Content for TS 23.433 Word version: 19.4.0
0…
4…
7…
8…
9.2…
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.4…
9.3…
9.3.2.2…
9.3.3…
9.3.4…
9.4…
9.5…
9.5.3…
9.5.4…
9.6…
9.7…
9.7.3…
9.7.4…
9.8…
9.9…
9.9.3…
9.10…
9.10.3…
9.11…
9.11.3…
9.12…
9.12.3…
9.13
10…
A…
C
D…
9.3.2.2 Client initiated E2E redundant transmission path establishment procedure
9.3.2.3 SEALDD enabled URLLC transmission connection establishment based on policy
9.3.2.4 SEALDD enabled URLLC transmission connection deletion based on policy
9.3.2.5 SEALDD client initiated connection release
...
...
9.3.2.2 Client initiated E2E redundant transmission path establishment procedure p. 50
Figure 9.3.2.2-1 illustrates the procedure for client initiated redundant transmission establishment for data transfer per application layer transaction.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEALDD client is authorized to request redundant transmission services on behalf of the VAL client when the VAL client initiates redundant transmission service.
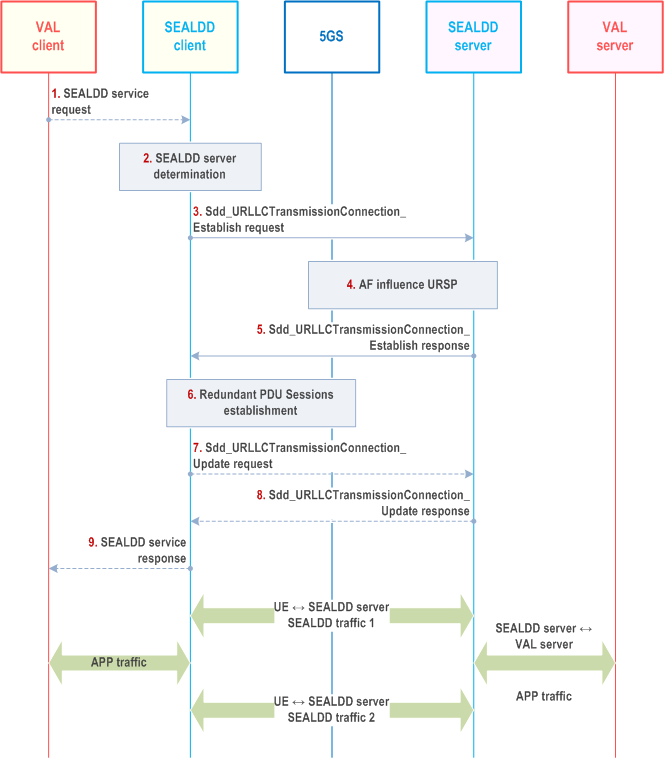
Step 1.
The VAL client sends application traffic to the SEALDD client, which duplicates the application data on the redundant PDU sessions. The SEALDD server receives the redundant traffic and reassembles the data to send to the VAL server. Similarly, the SEALDD server duplicates downlink traffic from the VAL server and sends the data to the SEALDD client on the redundant PDU sessions. The SEALDD client eliminates the redundant data and reassembles data to send to the VAL client.
A VAL client determines to use SEALDD service to ensure that the data transmission quality for the application traffic is met and makes a service request to the SEALDD client.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SEALDD client decides to establish redundant transmission path according to the QoS requirements. The SEALDD client discovers and selects the proper SEALDD server for the VAL application as specified in clause 9.4.3.
Step 3.
The SEALDD client sends a request to the SEALDD server to configure redundant transport for the application traffic. The SEALDD client allocates two different SEALDD-UU flow IDs mapping to the application traffic. The SEALDD client sends Sdd_URLLCTransmissionConnection_Establish request to SEALDD server. The request includes the SEALDD client ID, the SEALDD-UU flow IDs, the application ID, the UE ID/address, the VAL server ID/address, the QoS requirements, the UE location, and a request for redundant transport.
Step 4.
The SEALDD server allocates SEALDD-S connection information for the redundant transport paths and initiates the application guidance for URSP determination procedure with the 5G network to create or update URSP rules for the UE, as described in clause 4.15.6.10 of TS 23.502. The request includes the UE ID and application traffic descriptor containing the addresses allocated by SEALDD server. The UE receives the new or updated URSP rules from the 5G core network.
Step 5.
The SEALDD server responds to the SEALDD client providing the configuration status. The response includes the SEALDD-S connection information for the redundant transmission paths allocated in step 4. The SEALDD client and SEALDD server store the mapping between the application traffic and SEALDD traffic.
Step 6.
The UE establishes redundant PDU sessions with the 5G network using the new or updated URSP rules as specified in clause 5.33.2.1 of TS 23.501.
Step 7.
[Optional] The SEALDD client sends Sdd_URLLCTransmissionConnection_Update request to SEALDD server. The request includes the SEALDD client ID, the SEALDD-UU flow IDs, the application traffic descriptors for redundant transmission of the SEALDD client side (i.e. UE addresses and ports of the two redundant PDU Sessions). The two redundant SEALDD traffic use the same SEALDD-UU flow IDs for identification.
Step 8.
[Optional] The SEALDD server establishes connection with VAL server for the VAL client to transmit application traffic mapping to the redundant SEALDD traffic. The SEALDD server sends a response to the SEALDD client. After this step, the SEALDD client and SEALDD server both get the application traffic descriptors (including the UE's addresses/ports and SEALDD server's addresses/ports for the SEALDD traffic transmission). The SEALDD client and SEALDD server store the mapping between the application traffic and SEALDD traffic.
Step 9.
The SEALDD client responds with a SEALDD service response.
9.3.2.3 SEALDD enabled URLLC transmission connection establishment based on policy p. 51
The SEALDD servers has Data Delivery (DD) policy being provisioned. The DD policy includes reliable transmission service for the associated VAL traffic. Before the application communication between VAL client and VAL server starts, the DD policy is enforced by the SEALDD server to establish the SEALDD connection.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEALDD server has DD policies available.

The procedure is same as step 1 to 7 in clause 9.2.2.3 with differences that:
- in step 2, the SEALDD server enforces the policy to trigger URLLC transmission connection establishment.
- in step 5 and 6, the SEALDD server allocates dual SEALDD-S connection information for sending and receiving packet over SEALDD-UU reference point, then SEALDD server sends URLLC transmission connection establishment request to the SEALDD client with SEALDD-UU flow IDs, VAL service ID, the dual IP address and port. The request is responded by the SEALDD client. Dual UE IP address (and port) may be included by the SEALDD client in the response or sent in a separate update message by SEALDD client if a different UE IP address is to be used in SEALDD connection user plane.
9.3.2.4 SEALDD enabled URLLC transmission connection deletion based on policy |R19| p. 53
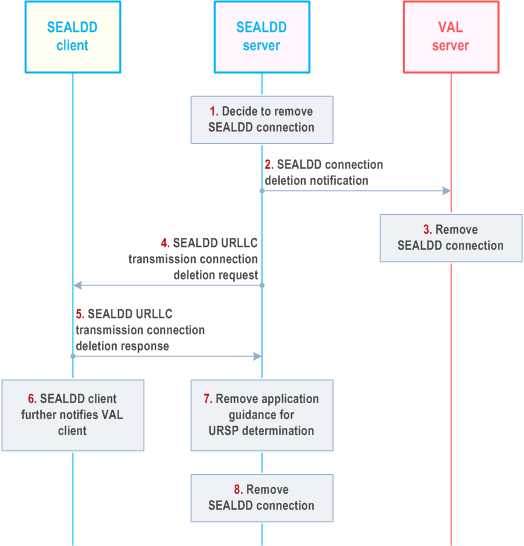
The procedure is same as step 1 to 8 in clause 9.2.2.4 with differences that in step 4 to 5, the SEALDD server requests URLLC transmission connection deletion to the SEALDD client and the SEALDD client responds with URLLC transmission connection deletion response.
9.3.2.5 SEALDD client initiated connection release |R19| p. 53
Figure 9.3.2.5-1 illustrates the procedure for SEALDD client initiated connection release procedure from the SEALDD client to the SEALDD server.
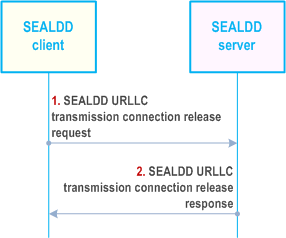
Step 1.
The SEALDD client sends the SEALDD URLLC connection release request to the SEALDD server to release the established connection.
Step 2.
The SEALDD server releases the SEALDD-UU redundant data transmission connection (which was established by SEALDD client or SEALDD server) and sends the response in the SEALDD URLLC connection release response message. Upon receiving the acknowledgement, the SEALDD client can release the connection resources.