Content for TS 23.433 Word version: 19.4.0
0…
4…
7…
8…
9.2…
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.4…
9.3…
9.3.2.2…
9.3.3…
9.3.4…
9.4…
9.5…
9.5.3…
9.5.4…
9.6…
9.7…
9.7.3…
9.7.4…
9.8…
9.9…
9.9.3…
9.10…
9.10.3…
9.11…
9.11.3…
9.12…
9.12.3…
9.13
10…
A…
C
D…
9.4 SEALDD server discovery and selection
9.4.1 General
9.4.2 SEALDD server discovery and selection for VAL server
9.4.2.1 General
9.4.2.2 Procedure
9.4.3 SEALDD server discovery and selection for SEALDD client
9.4.3.1 General
9.4.3.2 EDN scenario
9.4.3.2.1 VAL server registered to EES with associated SEALDD server address as VAL server endpoint
9.4.3.2.2 EAS registered to EES with associated SEALDD server information
9.4.3.2.3 VAL server and SEALDD server registered to EES
9.4.4 Information flows
9.4.5 APIs
...
...
9.4 SEALDD server discovery and selection p. 57
9.4.1 General p. 57
The following clauses specify procedures, information flow and APIs for SEALDD server discovery and selection for VAL server and SEALDD client.
There are two scenarios of how SEALDD service is used:
- Scenario (a): SEALDD service is used for both signalling and data traffic transfer.
- Scenario (b): SEALDD service is used only for data traffic transfer.
9.4.2 SEALDD server discovery and selection for VAL server p. 57
9.4.2.1 General p. 57
CAPIF architecture and functionalities can be reused to enable VAL server discover and select SEALDD server.
9.4.2.2 Procedure p. 57
The SEALDD server and VAL server may support CAPIF as shown in Figure 9.4.2.2-1. When CAPIF is supported:
- The SEALDD server shall support the CAPIF API provider domain functions (i.e. CAPIF-2/2e (SEALDD-S interface), CAPIF-3/3e, CAPIF-4/4e and CAPIF-5/5e as specified in TS 23.222);
- The VAL server shall act as API invoker and support the API invoker functions (i.e. CAPIF-1/1e and CAPIF-2/2e (SEALDD-S interface) as specified in TS 23.222); and
- The SEALDD server shall act as API invoker and support the API invoker functions (i.e. CAPIF-1/1e and CAPIF-2/2e (SEALDD-E interface) as specified in TS 23.222).
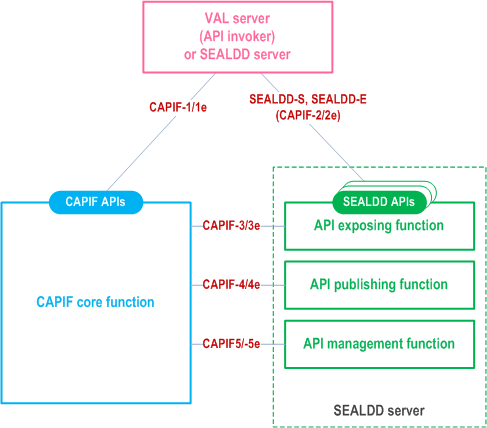
The VAL server can discover a proper SEALDD server from CAPIF core function with different discovery filters, e.g. expected AEF location. If a VAL server is changed during UE mobility, a new SEALDD server may be discovered and selected.This is also applicable for the VAL server acting as EAS to discover and select an SEALDD server in EDN scenario to use SEALDD-S services, if any.
9.4.3 SEALDD server discovery and selection for SEALDD client p. 58
9.4.3.1 General p. 58
The VAL client can use existing mechanisms (e.g. DNS query mechanism, application layer signalling mechanism) to find an appropriate SEALDD server in non-EDN scenario and EDN scenario. The VAL client can provide the SEALDD server information to the SEALDD client when the SEALDD service is required.
The EAS registration procedure of TS 23.558 can be enhanced to enable VAL/SEALDD client to discover and select proper SEALDD server in EDN scenario.
9.4.3.2 EDN scenario p. 59
9.4.3.2.1 VAL server registered to EES with associated SEALDD server address as VAL server endpoint p. 59
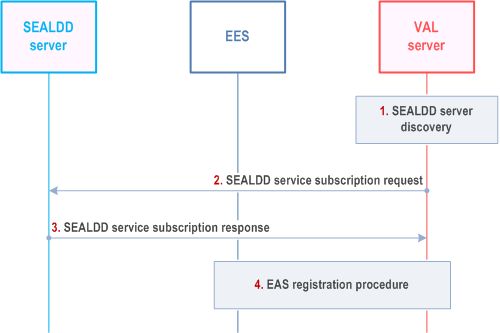
Step 1.
This procedure reuses the current procedure described in clause 8.4.3.2.2 of TS 23.558. The VAL server (as an EAS) registers to the EES with the associated SEALDD server address as the EAS Endpoint in the EAS profile. Then the EEC can use the EAS discovery procedure defined in clause 8.5 of TS 23.558 to find the VAL server's address which is SEALDD server's address. The VAL client can initiate SEALDD service via SEALDD client with the SEALDD server's address. This procedure can be used for scenario (a).
The VAL server can discover and select the SEALDD server (e.g. by CAPIF functions).
Step 2.
The VAL server decides to use SEALDD service to enhance data transmission and send a SEALDD data transmission subscription request (e.g. SEALDD enabled regular transmission request in clause 9.2.2) to the SEALDD server.
Step 3.
Upon receiving the request, the SEALDD server performs an authorization check and responds with a SEALDD data transmission subscription response (e.g. SEALDD enabled regular transmission response in clause 9.2.2).
Step 4.
The VAL server (as an EAS) registers to the EES as described in clause 8.4.3.2.2 of TS 23.558 with the associated SEALDD server address as EAS Endpoint in the EAS profile. The EAS ID used by VAL server in registration may indicate the application service association between the VAL service and SEALDD service implicitly or explicitly.
9.4.3.2.2 EAS registered to EES with associated SEALDD server information p. 59
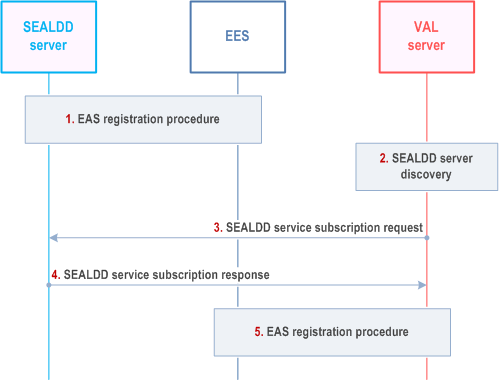
Step 1.
This procedure reuses the current procedure described in clause 8.4.3.2.2 of TS 23.558. The VAL server (as an EAS) registers to the EES with the associated SEALDD server information (i.e. SEALDD service and SEALDD server address) as associated EAS ID and EAS Endpoint in the EAS profile. Then the EEC can use the EAS discovery procedure defined in clause 8.5 of TS 23.558 to find the VAL server's address and associated SEALDD server's address. The VAL client can initiate SEALDD service via SEALDD client with the SEALDD server's address. For scenario (b), the VAL client can also establish the connection with VAL server using the VAL server's information for application signalling transfer and only use the SEALDD connection for application data transfer.
The SEALDD server (as an EAS) registered to EES with SEALDD profile (i.e. EAS profile) as an API provider.
Step 2.
The EAS (VAL) server can discover and select the SEALDD server (e.g. by CAPIF functions).
Step 3.
The EAS (VAL server) decides to use SEALDD service to enhance data transmission and send a SEALDD data transmission subscription request (e.g. SEALDD enabled regular transmission request in clause 9.2.2) to the SEALDD server.
Step 4.
Upon receiving the request, the SEALDD server performs an authorization check and responds with a SEALDD data transmission subscription response (e.g. SEALDD enabled regular transmission response in clause 9.2.2).
Step 5.
The VAL server (as an EAS) registers to the EES as described in clause 8.4.3.2.2 of TS 23.558 with the associated SEALDD server information (i.e. SEALDD service and SEALDD server address) as associated EAS ID and EAS Endpoint in the EAS profile.
9.4.3.2.3 VAL server and SEALDD server registered to EES p. 60
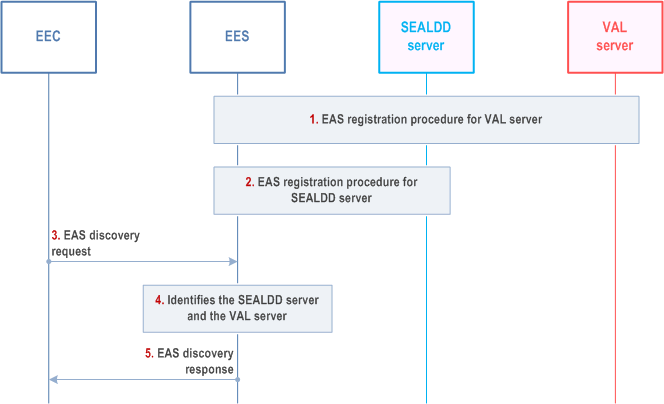
Step 1.
Upon receiving the SEALDD server address, the VAL server address, the VAL client can initiate SEALDD service via SEALDD client with the SEALDD server's address. The data transmission between the VAL client and the VAL server can be enabled via the SEALDD connection, as specified in clause 9.2.2.
The VAL server (acting as an EAS) registers to the EES, if the VAL server has not indicated the associated SEALDD server as described in clause 9.4.3.2.1 or clause 9.4.3.2.2, the VAL server includes an indication of whether using SEALDD service is needed.
Step 2.
Optionally, the SEALDD server (acting as an EAS) registers to the EES.
Step 3.
The EEC performs service provisioning procedure as described in clause 8.3.3.2.2 of TS 23.558. The EEC is responded with the EES which supports the SEALDD server and the VAL server. The EEC sends the EAS discovery request for EAS bundle including VAL service and SEALDD service. The EES may collect the performance of VAL server and SEALDD server (e.g. E2E latency between the SEALDD server and client and load information of SEALDD and VAL server) from the ADAE server when receiving the EAS discovery request, as specified in clause 8.2.2 (for transmission quality, e.g. E2E latency) and 8.8.2 (for edge load) of TS 23.436.
Step 4.
The EES identifies the VAL server and the associated SEALDD server based on the performance of VAL server and the performance of SEALDD server (e.g. to satisfy the AC service KPI).
Step 5.
The EES sends the EAS discovery response to EEC, including the SEALDD server address, the VAL server address.
9.4.4 Information flows p. 61
The information flow about the SEALDD server discovery for VAL server/SEALDD server can reuse the defined information flow in CAPIF (e.g. service API publish in clause 8.3.2, Service API discover in clause 8.7.2), as specified in TS 23.222.
For SEALDD server discovery for VAL client in EDN scenario, the information flows for EAS registration and EAS discovery in clause 8.4.3.3 and clause 8.5.3 of TS 23.558.
The information flow about regular SEALDD data transmission subscription can refer to the SEALDD enabled regular transmission request/response in clauses 9.2.3.1 and 9.2.3.2.
9.4.5 APIs p. 61
The APIs about SEALDD server discovery for VAL server/SEALDD server can reuse the defined APIs in CAPIF (e.g. CAPIF_Publish_Service_API in clause 10.3, CAPIF_Discover_Service _API in clause 10.2), as specified in TS 23.222.
The APIs about SEALDD server discovery for VAL client in EDN scenario, can reuse the defined APIs in EDGEAPP (e.g. Eees_EASRegistration API in clause 8.4.3.4, Eees_EASDiscovery API in clause 8.5.4), as specified in TS 23.558.
The APIs about regular SEALDD data transmission subscription can refer to the Sdd_RegularTransmission API, as defined in clause 9.2.4.