmission quality measurement procedure in clause 9.7.2.1, and detect whether the current transmission quality can satisfy the QoS requirements of VAL application.
Step 5.
The S-SEALDD server subscribes to 5GC for QoS monitoring of the specific UE related to the VAL user, as defined in clause 5.2.6.9 of TS 23.502. If the S-SEALDD server diagnoses that QoS deterioration is caused by N6/SEALDD overload (i.e., based on QoS monitoring between UE and UPF, and the E2E transmission quality measurement). The S-SEALDD server can determine to trigger the data transmission quality guarantee procedure (i.e., switching the connected SEALDD server according to SEALDD service policy) based on the QoS monitoring and E2E transmission quality measurement.
Step 6.
The S-SEALDD server performs target SEALDD server discovery procedure by using EEL, as specified in clause 9.4.
Step 7.
The S-SEALDD server can select the T-SEALDD server (i.e., SEALDD server #2) based on N6 traffic and/or SEALDD server load from performance of the available target SEALDD servers in step 6.
Step 8.
The SEALDD relocation procedure is performed for the switched SEALDD servers and the switched VAL servers, as specified in clause 9.6.2.2.
After the SEALDD relocation procedure, the SEALDD client can connect to the selected T-SEALDD server to obtain the data transmission quality guarantee service (i.e. the QoS requirements of VAL application can be satisfied).
9.9.2.2 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee with redundant transport p. 95
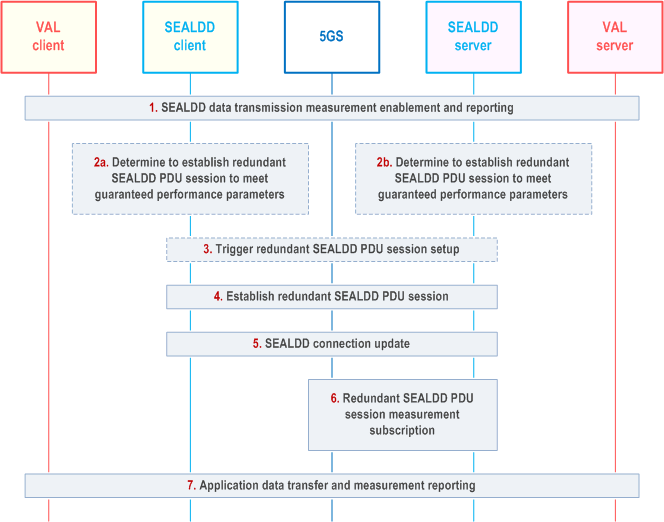
Figure 9.9.2.2-1 illustrates the procedure of using redundant transmission as the action to meet connection reliability requirements specified by a SEALDD service policy.
Pre-conditions:
- A SEALDD service policy, which includes data transmission quality guarantees, is available to SEALDD server. The policy can be used to configure measurements and determine the necessary SEALDD layer actions for meeting the service policy requirements.
- The SEALDD Client is authorized to request redundant transport services on behalf of the VAL client.
Step 1.
When the SEALDD measurement results indicating that the SEALDD data transmission has good performance according to policy guarantee threshold, if the measurement was started by the SEALDD client, the SEALDD client may release one transmission path and return back to single SEALDD connection mode, otherwise the SEALDD server may send a Transmission quality management request to the SEALDD client requesting to use single transmission, then the SEALDD client releases one transmission path and returns to single SEALDD connection mode.
A VAL client and server establish a SEALDD connection to transport the application data. As part of the connection establishment, the SEALDD service policy in precondition 1 is shared so that it is available to both the SEALDD client and the SEALDD Server. The SEALDD Server may use the data transmission quality requirements of this policy in conjunction with other local policies pre-provisioned at the SEALDD server. The SEALDD server determines whether to start data transmission quality measurement by itself or by the SEALDD client. As a result, SEALDD measurements (e.g. packet loss rate, latency) are configured either at the SEALDD client as described in clause 9.7.2.3 or at the SEALDD server as described in clause 9.7.2.1 and started accordingly. Then either the SEALDD client or server receives measurement reports.
Step 2.
Based on measurement reports and the SEALDD service policy, depending on the which entity started the measurement, either the SEALDD client or server determines to perform an action so that the data transmission quality requirements of the policy are met.
Step 3.
Specifically, if the measurement was started by the SEALDD client, the SEALDD client triggers the establishment of redundant transmission services. If the measurement was started by the SEALDD server, the SEALDD server triggers the establishment of redundant transmission services by sending a Transmission quality management request to the SEALDD client requesting to establish redundant transmission path.
Step 4.
The SEALDD client uses steps 6 to 9 of the procedure in clause 9.3.2.1 to request the use of redundant transmission service from the SEALDD server. As part of this step, the UE may end the initial PDU session and establish redundant PDU sessions.
Step 5.
The SEALDD client updates the SEALDD connection with the redundant transmission information, i.e., the UE addresses and ports for the redundant PDU sessions, the SEALDD-UU flow identifier, and the application traffic descriptors. The SEALDD client or server also configures the parameters for enabling any necessary SEALDD measurements for the new SEALDD-UU flow.
Step 6.
The SEALDD server may subscribe to receive notifications from the 5G network for user plane measurements (e.g., the network latency requirements specified in TS 28.541), network analytics (as specified in TS 28.104, etc.).
Step 7.
The SEALDD client and server handle data duplication and elimination of application traffic on the redundant SEALDD-UU flows and the necessary measurements are collected by the SEALDD client or server.
9.9.2.3 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee with BAT and periodicity adaptation |R19| p. 97
Figure 9.9.2.3-1 illustrates the procedure of using 3GPP CN (5GS) capability for BAT and periodicity report and application layer adjustment in SEALDD layer for data transmission.
Precondition:
- SEALDD layer connection needs to be established as described in clause 9.2 and clause 9.3.
- In policy driven SEALDD connection management, the VAL server has indicated quality optimization policy during SEALDD policy configuration procedure as described in clause 9.10.
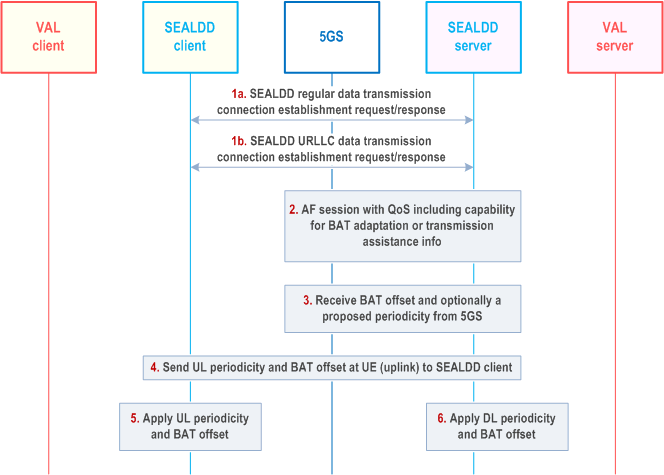
Step 1.
A VAL client and server establish a SEALDD regular or redundant connection to transport the application data as described in clause 9.2 or clause 9.3. The connection establishment may be triggered by either SEALDD server or SEALDD client. During the connection establishment, the SEALDD client includes an indication for data transmission adjustment request as part of the connection establishment over SEALDD-UU reference point.
In SEALDD-UU connection establishment, the SEALDD client also includes its capability for BAT and periodicity adaptation, or transmission assistance info to the SEALDD server in the connection establishment request (SEALDD client triggered establishment) or response (SEALDD server triggered establishment).
Step 2.
The SEALDD server, based on received data transmission adjustment request from VAL server or SEALDD client, its own capability and/or received capability from SEALDD client for BAT and periodicity adaptation, and its own DL transmission assistance info and/or received transmission assistance info from SEALDD client, subscribes to 5GS AF session with QoS service with capability for BAT adaptation or transmission assistance info as described in clause 4.15.6.6 and 4.16.6.4 of TS 23.502.
Step 3.
The SEALDD server receives BAT offset and optionally a proposed periodicity (which was adjusted in 5GS) in AF session with QoS notification from 5GS.
Step 4.
If the SEALDD client indicated its BAT and periodicity adaptation capability in step 1 during SEALDD connection establishment, the SEALDD server sends UL periodicity and BAT window to the SEALDD client in Transmission quality management request with transmission parameter adjustment action.
Step 5.
The SEALDD client applies UL periodicity and BAT offset for uplink SEALDD data.
Step 6.
The SEALDD server locally applies DL periodicity and BAT offset for downlink SEALDD data.
9.9.2.4 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee using Non-3GPP access |R19| p. 98
Figure 9.9.2.4-1 illustrates the procedure of using non-3gpp access for SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEALDD Client is authorized to use non-3GPP access on behalf of the VAL client.
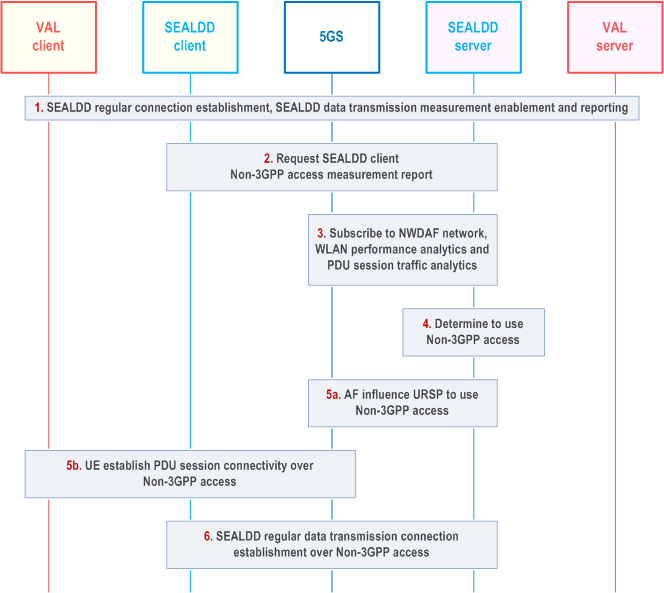
Step 1.
Based on continuous monitoring and measurement reports, the SEALDD server can decide to switch back to 3GPP access and use the SEALDD-UU connection over 3GPP access for data transmission.
A regular data transmission connection is established according to clause 9.2.2.2 or via clause 9.3.2.3 and SEALDD data transmission measurement reporting as per clause 9.7.2.1 or clause 9.7.2.2 to get the data transmission quality.
Step 2.
If Non-3GPP access measurement policy is available in the SEALDD server, the SEALDD server can request the SEALDD client to report the latest Non-3GPP access measurements(like RSRP, RSRQ, RSSI, SINR for the WLAN SSIDs) as per steps 3-4 of the procedure defined in clause 9.2.2.6.
If Non-3GPP access measurement policy is not available, the SEALDD server fetches the UE location using the SEAL location service defined in clause 9.3.12 of TS 23.434 and requests the SEALDD client to report the latest Non-3GPP access measurements of the nearby WLAN SSIDs. The SEALDD server uses the steps 3-4 of the procedure defined in clause 9.2.2.6 to get the report from the SEALDD client.
If the Non-3GPP access measurement values in the data transmission quality report or SEALDD connection status report defined in clause 9.2.2.6 are above the Signal strength thresholds mentioned in SEALDD Non-3GPP access measurement policy then the SEALDD server can offload the SEALDD-UU connection from 3GPP access to Non-3GPP access(WLAN) using steps 5-6.
Step 3.
The SEALDD server subscribes to NWDAF analytics service for subscription to network performance analytics with Analytics ID as Network Performance using the procedure described in clause 6.6.4 of TS 23.288. It also subscribes to PDU Session traffic analytics service using the procedure defined in clause 6.20 of TS 23.288.
The SEALDD server can subscribe to WLAN performance analytics using the procedure defined in clause 6.11 of TS 23.288. The SEALDD server uses the SEALDD Non-3GPP access measurement policy information or information received in step 2 for subscription to WLAN performance analytics.
Step 4.
Based on SEALDD client Non-3GPP access measurement reports, NWDAF analytics measurement reports(including predicted values), and data transmission quality measurement reports, the SEALDD server detects the 3GPP RAN congestion and determines to use non-3GPP access to meet the data transmission quality requirements.
Step 5.
The SEALDD server can request 5GS to create or update URSP rules using clause 4.15.6.10 of TS 23.502 to establish a PDU session connection over Non-3GPP access. The SEALDD server can create a URSP rule with Access Type Route selection descriptors as non-3GPP to establish PDU session. The request may include the UE ID and application traffic descriptor containing the addresses or ports allocated by SEALDD server.
Step 6.
The UE receives the new or updated URSP rules from the 5G core network. Based on the URSP rules, the UE establishes a PDU session connectivity over non-3GPP access with the 5GS.
Step 7.
On the successful establishment of PDU session connection over Non-3GPP access, the SEALDD client updates the SEALDD data transmission connection with the updated SEALDD client IP address as per steps 7-8 mentioned in clause 9.3.2.2.
9.9.2.5 SEALDD enabled data transmission quality guarantee to support the user group level QoS |R19| p. 99
Figure 9.9.2.5-1 illustrates the procedure to support the user group level QoS guarantee. The user group level QoS guarantee provides different QoS for different users in single service(e.g., XR service).
Pre-conditions:
- The SEALDD server acts as NSaaS provider, and is authorized to get network slice related information and capabilities in Network Slice ServiceProfile (TS 28.541) from NSCE server as defined in TS 23.435.
- The SEALDD policy for a group of users has been configured, by providing the VAL UE group ID (as defined in clause 7.5 of TS 23.434), VAL UE identity list, or slice identifier in the SEALDD policy configuration request.
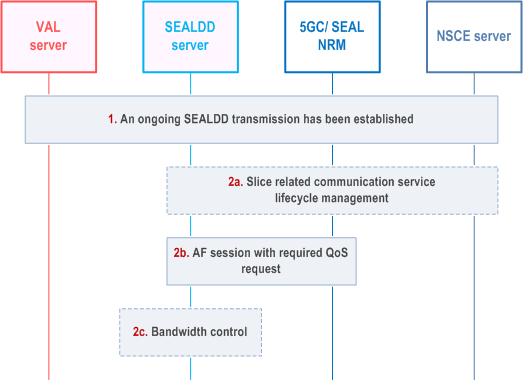
Step 1.
The regular data transmission connection is established according to clause 9.2.2.2.
Step 2a.
Based on the configured SEALDD policy and network slice related information received from NSCE, the SEALDD server determines whether the slice related communication service lifecycle management is needed, based on Network slice information, e.g., Slice Coverage Area, Latency, and, Data volume, which specify the Network Slice characteristics, as specified in clause of ServiceProfile in TS 28.541. If the performance of network slice identified by the provided Slice identifier is not satisfying, the SEALDD server could trigger slice related communication service Reconfiguration.
If the network slice related information of network slice identified by the provided Slice identifier is not received from NSCE before, the SEALDD server can get the Network slice information by invoking the Network Slice Information delivery as defined in clause 9.17 of TS 23.435.
Before triggering the network slice management service, to determine the target UE of network slice(s), the SEALDD server acting as AF, may receive a UE location report or a monitoring event report from 5GC (assuming that SEALDD server has subscribed to consume 5GC services like LCS or NEF monitoring events related to UE actual location, or UE mobility analytics from NWDAF) or Location service from SEAL.
Step 2b.
Based on the configured SEALDD policy, the SEALDD server initiates AF session with required QoS as defined in clause 4.15.6.6a of TS 23.502, or Multi-member AF session with required QoS as defined in clause 4.16.5.3 of TS 23.502, or QoS/resource management capability provided by SEAL NRM as defined in clause 14.3.5.2 of TS 23.434.
Step 2c.
Based on the configured SEALDD policy, the SEALDD server determines whether the SEALDD enabled bandwidth control is needed. If needed(e.g., multiple user groups have different bandwidth requirements), the SEALDD server may initiate the SEALDD enabled bandwidth control for different VAL users as defined in clause 9.8.2 of TS 23.433.