Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.5.1
1…
5…
6
7…
8…
9…
10…
10.1.5…
10.2…
10.2.6…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3.8…
10.8…
10.9…
10.9.3.9…
10.10…
10.10.3
10.11…
10.12…
10.13…
10.14…
10.15…
10.16…
10.17…
10.18…
10.18.3…
11…
11.5…
A…
B…
C…
E…
10.8 Affiliation and de-affiliation to/from MC service group(s)
10.8.1 General
10.8.2 Information flows
10.8.3 Affiliation
10.8.4 De-affiliation from MC service group(s)
10.8.5 Remote change of affiliation
...
...
10.8 Affiliation and de-affiliation to/from MC service group(s) p. 172
10.8.1 General p. 172
The following subclauses specify the procedures for affiliation and de-affiliation to a single MC service, and which are utilised by the following MC services:
MC service specific pre-requisites and resultant behaviour by functional entities in performing these procedures are specified in the respective MC service TSs as listed above.
10.8.2 Information flows p. 172
10.8.2.1 MC service group affiliation request p. 172
Table 10.8.2.1-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation request from the MC service client to the MC service server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate. |
10.8.2.2 MC service group affiliation request (MC service server - MC service server) p. 172
Table 10.8.2.2-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation request between the MC service servers.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
10.8.2.3 MC service group affiliation response p. 172
Table 10.8.2.3-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation response from the MC service server to the MC service client. This information flow is sent individually addressed on unicast or multicast.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate. |
| Affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.4 MC service group affiliation response (MC service server - MC service server) p. 173
Table 10.8.2.4-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation response between the MC service servers.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
| Affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.5 Void
10.8.2.6 MC service group de-affiliation request p. 173
Table 10.8.2.6-1 describes the information flow MC service group de-affiliation request from the MC service client to the MC service server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate. |
| Scope of De-affiliation request | M | Indicating, whether de-affiliation is requested for this specific MC service client only, or for all MC service clients where this MC service ID has logged on. |
10.8.2.7 MC service group de-affiliation request (MC service server - MC service server) p. 173
Table 10.8.2.7-1 describes the information flow MC service group de-affiliation request between the MC service servers.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
| Scope of De-affiliation request | M | Indicating, whether de-affiliation is requested for this specific MC service client only, or for all MC service clients where this MC service ID has logged on. |
10.8.2.8 MC service group de-affiliation response p. 173
Table 10.8.2.8-1 describes the information flow MC service group de-affiliation response from the MC service server to the MC service client. This information flow is sent individually addressed on unicast or multicast.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate. |
| De-affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the de-affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.9 MC service group de-affiliation response (MC service server - MC service server) p. 174
Table 10.8.2.9-1 describes the information flow MC service group de-affiliation response between MC service servers.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group de-affiliation request. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate and is defined in the destination MC system. |
| De-affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the de-affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.10 Void
10.8.2.11 MC service group affiliation change request p. 174
Table 10.8.2.11-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation change request from the MC service client to the MC service server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation change request. |
| MC service ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service IDs to which the originator intends to the change their MC service group affiliation relationship. |
| MC service group ID list (per listed MC service ID) | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to change their affiliation relationship with the target user. |
| Requested affiliation status (per group ID) | M | Indicates if the request is to affiliate or deaffiliate. |
| Change request type | M | Indicates the affiliation request type, i.e. mandatory or negotiated. |
10.8.2.12 MC service group affiliation change response p. 174
Table 10.8.2.12-1 describes the information flow MC service group affiliation change response from the MC service server to the MC service client. This information flow is sent individually addressed on unicast or multicast.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the originator who triggers the MC service group affiliation request. |
| MC service ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service IDs to which the originator intends to the change their MC service group affiliation relationship. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to change their affiliation relationship with the target user. |
| Affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the affiliation relationship change result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.13 MC service group de-affiliation notification |R15| p. 175
Table 10.8.2.13-1 describes the information flow MC service group de-affiliation notification from the MC service server to the MC service client. This information flow is sent individually addressed on unicast or multicast.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID of the MC service user that will be de-affiliated. |
| MC service group ID list | M | A list of one or more MC service group IDs to which the originator intends to de-affiliate. |
| De-affiliation status per MC service group ID | M | Indicates the de-affiliation result for every MC service group ID in the list. |
10.8.2.14 Notify group dynamic data request |R16| p. 175
Table 10.8.2.14-1 describes the information flow notify group dynamic data request from the MC service server to the group management server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MC service group ID | M | The MC service group ID to which the GMS has subscribed and for which the group dynamic data needs to be updated. |
| MC service ID | M | The MC service ID for which the group dynamic data (e.g. affiliation status, de-affiliation status) needs to be updated. |
| Affiliation or de-affiliation status | M | Indicates the affiliation status or de-affiliation status for the MC service group ID. |
10.8.3 Affiliation p. 175
10.8.3.1 MC service group affiliation procedure p. 175
Procedure for affiliation to MC service group(s) for a single MC service is described in Figure 10.8.3.1-1.
Pre-conditions:
- MC service client has already been provisioned (statically or dynamically) with the group information, or a pointer to the group information, that the MC service client is allowed to be affiliated;
- MC service server may have retrieved the user profile and group policy from the group configuration e.g. which user(s) are authorized to affiliate to what MC service group(s), priority, and other configuration data;
- MC service client may have indicated to the group management server that it wishes to receive updates of group configuration data for MC service groups(s) for which it is authorized (as described in subclause 10.1.5.3);
- The MC service client triggers the affiliation procedure. This is an explicit affiliation caused either by the MC service user or determined by a trigger event such as the MC service UE coming within a permitted geographic operational area of an MC service group; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
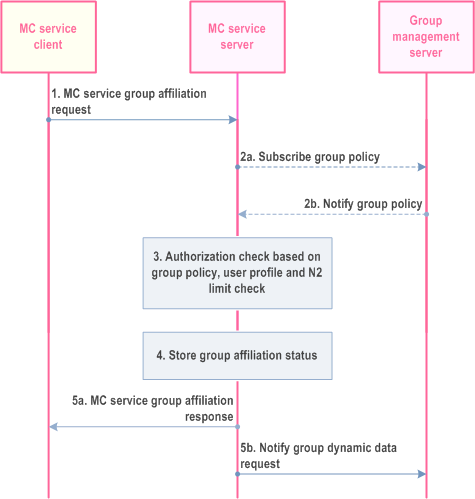
Step 1.
MC service client of the MC service user requests the MC service server to affiliate to an MC service group or a set of MC service groups.
Step 2a.
MC service server checks if the group policy is locally cached. If the group policy is not locally cached on the MC service server then MC service server requests the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server.
Step 2b.
MC service server receives the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server.
Step 3.
Based on the group policy from the group configuration and user profile, the MC service server checks if the MC service group(s) is enabled and if the MC service client is authorised to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s). The MC service server also performs the check for the maximum limit of the total number (N2) of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to simultaneously.
Step 4.
If the user of the MC service client is authorised to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s) then the MC service server stores the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 5.
MC service server confirms to the MC service client the affiliation (5a) and updates the group management server with the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) (5b).
10.8.3.2 Affiliation to MC service group(s) defined in partner MC system without topology hiding p. 176
10.8.3.2.1 Functional description p. 176
When an MC service client wants to affiliate to MC service group(s) which is defined in a partner MC system for a single MC service and where topology hiding is not required, it shall be subject to authorization from the partner MC system where the MC service group(s) is defined, and whether it subjects to authorization from the primary MC system is conditional.
10.8.3.2.2 Procedure p. 177
The procedure for affiliation to MC service group(s) which is defined in a partner MC system where topology hiding is not required for a single MC service is described in Figure 10.8.3.2.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service client has already been provisioned (statically or dynamically) with the group information, or a pointer to the group information, that the MC service client is allowed to be affiliated;
- The MC service server of the primary MC system may have locally cached the MC service group affiliation status of the MC service user;
- The MC service server of the partner MC system may have retrieved the group related information from the group management server;
- The MC service client may have indicated to the group management server of the partner MC system that it wishes to receive updates of group configuration data for MC service group(s) for which it is authorized (as described in subclause 10.1.5.3);
- The MC service user triggers the affiliation procedure. This is an explicit affiliation caused by the MC service user; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
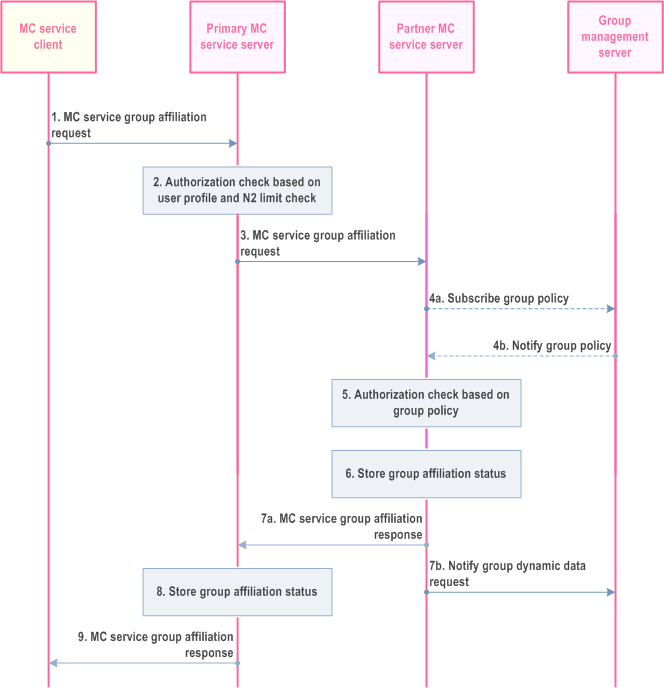
Step 1.
The MC service client requests the MC service server of the primary MC system to affiliate to an MC service group or a set of MC service groups.
Step 2.
The MC service server of the primary MC system checks if the MC service client is authorized to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s) based on the user profile. The MC service server also performs the check for the maximum limit of the total number (N2) of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to simultaneously.
Step 3.
Based on the group information included in the request, the MC service server of the primary MC system, it determines to send group affiliation request to the corresponding MC service server of the partner MC system. The request may be routed through intermediate signalling nodes.
Step 4a.
The MC service server of the partner MC system checks if the group policy is locally cached. If the group policy is not locally cached on the MC service server then MC service server subscribes to the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server.
Step 4b.
The MC service server of the partner MC system receives the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server via notification and locally caches the group policy from the group configuration.
Step 5.
Based on the group policy, the MC service server of the partner MC system checks if the MC service group(s) is not disabled and if the user of the MC service client is authorised to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s).
Step 6.
If the user of the MC service client is authorised to affiliate to the requested MC service group(s) then the MC service server of the partner MC system stores the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 7.
The MC service server of the partner MC system sends the affiliation status result of requested MC service group(s) to the MC service server of the primary MC system (7a) and updates the group management server with the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) (7b).
Step 8.
The MC service server of the primary MC system stores the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 9.
The MC service server of the primary MC system sends the group affiliation status result for the requested MC service group(s) to the MC service client.
10.8.3.2a Affiliation to MC service group(s) defined in partner MC system using topology hiding |R15| p. 178
10.8.3.2a.1 Functional description p. 178
When an MC service client wants to affiliate to MC service group(s) which is defined in a partner MC system for a single MC service using topology hiding, it shall be subject to authorization from the partner MC system where the MC service group(s) is defined, and may also be subject to authorization from the serving MC system of the MC service client.
10.8.3.2a.2 Procedure p. 178
Figure 10.8.3.2a.2-1 illustrates the group affiliation procedure to an MC service group defined in the partner MC system of the serving MC system of the MC service user, where topology hiding procedures are required.
Pre-conditions:
- MC service client 1 is service authorized within its serving MC system.
- The group host MC service server of the MC service group to which the MC service user of MC service client 1 wishes to affiliate is located in the partner MC system of the serving MC system of MC service client 1
- Topology hiding is required by both MC systems
- The serving MC system of MC service client 1 and the group home MC system are configured to allow topology hiding to take place.
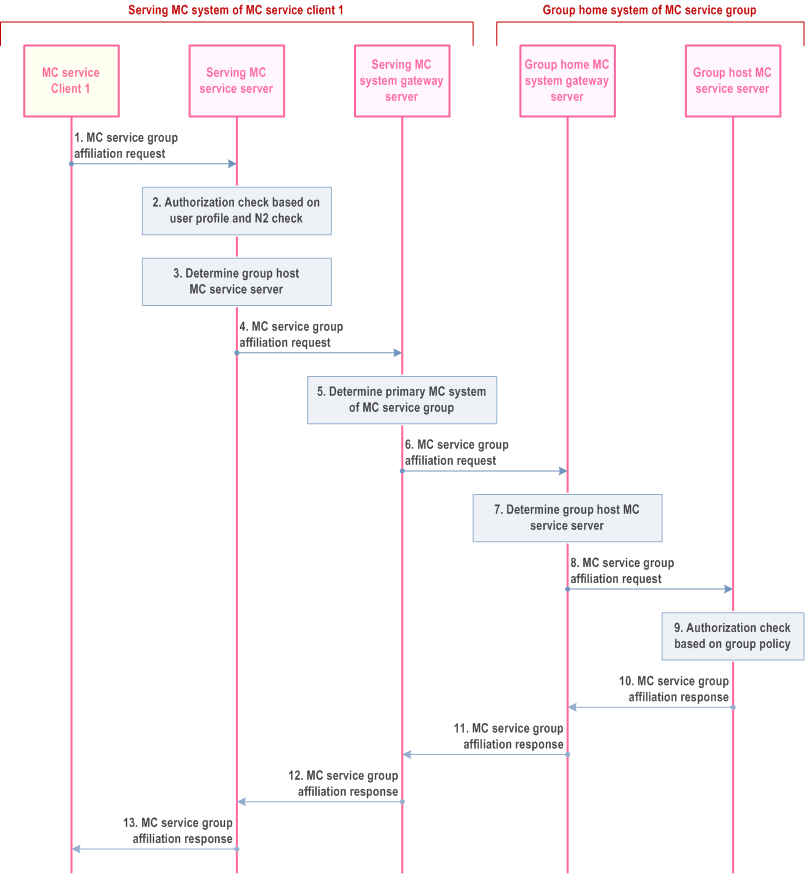
Step 1.
MC service client 1 initiates an MC service group affiliation request to the serving MC service server of MC service client 1 on behalf of its MC service user.
Step 2.
The MC service server of the serving MC system checks that the MC service client 1 is authorized to affiliate to the requested MC service group based on the user profile, and that the maximum number of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to (N2) has not been exceeded.
Step 3.
The MC service server determines the group host MC service server of the MC service group. The MC service group is identified to have a different group home MC system, and if topology hiding is required by the serving MC system of MC service client 1, the serving MC system gateway server is determined to act as proxy group host MC service server for the MC service group.
Step 4.
The MC service server of the serving MC system forwards the MC service group affiliation request to the gateway server of the serving MC system.
Step 5.
The gateway server determines which MC system is the group home system for the MC service group.
Step 6.
The gateway server in the serving system of MC service client 1 forwards the MC service group affiliation request to the gateway server of the group home MC system of the MC service group.
Step 7.
The gateway server of the group home MC system of the MC service group determines which MC service server is the group host MC service server for that MC service group.
Step 8.
The gateway server of the group home system of the MC service group forwards the MC service group affiliation request to the group host MC service server of the MC service group.
Step 9.
The group host MC service server in the partner MC system checks whether the user of MC service client 1 is authorized to affiliate to the MC service group based on the MC service group configuration. The group host MC service server may optionally subscribe to the GMS containing the group configuration information, and receive notification of group policy from the group configuration. The group host MC service server shall update the GMS with the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group by sending the notify group dynamic data request (not shown in the figure).
Step 10.
The group host MC service server sends an MC service group affiliation response to the gateway server in the group home MC system of the MC service group.
Step 11.
The gateway server in the group home MC system forwards the MC service group affiliation response to the gateway server in the serving MC system of MC service client 1.
Step 12.
The gateway server in the serving MC system of MC service client 1 forwards the MC service group affiliation response to the serving MC service server of MC service client 1.
Step 13.
The serving MC service server of MC service client 1 forwards the MC service group affiliation response to MC service client 1.
10.8.4 De-affiliation from MC service group(s) p. 180
10.8.4.1 General p. 180
When an MC service user does not want to communicate with an MC service group anymore for a single MC service, then the MC service user can revoke its affiliation to the MC service group.
10.8.4.2 MC service group de-affiliation procedure p. 180
The procedure for revoking the affiliation with an MC service group for a single MC service is described in Figure 10.8.4.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- MC service server has already subscribed to the MC service group information from group management server and has stored the data of MC service group(s) to which the MC service user is affiliated to;
- The MC service client triggers the de-affiliation procedure. This is an explicit de-affiliation requested either by the MC service user or determined by a trigger event such as the MC service UE moving outside a permitted geographic operational area of an MC service group; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
- The MC service server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
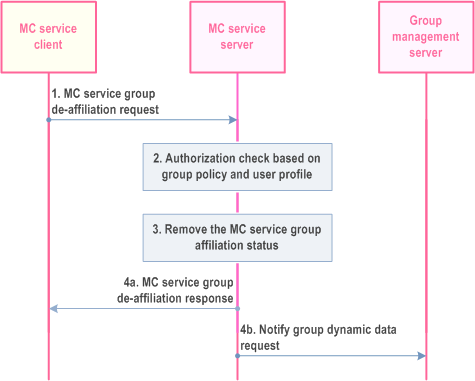
Step 1.
MC service client requests the MC service server to de-affiliate from an MC service group or a set of MC service groups.
Step 2.
Based on the user profile and stored group policy from the group configuration, the MC service server checks if the user of the MC service client is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s) and if the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s). The authorisation check includes whether the MC service user has activated a certain functional alias which prevents de-affiliating or whether the MC service user is the last user who has bound a certain functional alias to the group which also prevents de-affiliating.
Step 3.
If the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s), is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s) then the MC service server removes the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s), either for the requesting specific MC service client only, or for all MC service clients, where this user has logged on to.
Step 4.
MC service server provides to the MC service client the group de-affiliation response (4a). When the MC service user has logged into multiple MC service clients concurrently, the MC service server updates the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) only when the MC service ID de-affiliates for the provided MC service group(s) from the last MC service client. If the MC service user has logged into only one client then the MC service server and update the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) (4b).
10.8.4.3 De-affiliation from MC service group(s) defined in partner MC system p. 181
The procedure for de-affiliation from affiliated MC service group(s) which is defined in partner MC system for a single MC service is described in Figure 10.8.4.3-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The primary/partner MC service servers have already subscribed to the group information from group management server and stored the data of MC service group(s) to which the MC service user intends to de-affiliate; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
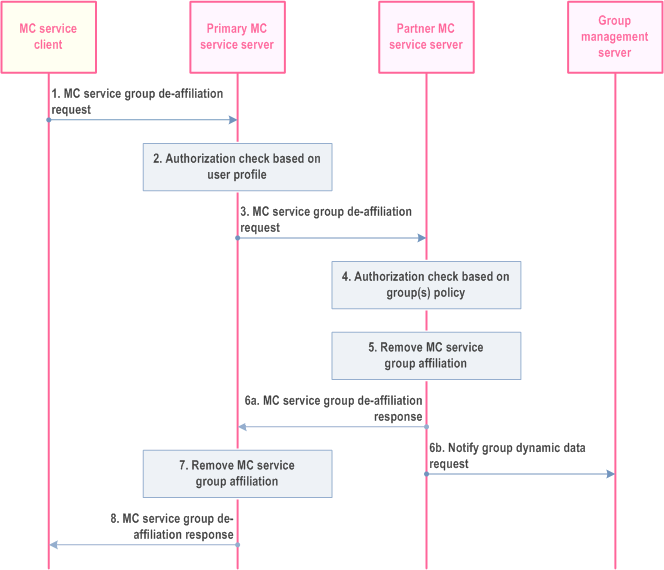
Step 1.
The MC service client requests the primary MC service server to de-affiliate from an MC service group or a set of MC service groups.
Step 2.
The primary MC service server checks if the MC service client is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s) based on the user profile. The primary MC service server performs the check if the user has affiliated to the MC service groups.
Step 3.
Based on the MC service group information included in the request, the primary MC service server determines to send MC service group de-affiliation request to the corresponding partner MC service server. The request may be routed through some intermediate signalling nodes.
Step 4.
Based on the stored group policy from the group configuration, the partner MC service server checks if the MC service group is not disabled and if the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s) and is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s).
Step 5.
If the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s) and is authorized to de-affiliate to the requested MC service group(s), then the partner MC service server removes the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s), either for the requesting specific MC service client only, or for all MC service clients, where this user has logged on to.
Step 6.
The partner MC service server sends the MC service group de-affiliation response to primary MC service server (6a) . When the MC service user has logged into multiple MC service clients concurrently, the MC service server updates the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) only when the MC service ID de-affiliates for the provided MC service group(s) from the last MC service client. If the MC service user has logged into only one client then the MC service server and updates the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) (6b).
Step 7.
The primary MC service server will remove any information stored about the user's affiliation with requested MC service group(s) of partner MC system, considering that the user may have logged on to multiple MC service clients and that de-affiliation may have been performed only for the specific MC service client from which the de-affiliation request has been sent, or for all MC service clients, where this user has been affiliated to this MC service group.
Step 8.
The primary MC service server sends the MC service group de-affiliation response to the MC service client.
10.8.4.4 MC server initiated group de-affiliation procedure |R15| p. 183
The procedure for the MC service server to trigger a de-affiliation with an MC service group is described in Figure 10.8.4.4-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service user has previously affiliated to the group, and the MC service server has stored the status of MC service group affiliation;
- Following a relevant trigger condition, e.g. the user moving outside the permitted geographical operational area of the MC service group, or the permitted geographical operational area is modified, causing user outside of the permitted geographical operational area, the MC service server de-affiliates the user from the MC service group; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
- The MC service server has subscribed to the MC service functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
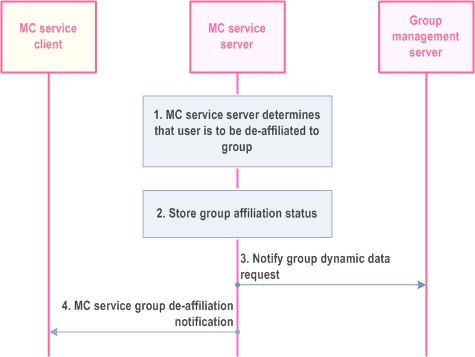
Step 1.
The MC service server determines the MC service client could be de-affiliated to the group again due to the trigger event, e.g. the permitted geographical operational area is modified, causing the user outside of the permitted geographical operational area of the MC service group, the MC service server needs to de-affiliate the MC Service user from the group.
Step 2.
The MC service server changes the affiliation status of the user.
Step 3.
The MC service server updates the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 4.
The MC service server provides a de-affiliation notification with the group information to the MC service client.
10.8.4.5 MC server initiated group de-affiliation from group defined in partner MC system |R15| p. 183
The procedure for the MC service server to trigger a de-affiliation from an MC service group which is defined in partner MC system is described in Figure 10.8.4.5-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service user has previously affiliated to the group, and the MC service server has stored the status of MC service group affiliation;
- Following a relevant trigger condition (e.g. the user moving outside the permitted geographical operational area of the MC service group, or the permitted geographical operational area is modified), the de-affiliation for the MC service user is initiated by the MC service server from the MC service group;
- The primary/partner MC service servers have already subscribed to the group information from group management server and stored the data of MC service group(s) to which the MC service user intends to de-affiliate; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
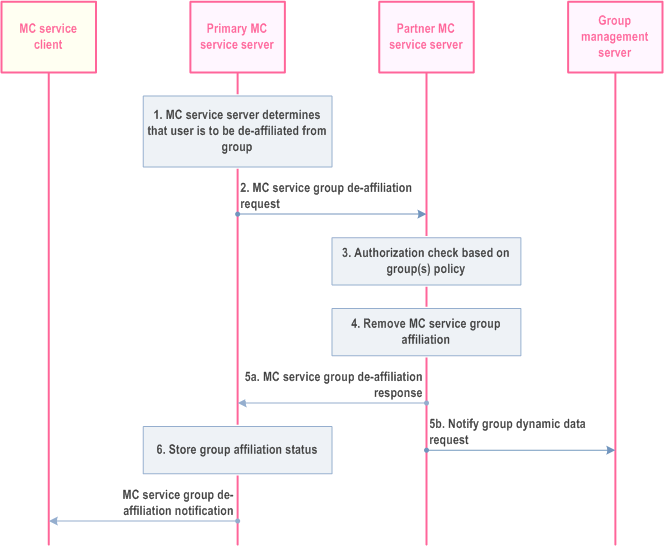
Step 1.
The MC service server determines the MC service client could be de-affiliated to the group due to the trigger event, e.g. the permitted geographical operational area is modified, causing the user outside of the permitted geographical operational area of the MC service group, the MC service server needs to de-affiliate the MC Service user from the group.
Step 2.
Based on the stored MC service group information, the primary MC service server determines to send MC service group de-affiliation request to the corresponding partner MC service server. The request may be routed through some intermediate signalling nodes.
Step 3.
Based on the stored group policy from the group configuration, the partner MC service server checks if the MC service group is not disabled and if the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s) and is authorized to de-affiliate from the requested MC service group(s).
Step 4.
If the user of the MC service client has affiliated to the requested MC service group(s) and is authorized to de-affiliate to the requested MC service group(s), then the partner MC service server removes the affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s).
Step 5.
The partner MC service server sends the MC service group de-affiliation response to primary MC service server (5a) and updates the group management server with the de-affiliation status of the user for the requested MC service group(s) (5b).
Step 6.
The primary MC service server changes the affiliation status of the user.
Step 7.
The MC service server provides a de-affiliation notification with the group information to the MC service client.
10.8.5 Remote change of affiliation p. 185
10.8.5.1 Remote change of affiliation for groups defined in primary MC system p. 185
10.8.5.1.1 Authorized user remotely changes another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) - mandatory mode p. 185
The procedure for an authorized user to remotely change another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) for a single MC service without requiring the target user's approval is described in Figure 10.8.5.1.1-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service client 1 (authorized user 1) has already been provisioned (statically or dynamically) with the target MC service user's information and its group information, that target MC service user 2 is allowed to be affiliated or de-affiliated;
- The primary MC service server may have retrieved the user profile or group policy from the group configuration e.g. information regarding user(s) authorization to affiliate or to de-affiliate to MC service group(s), priority, and other related configuration data; and
- The group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
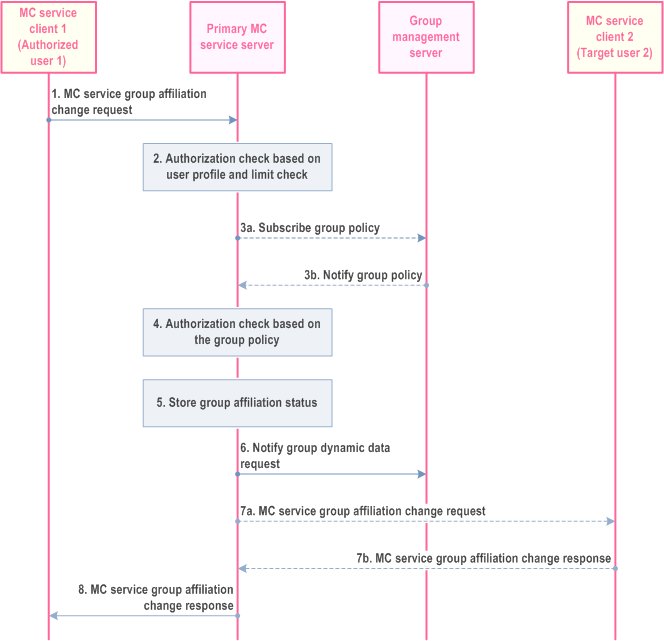
Step 1.
When an authorized user requires one or more MC service users to change the affiliation to an MC service group or set of MC service groups, the MC service client 1 of the authorized user 1 sends MC service group affiliation change request with the indication of mandatory mode to the primary MC service server. The information used to indicate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target MC service user 2 and the MC service group(s) shall be included.
Step 2.
The primary MC service server shall check if the MC service user 1 is authorized to initiate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target user 2 and the MC service group(s). The primary MC service server shall check if the target MC service user(s) are authorized for the requested affiliation relationship based on the user profile. The primary MC service server also performs the check for the maximum limit on the total number (N2) of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to simultaneously.
Step 3a.
The primary MC service server checks if the group policy is locally cached. If the group policy is not locally cached on the MC service server, then, the MC service server subscribes to the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server.
Step 3b.
The primary MC service server receives the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server via notification and locally caches the group policy from the group configuration.
Step 4.
Based on the group policy, the primary MC service server checks if the target MC service user 2 is authorized to affiliate or de-affiliate to the MC service group(s).
Step 5.
If the target MC service user 2 is authorized to affiliate or de-affiliate to the MC service group(s) then the primary MC service server stores the new requested affiliation status of the target MC service user 2 for the MC service group(s).
Step 6.
If the requested affiliation status is a change from the current affiliation status, then the primary MC service server updates the group management server with the affiliation status of the MC service user 2 for the MC service group(s).
Step 7a.
If the requested affiliation status is a change the primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change request with the indication of mandatory mode to MC service client 2 of the target MC service user 2. The target MC service user 2 receives the latest information about the affiliated MC service groups. The MC service client 2 may subscribe to the affiliated MC service groups information with the group management server.
Step 7b.
The MC service user 2 provides a response to the primary MC service server by sending an MC service group affiliation change response.
Step 8.
The primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change response to MC service client 1. If the requested affiliation status was not changed (see 7a), then the MC service server creates an appropriate (accept) MC service group affiliation change response to send to MC service client 1.
10.8.5.1.2 Authorized user remotely changes another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) - negotiated mode p. 186
The procedure for the authorized user to remotely change another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) for a single MC service with the target MC service user's approval is described in Figure 10.8.5.1.2-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service client 1 (authorized user 1) has already been provisioned (statically or dynamically) with target MC service user's information and its group information, that target MC service user 2 is allowed to be affiliated or de-affiliated;
- The primary MC service server may have retrieved the user profile or group policy from the group configuration e.g. information regarding user(s) authorization to affiliate or to de-affiliate to MC service group(s), priority, and other related configuration data.
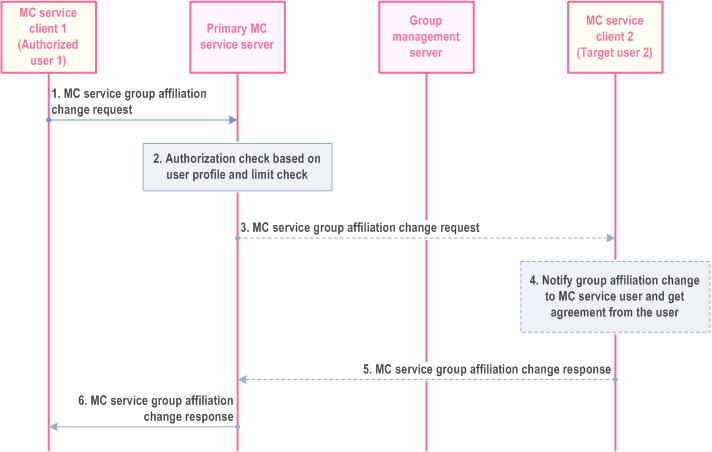
Step 1.
When an authorized user requires one or more MC service users to change the affiliation to an MC service group or set of MC service groups, the MC service client 1 of the authorized user 1 sends MC service group affiliation change request to the primary MC service server. The information (i.e. target MC service user(s) ID, MC service group(s) ID, requested affiliation status) used to indicate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target MC service user 2 and the MC service group(s) shall be included.
Step 2.
The primary MC service server checks if the MC service user 1 is authorized to initiate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target user 2 and the MC service group(s). The primary MC service server checks if the target MC service user(s) are authorized for the requested affiliation relationship based on the user profile and the group policy from the group configuration (i.e. if not available, the primary MC service server obtains the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server). The primary MC service server also performs the check for the maximum limit on the total number (N2) of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to simultaneously.
Step 3.
If the target MC service user 2 is authorized to accept the changes to its affiliated MC service group(s), then the primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change request to the MC service client 2 of the target MC service user 2.
Step 4.
If the requested affiliation status is different from the current affiliation status, then the MC service client 2 notifies the MC service group affiliation change request to the target MC service user 2 to receive the approval from the user on the proposed changes to the affiliated MC service group(s).
Step 5.
If the target MC service user 2 provides a response (accept or reject) to the notification, then the MC service client 2 sends an MC service group affiliation change response to the primary MC service server. A response indicating target user 2's acceptance to the requested affiliation change by authorized user 1, triggers the affiliation or de-affiliation procedures at the primary MC service server (see subclause 10.8.3.1 or subclause 10.8.4.2) as per the MC service user 1's requested changes to the target user 2's affiliated group(s).
Step 6.
The primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change response to the MC service client 1. If the requested affiliation status was not changed (see 4), then the MC service server creates an appropriate (accept) MC service group affiliation change response to send to MC service client 1.
10.8.5.2 Remote change of affiliation for groups defined in partner MC system p. 188
10.8.5.2.1 Authorized user remotely changes another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) defined in partner MC system - mandatory mode p. 188
The procedure for the authorized user to remotely change another MC service user's affiliated MC service group(s) defined in partner MC systems for a single MC service without requiring the target user's approval is described in Figure 10.8.5.2.1-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The MC service client 1 (authorized user) has already been provisioned (statically or dynamically) with the target MC service user 2's information and group information, that the target MC service user 2 is allowed to be affiliated or de-affiliated;
- The MC service client 1 (authorized user 1), MC service client 2 (target MC service user 2), and the primary MC service server belong to the same MC system;
- The partner MC service server may have retrieved the group related information from the group management server;
- The primary MC service server may have retrieved the user policy e.g. user related information regarding user(s) authorization to affiliate or to de-affiliate to MC service group(s), priority, and other related configuration data; and
- The partner group management server has subscribed to the MC service server within the MC system where the group is defined for affiliation status updates.
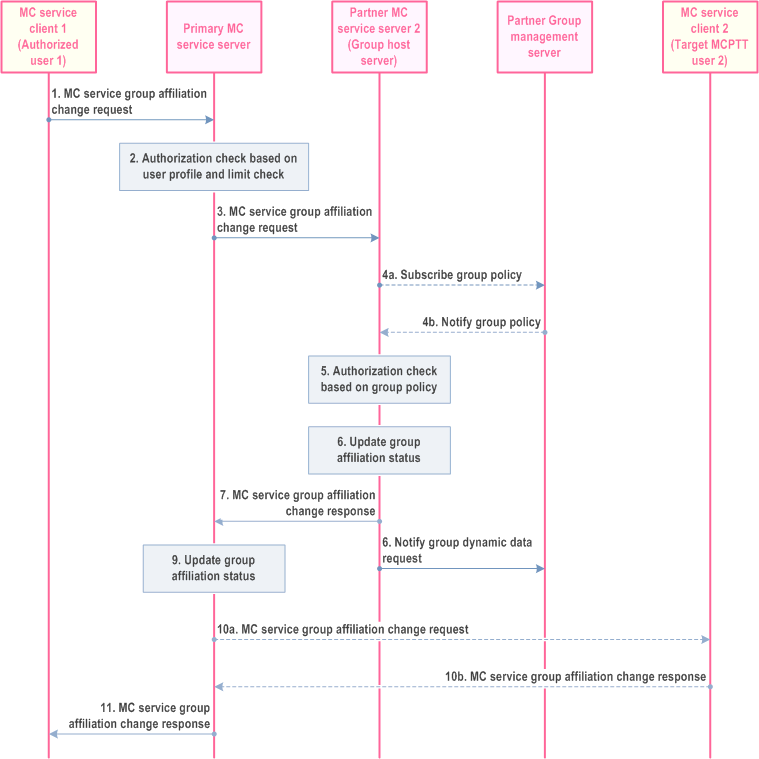
Step 1.
When an authorized user requires one or more MC service users to change the affiliation to an MC service group or set of MC service groups, the MC service client 1 of the authorized user 1 sends MC service group affiliation change request with the indication of mandatory mode to the primary MC service server. The information (i.e. target MC service user(s) ID, MC service group(s) ID, requested affiliation status) used to indicate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target MC service user 2 and the MC service group(s) shall be included.
Step 2.
The primary MC service server shall check if the MC service user 1 is authorized to initiate the change of the affiliation relationship between the target user 2 and the MC service group(s). The primary MC service server shall check if the target MC service user(s) are authorized for the requested affiliation relationship based on the user profile. The primary MC service server also performs the check for the maximum limit on the total number (N2) of MC service groups that the user can be affiliated to simultaneously.
Step 3.
Based on the MC service group information included in the request, the primary MC service server determines to send MC service group affiliation change request to the corresponding partner MC service server (group host server).
Step 4a.
The partner MC service server checks if the group policy is locally cached. If the group policy is not locally cached on the partner MC service server then the partner MC service server subscribes to the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server.
Step 4b.
The partner MC service server receives the group policy from the group configuration from the group management server via notification and locally caches the group policy from the group configuration.
Step 5.
Based on the group policy, the partner MC service server checks if the target MC service user 2 is authorized to affiliate to the MC service group(s). It is possible that the target MC service user 2 affiliates to one or more MC service groups and also de-affiliates from one or more MC service groups.
Step 6.
If the target MC service user 2 is authorized to affiliate or de-affiliate to the MC service group(s) and if the requested affiliation status is different to the current affiliation status, then the partner MC service server stores the new affiliation status of the target MC service user 2 for the MC service group(s).
Step 7.
The partner MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change response to the primary MC service server.
Step 8.
The partner MC service server updates the group management server with the affiliation status of the target MC service user 2 for the MC service group(s).
Step 9.
If the requested affiliation status is different to the current affiliation status, then the primary MC service server stores the new affiliation status of the target MC service user 2 for the MC service group(s).
Step 10a.
If the requested affiliation status is different to the current affiliation status, then the primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change request with the indication of mandatory mode to MC service client 2 of the target MC service user 2. The target MC service user 2 receives the latest information about the affiliated MC service groups. Further the MC service client 2 may subscribe for the affiliated MC service groups information with the group management server.
Step 10b.
The target MC service client 2 provides an MC service group affiliation change response to the MC service server.
Step 11.
The primary MC service server sends the MC service group affiliation change response to MC service client 1 (authorized user). If the requested affiliation status was not changed (see 10a), then the MC service server creates an appropriate (accept) MC service group affiliation change response to send to MC service client 1.