Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.3.1
1…
5…
5.2.8…
6
7…
7.3.2
7.4…
7.4.3…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2…
9.3…
10…
10.1.2…
10.1.3…
10.1.4.3…
10.1.4.5…
10.1.5…
10.1.6…
10.2…
10.2.3…
10.2.4.2…
10.2.4.3…
10.2.5…
10.2.7…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3…
10.7.3.4…
10.7.3.7…
10.7.3.7.3
10.7.3.8…
10.7.3.10…
10.8…
10.8.4…
10.8.5…
10.9…
10.9.3…
10.9.3.5…
10.9.3.8…
10.9.3.9…
10.9.3.9.3…
10.9.3.9.4…
10.9.3.10…
10.9.3.10.4…
10.9.3.10.6…
10.10…
10.10.1.2.3…
10.10.2…
10.10.3…
10.10.3.3…
10.10.3.4…
10.11…
10.11.5…
10.12…
10.13…
10.13.3…
10.13.7…
10.13.10…
10.14…
10.15…
10.15.3…
10.15.3.3…
10.15.3.4…
10.16…
10.17…
10.17.3…
10.17.5…
11…
11.3…
11.5…
11.5.2…
11.5.3…
11.5.3.3.2A…
A…
B…
C…
E…
11 MC gateway UE
11.1 General
11.2 Functional Model
11.2.0 General
11.2.1 Functional model
11.2.2.1 General
11.2.2.4 Reference points MCX-n, CSC-n, SIP-1 and HTTP-1
...
...
11 MC gateway UE |R18| p. 334
11.1 General p. 334
An MC gateway UE enables MC service access for a MC service user residing on non-3GPP devices which may or may not have the ability to host MC service clients. In order to be able to participate in a MC service, the MC gateway UE provides the following necessary functions to enable the MC service access for such MC clients:
- 3GPP transport resources: Sharing of MC gateway UE 3GPP transport resources among the associated MC service clients.
- MC client identification: Independent MC service client identification, MC service client authorisation and MC service profile association.
- Location Management: Providing location management support for the associated MC clients to handle the location information and triggers related to 3GPP access network.
- MC client communication integrity: Ensure that signalling, media content and traffic attributes, e.g. priority and QoS, of communications between the MC system and MC service client remains unaltered.
-
Transparent MC traffic forwarding: The MC gateway UE forwards MC traffic without altering the content to the non-3GPP device whether it hosts or does not host an MC client. For the case the MC client is hosted at the non-3GPP device, the MC gateway UE forwards:
- the signalling between the MC client in the non-3GPP device and the MC service server/ CSC server
- the signalling between the user agent in the non-3GPP device and the SIP core
- the signalling between the HTTP client in the non-3GPP device and the HTTP proxy
- the media between the MC service server and the MC client in the non-3GPP device
11.2 Functional Model p. 335
11.2.0 General p. 335
The MC gateway UE offers access to the MC server for several MC clients as shown in Figure 11.2.0-1. The MC clients can be either located in the MC gateway UE or in the non-3GPP devices connected to the MC gateway UE via non-3GPP access. The configuration data defined in Annex A is needed in the MC client and the UE that is hosting the MC clients, i.e., either non-3GPP device or MC gateway UE, to access the MC service.
For non-3GPP devices which can host an MC client, the MC gateway UE enables connectivity to the MC server. For non-3GPP devices which cannot host the MC client, the MC gateway UE hosts the instantiation of the MC client on behalf of the non-3GPP device.
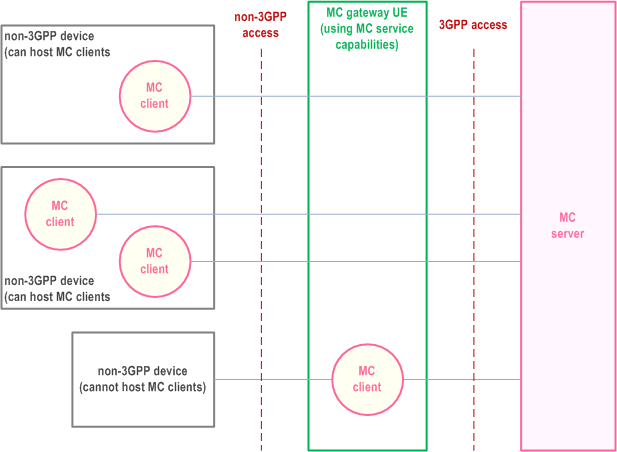
The MC gateway UE obtains MC service access via 3GPP network using the procedures as defined in TS 33.180.
The non-3GPP connection between the non-3GPP device and the MC gateway UE is out of scope of 3GPP.
For non-3GPP devices which cannot host MC clients, the MC gateway UE instantiates an MC client, acting on behalf of the non-3GPP device, to provide the requested services (e.g. emergency call, group calls, short data messages services, etc.). The communication interworking and the definition of associated procedures between the MC client (initiated at the MC gateway UE) and the non-3GPP devices is out of scope of this document.
For non-3GPP devices that host MC clients, MC service access is through the MC gateway UE. The MC gateway UE forwards (unmodified) signalling and media from the individual MC clients to the MC server and vice versa.
If the MC service user on the non-3GPP device utilizes multiple MC services simultaneously, the MC service access may also be provided via one or multiple MC gateway UEs as shown in Figure 11.2.0-2. In this case, each MC service is restricted to one MC gateway UE (e.g. MCPTT via MC gateway UE1, MCData via MC gateway UE2).
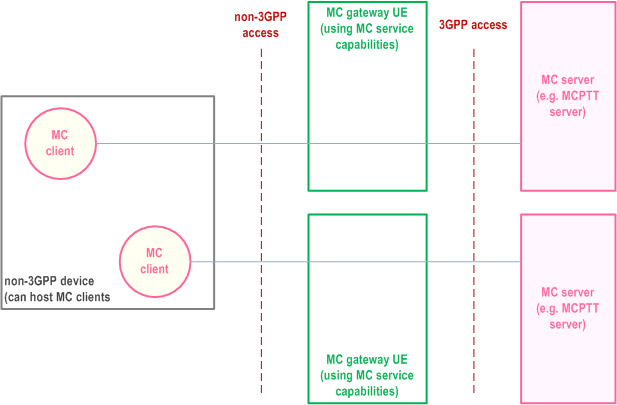
11.2.1 Functional model p. 336
The authentication and authorisation of the MC clients hosted on the MC gateway UE follows the procedures described in TS 33.180. Upon successful authentication and authorisation the MC clients can access a MC server via an MC gateway UE.
The MC gateway UE supports the authentication and authorisation of the MC client residing at the non-3GPP device by forwarding the unmodified application layer signalling between the MC client and the corresponding MC server. The authentication and authorisation of the MC client in the non-3GPP device follows the procedures described in TS 33.180.
Figure 11.2.1-1 represents the functional model for the application plane for utilizing MC gateway UE to enable MC services to non-3GPP devices that can host an MC client.
Figure 11.2.1-2 represents the functional model for the signalling plane for utilizing MC gateway UE to enable MC services to non-3GPP devices that can host an MC client.
Figure 11.2.1-3 represents the functional model for the application plane for non-3GPP devices that cannot host an MC client.
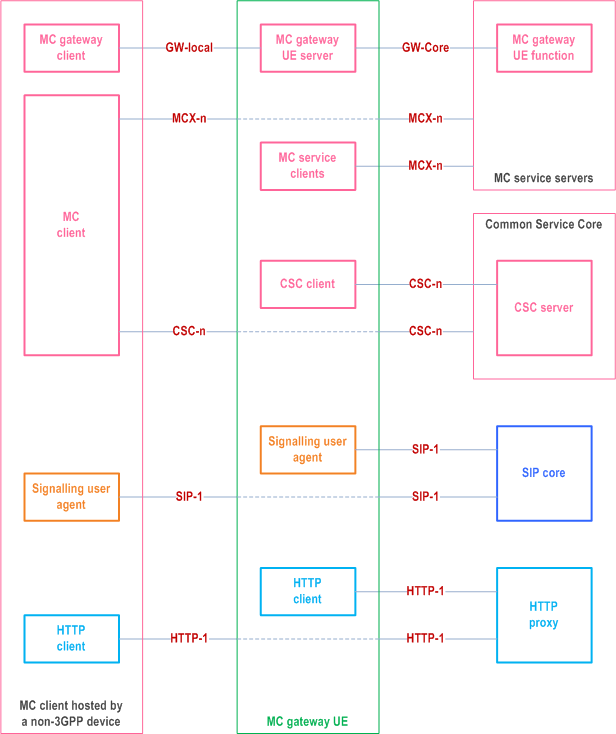
Figure 11.2.1-1: Functional model of MC gateway UE application plane with MC client hosted in the non- 3GPP device
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
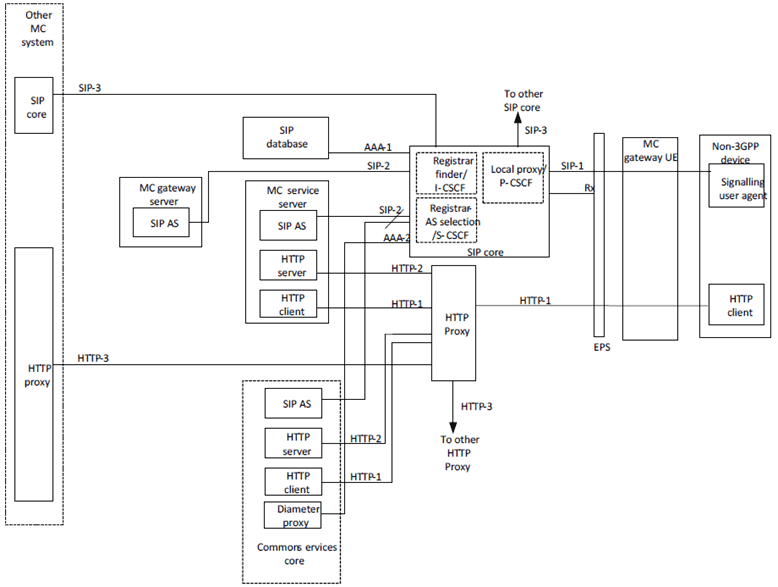
Figure 11.2.1-2: Functional model of MC gateway UE signalling plane with MC client hosted in the non- 3GPP device
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
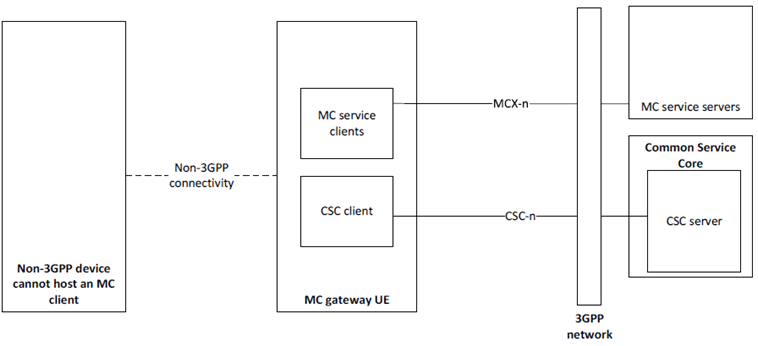
Figure 11.2.1-3: Functional model of MC gateway UE application plane with MC client hosted in the MC gateway UE
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
The functional model for the signalling control plane as described in Figure 7.3.1-2 is applicable to Figure 11.2.1-3.
11.2.2.1 General p. 338
The reference points for the use of the MC gateway UE are described in the following subclauses.
11.2.2.2 Void
11.2.2.3 Void
11.2.2.4 Reference points MCX-n, CSC-n, SIP-1 and HTTP-1 p. 338
The reference points MCX-n and CSC-n belonging to the application plane, and the reference points SIP-1 and HTTP-1 belonging to the signalling control plane, are relayed by the MC gateway UE between MC client on the non-3GPP device and the corresponding MC service server.
MCX-n, CSC-n, SIP-1 and HTTP-1 reference points are specified in the present specification. The MCX-n reference points are specified in TS 23.379, TS 23.281 and TS 23.282.