Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.5.1
1…
5…
6
7…
8…
9…
10…
10.1.5…
10.2…
10.2.6…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3.8…
10.8…
10.9…
10.9.3.9…
10.10…
10.10.3
10.11…
10.12…
10.13…
10.14…
10.15…
10.16…
10.17…
10.18…
10.18.3…
11…
11.5…
A…
B…
C…
E…
10.18 Recording and replay
10.18.1 Service configuration
10.18.2 Target group and target user configuration
...
...
10.18 Recording and replay |R19| p. 365
10.18.1 Service configuration p. 365
10.18.1.1 Service ID and user profile p. 365
A recording admin and/or replay user is identified by an MCRec ID. An MCRec ID is associated with one user profile. This is depicted in Figure 10.18.1.1-1.
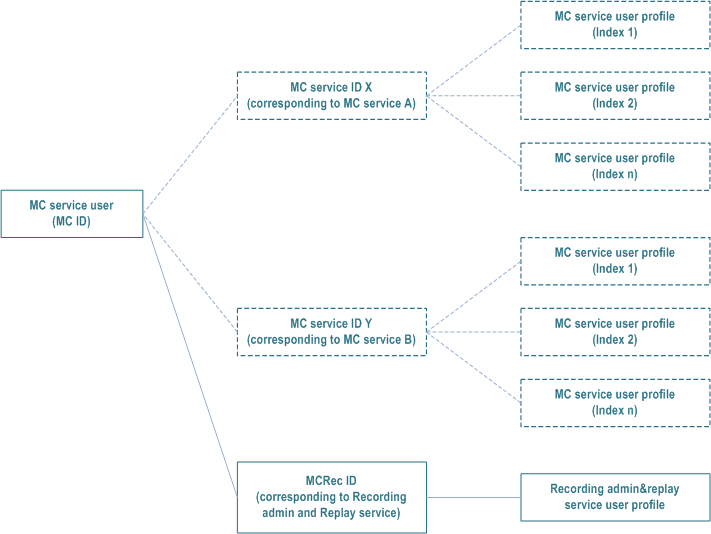
One MC service user (MC ID) may have one or zero MCRec ID.
An MC service user (MC ID), who is authorized to use recording admin and/or replay service, may be authorized to use also MC services (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData). However, the MCRec ID cannot have the same value as the MC service IDs for the same MC service user.
The recording admin and/or replay service user profile is applicable only in the user's home system. I.e. the user profile is not valid in a partner system even if the MC service user with active MC services would migrate.
10.18.1.2 Recording admin service configuration p. 366
Depicted in Figure 10.18.1.2-1 is a recording admin service configuration time sequence, representing the general lifecycle of a Recording admin UE using recording admin service.
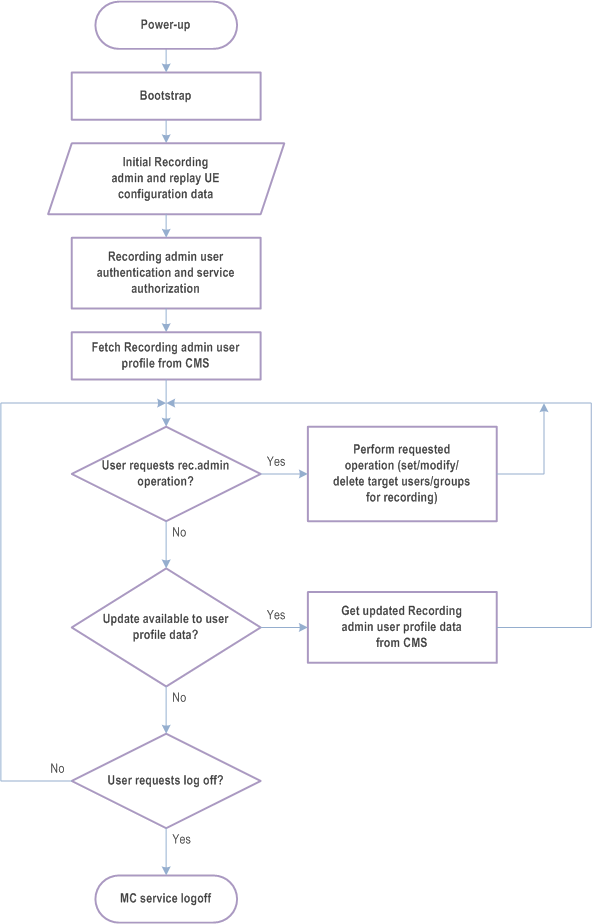
Figure 10.18.1.2-1: Recording admin UE configuration time sequence and associated configuration data
The recording admin UE is provided with initial recording admin UE and/or replay UE configuration (see clause A.10) via a bootstrap procedure that provides the recording admin UE's identity management client and configuration management client with critical information needed to connect to the MC system.
After user authentication and service authorization with IdMS (clause 5.1.2 of TS 33.180) the CM client obtains the recording admin and/or replay service user profile (clause A.11) from the CMS (clause 10.18.1.5.1).
The UE can now perform recording admin operations (set or modify target users and groups), see clause 10.18.2.
During the service the user may get notifications that its user profile data has been updated. After a notification the CM client shall obtain the updated profile data from CMS (clause 10.18.1.5.2).
10.18.1.3 Replay service configuration p. 367
Depicted in Figure 10.18.1.3-1 is a replay service configuration time sequence, representing the general lifecycle of a Replay UE using replay service.
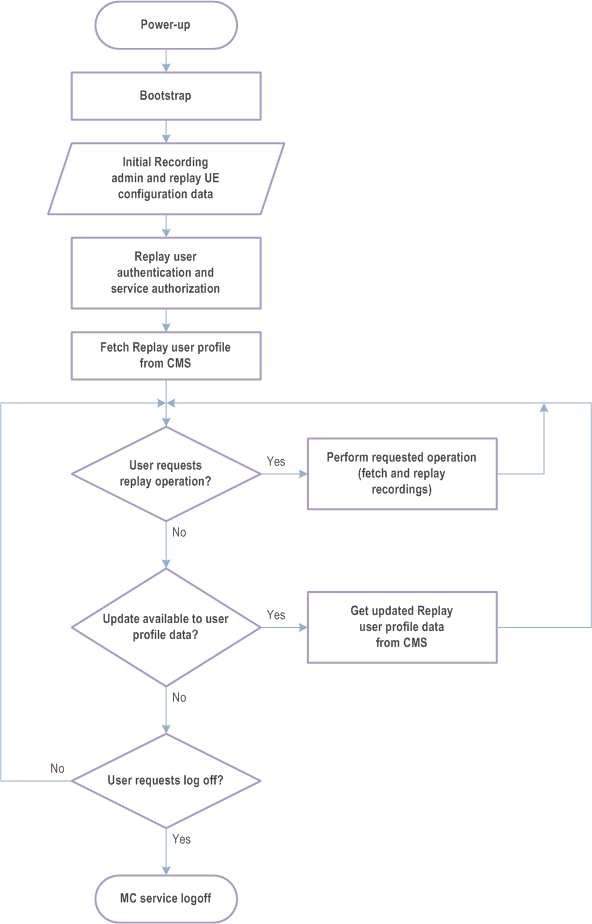
The replay UE is provided with initial recording admin UE and/or replay UE configuration (see clause A.10) via a bootstrap procedure that provides the Replay UE's identity management client and configuration management client with critical information needed to connect to the MC system.
After user authentication and service authorization with IdMS (clause 5.1.2 of TS 33.180) the CM client obtains the recording admin and/or replay service user profile (clause A.11) from the CMS (clause 10.18.1.5.1).
The UE can now perform replay operations, see clause 10.18.4.
During the service the user may get notifications that its user profile data has been updated. After a notification the CM client shall obtain the updated profile data from CMS (clause 10.18.1.5.2).
10.18.1.4 Information flows for recording admin and replay service user profiles p. 369
10.18.1.4.1 Get recording admin and replay service user profile request p. 369
Table 10.18.1.4.1-1 describes the information flow get recording admin and replay service user profile request from the configuration management client to the configuration management server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCRec ID | M | The MCRec ID of the recording admin and/or replay service user. |
10.18.1.4.2 Get recording admin and replay service user profile response p. 369
Table 10.18.1.4.2-1 describes the information flow get recording admin and replay service user profile response from the configuration management server to the configuration management client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Recording admin and/or replay service user profile data | M | The recording admin and/or replay service user profile (clauses 10.18.1.1, A.11) associated with the MCRec ID provided in the associated get recording admin and replay service user profile request. |
10.18.1.4.3 Notification for recording admin and replay service user profile data update p. 369
Table 10.18.1.4.3-1 describes the information flow notification for recording admin and replay service user profile data update from the configuration management server to the configuration management client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pointer to the modified recording admin and/or replay service user profile data | M | Pointer to the modified recording admin and/or replay service user profile data. |
10.18.1.4.4 Get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data request p. 369
Table 10.18.1.4.4-1 describes the information flow get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data request from the configuration management client to the configuration management server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MCRec ID | M | The MCRec ID of the recording admin and/or replay service user. |
| Pointer to the modified recording admin and/or replay service user profile data | M | Pointer to the modified recording admin and/or replay service user profile data. |
10.18.1.4.5 Get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data response p. 370
Table 10.18.1.4.5-1 describes the information flow get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data response from the configuration management server to the configuration management client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Updated recording admin and/or replay service user profile data | M | Recording admin and/or replay service user profile data that has been modified. |
10.18.1.5 Procedures for recording admin and replay service user profiles p. 370
10.18.1.5.1 Get recording admin and replay service user profile p. 370
Pre-conditions:
- The recording admin and replay service user has performed user authentication in the identity management server.
- The UE has secure access to the configuration management server.
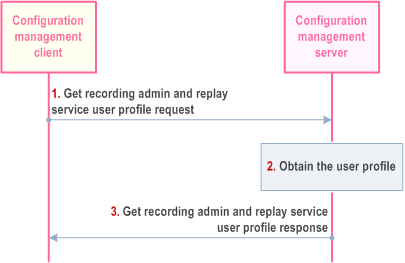
Step 1.
The configuration management client sends a get recording admin and replay service user profile request message to the configuration management server, which includes the MCRec ID.
Step 2.
The configuration management server obtains the recording admin and/or replay service user profile information.
Step 3.
The configuration management server sends get recording admin and replay service user profile response message to the configuration management client.
10.18.1.5.2 Get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data p. 370
Pre-conditions:
- The recording admin and replay service user has performed user authentication with the identity management server.
- The UE has secure access to the configuration management server.
- The UE has already obtained a recording admin and/or replay service user profile.
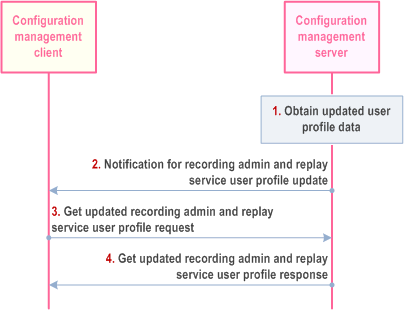
Step 1.
The configuration management server obtains updated recording admin and/or replay service user profile data.
Step 2.
The configuration management server sends a notification for recording admin and replay service user profile data update to the configuration management client.
Step 3.
The configuration management client sends a get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data request to the configuration management server, which includes the MCRec ID.
Step 4.
The configuration management server sends get updated recording admin and replay service user profile data response to the configuration management client which includes the updated user profile data.
10.18.2 Target group and target user configuration p. 371
10.18.2.1 Store target group configuration at the GMS p. 371
The procedure for store target group configurations at the group management server is described in Figure 10.18.2.1-1.
A recording admin shall use this procedure to set/modify/remove target group(s) for recording.
Pre-conditions:
- The recording admin service user has performed user authentication and service authorization with the IdMS and downloaded its own service profile from CMS.
- The UE has secure access to the group management server.
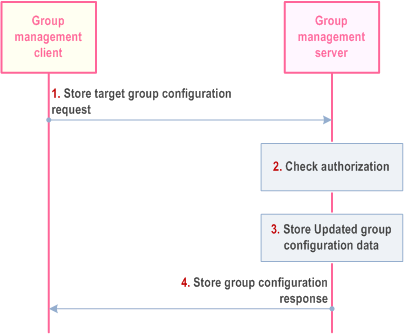
Step 1.
The group management client - triggered by a recording admin user - sends a store target group configuration request to the group management server.
Step 2.
The group management server checks the authorization of the originator (MCRec ID) for this operation.
Step 3.
The group management server stores the updated group configuration data.
Step 4.
The group management server provides a store group configuration response indicating success or failure.
10.18.2.2 Update target MC service user profile data to the CMS p. 372
The procedure for update target MC service user profile data to CMS is illustrated in Figure 10.18.2.2-1.
A recording admin shall use this procedure to set/modify/remove target MC service user (s) for recording.
Pre-conditions:
- The recording admin service user has performed user authentication and service authorization with the IdMS and downloaded its own service profile from CMS.
- The UE has secure access to the configuration management server.
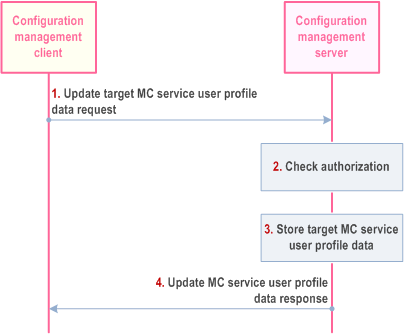
Step 1.
The configuration management client - triggered by a recording admin user - sends the update target MC service user profile data request to the configuration management server.
Step 2.
The configuration management server checks that the target MC service user is under the requestor's (MCRec ID) authority.
Step 3.
The configuration management server stores the received target MC service user profile data. If this target MC service ID is associated with multiple MC service user profiles, the same update must be done by CMS to all these profiles.
Step 4.
The configuration management server sends update MC service user profile data response to the configuration management client.