Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.5.0
1…
5…
6
7…
8…
9…
10…
10.1.5…
10.2…
10.2.6…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3.8…
10.8…
10.9…
10.9.3.9…
10.10…
10.10.3
10.11…
10.12…
10.13…
10.14…
10.15…
10.16…
10.17…
10.18…
10.19…
11…
11.5…
A…
B…
C…
E…
10.17 Sharing administrative configuration between interconnected MC systems
10.17.1 General
10.17.2 Information flows
10.17.3 Common ACM procedures
10.17.4 ACM Group configuration management
10.17.5 ACM user migration management
10.17.6 ACM updating MC service UE initial configuration for migration
10.17.7 ACM updating MC service user profiles assigned from partner MC system
...
...
10.17 Sharing administrative configuration between interconnected MC systems |R19| p. 338
10.17.1 General p. 338
Cooperation between MC systems encompasses a number of cases of mutual operation between them, e.g:
- Provisioning connectivity information of partner MC system(s) for MC service UE migration as specified in subclause 10.1.6.
- Migration of MC service users from an MC system considered as primary or home MC system to a partner MC system as specified in subclause 10.6.3
- Migration during ongoing group or private call communication as specified in subclause 10.16.
- Generic procedures for interconnection as specified in clause 10.14.
- Shared MC service groups which can be configured as described in clause 10.2.7.
10.17.2 Information flows p. 339
10.17.2.1 ACM data notification p. 339
Table 10.17.2.1-1 describes the information flow of the ACM data notification from the ACM server to the ACM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user towards the pending ACM data notification is sent. |
10.17.2.2 Get ACM data request p. 339
Table 10.17.2.2-1 describes the information flow of Get ACM data request from an ACM client to the ACM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user requesting for the download of the pending ACM data. |
10.17.2.3 Get ACM data response p. 339
Table 10.17.2.3-1 describes the information flow of Get ACM data response from an ACM server to the ACM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user requesting for the download of the pending ACM data. |
| ACM Data | M | Contains all ACM requests which are pending for this user. |
10.17.2.4 Group membership update request p. 339
Table 10.17.2.4-1 describes the information flow group membership update request from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the primary MC system who requests the information update. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system who requests the information update. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE) | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards the information update is sent. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards the information update is sent. |
| MC service group ID | M | Identity of the MC service group. |
| MC service ID list | M | List of identities of the MC service users that are affected by this operation. |
| Operation | M | Add to or delete from the group. |
| Urgency | O | Indicates the level of operational urgency of the group membership update request. |
|
NOTE:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
|
||
10.17.2.5 Group membership update response p. 340
Table 10.17.2.5-1 describes the information flow group membership update response from ACM client to ACM server in partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the group membership update. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the group membership update. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| MC service group ID | M | Identity of the MC service group. |
| Result | M | Indicates the acceptance or rejection to perform the operation. |
10.17.2.6 Process indication p. 340
Table 10.17.2.6-1 describes the information flow of Process indication from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user requesting for an ACM operation at partner MC system. |
| Acknowledgement | M | ACM request has been received, stored and processing is in progress. |
10.17.2.7 Interconnection group identity provision request p. 340
Table 10.17.2.7-1 describes the information flow of the interconnection group identity provision request sent from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers the interconnection group identity provision request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers the interconnection group identity provision request. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE) | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the interconnection group identity provision request is sent. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the interconnection group identity provision request is sent. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more interconnection MC service group IDs. |
| Group description per MC service group ID | O | A text description indicating the intended operational use for every interconnection MC service group ID in the list. |
|
NOTE:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
|
||
10.17.2.8 Interconnection group identity provision response p. 341
Table 10.17.2.8-1 describes the information flow of the interconnection group identity provision response sent from ACM client to ACM server in the partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system who generates the interconnection group identity provision response. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system who generates the interconnection group identity provision response. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| Provision status | M | Indicates the provisioning result. |
10.17.2.9 Add user configuration request p. 341
Table 10.17.2.9-1 describes the information flow of the add user configuration request sent from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the primary MC system which sends the request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system which sends the request. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE) | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the request is sent. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the request is sent. |
| MC service ID list | M | Set of identities of the migrating MC service user(s). |
| Request category | O | A set of request notification identifiers, e.g. high, medium, low for alerting partner MC system of specific urgencies. |
| Request duration | O | A set of time and date information for each MC service user to inform the partner MC system when the user is expected to attain service at the partner MC system and for how long that MC service user is expected to receive service(s). |
| Additional Information | O | Additional set of MC service user or UE identification information, such as labels, hardware UE identifiers or other identifying information, which may include device descriptions and user capability information. This information is linked to a particular MC service user of the MC service ID list provided. |
|
NOTE:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
|
||
10.17.2.10 Add user configuration response p. 342
Table 10.17.2.10-1 describes the information flow of the add user configuration response sent from ACM client to ACM server in the partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received add user configuration request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received add user configuration request. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| MC service ID list | M | Set of MC service IDs used in the primary MC system of the migrating MC service user(s). |
| MC service ID list | M
(see NOTE) | Set of MC service IDs of the migrating MC service user(s) created by the partner MC system of the migrating MC service user, corresponding to the MC service IDs above. |
| MC service user profile | M | Set of MC service user profiles that corresponds to each MC service ID in the list above. The user profile contains the initial UE configuration to access the partner MC system as defined in Table A.6-1 of TS 23.280, and limited information for migration for each MC service user. |
| Response | M | Result information of the add user configuration request. |
|
NOTE:
The primary MC system of the migrated MC service user keeps a mapping of the MC service IDs used by MC service user(s) in the partner MC system(s).
|
||
10.17.2.11 Remove user configuration request p. 343
Table 10.17.2.11-1 describes the information flow of the remove user configuration request sent from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which sends the request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system which sends request. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE) | The identity of the authorized user in the partner MC system which is target of the request. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the request is sent. |
| MC service ID list | M | The list of users in the partner MC system that are being requested to be removed from migration. |
| Additional information list | O | Additional information describing the reason for removing each requested user in the list for migration from the primary MC system to the partner MC system. |
|
NOTE:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
|
||
10.17.2.12 Remove user configuration response p. 343
Table 10.17.2.12-1 describes the information flow of the remove user configuration response sent from ACM client to ACM server in the partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the partner MC system which is sending the remove user configuration response. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system which is sending the remove user configuration response. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| MC service ID list | M | The list of users in the partner MC system that were requested to be removed from migration. |
| Response | M | Result information for each user in the list for removal. Success or fail. |
| Reason | O | Additional information that explains the response for each user in the list. |
10.17.2.13 Update MC service UE initial configuration request p. 344
Table 10.17.2.13-1 describes the information flow sent from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system for updating initial MC service UE configuration data information that is required by the partner MC system for preparing migrating MC service UEs.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers the update request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers the update request. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE 1) | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the update request is sent. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE 1) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the update request is sent. |
| MC service ID list | M | Set of MC service IDs of the migrating MC service users that belong to the primary MC system. |
| MC service UE initial configuration data | M
(see NOTE 2) | This information element contains the information as specified in Table A.6-1 corresponding to the MC service IDs above. |
|
NOTE 1:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
NOTE 2:
The optional MC service UE label defined in Annex A.6 is sent as blank information. present.
|
||
10.17.2.14 Update MC service UE initial configuration response p. 344
Table 10.17.2.14-1 describes the information flow sent from ACM client to ACM server in the partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received update request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received update request. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| Result | M | Result information of the update MC service UE initial configuration. |
10.17.2.15 MC service user profile update request p. 345
Table 10.17.2.15-1 describes the information flow sent from ACM client to ACM server in the primary MC system, from ACM server of primary MC system to ACM server of partner MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in partner MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers the request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the primary MC system which triggers request. |
| MC service ID | O
(see NOTE) | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the request is sent. |
| Functional alias | O
(see NOTE) | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system towards which the request is sent. |
| MC service ID | M | MC service ID of MC service user permitted to migrate, created by the partner MC system. |
| MC service user profile | M | The suggested updated MC service user profile on the partner MC system. |
| Additional Information | O | Additional information regarding the suggested updated MC service user profile on the partner MC system. |
|
NOTE:
Either the MC service ID or the functional alias must be present.
|
||
10.17.2.16 MC service user profile update response p. 345
Table 10.17.2.16-1 describes the information flow sent from ACM client to ACM server in the partner MC system, from ACM server in partner MC system to ACM server in primary MC system and from ACM server to ACM client in primary MC system.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received request. |
| Functional alias | O | The functional alias of the MC service user at the partner MC system which handled the received request. |
| MC service ID | M | The identity of the authorized user in the primary MC system which is target of the response. |
| MC service ID | M | MC service ID of MC service user permitted to migrate, created by the partner MC system. |
| Result | M | Result information of the MC service user profile update request. |
10.17.3 Common ACM procedures p. 346
10.17.3.0 Introduction p. 346
Processing of the incoming ACM commands can be handled by the ACM entities through one of the following methods:
- manually by an ACM client of an authorized user or an administrator as described under the pending requests method in clause 10.17.3.1.
- automatically either by an ACM server, or by an automated ACM client as described under clause 10.17.3.2.
10.17.3.1 Pending requests p. 346
10.17.3.1.1 General p. 346
This procedure provides the means to manage and respond to the incoming requests manually. It describes the manual option which is performed by the ACM client of an authorized MC service user or administrator.
This procedure provides the detailed description of the steps that are not included in other procedures for simplicity.
10.17.3.1.2 Procedure p. 346
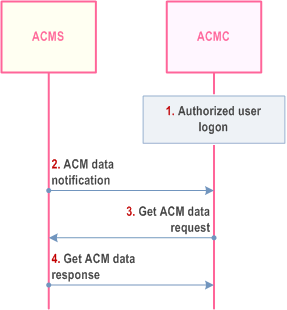
Upon receiving an ACM request the ACM server should forward the request to the authorized user at its MC system. Performing this process might require considerable waiting time if the target authorized user is not logged on.
In addition, when an ACM server receives a response to a previously sent ACM request, where the authorized user is not logged on, the ACM server should store the response and notify the authorized user when the user logs on again.
The common procedure for pending ACM request/response is shown in Figure 10.17.3.1.2-1.
Pre-conditions
- The ACM server has received an ACM request, or a response, and has stored it.
- The ACM server has received an ACM request that should be validated by an authorized user.
- The targeted ACM authorized user is currently not logged on.
10.17.3.2 Processing incoming requests automatically p. 347
10.17.3.2.1 General p. 347
This procedure provides the means to manage and respond to the incoming requests automatically. It describes the automation options performed in the ACM server or by an automated ACM client.
This procedure provides the detailed description of the steps that are not included in other procedures for simplicity.
10.17.3.2.2 Automation performed by ACM server p. 347
The partner ACM server verifies the request and sends a response to the primary MC system. Automation performed by ACM server shown in Figure 10.17.3.2.2-1.
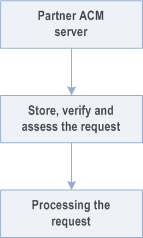
The following applies:
- The partner ACM server audits the request and, based on local policy, decides to automatically apply the configurations.
- The partner ACM server takes whatever actions are needed to apply the configurations to the partner MC system. The actions within the partner MC system to apply the configurations, including the interaction with other servers, are outside the scope of the 3GPP specification.
- The partner ACM server provides the means for the authorized users in the partner MC system to update the automation rules, or to terminate this automation, if required.
- The partner ACM server provides a tracking mechanism for the authorized users in the MC system for all automatically performed actions.
10.17.3.2.3 Automation performed by automated ACM client p. 348
The ACM server of the partner MC system sends the received ACM request to an automated ACM client for processing and sending a ACM response automatically to the primary MC system without human interaction, as shown in Figure 10.17.3.2.3-1.
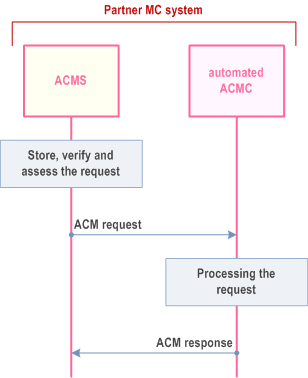
The following applies:
- The automated ACM client is enabled/logged-in and connected to ACM server
- The ACM server audits and verifies the request and, based on local policy, decides to forward the ACM request to an automated ACM client.
- The automated ACM client takes whatever actions that are needed to apply the configurations to the partner MC system. The actions within the partner MC system to apply the configurations are outside the scope of the 3GPP specification.
- The MC system provides the possibility for the authorized users in the partner MC system to update the automation rules, or to terminate the automated ACM client, if required.
- The partner ACM server provides a tracking mechanism for the authorized users in the partner MC system for all automatically performed actions by an automated client.
10.17.4 ACM Group configuration management p. 349
10.17.4.1 ACM Group membership configuration p. 349
10.17.4.1.1 General p. 349
The procedures in this clause provide the means to:
- manage users from the primary system in an interconnection MC service group that is defined in a partner MC system; and
- inform a partner MC system about interconnection MC service groups in the primary MC system.
10.17.4.1.2 Procedure p. 349
10.17.4.1.2.1 Group membership update by authorized user from a partner MC system p. 349
The procedure for an authorized MC service user in a primary MC system to manage group membership in an interconnection group that is defined in a partner MC system is shown in Figure 10.17.4.1.2.1-1.
Pre-conditions
- Primary MC system and partner MC system are interconnected
- Primary MC system and partner MC system have implemented an ACMS
- Partner MC system is the MC service group home system of an interconnection group
- The authorized MC service user of the primary MC system wants to modify the membership of MC users of the primary system in the interconnection group for which the partner MC system is the MC service group home system.
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the ACM server of the primary MC system has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the ACM server of partner MC system has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
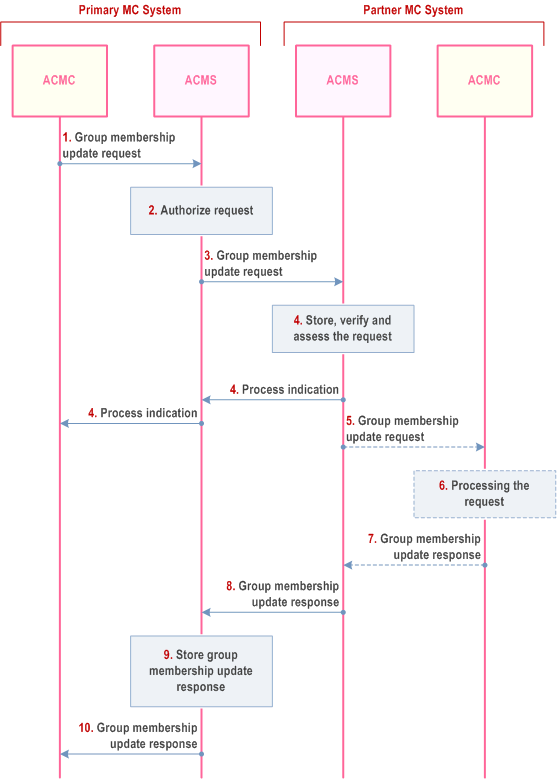
Step 1.
The ACM client in primary MC system sends a group membership update request to the ACM server in his MC system, requesting to modify the membership of users from primary MC system in an interconnection group for which partner MC system is the MC service group home system.
Step 2.
The ACM server of the primary MC system checks whether the MC service user at the ACM client is authorized for the request.
Step 3.
The ACM server of the primary MC system sends the group membership update request to the ACM server of the partner MC system, the MC service group home system of the interconnection group.
Step 4.
The ACMS of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACMS of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8, or
- the ACM server of the partner MC system requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The ACM server of the partner MC system sends the stored group membership update request to the ACM client of partner MC system.
Step 6.
The authorized MC service user of the partner MC system (manually) screens the content of the group membership update request and decides whether to approve it or not. The authorized user in the partner MC system takes whatever actions are needed to apply the group membership update. The actions within the partner MC system to apply these configurations are outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Step 7.
The ACM client of the partner MC system sends a group membership update response to the ACM server of the partner MC system.
Step 8.
The ACM server of the partner MC system sends the group membership update response to the ACM server of the primary MC system.
Step 9.
The ACM server of primary MC system stores the group membership update response. If the ACM client of primary MC system is not logged on the ACMS of primary MC system it will follow the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The ACM server of primary MC system sends the group membership update response to the ACM client of the primary MC system.
10.17.4.2 Providing interconnection MC service group ID p. 351
10.17.4.2.1 General p. 351
The MC system where the interconnection MC service group is defined, the primary MC systems, has to provide the identity of the group to the interconnected partner MC system. The procedure specified in this clause shows how an authorized user of an ACM client in primary MC system can provide the ACM server of partner MC system, or an authorized ACM client of partner MC system with one or more new interconnection MC service group IDs.
10.17.4.2.2 Providing identity of interconnection MC service group p. 351
The procedure, which enables an authorized MC service user of a primary MC system to provide a list of interconnection group ID(s) to a selected authorized user of a partner MC system, is shown in Figure 10.17.4.2.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- Primary MC system and partner MC system are interconnected.
- Both MC systems have implemented an ACM functionality.
- The primary MC system is the MC service group home system for one or more interconnection groups.
- An MC service user of the primary MC system is authorized to provide a list of interconnection group IDs to partner MC system.
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the primary ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the partner ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
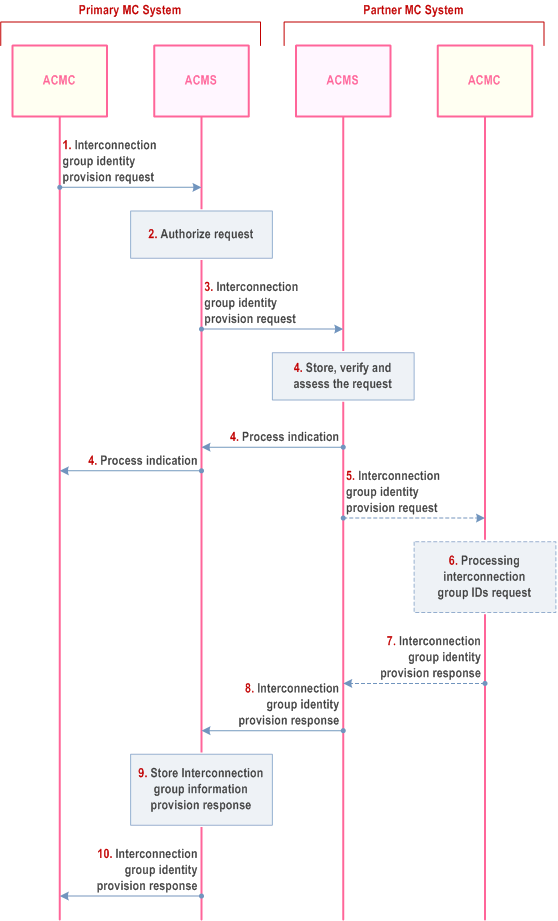
Step 1.
The ACM client in the primary MC system sends an interconnection group identity provision request to the ACM server in the primary MC system, providing a list of interconnection group IDs and the ID of the selected authorized user in the partner MC system.
Step 2.
The ACM server of the primary MC system checks whether the MC service user at ACM client is authorized for the request. If the authorization check fails, the procedure is stopped.
Step 3.
The ACM server of the primary MC system forwards the interconnection group identity provision request to the ACM server in the partner MC system.
Step 4.
The ACMS of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACMS of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8,
-
the ACM server requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias, the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The ACM server of the partner MC system forwards the stored interconnection group identity provision request to the ACM client of the partner MC system.
Step 6.
The selected authorized user of the partner MC System processes the interconnection group IDs, e.g. by saving the information for future use. The authorized user in the partner MC system takes whatever actions are needed to handle the request. The actions taken within the partner MC system are outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Step 7.
The ACM client of the partner MC system sends a interconnection group identity provision response to the ACM server of the partner MC system.
Step 8.
The ACM server of the partner MC system forwards the interconnection group identity provision response to the ACM server in the primary MC system.
Step 9.
The ACM server of the primary MC system stores the interconnection group identity provision response. If the primary ACM client is not logged on, the primary ACM server will follow the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The ACM server of the primary MC system forwards the interconnection group identity provision response to the ACM client of primary MC system, informing the authorized user of the primary MC system that the list of interconnection group IDs has been provided to the selected authorized user of the partner MC system.
10.17.5 ACM user migration management p. 353
10.17.5.1 General p. 353
User migration management enables adding or removing of MC service users of the primary MC system for migration at a partner MC system. An authorized MC service user can request adding or removing MC service users of his primary MC system for migration at a partner MC system by means of his ACM client.
10.17.5.2 Adding users for migration to a partner MC system p. 353
The procedure for an authorized MC service user in a primary MC system to request a partner MC system to authorize a list of MC user IDs from its MC System to migrate to that partner MC System is shown in Figure 10.17.5.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The primary MC system and the partner MC system are interconnected.
- The primary MC system and the partner MC system have implemented an ACMS.
- The MC service user at the ACM client of the primary MC system is authorized to request adding users for migration to the partner MC system.
- The MC service user at the ACM client of the partner MC system is authorized to respond to requests for adding a list of users for migration from the primary MC system.
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the primary ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the partner ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
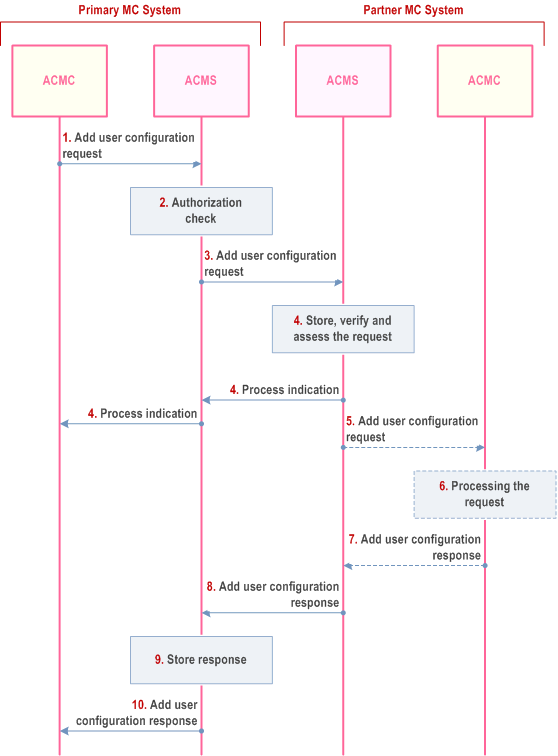
Step 1.
The primary ACMC sends add user configuration request to the primary ACMS, requesting to authorize a list of MC users from the primary MC System to migrate to the partner MC System.
Step 2.
The primary ACMS performs an authorization check to verify that the MC service user is authorized to perform this action. If the authorization check fails, the procedure is stopped.
Step 3.
The primary ACMS sends the add user configuration request to the partner ACMS.
Step 4.
The ACMS of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACMS of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8,
-
the ACM server requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias, the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The partner ACMS sends the stored add user configuration request to the partner ACM client.
Step 6.
The authorized MC service user of partner MC system checks the content of the add user configuration request and decides whether to approve it or not. The authorized user in the partner MC system takes whatever actions are needed to apply the configurations. The actions within the partner MC system to apply the configurations are outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Step 7.
The partner ACM client sends add user configuration response to the partner ACM server.
Step 8.
The partner ACM server sends add user configuration response to the primary ACM server.
Step 9.
The primary ACM server stores the add user configuration response. If the primary ACM client is not logged on the primary ACM server will follow the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The primary ACM server sends the add user configuration response to the primary ACM client.
10.17.5.3 Removing users for migration from a partner MC system p. 355
The procedure for an authorized MC service user in the primary MC system, that is sent to an authorized user in the partner MC system, to request that certain users be removed from migration access in the partner MC system is shown in Figure 10.17.5.3-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The primary MC system and the partner MC system are interconnected.
- The primary MC system and the partner MC system have implemented an ACMS.
- The MC service user in the primary MC system is authorized to request a list of MC service users be removed from the partner MC system for migration from the primary MC system.
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the primary ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the partner ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
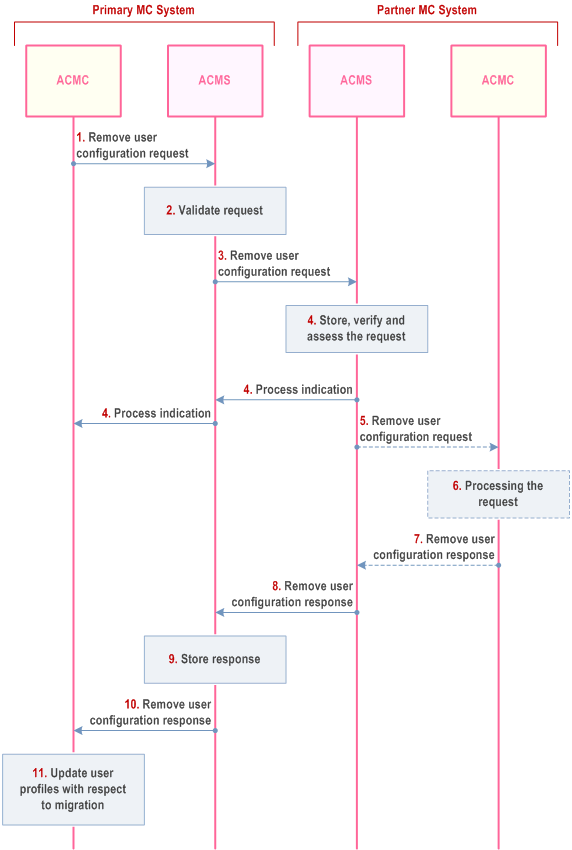
Step 1.
The ACM client in the primary MC system sends a remove user configuration request to the ACM server in the primary MC system. This request includes a list of MC service users to be removed for migration access in the partner MC system.
Step 2.
The ACM server in the primary MC system validates whether the MC service user is authorized for the request. If the authorization check fails, the procedure is stopped.
Step 3.
The ACM server in the primary MC system sends the remove user configuration request to the ACM server in the partner MC system.
Step 4.
The ACM server of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACM server of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8,
-
the ACM server requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias, the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The ACM server in the partner MC System sends the remove user configuration request to the ACM client in the partner MC system.
Step 6.
The authorized MC service user of partner MC system checks the content of the request and decides whether to approve it or not. The authorized MC service user in the partner MC system takes whatever actions are needed to remove the requested user from migration access to the partner MC system. The actions within the partner MC system to remove users are outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Step 7.
The ACM client of the partner MC system sends a remove user configuration response to the ACM server in the partner MC system. The target of this response is the original MC service user in the primary MC system that sent the remove user configuration request.
Step 8.
The ACM server in the partner MC system sends the remove user configuration response to the ACM server in the primary MC system.
Step 9.
The ACM server in the primary MC system stores the remove user configuration response. If the primary ACM client is not logged on the primary ACM server will follow the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The ACM server in the primary MC system sends the remove user configuration response to the ACM client in the primary MC system.
Step 11.
The authorized MC service user in the primary MC system takes whatever actions are needed (if any) to update the user profiles in the primary MC system for those users that no longer have migration access to the partner MC system.
10.17.6 ACM updating MC service UE initial configuration for migration p. 357
10.17.6.1 General p. 357
MC service UE initial configuration for migration is essential to perform migration because this configuration contains connectivity information such as APN, server URIs and other connectivity information of the partner MC system. MC service users which had been added (clause 10.17.5.2) for migration to a partner MC system will have received user profiles containing this configuration (table A.6-1) which enables them to get connected to the partner MC system.
In case changes to the connectivity information occurs, the MC service UE initial configuration shall be updated.
10.17.6.2 Procedure p. 357
The procedure for an authorized MC service user in a primary MC system to update initial MC service UE configuration data information in the partner MC system is shown in Figure 10.17.6.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- Primary MC system and partner MC system are interconnected.
- Both MC systems have implemented ACM functionality.
- The set of MC service IDs and the MC service UE initial configuration of the migrating MC service users have been already sent by the primary MC system to the partner MC system, as specified in clause 10.17.5 ACM user migration management (between interconnected MC systems).
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the primary ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the partner ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
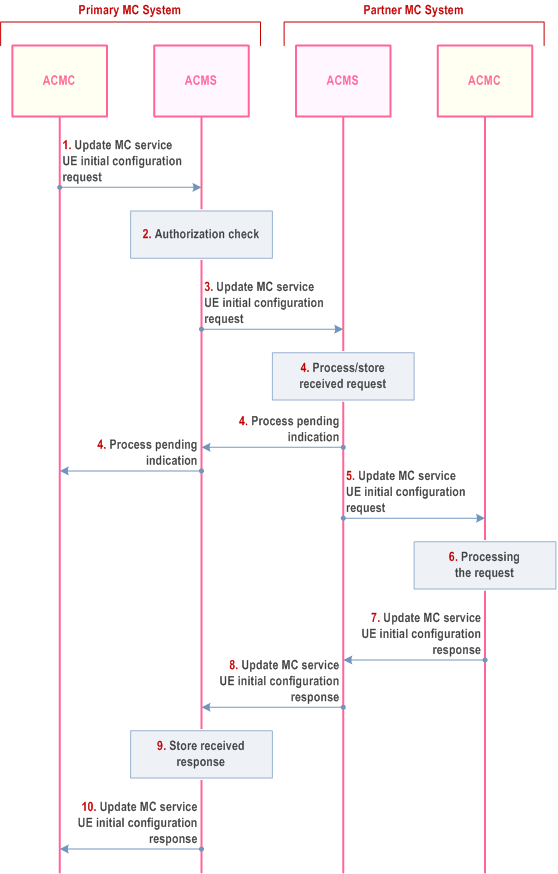
Step 1.
The primary ACM client sends an update MC service UE initial configuration request to the primary ACM server, providing the initial MC service UE configuration data as specified in TS 23.280, Annex 6 to the primary MC System.
Step 2.
The primary ACM server performs an authorization check to verify that the MC service user is authorized to perform this action. If the authorization check fails, the procedure is stopped.
Step 3.
The primary ACM server sends the update MC service UE initial configuration request to the partner ACM server.
Step 4.
The ACM server of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACM server of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8,
-
the ACM server requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias, the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The partner ACM server forwards the stored update MC service UE initial configuration request to the partner ACM client.
Step 6.
The authorized MC service user of partner MC system processes the received update MC service UE initial configuration request.
Step 7.
The partner ACM client sends update MC service UE initial configuration response to the partner ACM server.
Step 8.
The partner ACM server sends update MC service UE initial configuration response to the primary ACM server.
Step 9.
The primary ACM client stores the update MC service UE initial configuration response as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The primary ACM server forwards the update MC service UE initial configuration response to the primary ACM client.
10.17.7 ACM updating MC service user profiles assigned from partner MC system p. 359
10.17.7.1 General p. 359
A primary MC system may request through ACM entities to add a list of its MC service users for migration to a connected partner MC system as specified in clause 10.17.5 ACM user migration management. In case the partner MC system agrees to accept these users for migration it will reply with a response containing assigned MC service user identities and MC service user profiles. Those will be applicable and valid while the requested primary MC service users are migrated into the partner MC system.
In case, the primary MC system may want to update the received MC service user profiles from the partner MC system it can send a request for updating those as described in this clause.
10.17.7.2 Procedure p. 359
The procedure for an authorized MC service user in a primary MC system to request MC service user profile update from a partner MC system is shown in Figure 10.17.7.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- Primary MC system and partner MC system are interconnected.
- Both MC systems have implemented ACM functionality.
- When a functional alias is used as the target of the request by an ACM client in the primary MC system, it is required that the primary ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the primary MC system, and that the partner ACM server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the partner MC system.
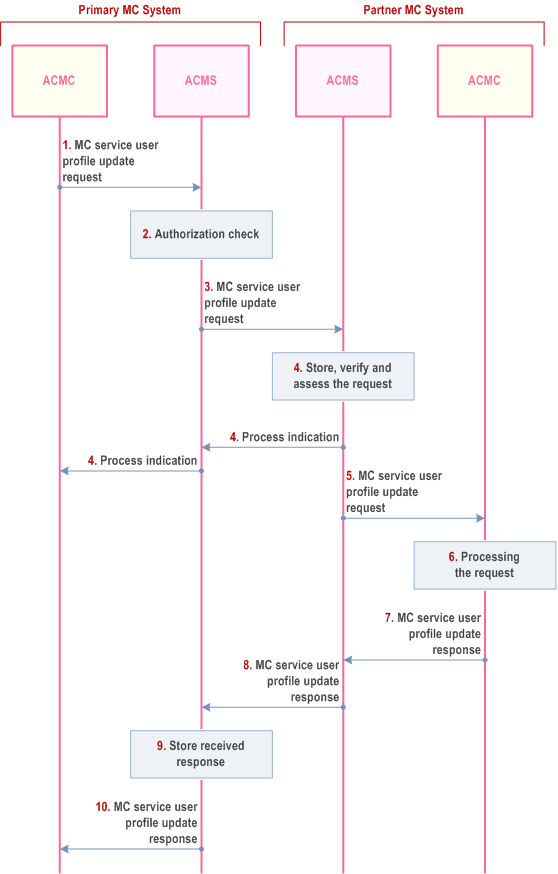
Step 1.
The primary ACMC sends MC service user profile update request to the primary ACMS providing the required changes for the MC service user that is migrated to the partner MC System.
Step 2.
The primary ACMS performs an authorization check to verify that the MC service user is authorized to perform this action. If the authorization check fails, the procedure is stopped.
Step 3.
The primary ACMS sends the MC service user profile update request to the partner ACMS.
Step 4.
The ACMS of the partner MC system sends a process indication to primary MC system, and stores, verifies and assesses the incoming request.
Based on local policy,
Step 5.
- the ACMS of the partner MC system may automatically handle the request as described in clause 10.17.3.2 and continues with step 8,
-
the ACM server requests verification by an ACM client: If the authorized user in the partner MC system is not logged on, the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1 is followed. If the request targets a functional alias, the ACM server of the partner MC system resolves the functional alias (based on the current state of the functional alias) and proceeds as follows:
- if the functional alias is active for one ACM client, the request is sent to the ACM client;
- if the functional alias is active for more than one ACM client, the ACM server sends the request to one of these ACM clients based on the local policy;
- if the functional alias is not currently active, the ACM server of the partner MC system stores the request.
The partner ACMS forwards the stored MC service user profile update request to the partner ACMC.
Step 6.
The authorized MC service user of partner MC system checks the content of the MC service user profile update request and decides whether to approve it or not. The authorized user in the partner MC system takes whatever actions are needed to apply the MC service user profile update. The actions within the partner MC system to apply this configuration are outside the scope of the 3GPP specifications.
Step 7.
The partner ACMC sends MC service user profile update response to the partner ACMS.
Step 8.
The partner ACMS sends MC service user profile update response to the primary ACMS.
Step 9.
The primary ACMS stores the MC service user profile update response. If the primary ACMC is not logged on the primary ACMS will follow the pending request procedure as described in clause 10.17.3.1.
Step 10.
The primary ACMS forwards the MC service user profile update response to the primary ACMC.